Identification and functional analysis of SNP from transcriptome of cobia (Rachycentron canadum) in response to hypoxia stress
-
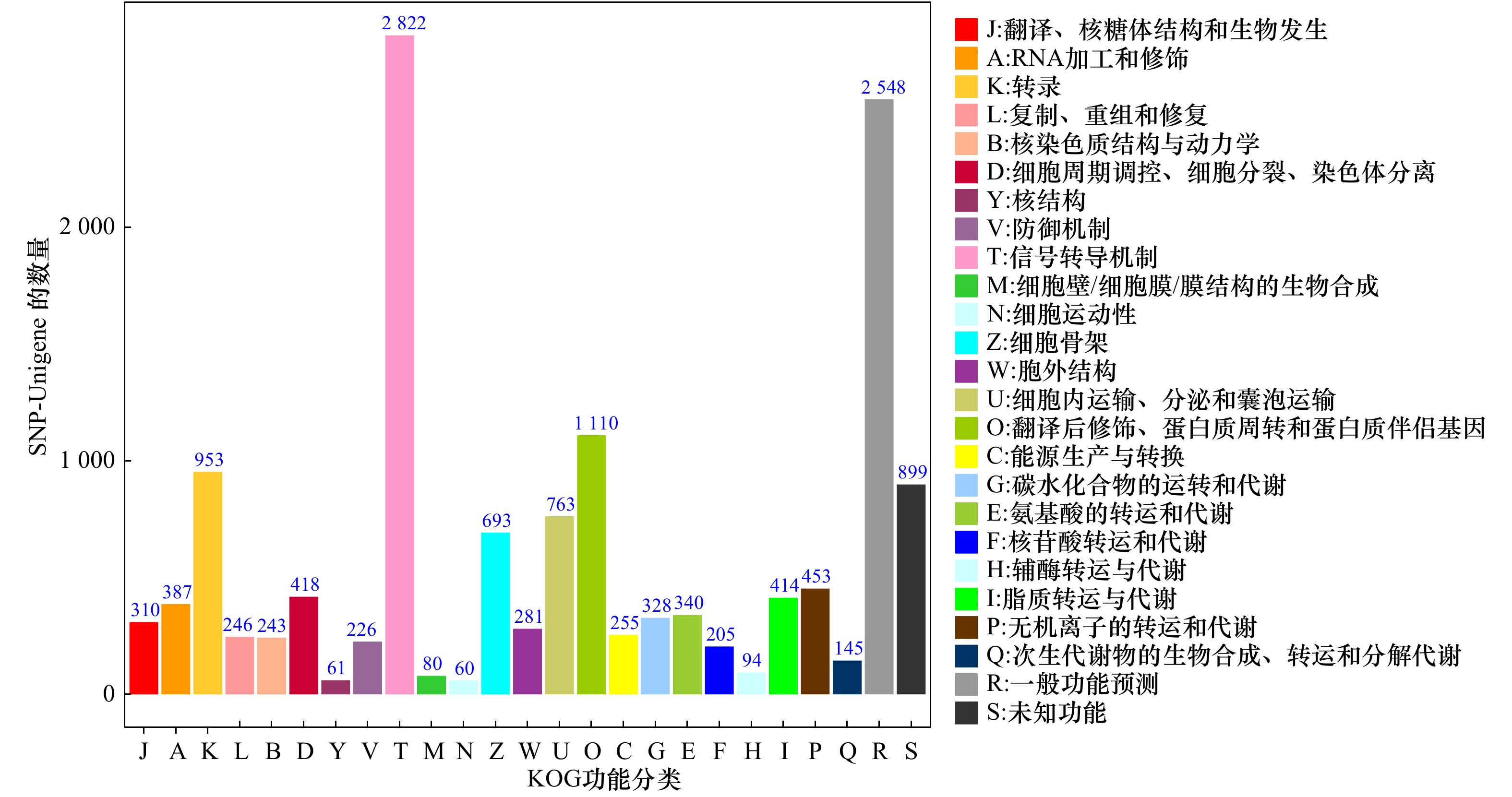
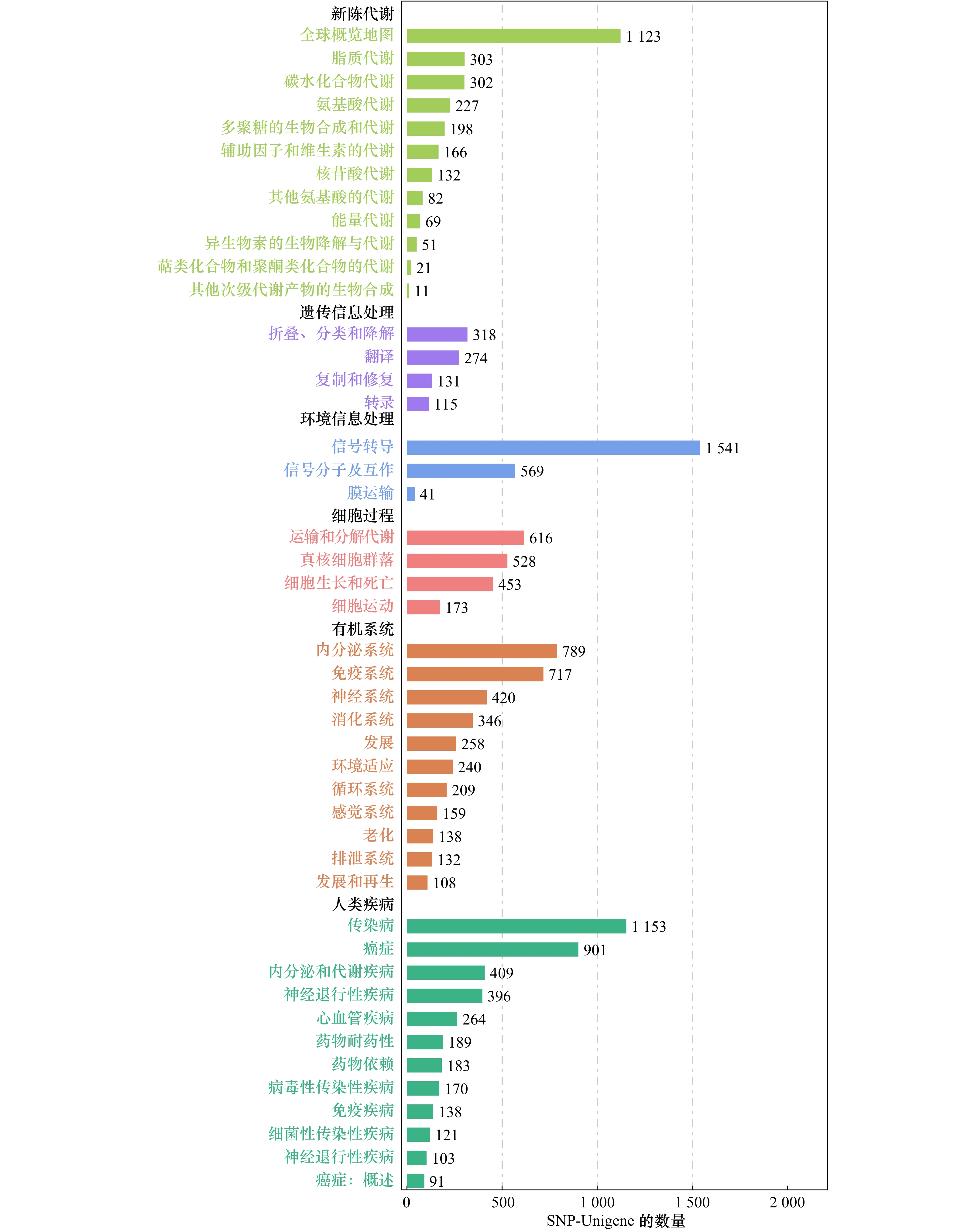
摘要: 为了研究低氧胁迫下军曹鱼肠道转录组中单核苷酸多态性(SNP)标记位点及SNP所在基因SNP-Unigene的作用,通过SOAPsnp软件对军曹鱼幼鱼对照组和低氧胁迫转录组测序结果进行SNP检测,并将其比对到GO、KOG、KEGG数据库进行功能注释。结果显示,军曹鱼转录组SNP位点分布在26 120条SNP-Unigene上,共检测到431 845个SNP位点,SNP平均发生频率约为1/171 bp;SNP-Unigene功能注释发现,在低氧胁迫条件下,军曹鱼SNP-Unigene主要涉及信号转导、传染病、癌症和内分泌系统等信号通路。进一步筛选到3 417条SNP-Unigene被注释到MAPK信号通路等35条与免疫相关的通路中。基于转录组差异基因分析,检测了其中7个重要免疫通路中18个免疫相关基因的SNP位点分布情况。同时,也检测了HIF-1信号通路中PIK3CA等8个差异基因的SNP位点分布情况。研究结果将为进一步挖掘免疫及低氧相关SNP的分子遗传标记奠定基础,为军曹鱼低氧适应机制的深入研究提供科学参考。Abstract: In order to mine single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites relates to hypoxia stress and study the function of the gene SNP-Unigene from Rachycentron canadum. SOAPsnp software is mainly used to detect the SNP of the intestinal transcriptome sequencing results of cobia juveniles under hypoxia stress conditions, and then annotation of them in the databases of GO, KOG, and KEGG are compared. The results show that the transcriptome SNP locus are distributed on 26 120 SNP-Unigene, with a total of 431 845 SNP sites are detected, the average frequency of SNP occurrence is about 1/171 bp. SNP-Unigene functional annotation showes that the cobia is mainly involved in signal transduction, infectious disease, cancer and endocrine system under hypoxia stress. Further, 3 417 SNP-Unigene are annotated to 35 immune-related pathways including MAPK signaling pathway. Based on the transcriptome differential gene analysis, the distribution of SNP sites of 18 immune-related genes in 7 important immune pathways is examined. At the same time, the distribution of SNP sites of 8 differential genes such as PIK3CA in the HIF-1 signaling pathway is also detected. The research results will lay the foundation for further mining of the molecular genetic markers of immune and hypoxia-related SNPs, and provide a scientific reference for the in-depth study of cobia’s hypoxia adaptation mechanism.
-
Key words:
- Rachycentron canadum /
- hypoxia stress /
- transcriptomics /
- immune gene /
- SNP
-
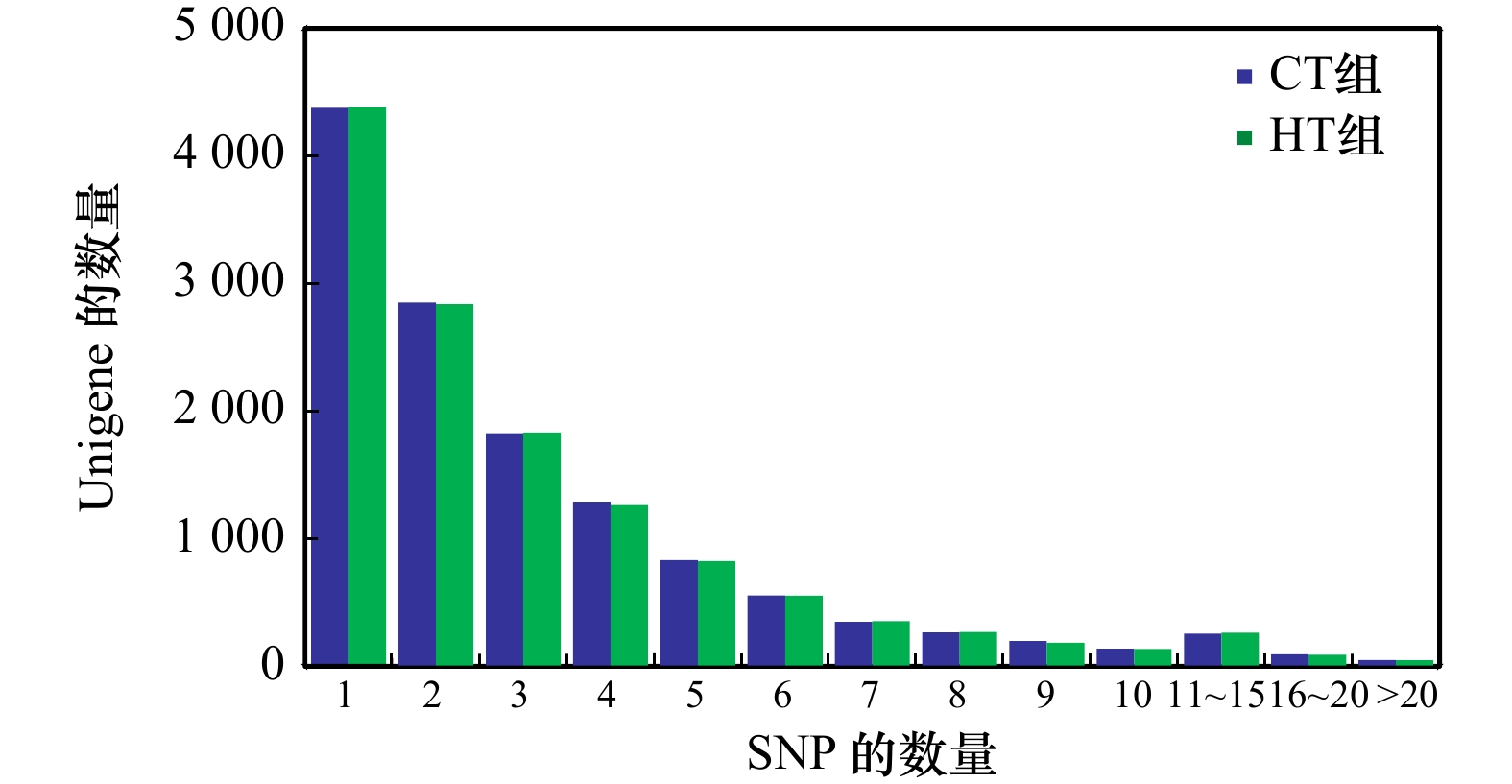
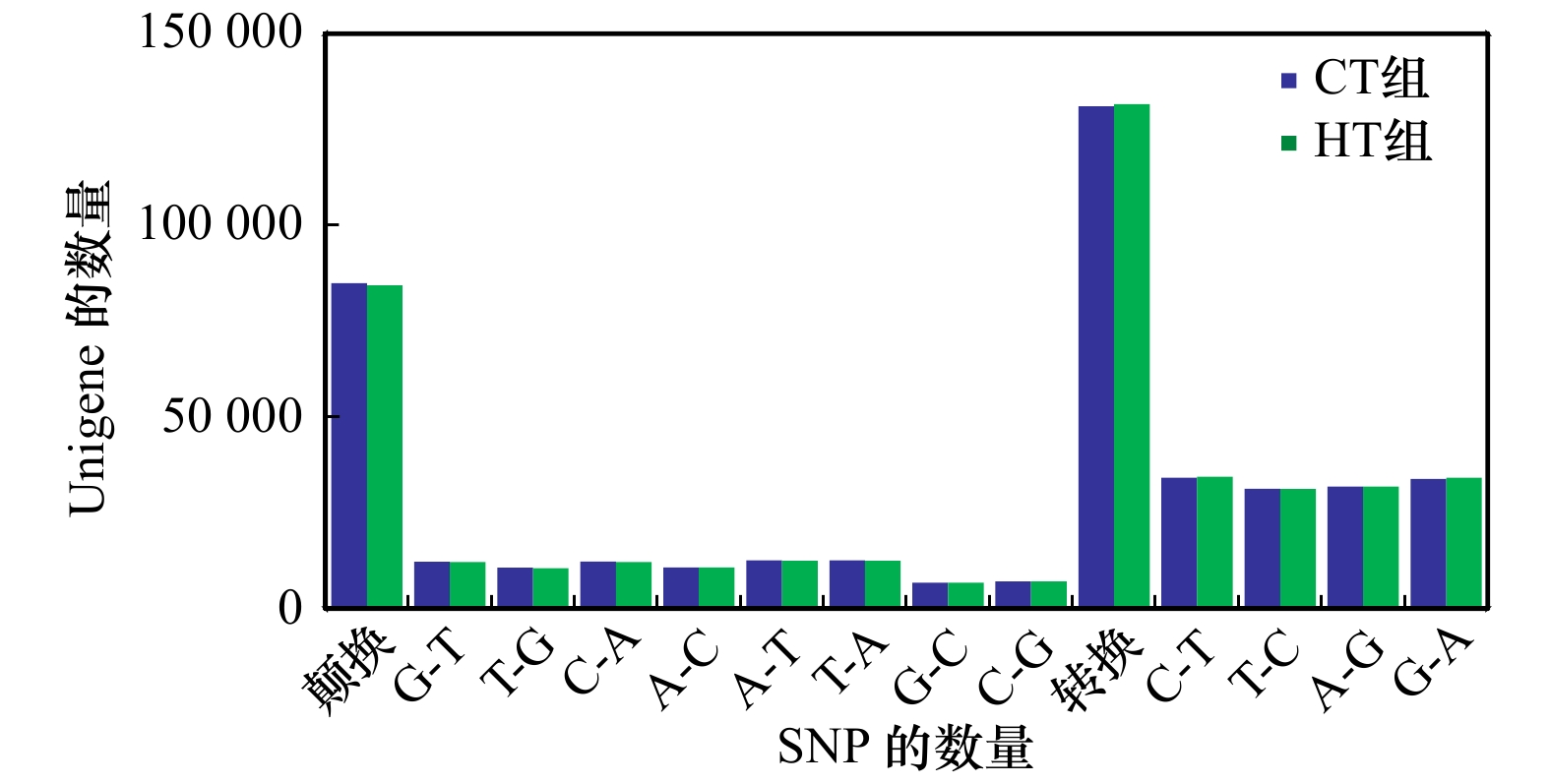
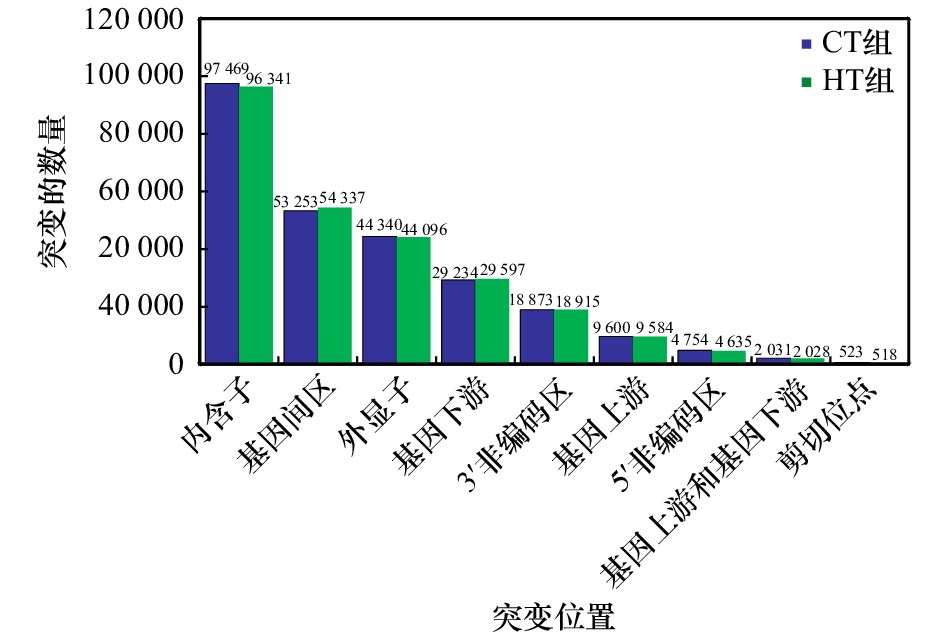
表 1 SNP位点数量概况
Tab. 1 The number of the SNP sites
组别 CT组 HT组 合计 SNP-Unigene数 13 076 13 044 26 120 SNP位点总数 215 953 215 892 431 845 纯合SNP位点数 76 550 76 092 152 642 表 2 免疫防御相关SNP-Unigene的KEGG富集分析
Tab. 2 KEGG enrichment analysis of immune-related SNP-Unigene
KEGG信号通路 信号通路ID SNP-Unigene数目 MAPK信号通路 ko04010 262 神经活性配体−受体相互作用 ko04080 228 Rap1信号通路 ko04015 190 Ras信号通路 ko04014 164 Wnt信号通路 ko04310 144 细胞因子−细胞因子受体相互作用 ko04060 137 细胞凋亡 ko04210 130 mTOR信号通路 ko04150 129 吞噬体 ko04145 123 趋化因子信号通路 ko04062 117 血小板活化 ko04611 117 FoxO信号通路 ko04068 117 NOD样受体信号通路 ko04621 113 白细胞经内皮迁移 ko04670 101 TNF信号通路 ko04668 95 Jak-STAT信号通路 ko04630 93 T细胞受体信号通路 ko04660 92 TRP通道的炎症介质调节 ko04750 89 NF-κB信号通路 ko04064 81 TGF-β信号通路 ko04350 80 Fcγ-R介导的吞噬作用 ko04666 79 B细胞受体信号通路 ko04662 73 造血细胞系 ko04640 72 Toll样受体信号通路 ko04620 71 自然杀伤细胞介导的细胞毒性 ko04650 69 Notch信号通路 ko04330 63 PPAR信号通路 ko03320 56 IL-17信号通路 ko04657 55 补体和凝血级联 ko04610 53 Fc ε RI信号通路 ko04664 47 抗原处理与呈递 ko04612 47 RIG-I样受体信号通路 ko04622 45 Toll和Imd信号通路 ko04624 35 肠道免疫网络Ig A的产生 ko04672 27 细胞质DNA传感通路 ko04623 23 合计 3 417 表 3 CT和HT转录组中差异表达免疫防御及低氧相关基因SNP位点分析
Tab. 3 SNP identified in differentially expressed immune and hypoxia-related genes in CT and HT transcriptomes
信号通路 基因名称 低氧后表达
水平CT-SNP
数目HT-SNP
数目MAPK信号通路 IL1R1 上调 4 4 ERBB3 上调 5 5 CACNA1E 上调 4 4 Wnt信号通路 FZD3 下调 3 1 LRP5 下调 5 5 PLCB2 上调 10 11 PLCB3 下调 7 7 NFATC4 上调 6 6 mTOR信号通路 LPIN1 上调 9 9 LPIN2 下调 3 3 DDIT4 上调 2 2 Jak-STAT信号通路 GHR 下调 8 8 LEPR 上调 5 5 IL4RA 上调 9 9 NOD样受体信号通路 TRPM7 下调 17 17 Toll和Imd信号通路 ANK3 上调 18 18 NF-κB信号通路 BTK 下调 3 3 TNFRSF11A 下调 2 2 HIF-1信号通路 PIK3CA 下调 5 4 HK1 上调 4 4 EPAS1 下调 3 3 GAPDH 下调 2 2 EDN1 下调 1 1 ENO3 下调 1 1 ANGPT1 上调 4 4 ANGPT2 上调 1 1 -
[1] Fan Shiliang, Li Haidong, Zhao Rui. Effects of normoxic and hypoxic conditions on the immune response and gut microbiota of Bostrichthys sinensis[J]. Aquaculture, 2020, 525: 735336. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735336 [2] 贾玉东, 王嘉伟, 李娟, 等. 溶解氧对鱼类生理功能影响及调控机制[J]. 水产研究, 2020, 7(1): 8−14. doi: 10.12677/OJFR.2020.71002Jia Yudong, Wang Jiawei, Li Juan, et al. Effect of dissolved oxygen on physiological functions and mechanism in fish[J]. Open Journal of Fisheries Research, 2020, 7(1): 8−14. doi: 10.12677/OJFR.2020.71002 [3] 穆景利, 靳非, 赵化德, 等. 水体低氧的早期暴露对青鳉(Oryzias latipes)后期的生长、性别比和繁殖能力的影响[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2017, 12(2): 137−146. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20160508002Mu Jingli, Jin Fei, Zhao Huade, et al. Early-life exposure to hypoxia altered growth, sex ratio, and reproduction in Medaka (Oryzias latipes)[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2017, 12(2): 137−146. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20160508002 [4] Vanderplancke G, Claireaux G, Quazuguel P, et al. Hypoxic episode during the larval period has long-term effects on European sea bass juveniles (Dicentrarchus labrax)[J]. Marine Biology, 2015, 162(2): 367−376. doi: 10.1007/s00227-014-2601-9 [5] 林艾影, 王维政, 陈刚, 等. 2种乳酸菌对军曹鱼幼鱼生长及消化酶、免疫酶活性的影响[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2020, 40(5): 112−117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2020.05.014Lin Aiying, Wang Weizheng, Chen Gang, et al. Effects of two lactic acid bacteria on growth performance and activities of digestive and non-specific immune enzymes of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum)[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2020, 40(5): 112−117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2020.05.014 [6] 勾效伟, 区又君, 廖锐. 我国军曹鱼研究现状[J]. 海洋渔业, 2007, 29(1): 84−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2007.01.016Gou Xiaowei, Ou Youjun, Liao Rui. Present status on studies of cobia Rachycentron canadum in China[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2007, 29(1): 84−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2007.01.016 [7] 王维政, 曾泽乾, 黄建盛, 等. 低氧胁迫对军曹鱼幼鱼生长、血清生化和非特异性免疫指标的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(2): 49−58.Wang Weizheng, Zeng Zeqian, Huang Jiansheng, et al. Hypoxia stress on growth, serum biochemical and non-specific immune indexes of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum)[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(2): 49−58. [8] 王维政, 曾泽乾, 黄建盛, 等. 低氧胁迫对军曹鱼幼鱼抗氧化、免疫能力及能量代谢的影响[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2020, 40(5): 12−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2020.05.002Wang Weizheng, Zeng Zeqian, Huang Jiansheng, et al. Effects of hypoxia stress on antioxidation, immunity and energy metabolism of juvenile cobia, Rachycentron canadum[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2020, 40(5): 12−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2020.05.002 [9] 李洪娟, 陈刚, 郭志雄, 等. 军曹鱼(Rachycentron canadum)幼鱼对环境低氧胁迫氧化应激与能量利用指标的响应[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(4): 12−19.Li Hongjuan, Chen Gang, Guo Zhixiong, et al. Oxidative stress and energy utilization responses of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum) to environmental hypoxia stress[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(4): 12−19. [10] 郭志雄, 曾泽乾, 黄建盛, 等. 急性低氧胁迫对大规格军曹鱼幼鱼肝脏氧化应激、能量利用及糖代谢的影响[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2020, 40(3): 134−140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2020.03.017Guo Zhixiong, Zeng Zeqian, Huang Jiansheng, et al. Effects of acute hypoxia on oxidative stress, energy utilization and carbohydrate metabolism in liver of large-sized juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum)[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2020, 40(3): 134−140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2020.03.017 [11] 黄建盛, 陆枝, 陈刚, 等. 急性低氧胁迫对军曹鱼大规格幼鱼血液生化指标的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(6): 76−84.Huang Jiansheng, Lu Zhi, Chen Gang, et al. Acute hypoxia stress on blood biochemical indexes of large-sized juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum)[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(6): 76−84. [12] Wang Weizheng, Huang Jiansheng, Zhang Jiandong, et al. Effects of hypoxia stress on the intestinal microflora of juvenile of cobia (Rachycentron canadum)[J]. Aquaculture, 2021, 536: 736419. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.736419 [13] 张晓萌, 马普, 王洪迪, 等. SNPs在水产动物中的研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2013(8): 7−11.Zhang Xiaomeng, Ma Pu, Wang Hongdi, et al. Progresses of SNPs studies in aquaculture animals[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2013(8): 7−11. [14] 赵莲, 薛蓓, 高焕, 等. SNP分子标记技术在经济甲壳动物中的应用进展[J]. 海洋渔业, 2017, 39(2): 233−240. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2017.02.013Zhao Lian, Xue Bei, Gao Huan, et al. Progress on the SNP molecular markers in economic crustaceans[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2017, 39(2): 233−240. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2017.02.013 [15] 侯振平, 蒋思文. 单核苷酸多态性的研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2004, 40(4): 45−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7033.2004.04.017Hou Zhenping, Jiang Siwen. Advance in single nucleotide polymorphism[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2004, 40(4): 45−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7033.2004.04.017 [16] 王婷, 黄智慧, 马爱军, 等. 基于转录组数据的大菱鲆(Scophthalmus maximus)SNP标记开发及多态性分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2014, 45(6): 1300−1307.Wang Ting, Huang Zhihui, Ma Aijun, et al. Development and polymorphic analysis of SNP markers in Scophthalmus maximus based on transcriptome database[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2014, 45(6): 1300−1307. [17] Tsai H Y, Robledo D, Lowe N R, et al. Construction and annotation of a high density SNP linkage map of the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) genome[J]. G3 Genes| Genomes| Genetics, 2016, 6(7): 2173−2179. [18] 刘敬文. 凡纳滨对虾免疫基因SNPs开发及其与WSSV抗性的关联分析[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2014.Liu Jingwen. SNPs identification of immune related genes from Litopenaeus vannamei and their association analyses to WSSV resistance[D]. Qingdao: The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014. [19] 张德宁, 吕建建, 刘萍, 等. 三疣梭子蟹生长相关SNP位点的鉴定[J]. 中国水产科学, 2015, 22(3): 393−401.Zhang Dening, Lü Jianjian, Liu Ping, et al. Identifying SNP markers correlated with growth of swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) based on a comparative transcriptome[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2015, 22(3): 393−401. [20] 王忠良, 丁燏, 许尤厚, 等. 马氏珠母贝(Pinctada fucata)血细胞转录组测序数据中SNP标记的开发及其功能注释分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(2): 403−412.Wang Zhongliang, Ding Yu, Xu Youhou, et al. SNP discovery and functional annotation in transcriptome datasets from hemocytes of Pinctada fucata[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(2): 403−412. [21] 李纪勤, 包振民, 李玲, 等. 栉孔扇贝EST-SNP标记开发及多态性分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2013, 43(1): 56−63.Li Jiqin, Bao Zhenmin, Li Ling, et al. Development and characterization of EST-SNP in Chlamys farreri[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2013, 43(1): 56−63. [22] 雒林通, 马芳, 唐德富, 等. 基于益生菌调节的太平鸡回肠SNP位点分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2020, 48(21): 86−90, 94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2020.21.023Luo Lintong, Ma Fang, Tang Defu, et al. SNP site analysis of Taiping chicken ileum based on probiotic regulation[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(21): 86−90, 94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2020.21.023 [23] 王菁, 刘付柏, 许尤厚, 等. 基于转录组测序的方斑东风螺单核苷酸多态性位点挖掘及功能注释[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2021, 41(1): 111−118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2021.01.015Wang Jing, Liu Fubai, Xu Youhou, et al. SNP site biological analysis of Babylonia areolata based on RNA-seq technology[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2021, 41(1): 111−118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2021.01.015 [24] 唐修阳, 王传聪, 项杰, 等. 罗氏沼虾转录组免疫相关SNP的挖掘与分析[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(4): 145−148.Tang Xiuyang, Wang Chuancong, Xiang Jie, et al. Mining and analysis of immune-related SNPs in transcriptome of Macrobrachium rosenbergii[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(4): 145−148. [25] 陈柏湘, 王伟峰, 王卫民, 等. 团头鲂低氧耐受相关SNPs标记的开发[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2019, 38(2): 23−29.Chen Boxiang, Wang Weifeng, Wang Weimin, et al. Isolation of SNP markers associated with hypoxia tolerance in Megalobrama amblycephala[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2019, 38(2): 23−29. [26] An Rui, Fu Jianjun, Jiang Bingjie, et al. Development of SNP markers for the bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) by using transcriptomic sequences[J]. Conservation Genetics Resources, 2020, 12(3): 409−412. doi: 10.1007/s12686-020-01133-z [27] 曹丹煜. 军曹鱼幼鱼盐度适应特性及渗透压调节分子机制的初步分析[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学, 2020.Cao Danyu. Preliminary analysis of salinity adaptation characteristics and osmotic pressure regulation molecular mechanism of juvenile cobia, Rachycentron canadum[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2020. [28] 王伟佳, 韩兆方, 李完波, 等. 大黄鱼雌雄性腺长链非编码RNA的挖掘与差异分析[J]. 中国水产科学, 2019, 26(5): 852−860.Wang Weijia, Han Zhaofang, Li Wanbo, et al. The identification and analysis of long noncoding RNA in testes and ovaries of the large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea)[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2019, 26(5): 852−860. [29] 张美彦, 宋春艳, 于海龙, 等. 基于SNP分型的香菇交配型AS-PCR鉴定[J]. 食用菌学报, 2019, 26(2): 1−9.Zhang Meiyan, Song Chunyan, Yu Hailong, et al. Mating-type identification of Lentinula edodes based on SNP genotyping by AS-PCR[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2019, 26(2): 1−9. [30] 范欢欢, 王天骄, 董依萌, 等. 马鹿特异性SNP分子标记的验证[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2021, 48(4): 1313−1322.Fan Huanhuan, Wang Tianjiao, Dong Yimeng, et al. Verification of red deer specific molecular marker SNP[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2021, 48(4): 1313−1322. [31] Wang Kai, Li Mingyao, Hakonarson H. ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 38(16): e164. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq603 [32] Wang Wenji, Yi Qilin, Ma Liman, et al. Sequencing and characterization of the transcriptome of half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis)[J]. BMC Genomics, 2014, 15(1): 470. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-470 [33] Wang Panpan, Xiao Shijun, Han Zhaofang, et al. SNP discovery in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) using Roche 454 pyrosequencing sequencing platform[J]. Conservation Genetics Resources, 2015, 7(4): 777−779. doi: 10.1007/s12686-015-0481-z [34] Hayes B, Laerdahl J K, Lien S, et al. An extensive resource of single nucleotide polymorphism markers associated with Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) expressed sequences[J]. Aquaculture, 2007, 265(1/4): 82−90. [35] Zhao Hui, Li Qizhai, Li Jun, et al. The study of neighboring nucleotide composition and transition/transversion bias[J]. Science in China Series C: Life Sciences, 2006, 49(4): 395−402. doi: 10.1007/s11427-006-2002-5 [36] 李胜杰, 白俊杰, 赵荦, 等. 大口黑鲈EST-SNP标记开发及其与生长性状的相关性分析[J]. 海洋渔业, 2018, 40(1): 38−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2018.01.005Li Shengjie, Bai Junjie, Zhao Luo, et al. Development of EST-SNPs in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) and analysis of their correlation with growth traits[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2018, 40(1): 38−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2018.01.005 [37] 李彦杰, 贾洪沅, 李庆天, 等. 基于转录组数据的三峡库区消落带适生狗牙根SNPs和SSRs分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 2020, 33(3): 524−528.Li Yanjie, Jia Hongyuan, Li Qingtian, et al. Analysis of SNPs and SSRs of suitable Cynodon dactylon in fluctuating zone of Three Gorges Reservoir Area based on transcriptome data[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 33(3): 524−528. [38] Zhao Zhongming, Boerwinkle E. Neighboring-nucleotide effects on single nucleotide polymorphisms: a study of 2.6 million polymorphisms across the human genome[J]. Genome Research, 2002, 12(11): 1679−1686. doi: 10.1101/gr.287302 [39] 唐立群, 肖层林, 王伟平. SNP分子标记的研究及其应用进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2012, 28(12): 154−158. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2012-0074Tang Liqun, Xiao Cenglin, Wang Weiping. Research and application progress of SNP markers[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2012, 28(12): 154−158. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2012-0074 [40] 谭新, 童金苟. SNPs及其在水产动物遗传学与育种学研究中的应用[J]. 水生生物学报, 2011, 35(2): 348−354. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1035.2011.00348Tan Xin, Tong Jingou. SNPs and their applications in studies on genetics and breeding of aquaculture animals[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2011, 35(2): 348−354. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1035.2011.00348 [41] 孙明洁, 张娜, 徐善良, 等. 两种弧菌感染大黄鱼免疫相关基因的SNP位点分析[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2019, 28(5): 772−781. doi: 10.12024/jsou.20190402623Sun Mingjie, Zhang Na, Xu Shanliang, et al. Analysis of SNP loci in immune-related genes of two species of Vibrio infecting large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea)[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2019, 28(5): 772−781. doi: 10.12024/jsou.20190402623 [42] 张磊. 鮸鱼microRNA-21对IL1R1的免疫调控机制研究[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋大学, 2020.Zhang Lei. Study on the immune regulation mechanism of microRNA-21 on IL1R1 in Miichthys miiuy[D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University, 2020. [43] Lam S Y, Tipoe G L, Liong E C, et al. Chronic hypoxia upregulates the expression and function of proinflammatory cytokines in the rat carotid body[J]. Histochemistry and Cell Biology, 2008, 130(3): 549−559. doi: 10.1007/s00418-008-0437-4 [44] 郭旗, 李超. IL1R1和IL1R2基因多态性与缺血性脑卒中患病风险的相关性[J]. 贵州医科大学学报, 2018, 43(3): 294−298.Guo Qi, Li Chao. Association of IL1R1 and IL1R2 gene polymorphisms with risk of ischemic stroke[J]. Journal of Guizhou Medical University, 2018, 43(3): 294−298. [45] 胡亮. 藏系绵羊种质资源鉴定技术的研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2019.Hu Liang. Study on identification techniques of Tibetan Sheep germplasm resources[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2019. [46] 赵亚男, 刘明, 张玥, 等. Wnt信号通路与皮肤创面愈合的关系[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2015, 15(11): 2173−2176, 2184.Zhao Ya’nan, Liu Ming, Zhang Yue, et al. The relationship between Wnt signaling pathway and skin wound healing[J]. Progress in Modern Biomedicine, 2015, 15(11): 2173−2176, 2184. [47] 陈爽, 张晓敏. Wnt信号通路在自身免疫性疾病中的作用研究进展[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2021, 37(2): 254−258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2021.02.025Chen Shuang, Zhang Xiaomin. Research progress on role of Wnt signaling pathway in autoimmune diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Immunology, 2021, 37(2): 254−258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2021.02.025 [48] 张丽晗, 罗智, 有文静, 等. 黄颡鱼FZD家族4个基因的克隆、组织表达及对铜的响应[J]. 水产学报, 2018, 42(5): 625−632.Zhang Lihan, Luo Zhi, You Wenjing, et al. Molecular characterization and tissue distribution of Frizzled (FZD) in yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) by copper exposure[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2018, 42(5): 625−632. [49] Zhao Bingru, Fu Xuefeng, Tian Kechuan, et al. Identification of SNPs and expression patterns of FZD3 gene and its effect on wool traits in Chinese Merino sheep (Xinjiang Type)[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2019, 18(10): 2351−2360. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(19)62735-8 [50] 张璐. 环境因素及LRP5基因与2型糖尿病发病关联的队列研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2017.Zhang Lu. Association of environmental factors and LRP5 gene with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a cohort study[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2017. [51] Eaton J M, Mullins G R, Brindley D N, et al. Phosphorylation of lipin 1 and charge on the phosphatidic acid head group control its phosphatidic acid phosphatase activity and membrane association[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2013, 288(14): 9933−9945. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.441493 [52] Lu Shuxian, Lü Zhaojie, Wang Zhihao, et al. Lipin 1 deficiency causes adult-onset myasthenia with motor neuron dysfunction in humans and neuromuscular junction defects in zebrafish[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(6): 2788−2805. doi: 10.7150/thno.53330 [53] Mylonis I, Sembongi H, Befani C, et al. Hypoxia causes triglyceride accumulation by HIF-1-mediated stimulation of lipin 1 expression[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 2012, 125(14): 3485−3493. [54] He Xiaoping, Xu Xuewen, Zhao Shuhong, et al. Investigation of Lpin1 as a candidate gene for fat deposition in pigs[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2009, 36(5): 1175−1180. doi: 10.1007/s11033-008-9294-4 [55] 郭志雄. 低氧环境对军曹鱼幼鱼生化指标、相关基因表达的影响及其转录组学分析[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学, 2020.Guo Zhixiong. Effects of hypoxic environment on biochemical indexes, related gene expression and transcriptome analysis of cobia juveniles[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2020. [56] Zhang Kai, Liu Xiumei, Han Miao, et al. Functional differentiation of three phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA) in response to Vibrio anguillarum infection in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus)[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2019, 92: 450−459. [57] Engelman J A, Luo Ji, Cantley L C. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2006, 7(8): 606−619. doi: 10.1038/nrg1879 [58] Wu Xiaoyun, Ding Xuezhi, Chu Min, et al. Novel SNP of EPAS1 gene associated with higher hemoglobin concentration revealed the hypoxia adaptation of yak (Bos grunniens)[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2015, 14(4): 741−748. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(14)60854-6 [59] 朱莉, 李根, 孔小艳, 等. 藏绵羊血红蛋白、EPAS1基因与低氧适应相关性研究[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 35(3): 436−442.Zhu Li, Li Gen, Kong Xiaoyan, et al. The association of genes hemoglobin and EPAS1 with hypoxia adaptation in the Tibetan Sheep[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2020, 35(3): 436−442. -





 下载:
下载: