Wind tunnel test and numerical simulation of partial wind field characteristics of islands
-
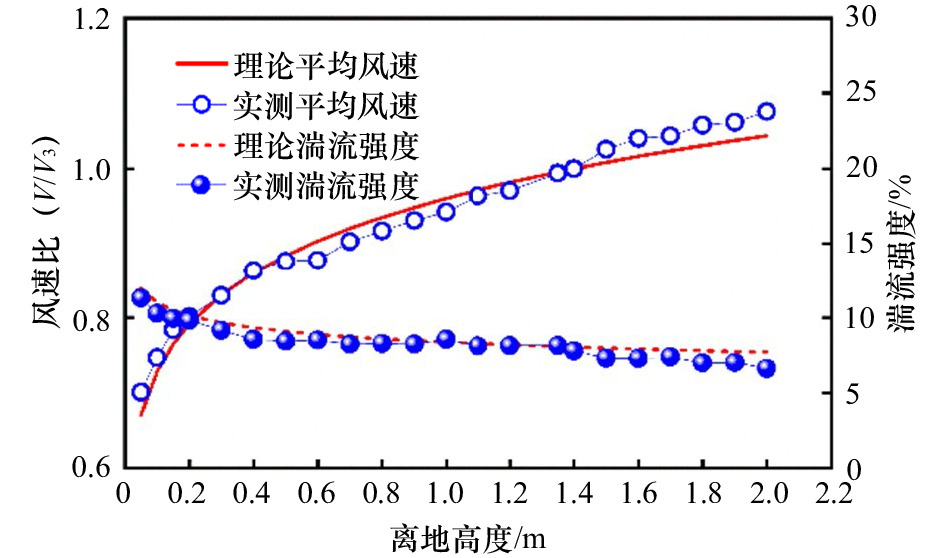
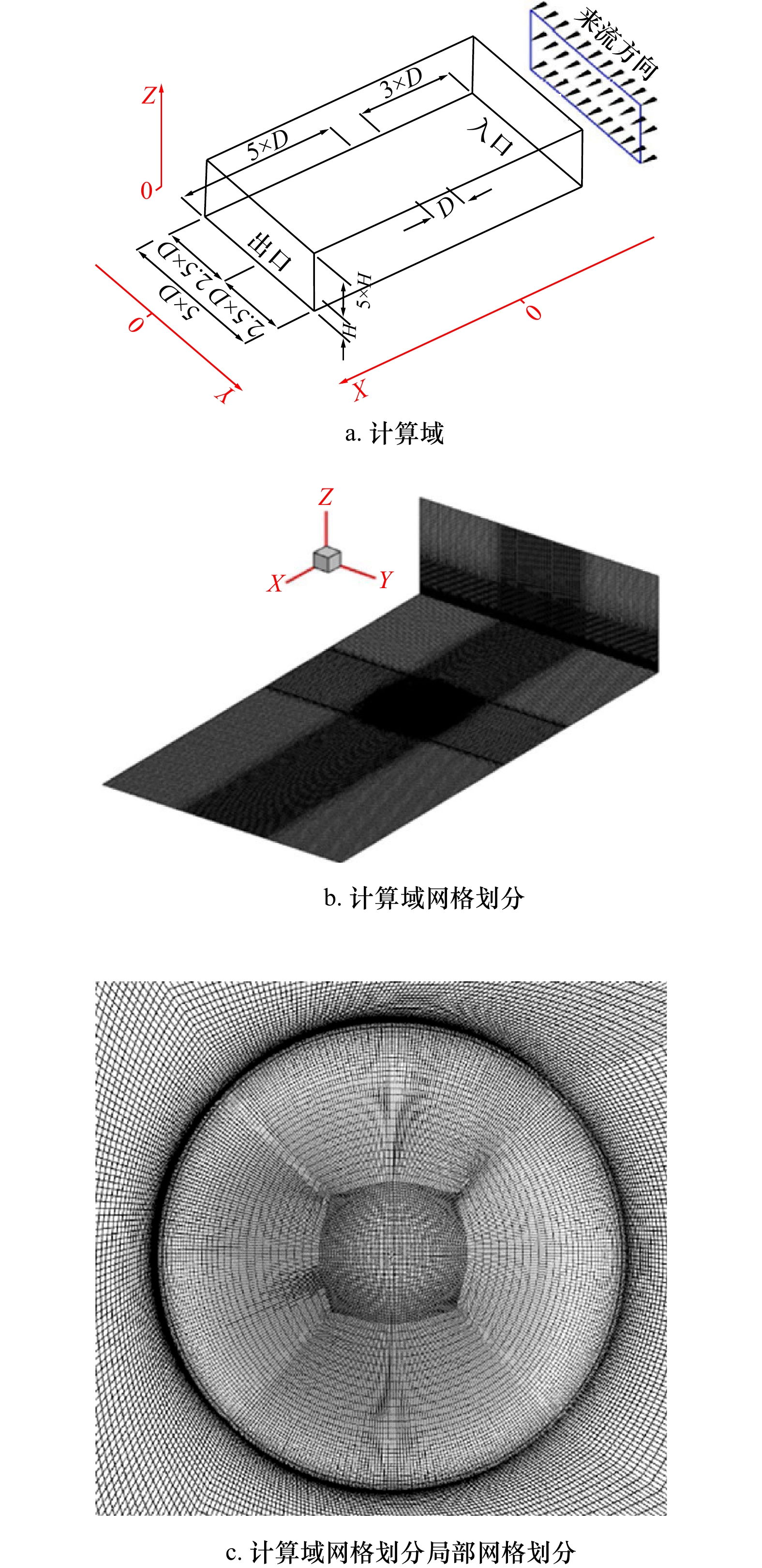
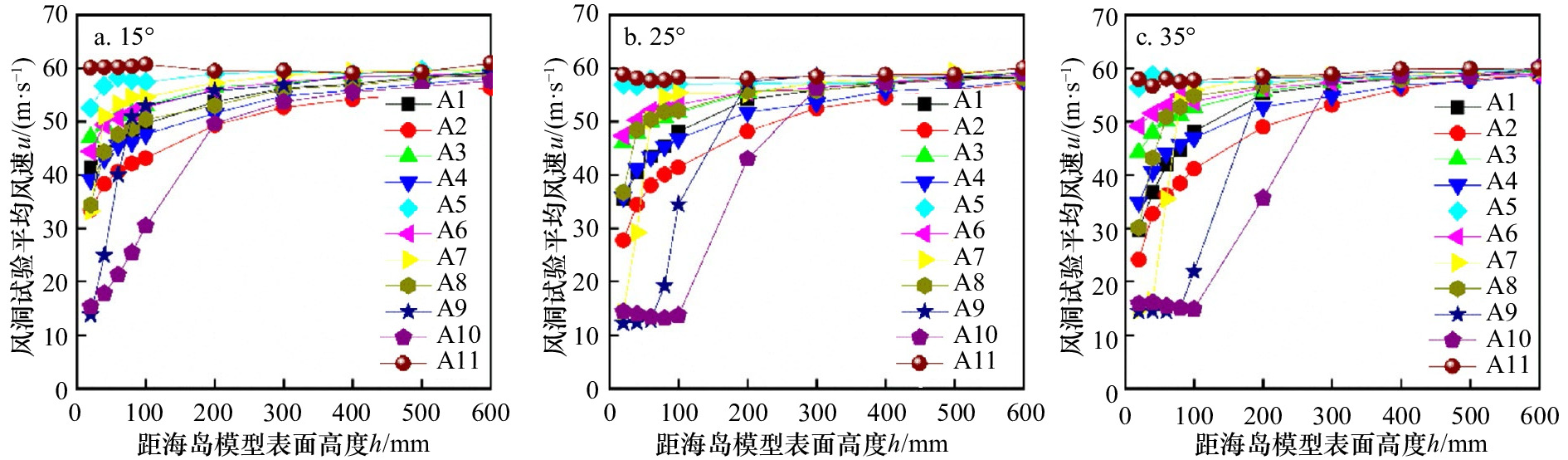
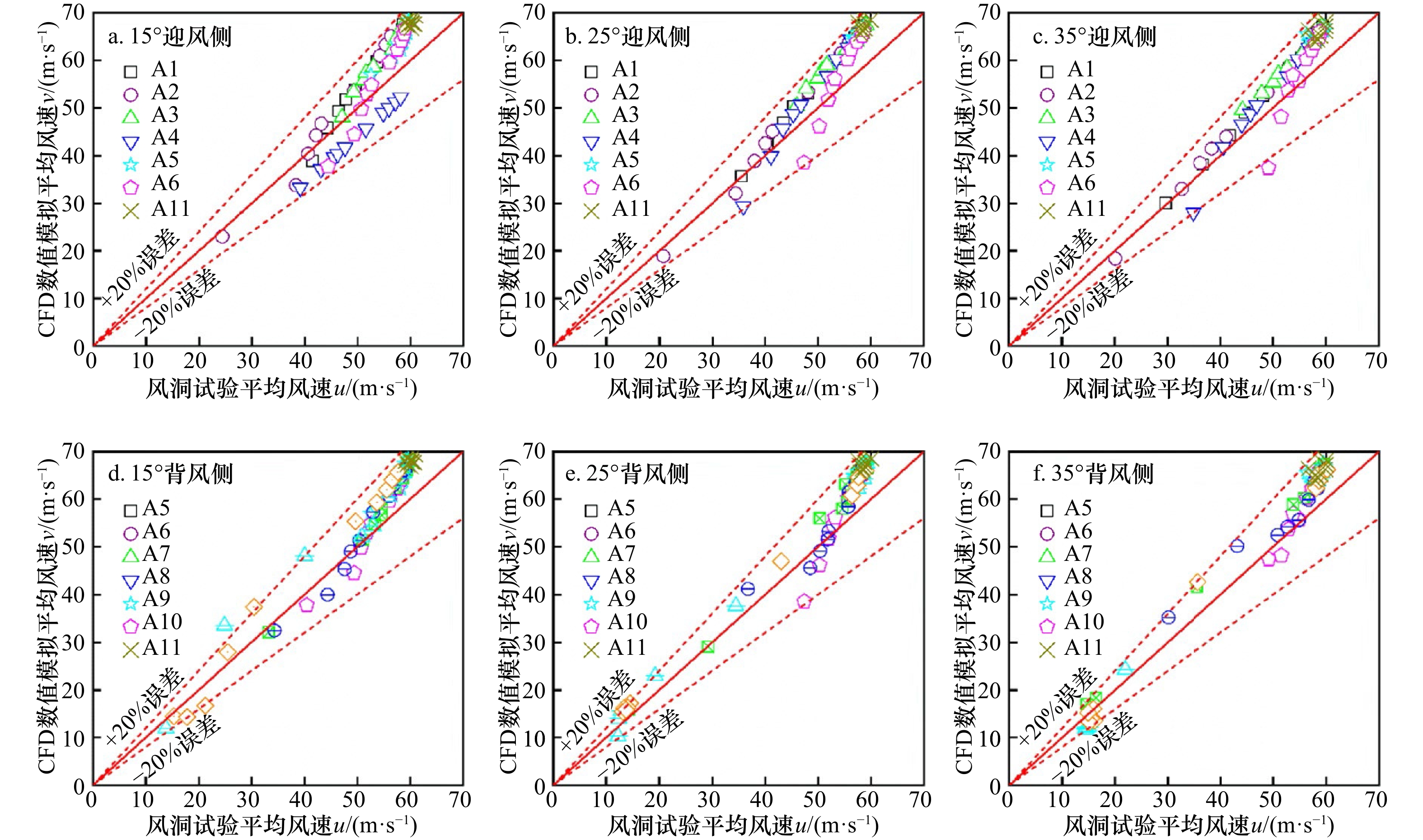
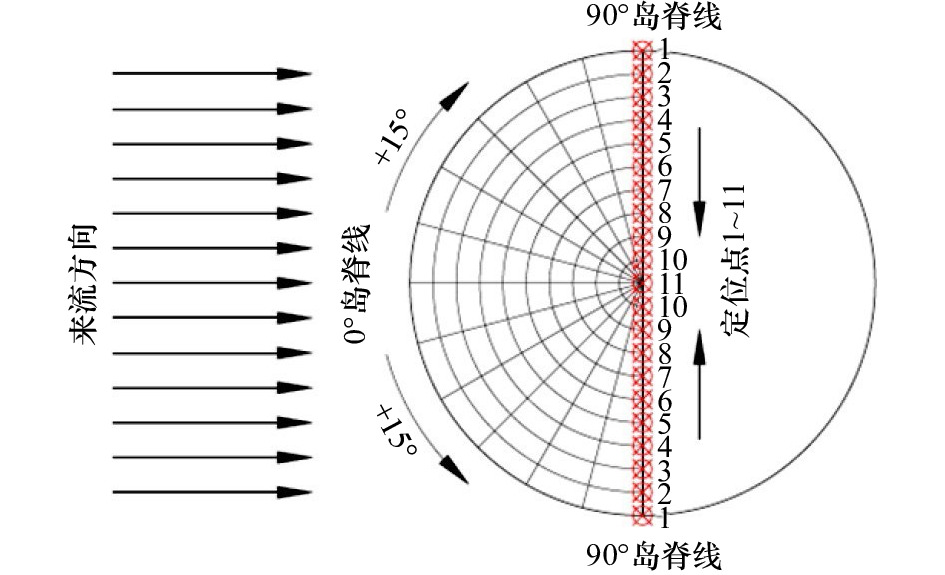
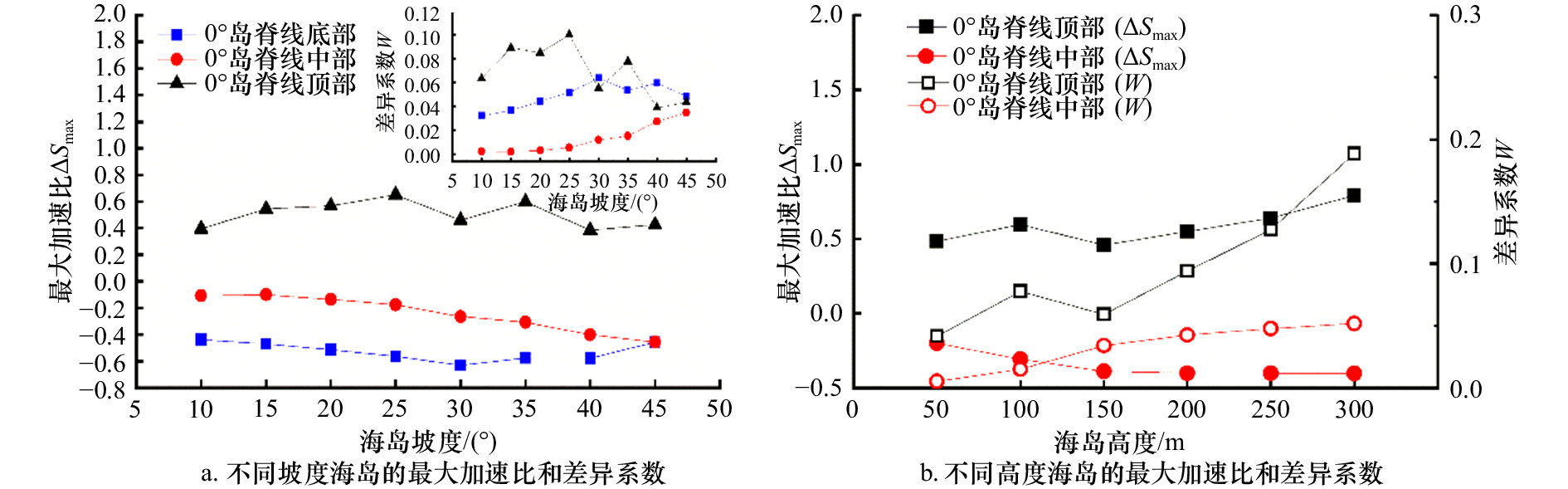
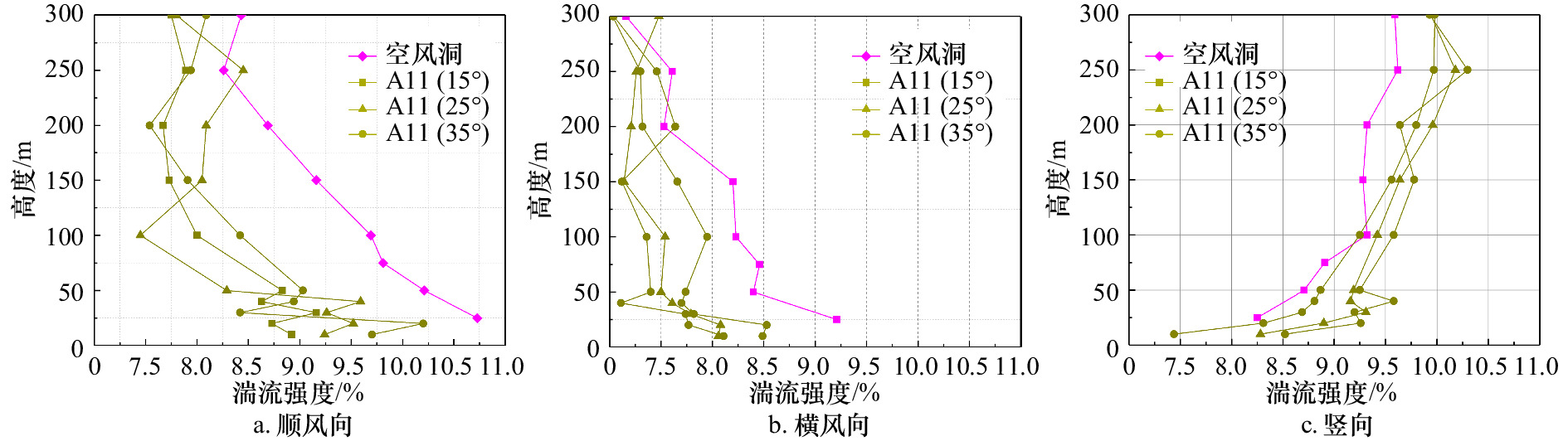
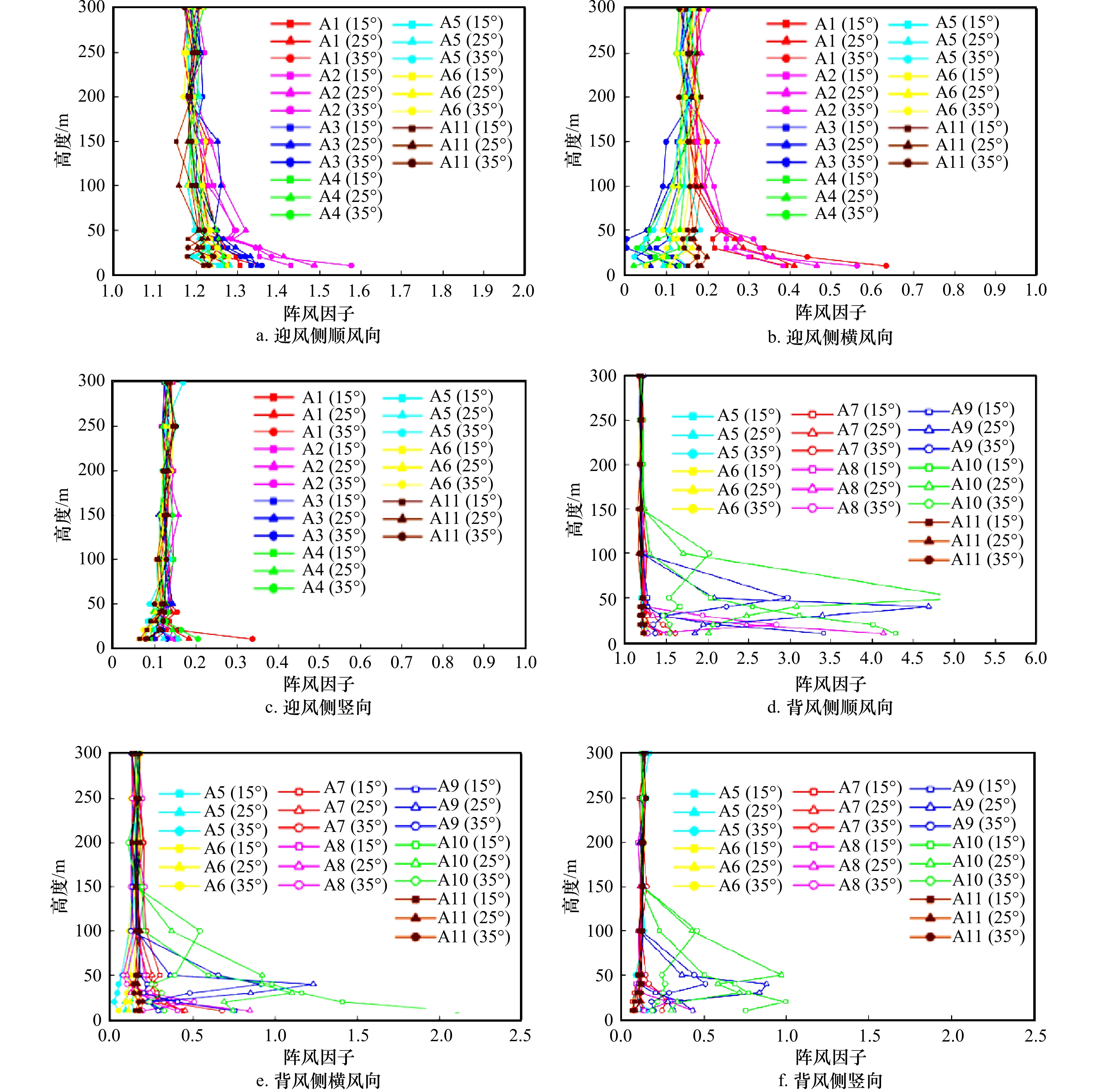
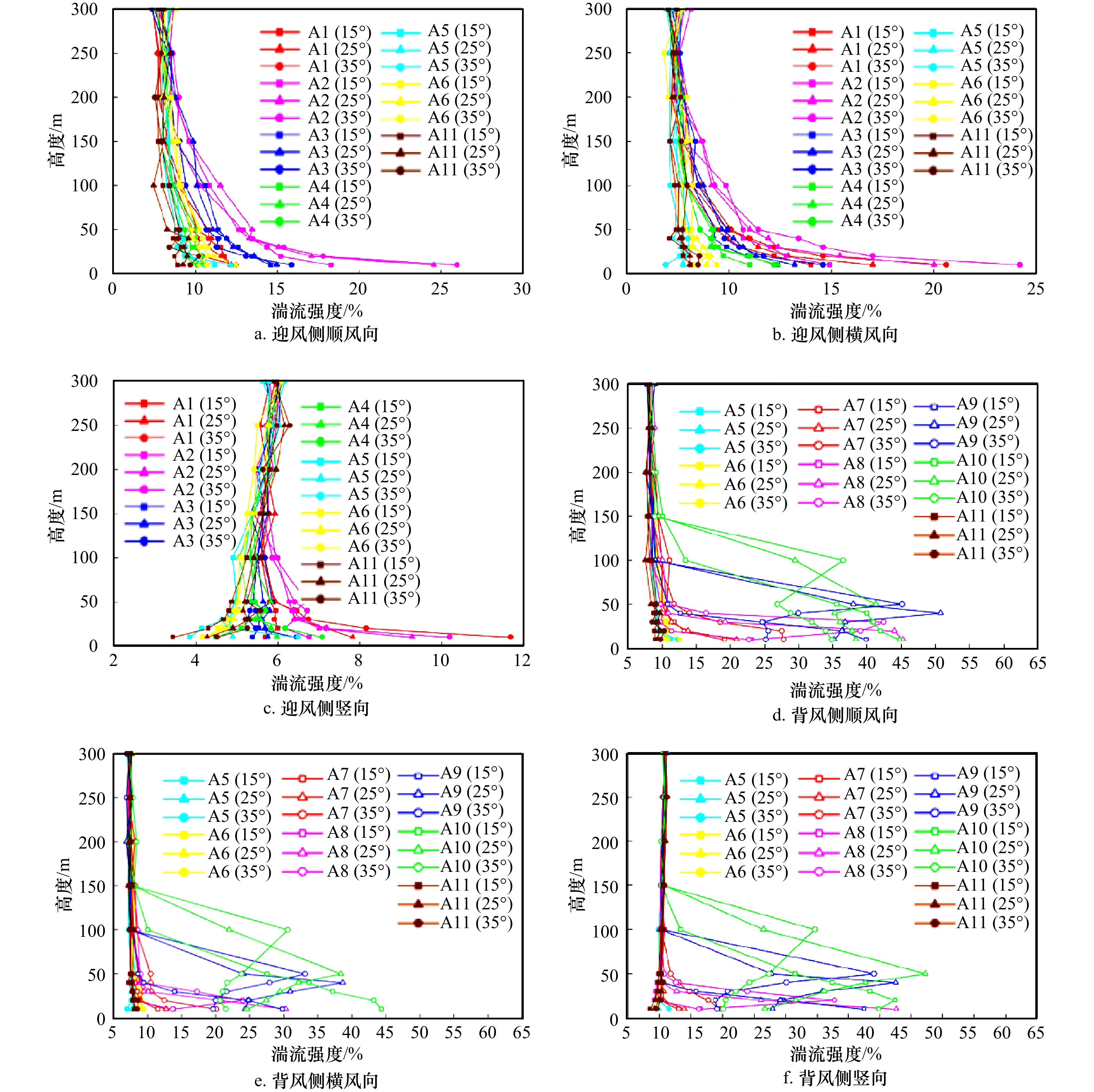
摘要: 针对海岛局部风效应突出的问题,采用边界层风洞试验与数值模拟相结合的方法,对3种坡度的理想化海岛地形的风剖面进行了数值拟合,定义了差异系数来描述风剖面变化,利用数值模拟研究了差异系数和最大加速比在迎风侧的分布,重点探讨了海岛坡度和高度对最大加速比和差异系数的影响;基于风洞数据,对迎风侧和背风侧顺风向、横风向和竖向湍流强度和阵风因子分布进行了研究。结果表明:数值模拟与风洞试验结果较接近,风剖面指数在迎风侧较小;靠近坡顶的加速效应尤为明显,其最大加速比为0.4~1.0;坡腰处的差异系数较小,随着岛脊线角度的增加,差异系数为0的位置有向坡脚靠近的趋势;坡度增大到25°、0°岛脊线上最大加速比和差异系数均较大;迎风侧的三向湍流强度分布较规律,而背风侧的三向湍流强度分布较杂乱,尤其是在距海岛表面100 m高度范围内;阵风因子和湍流强度的变化趋势具有较高的一致性。Abstract: In view of the prominent partial wind effect on islands, the wind profiles of idealized islands topography with three slopes are fitted by means of boundary layer wind tunnel test and numerical simulation. The difference factor is defined to describe the variation of wind profile, the distribution of maximum acceleration ratio and difference factor on the windward side of islands is studied by numerical simulation, and the effects of island slope and height on maximum acceleration ratio and difference factor are discussed comprehensively. Moreover, based on the wind tunnel data, the along-wind, cross-wind and vertical turbulence intensity and gust factor of the windward and leeward sides are studied. The results show that the numerical simulation is basically consistent with the wind tunnel test results and the wind profile exponent (α) is smaller on the windward side of islands. It also shows acceleration effect near the top of the island is particularly obvious and its maximum acceleration ratio is between 0.4 and 1.0. Moreover, the difference factor at the hillside is lower, and with the increase of the angle of the island ridge, the position where the difference factor is 0 tends to approach the slope toe. As the island slope increases to 25°, the maximum acceleration ratio and difference factor on the 0° island ridge are large. The distribution of three-dimensional turbulence intensity on the windward side is relatively regular, while that on the leeward side is disordered especially in the range of 100 m away from the island’s surface. It is worth noting that the trends of gust factor and turbulence intensity are highly consistent.
-
表 1 海岛参数
Tab. 1 Island parameters
序号 高度H/m 底面直径D/m 坡度(2H/D) 海岛 海岛模型 海岛 海岛模型 1 100.00 0.20 746.41 1.49 15° 2 100.00 0.20 428.90 0.86 25° 3 100.00 0.20 285.63 17 35° -
[1] Guo Jian. Key technical innovation of Xihoumen Bridge—the longest steel box gird suspension bridge in the world[J]. Engineering Sciences, 2010, 8(4): 18−22. [2] 肖仪清, 李朝, 欧进萍, 等. 复杂地形风能评估的CFD方法[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 37(9): 30−35.Xiao Yiqing, Li Chao, Ou Jinping, et al. CFD approach to evaluation of wind energy in complex terrain[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 37(9): 30−35. [3] Wang Tong, Cao Shuyang, Ge Yaojun. Effects of inflow turbulence and slope on turbulent boundary layer over two-dimensional hills[J]. Wind and Structures, 2014, 19(2): 219−232. doi: 10.12989/was.2014.19.2.219 [4] Cao Shuyang, Wang Tong, Ge Yaojun, et al. Numerical study on turbulent boundary layers over two-dimensional hills-effects of surface roughness and slope[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2012, 104−106: 342−349. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2012.02.022 [5] 李正良, 孙毅, 魏奇科, 等. 山地平均风加速效应数值模拟[J]. 工程力学, 2010, 27(7): 32−37.Li Zhengliang, Sun Yi, Wei Qike, et al. Numerical simulation of mean velocity speed-up effect in hilly terrain[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2010, 27(7): 32−37. [6] 孙毅, 李正良, 黄汉杰, 等. 山地风场平均及脉动风速特性试验研究[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2011, 29(5): 593−599. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-1825.2011.05.010Sun Yi, Li Zhengliang, Huang Hanjie, et al. Experimental research on mean and fluctuating wind velocity in hilly terrain wind field[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2011, 29(5): 593−599. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-1825.2011.05.010 [7] 李正昊, 楼文娟, 章李刚, 等. 地貌因素对垭口内风速影响的数值模拟[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2016, 50(5): 848−855. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008973X.2016.05.006Li Zhenghao, Lou Wenjuan, Zhang Ligang, et al. Numerical simulation of effects of topographic factors on wind speed in col[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2016, 50(5): 848−855. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008973X.2016.05.006 [8] 陈政清, 李春光, 张志田, 等. 山区峡谷地带大跨度桥梁风场特性试验[J]. 实验流体力学, 2008, 22(3): 54−59, 67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9897.2008.03.012Chen Zhengqing, Li Chunguang, Zhang Zhitian, et al. Model test study of wind field characteristics of long-span bridge site in mountainous valley terrain[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, 2008, 22(3): 54−59, 67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9897.2008.03.012 [9] 李永乐, 蔡宪棠, 唐康, 等. 深切峡谷桥址区风场空间分布特性的数值模拟研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2011, 44(2): 116−122.Li Yongle, Cai Xiantang, Tang Kang, et al. Study of spatial distribution feature of wind fields over bridge site with a deep-cutting gorge using numerical simulation[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2011, 44(2): 116−122. [10] 于舰涵, 李明水, 廖海黎. 山区地形对桥位风场影响的数值模拟[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(4): 654−662. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.04.008Yu Jianhan, Li Mingshui, Liao Haili. Numerical simulation of effect of mountainous topography on wind field at bridge site[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(4): 654−662. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.04.008 [11] Vladut A C, Cosoiu C I, Georgescu A M, et al. Wind tunnel and numerical modeling of atmospheric boundary layer flow over Bolund Island[J]. Energy Procedia, 2016, 85: 603−611. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2015.12.250 [12] 杨秋彦, 苗峻峰, 王语卉. 海南岛地形对局地海风环流结构影响的数值模拟[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(3): 24−43.Yang Qiuyan, Miao Junfeng, Wang Yuhui. A numerical study of impact of topography on sea breeze circulation over the Hainan Island[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(3): 24−43. [13] 宋超辉, 王楠, 王阔, 等. 基于1988−2017年CCMP数据的浙江沿海海表风速变化及成因[J]. 大气科学学报, 2019, 42(4): 562−570.Song Chaohui, Wang Nan, Wang Kuo, et al. Variation and cause of sea surface wind speed in Zhejiang coastal area based on CCMP data from 1988 to 2017[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2019, 42(4): 562−570. [14] Chou Jieming, Dong Wenjie, Tu Gang, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution of landing tropical cyclones and disaster impact analysis in coastal China during 1990−2016[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 2020, 115: 102830. doi: 10.1016/j.pce.2019.102830 [15] 交通运输部. JTG/T 3360−01−2018, 公路桥梁抗风设计规范[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2018.Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. JTG/T 3360−01−2018, wind-resistant design specification for highway bridges[S]. Beijing: People’s Communications Press, 2018. [16] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. GB 50009−2012, 建筑结构荷载规范[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012: 30−33, 218−222.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. GB 50009−2012, load code for the design of building structures[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2012: 30−33, 218−222. [17] 唐煜, 郑史雄, 赵博文, 等. 平衡大气边界层自保持问题的研究[J]. 工程力学, 2014, 31(10): 129−135. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2013.04.0376Tang Yu, Zheng Shixiong, Zhao Bowen, et al. Numerical investigation on the self-sustaining of equilibrium atmosphere boundary layers[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 31(10): 129−135. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2013.04.0376 [18] Weng Wensong, Taylor P A, Walmsley J L. Guidelines for airflow over complex terrain: Model developments[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2000, 86(2/3): 169−186. [19] 王福军. 计算流体动力学分析[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004.Wang Fujun. Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004. [20] Richards P J, Younis B A. Comments on “Prediction of the wind-generated pressure distribution around buildings” by E. H. Mathews[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1990, 34(1): 107−110. doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(90)90152-3 [21] Architectural Institute of Japan. AIJ Recommendations for loads on buildings[S]. Tokyo: Architectural Institute of Japan Press, 2004. [22] 张善文, 刘建都, 韩小斌. 基于遗传算法的一种数据拟合方法[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 8(1): 66−68.Zhang Shanwen, Liu Jiandu, Han Xiaobin. A data fitness method based on genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 8(1): 66−68. [23] Chen Fazu. Turbulent characteristics over a rough natural surface part I: Turbulent structures[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 1990, 52(1/2): 151−175. [24] Batchvarova E, Gryning S E. Wind climatology, atmospheric turbulence and internal boundary-layer development in Athens during the MEDCAPHOT-TRACE experiment[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 1998, 32(12): 2055−2069. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(97)00422-6 [25] 洪新民, 郭文华, 熊安平. 山区峡谷风场分布特性及地形影响的数值模拟[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 37(5): 56−64.Hong Xinmin, Guo Wenhua, Xiong Anping. Numerical simulation of distribution characteristic of wind fields and terrain’s influence in mountain canyon[J]. Journal of Chang’an University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 37(5): 56−64. [26] 李加武, 徐润泽, 党嘉敏, 等. 喇叭口河谷地形基本风特性实测[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 40(6): 47−56.Li Jiawu, Xu Runze, Dang Jiamin, et al. Field measurement of basic wind characteristics of trumpet river valley[J]. Journal of Chang’an University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 40(6): 47−56. -




 下载:
下载: