Spatiotemporal characteristics and driving factors of water transparency in the South Yellow Sea
-
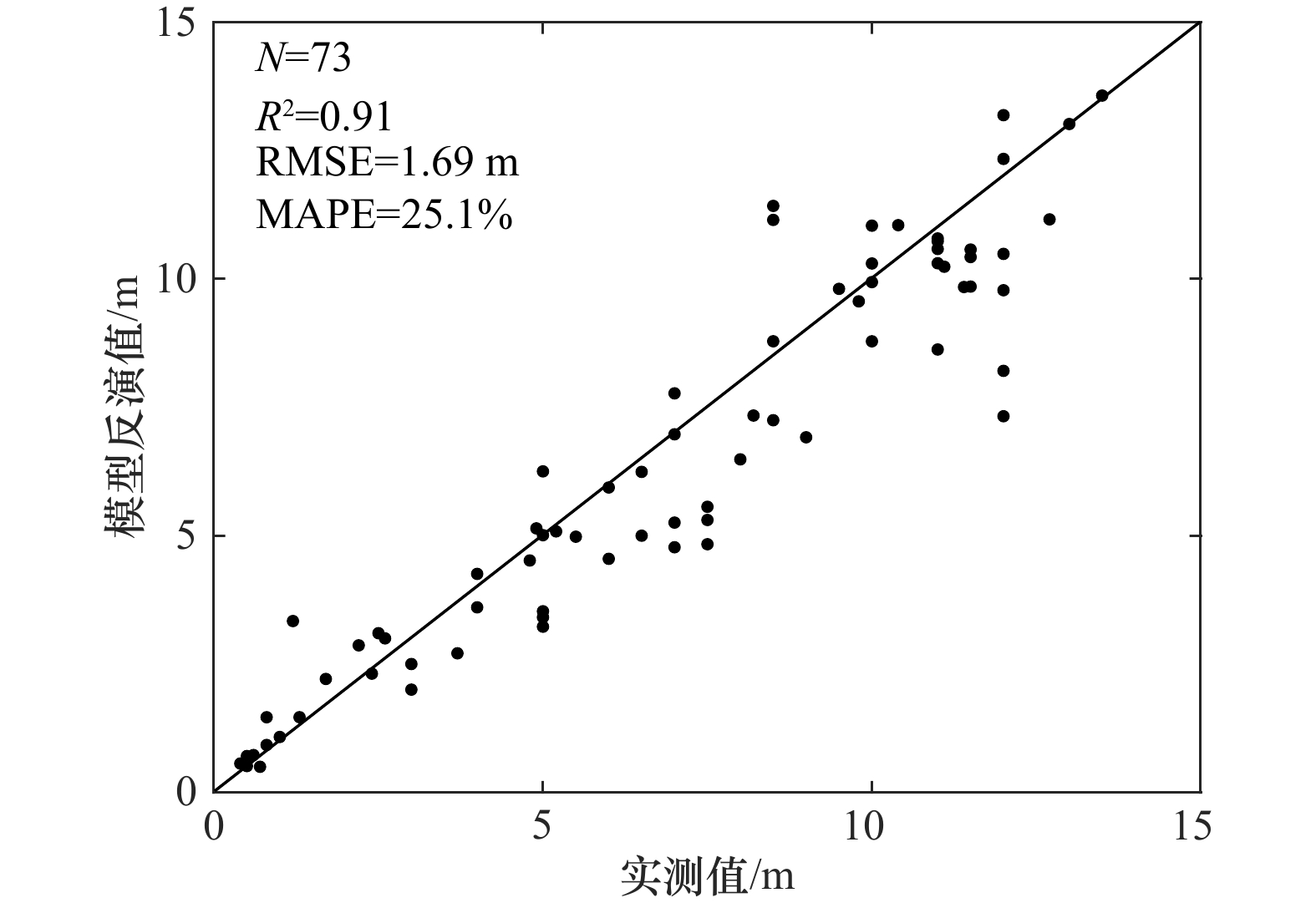
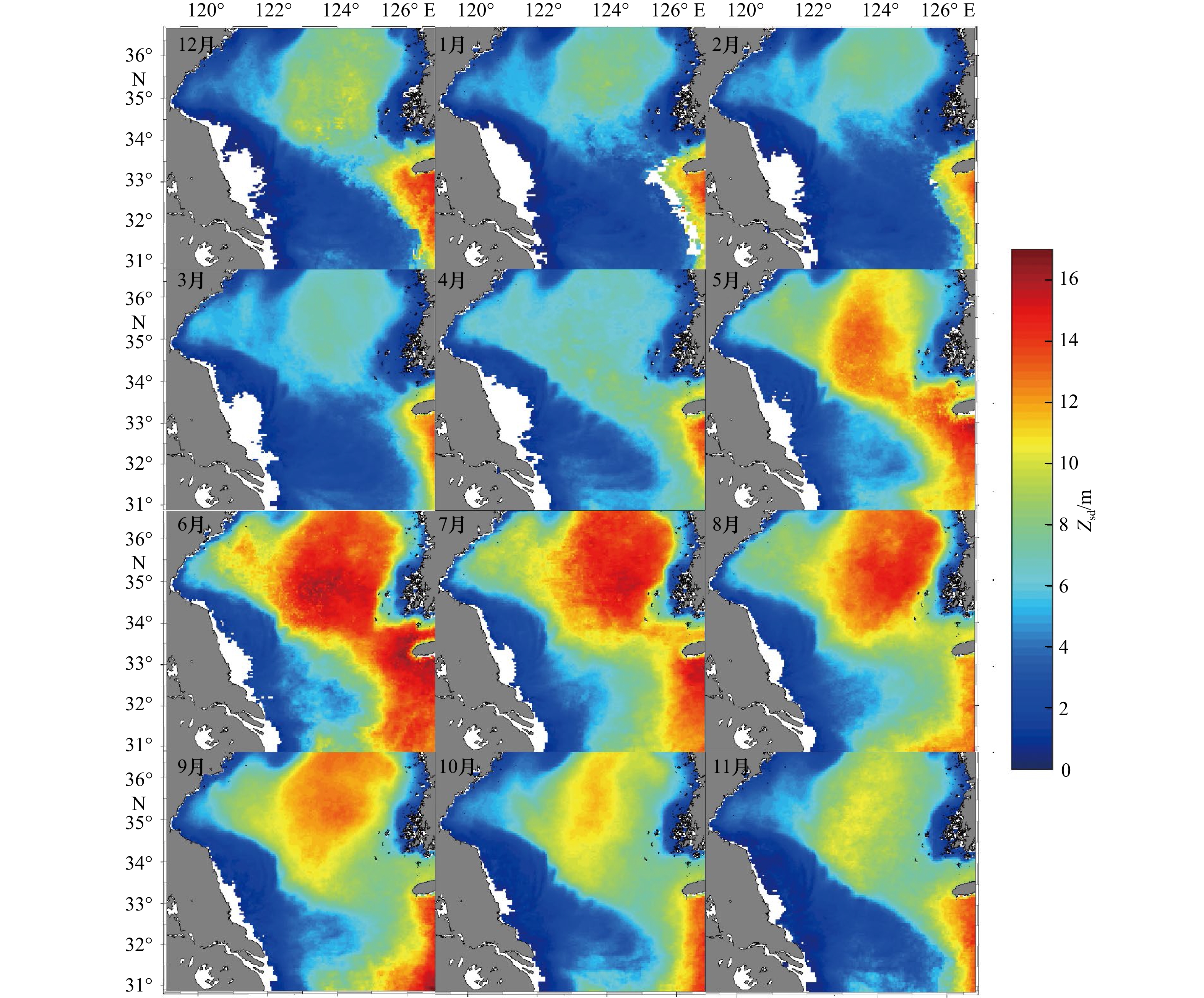
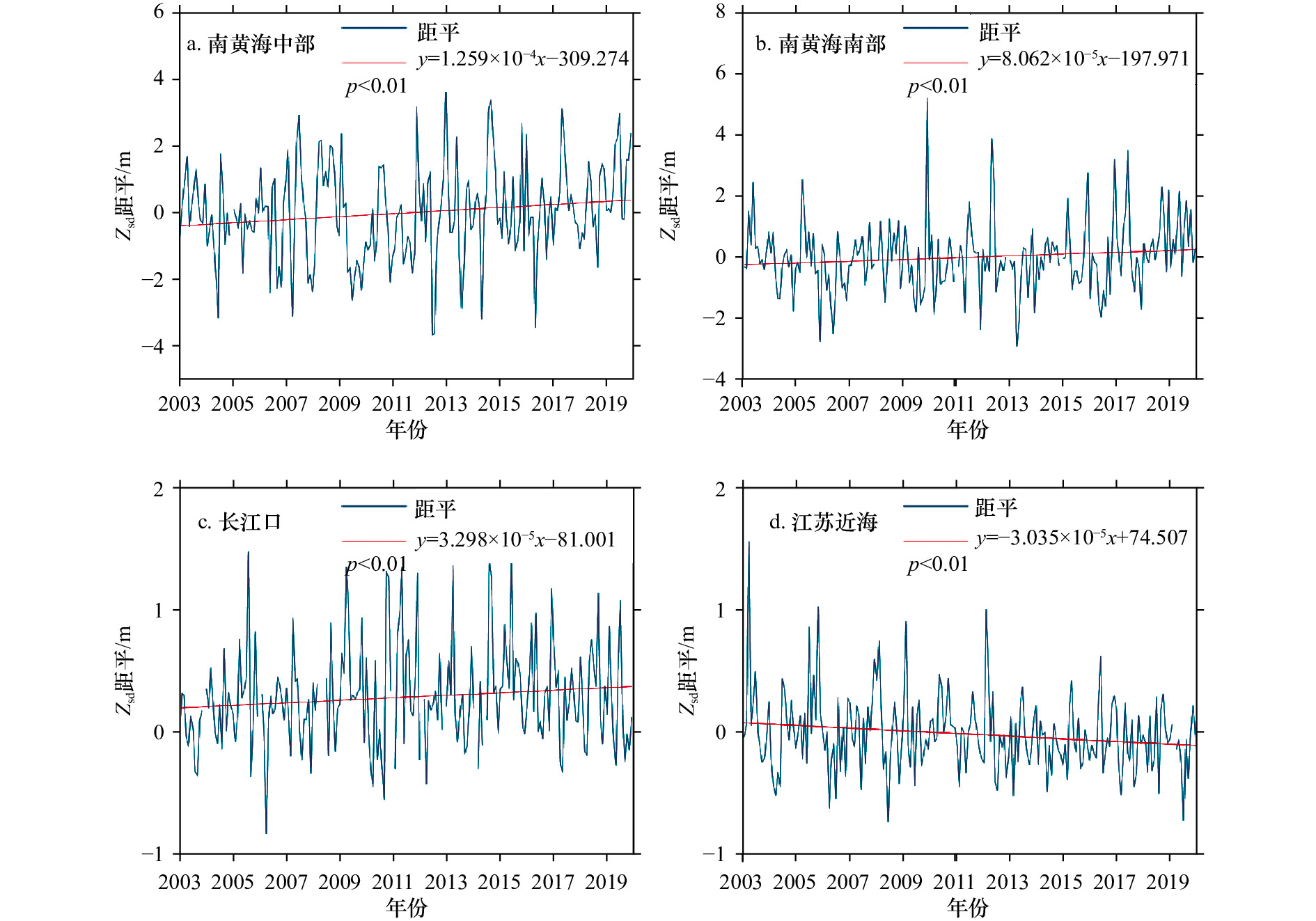
摘要: 水体透明度(Zsd)是评价水质状况的重要光学参数。本文针对南黄海海域,面向MODIS传感器校正了Zsd遥感反演模型,进而利用MODIS近20年(2002–2020年)数据分析了南黄海Zsd的时空变化特征及其驱动力,结果显示:建立的Zsd反演模型具有良好的精度(决定系数为0.91,均方根误差为1.69 m,平均相对误差绝对值为25.1%);南黄海Zsd在空间上呈现外海高近岸低的特点、在时间上呈现冬低夏高的季节变化特征,近20年来南黄海中部、南黄海南部、长江口的Zsd均在缓慢增加,而江苏近岸的Zsd呈现出缓慢降低趋势;Zsd受悬浮颗粒物浓度的负向驱动,其影响最大;此外,海表温度和光照强度对Zsd都呈正向驱动,而风速呈负向驱动。Abstract: Water transparency (Zsd) is an important optical parameter for evaluating water quality. This paper tuned a remote sensing model for estimating Zsd from MODIS (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer) data in the South Yellow Sea. This model was then used to analyze the spatial and temporal variations of Zsd in the South Yellow Sea based long-term MODIS data in the past 20 years (2002–2020), and their driving factors were examined. The results show that the Zsd estimation model has good accuracy with R2, root mean square error and mean absolute percent error values of 0.91, 1.69 m and 25.1%, respectively. The Zsd levels are generally high in the offshore but low in the coastal area. Meanwhile, Zsd indicates high values in summer but low values in winter. In the past 20 years, Zsd in the central South Yellow Sea, the southern South Yellow Sea and the Changjiang River Estuary showed slowly increase trends, while Zsd in the Jiangsu coast was decreasing slowly. In general, the Zsd is negatively driven by the concentration of suspended particulate matter, of which the influence is the greatest. In addition, sea surface temperature and solar radiation have positive driving effects on Zsd, while wind speed has negative driving effect.
-
Key words:
- water transparency /
- MODIS data /
- South Yellow Sea /
- spatiotemporal variations /
- driving factors
-
表 1 本研究中现场实测数据的相关信息及用途
Tab. 1 Information of field measured data used in this study
数据源 采样时间 测量参数 样本数 用途 子集A 2002年4月、8月和11月 Rrs和Kd 42 校正毛颖等[13]的Kd
遥感反演联合算法2003年3月和9月 Rrs和Kd 156 子集B 2014年5月 Rrs、Kd和Zsd 13 验证评价Zsd的
遥感估算精度2014年11月 Rrs、Kd和Zsd 20 2015年8月 Rrs、Kd和Zsd 10 2016年7月 Rrs、Kd和Zsd 30 注:Rrs表示遥感反射率,Kd表示漫衰减系数,Zsd表示水体透明度。 -
[1] Megard R O, Berman T. Effects of algae on the Secchi transparency of the southeastern Mediterranean Sea[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1989, 34(8): 1640−1655. doi: 10.4319/lo.1989.34.8.1640 [2] He Xianqiang, Pan Delu, Bai Yan, et al. Recent changes of global ocean transparency observed by SeaWiFS[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2017, 143: 159−166. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2016.09.011 [3] 薛宇欢, 熊学军, 刘衍庆. 中国近海海水透明度分布特征与季节变化[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2015, 33(1): 38−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2015.01.005Xue Yuhuan, Xiong Xuejun, Liu Yanqing. Distribution features and seasonal variability of the transparency in offshore waters of China[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2015, 33(1): 38−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2015.01.005 [4] 张绪琴. 海水透明度[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1982(4): 14−18.Zhang Xuqin. Seawater transparence[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 1982(4): 14−18. [5] Lee Z, Shang Shaoling, Qi Lin, et al. A semi-analytical scheme to estimate Secchi-disk depth from Landsat-8 measurements[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 177: 101−106. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.02.033 [6] 张居诗, 魏国妹, 林供, 等. 一个基于固有光学特性的透明度半分析算法适用性探讨[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 53(4): 549−554.Zhang Jushi, Wei Guomei, Lin Gong, et al. Evaluation of the applicability of an IOP-based algorithm to derive secchi depth[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2014, 53(4): 549−554. [7] 郝艳玲, 曹文熙, 崔廷伟, 等. 基于半分析算法的赤潮水体固有光学性质反演[J]. 海洋学报, 2011, 33(1): 52−65.Hao Yanling, Cao Wenxi, Cui Tingwei, et al. The retrieval of oceanic inherent optical properties based on semianalytical algorithm during the red ride[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2011, 33(1): 52−65. [8] 何贤强, 潘德炉, 毛志华, 等. 利用SeaWiFS反演海水透明度的模式研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(5): 55−62.He Xianqiang, Pan Delu, Mao Zhihua, et al. The study on the inversing model of water transparency using the SeaWiFS data[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2004, 26(5): 55−62. [9] Lee Z, Shang Shaoling, Hu Chuanmin, et al. Secchi disk depth: A new theory and mechanistic model for underwater visibility[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2015, 169: 139−149. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.08.002 [10] Mao Ying, Wang Shengqiang, Qiu Zhongfeng, et al. Variations of transparency derived from GOCI in the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(9): 12191−12209. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.012191 [11] 贾后磊, 苏文, 黄华梅, 等. 海岸带和内陆水体透明度动态变化特征及其主导影响因素[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(3): 0301001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0301001Jia Houlei, Su Wen, Huang Huamei, et al. Dynamic change characteristics and its dominant influencing factors of secchi disk depth in coastal and inland waters[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(3): 0301001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0301001 [12] Bai Shuying, Gao Jixi, Sun Deyong, et al. Monitoring water transparency in shallow and eutrophic lake waters based on GOCI observations[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(1): 163. doi: 10.3390/rs12010163 [13] 毛颖, 丘仲锋, 孙德勇, 等. 渤黄海水体漫衰减系数的遥感反演[J]. 广西科学, 2016, 23(6): 513−519.Mao Ying, Qiu Zhongfeng, Sun Deyong, et al. A novel remote sensing algorithm for estimating diffuse attenuation coefficient in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2016, 23(6): 513−519. [14] Wang Shengqiang, Huan Yu, Qiu Zhongfeng, et al. Remote sensing of particle cross-sectional area in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea: Algorithm development and application implications[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(10): 841. doi: 10.3390/rs8100841 [15] 殷子瑶, 江涛, 杨广普, 等. 1986−2017年胶州湾水体透明度时空变化及影响因素研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2020, 44(4): 21−32. doi: 10.11759/hykx20190909001Yin Ziyao, Jiang Tao, Yang Guangpu, et al. The spatial-temporal variation of water clarity and its influencing factors in Jiaozhou Bay from 1986 to 2017[J]. Marine Sciences, 2020, 44(4): 21−32. doi: 10.11759/hykx20190909001 [16] Shang Shaoling, Lee Z, Shi Lianghai, et al. Changes in water clarity of the Bohai Sea: Observations from MODIS[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 186: 22−31. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.08.020 [17] Lee Z, Carder K L, Arnone R A. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters[J]. Applied Optics, 2002, 41(27): 5755−5772. doi: 10.1364/AO.41.005755 [18] Siswanto E, Tang Junwu, Yamaguchi H, et al. Empirical ocean-color algorithms to retrieve chlorophyll-a, total suspended matter, and colored dissolved organic matter absorption coefficient in the Yellow and East China Seas[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2011, 67(5): 627−650. doi: 10.1007/s10872-011-0062-z [19] 何贤强, 潘德炉, 黄二辉, 等. 中国海透明度卫星遥感监测[J]. 中国工程科学, 2004, 6(9): 33−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2004.09.007He Xianqiang, Pan Delu, Huang Erhui, et al. Monitor of water transparency in the China Sea by using satellite remote sensing[J]. Engineering Science, 2004, 6(9): 33−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2004.09.007 [20] 李娜. 中国东部近海热状况变化特征及与华北夏季气候变化关系的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012: 15−17.Li Na. Analysis about thermal condition characteristics in marginal seas east of china and relationship between it and North China climate change[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012: 15−17. [21] 任杰, 刘宏坤, 贾良文, 等. 磨刀门水道盐度混合层化机制[J]. 水科学进展, 2012, 23(5): 715−720.Ren Jie, Liu Hongkun, Jia Liangwen, et al. Research on salinity mixing and stratification mechanisms at the Modaomen channel[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2012, 23(5): 715−720. [22] 禹定峰. 海水透明度的遥感研究[D]. 烟台: 中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所, 2013: 89−90.Yu Dingfeng. Remote sensing of secchi disk depth[D]. Yantai: Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013: 89−90. [23] Kukushkin A S. River runoff effects on the coastal water transparency in the western black sea[J]. Russian Meteorology and Hydrology, 2018, 43(7): 464−472. doi: 10.3103/S1068373918070063 [24] 丁梦娇, 丘仲锋, 张海龙, 等. 基于NPP-VIIRS卫星数据的渤黄海浊度反演算法研究[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39(6): 0601002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0601002Ding Mengjiao, Qiu Zhongfeng, Zhang Hailong, et al. Inversion algorithm for turbidity of Bohai and Yellow Seas based on NPP-VIIRS satellite data[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(6): 0601002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0601002 -





 下载:
下载: