基于次溴酸钠氧化−氨基磺酸还原测定沉积物15N加富培养样品中的15${{\bf{NH}}}^{{\bf{+}}}_{{\bf 4}}$ 的方法探索
doi: 10.12284/hyxb2022024
A sodium hypobromite oxidation-sulfamic acid reduction method for determination of 15$ {\bf{NH_4^+}}$ in 15N enrichment sediment slurry incubation samples
-
摘要: 沉积物中的异化硝酸盐还原过程是海洋中活性氮转化的关键过程之一。不同于反硝化和厌氧铵氧化,异化硝酸盐还原为铵(DNRA)是将硝酸盐直接还原为铵,而不是以氮气的形态移除,这有可能会加重水体富营养化和缺氧。目前测定沉积物中异化硝酸盐还原过程的主要手段是15N标记培养技术。为了准确评估DNRA的潜在速率,首先要准确测定加富样品中的15
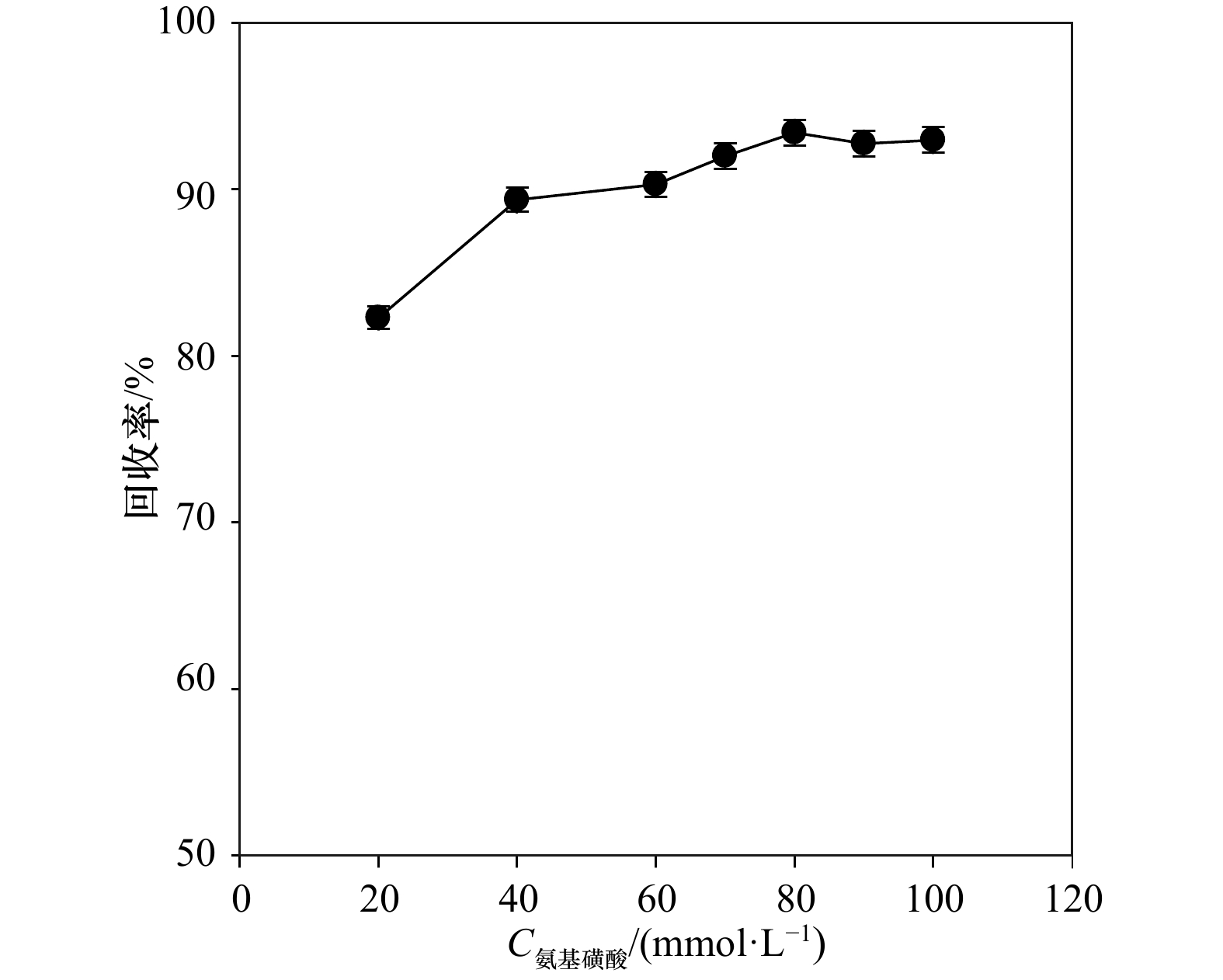
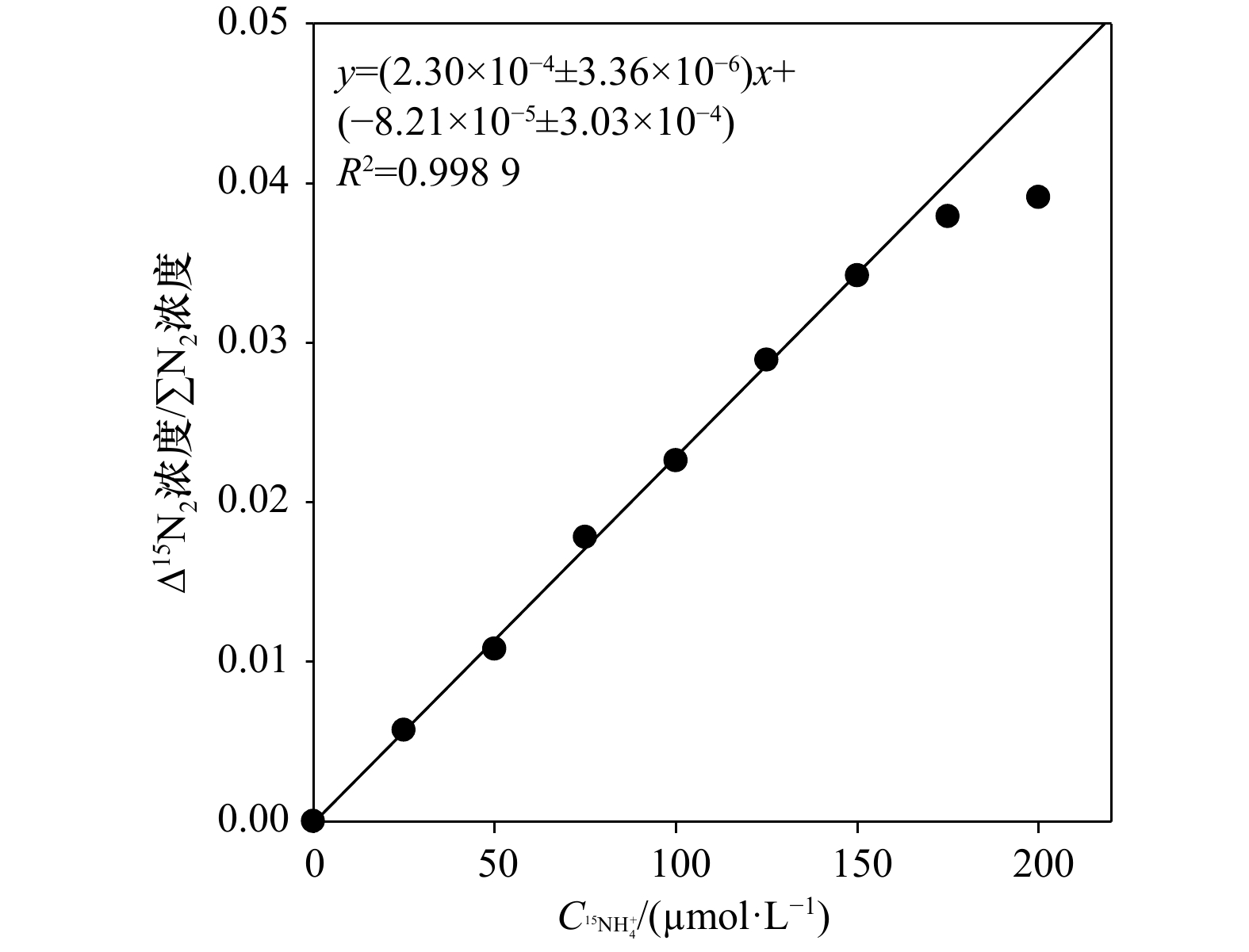
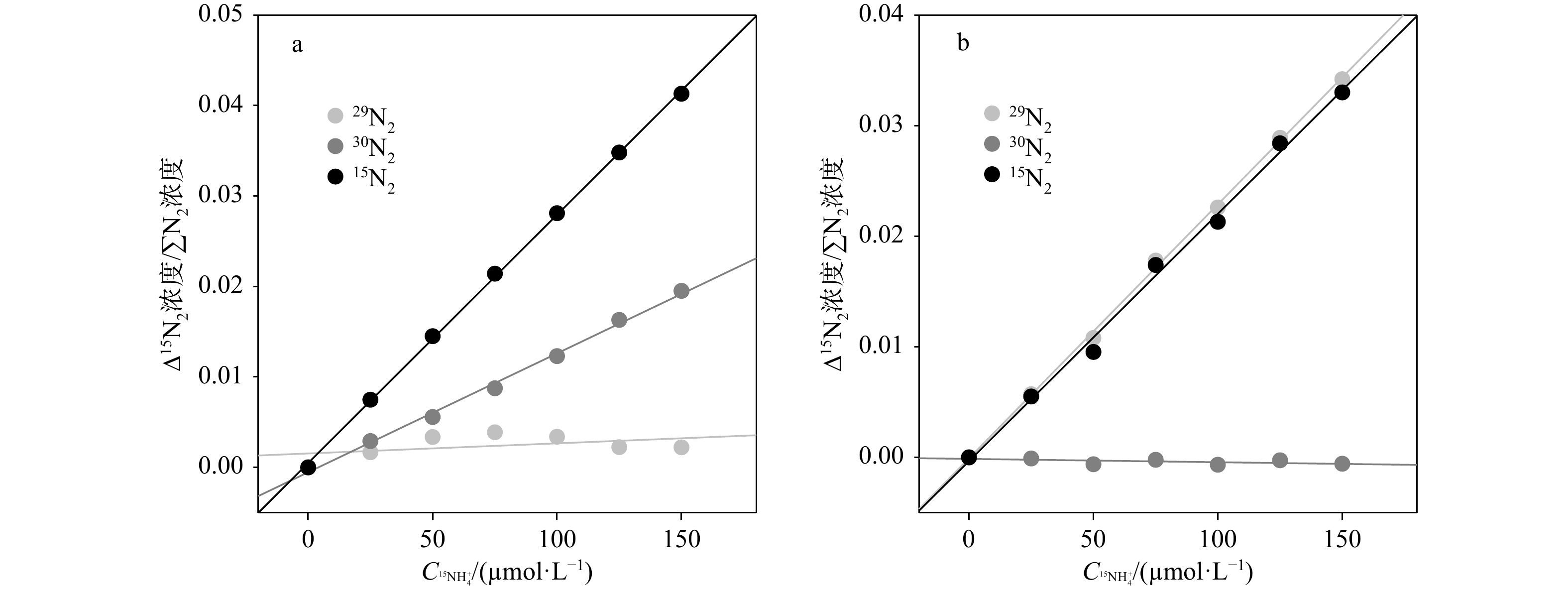
${\rm {NH}}_4^+ $ 浓度。常用测定15${\rm {NH}}_4^+ $ 的方法为基于次溴酸钠−碘氧化膜进样的四极杆质谱法。然而此方法的分析物之一30N2在分析时容易存在两个问题而导致结果失真:一是易受样品中O2干扰而导致30N2含量被显著高估;二是30N2在检测器中平衡较慢从而导致测试时间较长且精密度较差。为解决上述问题,本研究采用次溴酸钠氧化−氨基磺酸还原的方法将15${\rm {NH}}_4^+ $ 转化为29N2后通过膜进样的四极杆质谱仪进行测定(简称Redox-MIMS法)。结果表明,Redox-MIMS法在氨基磺酸还原剂浓度为80~100 mmol/L时还原效率最好;方法的检测限约为0.5 μmol/L,精密度为0.8%,工作曲线的线性范围可以达到0~150 μmol/L。相对于次溴酸钠−碘氧化法,Redox-MIMS法反应条件温和,反应试剂相对易得,产物为29N2,有效解决了30N2分析的一系列问题,并显著提高了测定效率(2 min/样品)。分别采用Redox-MIMS法和次溴酸钠−碘氧化法测定莱州湾沉积物实际样品,两种方法所测得的DNRA速率以及DNRA占异化硝酸盐还原的比例均无显著性差异,证明Redox-MIMS法是一种准确、高效地测定15N加富培养样品中15${\rm {NH}}_4^+ $ 的方法。-
关键词:
- 沉积物 /
- 氮循环 /
- 异化硝酸盐还原为铵 /
- 膜进样质谱 /
- 次溴酸钠氧化−氨基磺酸还原
Abstract: Dissimilatory nitrate reduction in marine sediment is one of the key nitrogen loss processes in the ocean. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA), unlike denitrification and anammox by which nitrate is reduced to N2 and removed from the environment eventually, directly reduce nitrate to ammonium, could lead to eutrophication and water hypoxia afterwards. 15N labeled technique is the main method to investigate dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in sediments. Accurate determination of 15${\rm {NH}}_4^+ $ in isotope enrichment samples is primarily required to evaluate the potential rate of DNRA. The commonly used method for the determination of 15${\rm {NH}}_4^+ $ at present is the hypobromite iodine oxidation-membrane inlet quadrupole mass spectrometer determination method. However, 30N2 as the final analyte of the method has two problems which lead to an analysis error: firstly, 30N2 determined can be significantly overestimated due to the O2 interference; secondly, the low equilibrium rate of 30N2 in the detector could influence the precision of the method and low down the analysis speed. To solve the problems mentioned, a sodium hypobromite oxidation-sulfamic acid reduction method by which 15${\rm {NH}}_4^+ $ is transformed to 29N2 only and detected using membrane inlet quadrupole mass spectrometer afterwards (Redox-MIMS method) is reported in this article. The results indicate that the optical concentration of sulfamic acid is 80−100 mmol/L; the detection limit is 0.5 μmol/L and the precision (RSD) is 0.8%; the dynamic range of standard curve is 0−150 μmol/L. Comparing with the hypobromite iodine oxidation method, the Redox-MIMS method not only has the advantages of mild reaction conditions and easily obtained reagents, the memory effect of 30N2 in the detector can also be solved effectively for most of the produced 15N2 is 29N2 which improves detection efficiency (2 min per sample) meanwhile. Determination results of rates of DNRA and the contribution of DNRA to all dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in the Laizhou Bay sediments using both hypobromite iodine oxidation and Redox-MIMS methods shows no significant difference. These make the Redox-MIMS method an accurate and high-efficient method for determination of 15${\rm {NH}}_4^+ $ in isotope enrichment samples. -
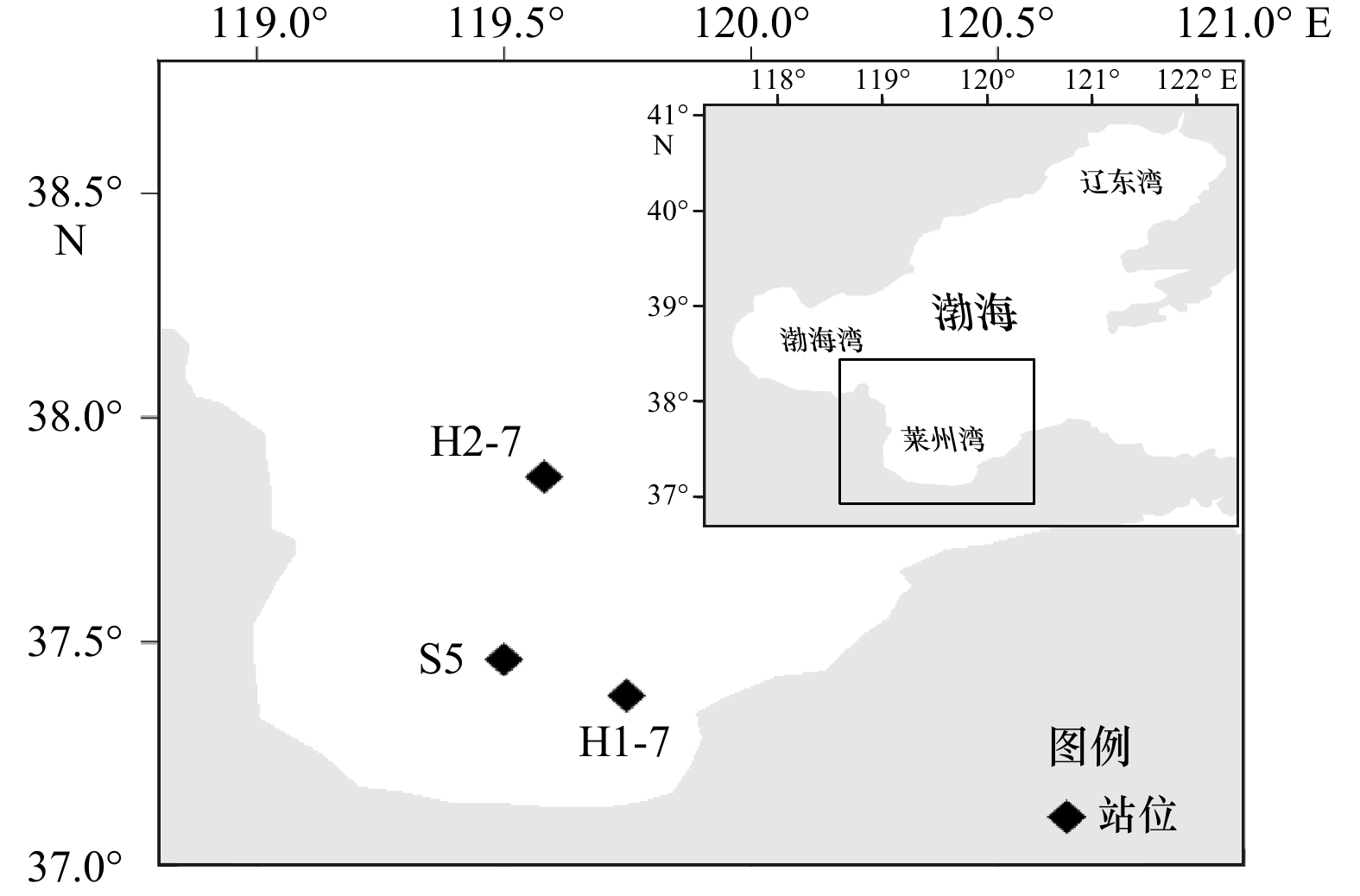
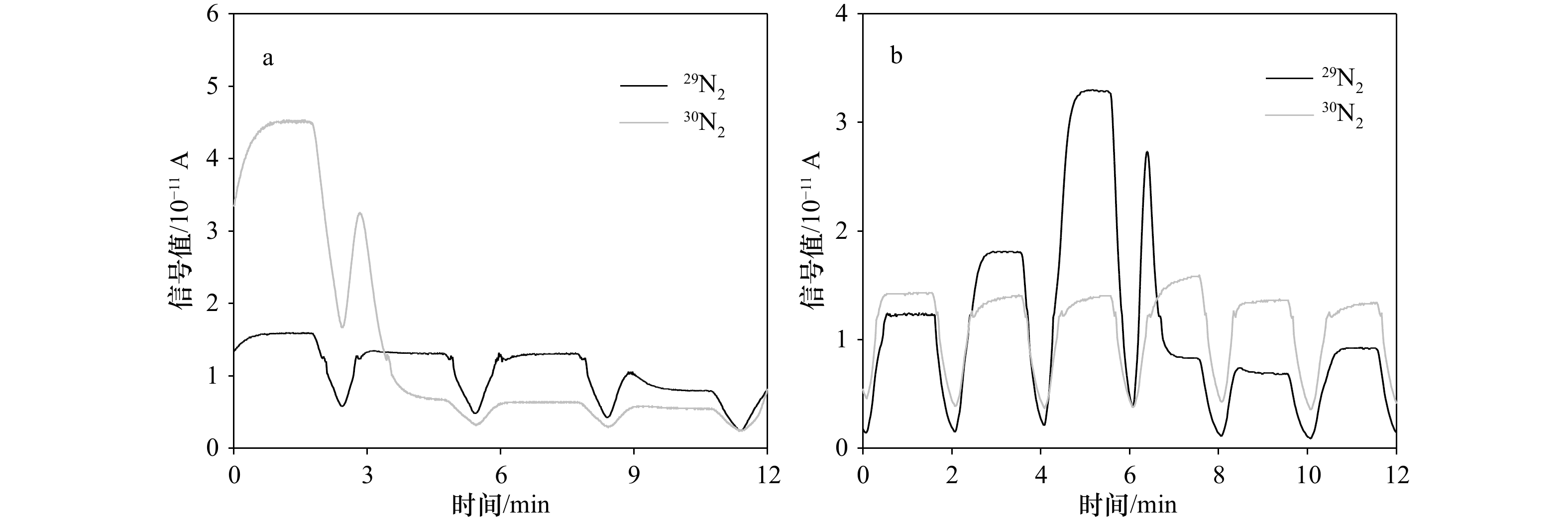
图 7 莱州湾H1-7、S5、H2-7站位沉积物不同15N加富培养体系中15N2和15
$ {\rm{NH}}_4^+$ 浓度随时间变化a1−a3. 加富15$ {\rm{NO}}_3^-$,产生15N2; b1−b3. 加富15$ {\rm{NH}}_4^+$,产生15N2; c1−c3. 加富15$ {\rm{NH}}_4^+$+14$ {\rm{NO}}_3^-$,产生15N2; d1−d3. 加富15$ {\rm{NO}}_3^-$,产生15$ {\rm{NH}}_4^+$
Fig. 7 15N2 and 15
$ {\rm{NH}}_4^+$ concentration production with time changes in different 15N tracer enrichment incubation systems of sediments in stations H1-7, S5, H2-7 in the Laizhou Baya1−a3. 15$ {\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ enrichment with 15N2 produced; b1−b3. 15$ {\rm{NH}}_4^{+}$ enrichment with 15N2 produced; c1−c3. 15$ {\rm{NH}}_4^+$+14$ {\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ enrichment with 15N2 produced; d1−d3. 15$ {\rm{NO}}_3^{-}$ enrichment with 15$ {\rm{NH}}_4^+$ produced
-
[1] Tiedje J M. Ecology of denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium[M]//Zehnder A J B. Biology of Anaerobic Microorganisms. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. , 1988: 179−244. [2] Devol A H. Denitrification, anammox, and N2 production in marine sediments[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2015, 7: 403−423. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010213-135040 [3] Gardner W S, McCarthy M J, An S, et al. Nitrogen fixation and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) support nitrogen dynamics in Texas estuaries[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2006, 51(1part2): 558−568. doi: 10.4319/lo.2006.51.1_part_2.0558 [4] Giblin A E, Tobias C R, Song B, et al. The importance of dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) in the nitrogen cycle of coastal ecosystems[J]. Oceanography, 2013, 26(3): 124−131. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2013.54 [5] Smith C J, Dong L F, John W, et al. Seasonal variation in denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonia process rates and corresponding key functional genes along an estuarine nitrate gradient[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2015, 6: 542. [6] Song Guodong, Liu Sumei, Marchant H, et al. Anammox, denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in the East China Sea sediment[J]. Biogeosciences, 2013, 10(11): 6851−6864. doi: 10.5194/bg-10-6851-2013 [7] Freyer H D. Seasonal trends of ${{\rm{NH}}_4^+} $ and${{\rm{NO}}^-_3 }$ nitrogen isotope composition in rain collected at Jülich, Germany[J]. Tellus, 1978, 30(1): 83−92. doi: 10.3402/tellusa.v30i1.10319[8] Holmes R M, McClelland J W, Sigman D M, et al. Measuring 15 ${{\rm N}\text{-}{\rm{NH}}_4^+} $ in marine, estuarine and fresh waters: an adaptation of the ammonia diffusion method for samples with low ammonium concentrations[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1998, 60(3/4): 235−243.[9] Lehmann M F, Bernasconi S M, McKenzie J A. A method for the extraction of ammonium from freshwaters for nitrogen isotope analysis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 73(19): 4717−4721. doi: 10.1021/ac010212u [10] Zhang Lin, Altabet M A, Wu Taixing, et al. Sensitive measurement of ${{\rm{NH}}_4^+} $ 15N/14N (δ15${{\rm{NH}}_4^+} $ ) at natural abundance levels in fresh and saltwaters[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2007, 79(14): 5297−5303. doi: 10.1021/ac070106d[11] Felix J D, Elliott E M, Gish T J, et al. Characterizing the isotopic composition of atmospheric ammonia emission sources using passive samplers and a combined oxidation-bacterial denitrifier approach[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2013, 27(20): 2239−2246. doi: 10.1002/rcm.6679 [12] Liu Dongwei, Fang Yunting, Tu Ying, et al. Chemical method for nitrogen isotopic analysis of ammonium at natural abundance[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(8): 3787−3792. doi: 10.1021/ac403756u [13] Yin Guoyu, Hou Lijun, Liu Min, et al. A novel membrane inlet mass spectrometer method to measure 15 ${{\rm{NH}}_4^+} $ for isotope-enrichment experiments in aquatic ecosystems[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(16): 9555−9562.[14] Deng Fengyu, Hou Lijun, Liu Min, et al. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes and associated contribution to nitrogen removal in sediments of the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2015, 120(8): 1521−1531. doi: 10.1002/2015JG003007 [15] Yin Guoyu, Hou Lijun, Liu Min, et al. DNRA in intertidal sediments of the Yangtze estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2017, 122(8): 1988−1998. doi: 10.1002/2017JG003766 [16] 谢成军, 宋国栋, 刘素美, 等. 自组装膜进样质谱系统及其在砂质沉积物异化硝酸盐还原研究中的应用[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(2): 22−29.Xie Chengjun, Song Guodong, Liu Sumei, et al. Self-assembled membrane injection mass spectrometry system and its application on the study of dissimilatory nitrate reduction in sandy sediments[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(2): 22−29. [17] Jensen K M, Jensen M H, Cox R P. Membrane inlet mass spectrometric analysis of N-isotope labelling for aquatic denitrification studies[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 1996, 20(2): 101−109. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.1996.tb00309.x [18] Lunstrum A, Aoki L R. Oxygen interference with membrane inlet mass spectrometry may overestimate denitrification rates calculated with the isotope pairing technique[J]. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 2016, 14(7): 425−431. doi: 10.1002/lom3.10101 [19] Warembourg F R. Nitrogen fixation in soil and plant systems[M]//Knowles R, Blackburn T H. Nitrogen Isotope Techniques. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc. , 1993: 127−156. [20] Füssel J, Lam P, Lavik G, et al. Nitrite oxidation in the Namibian oxygen minimum zone[J]. The ISME Journal, 2012, 6(6): 1200−1209. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2011.178 [21] Granger J, Sigman D M. Removal of nitrite with sulfamic acid for nitrate N and O isotope analysis with the denitrifier method[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2009, 23(23): 3753−3762. doi: 10.1002/rcm.4307 [22] Song Guodong, Liu Sumei, Kuypers M M M, et al. Application of the isotope pairing technique in sediments where anammox, denitrification, and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium coexist[J]. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 2016, 14(12): 801−815. doi: 10.1002/lom3.10127 [23] 高凤鸣, 张淑华, 汪心源, 等. 用次溴酸钠氧化法测定海水中氨氮的研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1980(4): 41−47.Gao Fengming, Zhang Shuhua, Wang Xinyuan, et al. Study on the determination of ammonia-nitrogen in seawater with the sodium hypobromite oxidation method[J]. Transactions of Oceanography and Limnology, 1980(4): 41−47. -









 下载:
下载: