Seasonal distribution and driving forces of suspended particulate matter in the northern Yellow River Delta
-
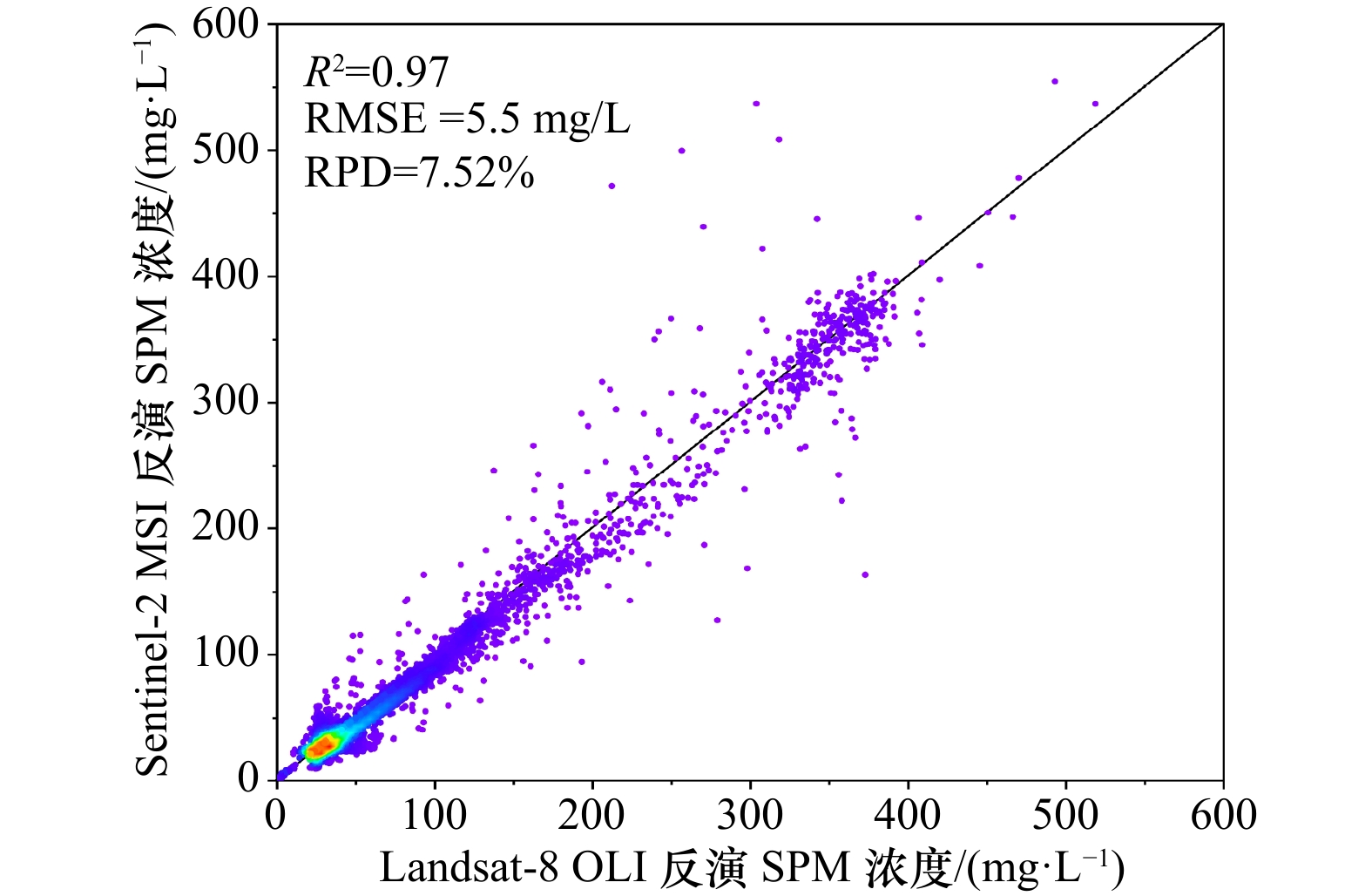
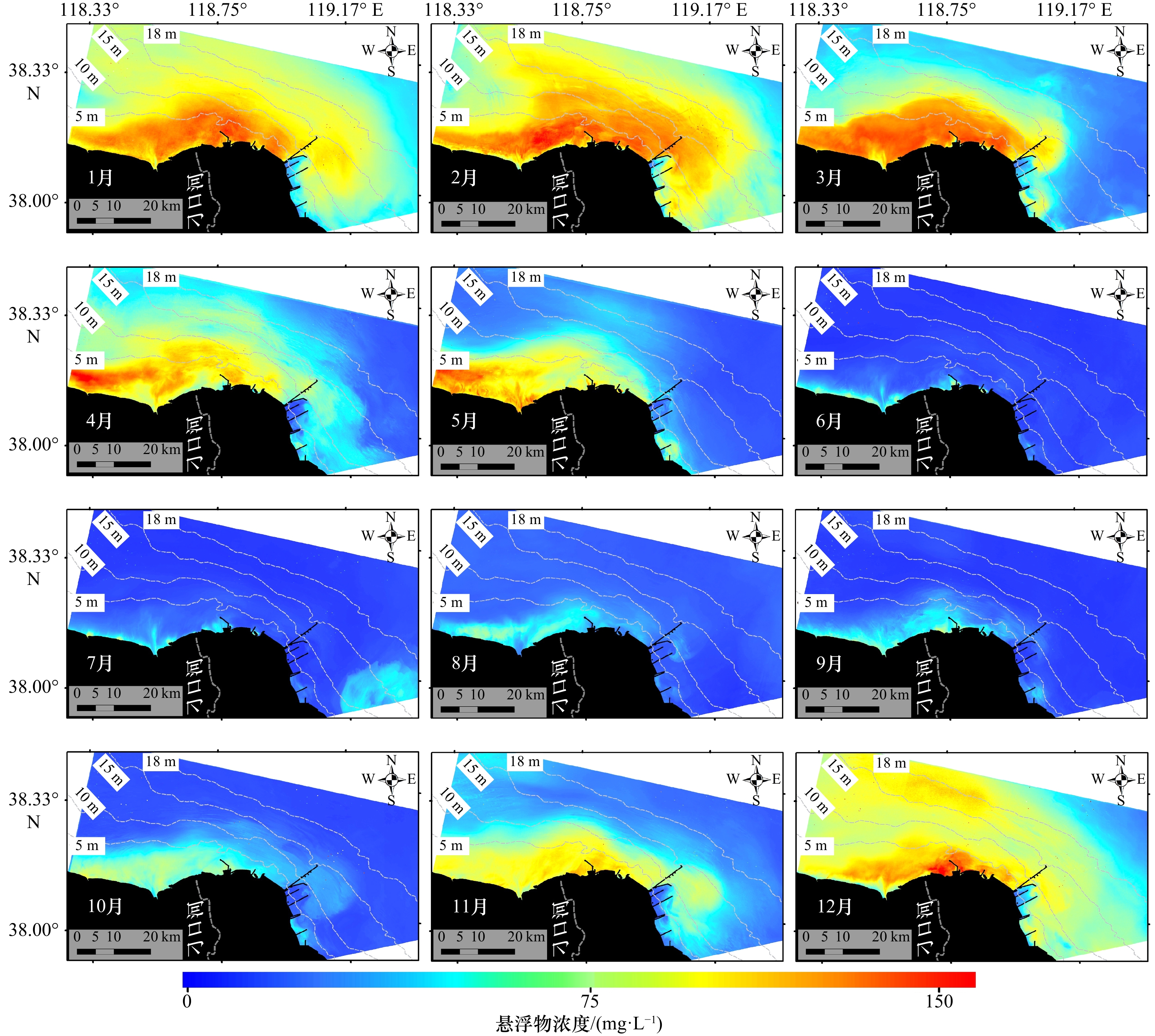
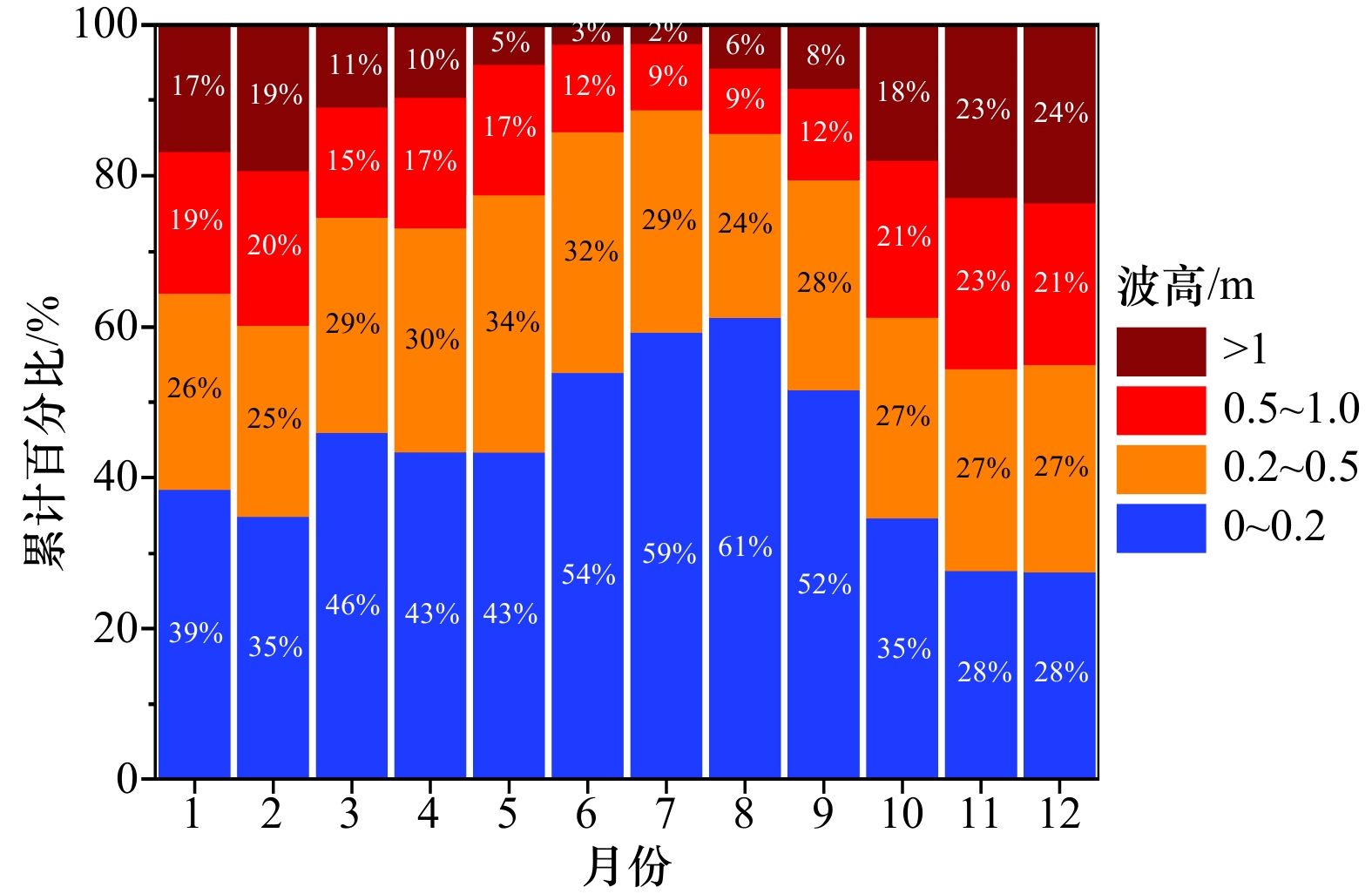
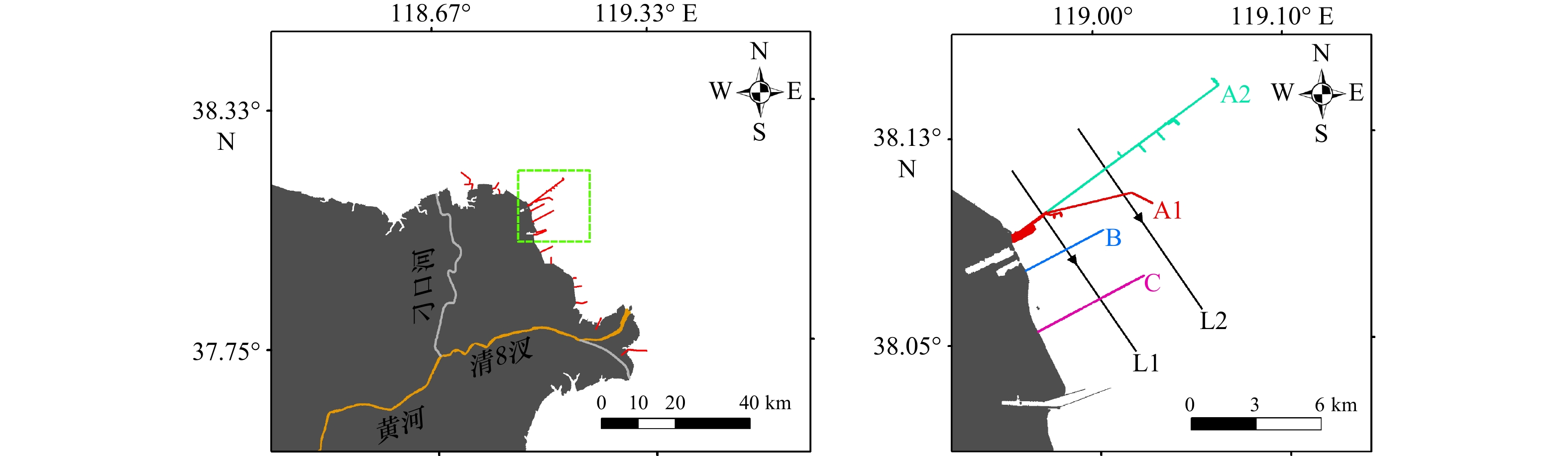
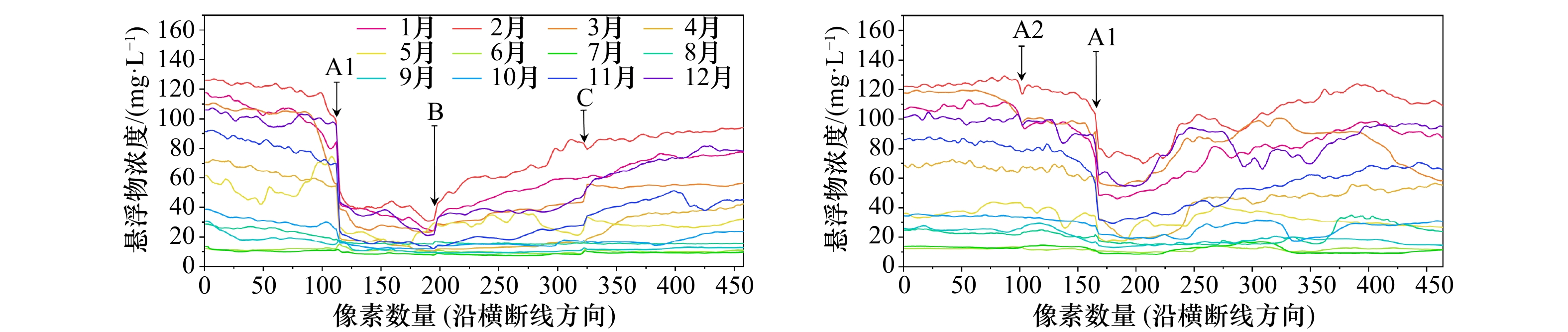
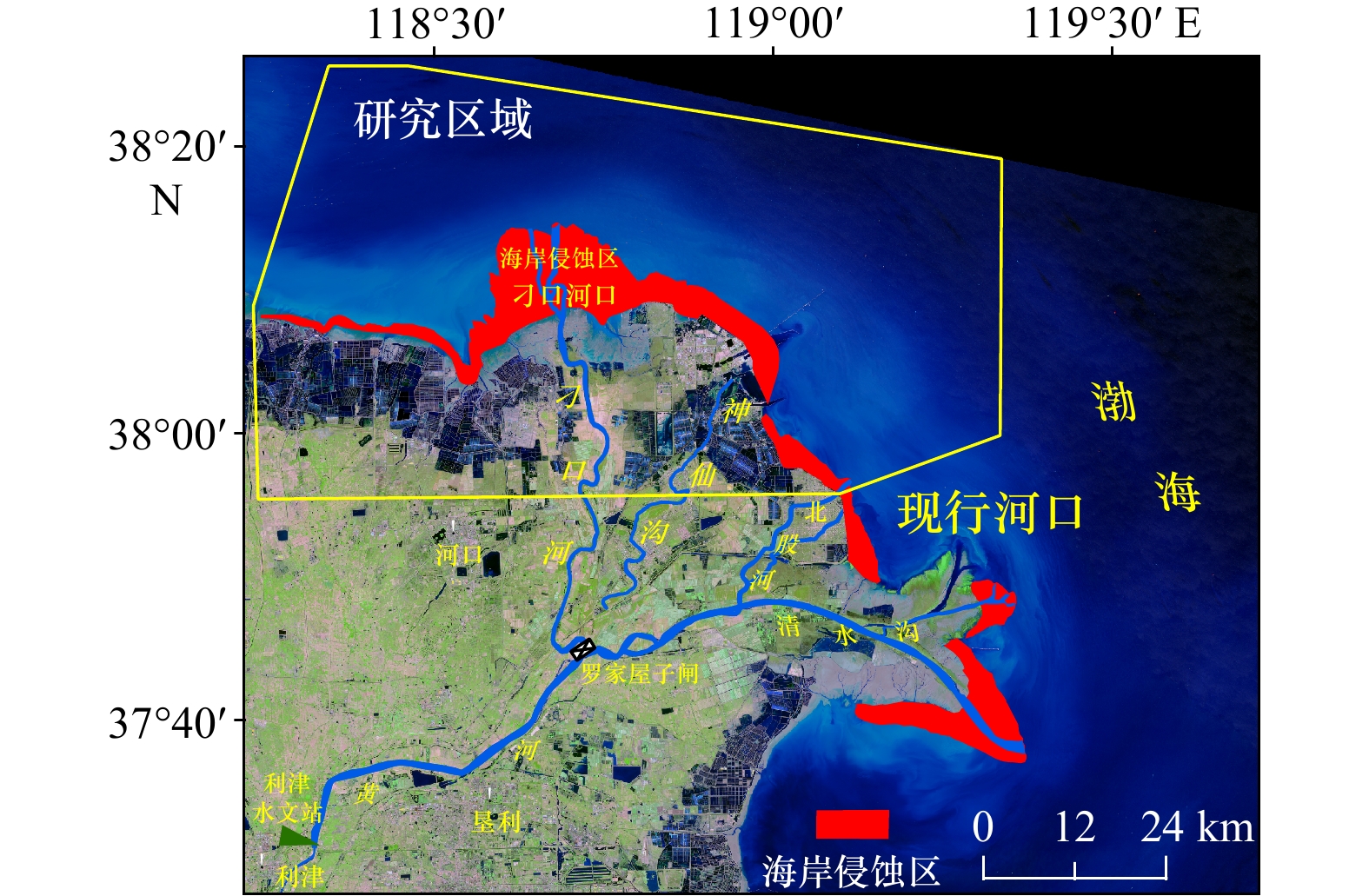
摘要: 近岸海域悬浮颗粒物的分布与扩散对水体生态环境、海岸地貌演变、水产养殖以及海岸工程等有重要影响。由于刁口河流路的改道,黄河三角洲北部成为强烈侵蚀岸段,揭示该区域的悬浮物浓度变化特征和规律是防护工程安全维护的基础。利用经良好检验的模型反演近岸海域悬浮物浓度,Landsat-8和Sentinel-2卫星影像反演结果的交叉验证表明,基于两种传感器反演的悬浮物浓度具有较强的一致性,两种卫星数据可以结合使用。研究区近岸海域悬浮物浓度季节变化明显,冬季和春季悬浮物浓度较高,夏季较低,秋季是悬浮物浓度从低向高转换的季节。冬、春季该区域风浪较大,在波浪掀沙和潮流输沙的联合作用下,底床泥沙强烈再悬浮,是形成悬浮物的主要来源,丁坝群的修建也在一定程度上改变了悬浮物的时空分布。
-
关键词:
- 黄河三角洲强侵蚀岸段 /
- 悬浮物浓度 /
- 遥感反演 /
- 季节性分布 /
- 驱动因素
Abstract: The distribution and diffusion of suspended particulate matter (SPM) in coastal waters play an important role on ecological environment, coastal geomorphic evolution, aquaculture and coastal engineering. The northern Yellow River Delta is a strong coastal erosion area due to the diversion of Diaokou course. Revealing the variation characteristics and laws of SPM concentration in this area is the basis for maintaining the safety of protection projects. Using the well-validated model to retrieve the SPM concentration in the coastal waters, the cross validation results of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 satellite sensors show that the SPM concentrations retrieved by the two sensors have strong consistency, and the two kinds of satellite data can be used together. The seasonal variation of SPM concentration in the study area is obvious. The concentration of SPM is higher in spring and winter, and lower in summer. Autumn is the season when SPM concentration changes from low to high. In winter and spring, the wind and waves are large in this area. Under the combined action of waves and current, strong sediment resuspension occurs, which is the main source of SPM. The construction of spur dike group altered the spatial and temporal distribution of SPM to a certain extent. -
图 7 黄河三角洲近岸大潮期间的数值模拟
a. 涨急流速分布;b. 落急流速分布;c. 只考虑潮流过程的悬沙浓度分布;d. 波流共同作用下的悬沙浓度分布
Fig. 7 Numerical simulation during spring in the Yellow River Delta
a.Velocity distribution in maximum flood phrase; b.velocity distribution in maximum ebb phrase; c.suspended particulate matter distribution in the tidal flow alone; d. suspended particulate matter distribution under the combined action of wave and current
表 1 本研究中卫星影像的数量分布
Tab. 1 The number distribution of satellite images in this study
月份 传感器类型 合计 Landsat-8 OLI Sentinel-2A MSI Sentinel-2B MSI 1 3 2 2 7 2 2 3 3 8 3 3 3 2 8 4 2 4 3 9 5 2 5 1 8 6 3 1 2 6 7 2 2 2 6 8 3 2 2 7 9 3 3 3 9 10 3 3 2 8 11 1 5 3 9 12 2 4 2 8 表 2 研究区月均悬浮物分布不同浓度等级的面积统计(单位:km2)
Tab. 2 Area statistics of different concentrations of suspended particulate matter distribution in the study area (unit: km2)
悬浮物浓度/(mg·L−1) 春季 夏季 秋季 冬季 3月 4月 5月 6月 7月 8月 9月 10月 11月 12月 1月 2月 <30 799.8 830.0 1 999.6 3 473.5 3 267.3 3 208.1 3 261.4 2 786.9 1 288.0 61.1 0 0 30~60 1 238.8 1 219.0 788.1 117.1 323.6 343.9 329.4 523.5 1 285.6 493.6 511.4 283.1 60~100 781.6 1 097.9 525.9 0 0 37.9 0 279.8 876.1 2 403.2 2 170.3 1 912.3 >100 770.6 443.9 277.2 0 0 0 0 0 141.1 632.3 908.4 1 395.6 -
[1] Zhou Liangyong, Liu Jian, Saito Y, et al. Coastal erosion as a major sediment supplier to continental shelves: Example from the abandoned old Huanghe (Yellow River) Delta[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 82: 43−59. [2] Zhang Minwei, Dong Qing, Cui Tingwei, et al. Suspended sediment monitoring and assessment for Yellow River Estuary from Landsat TM and ETM + imagery[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 146: 136−147. [3] Qiu Zhongfeng, Xiao Cong, Perrie W, et al. Using Landsat 8 data to estimate suspended particulate matter in the Yellow River Estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2017, 122(1): 276−290. [4] 周媛, 郝艳玲, 刘东伟, 等. 基于Landsat 8影像的黄河口悬浮物质量浓度遥感反演[J]. 海洋学研究, 2018, 36(1): 35−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2018.01.004Zhou Yuan, Hao Yanling, Liu Dongwei, et al. Estimation of suspended particulate matter concentration based on Landsat 8 data in the Yellow River Estuary[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2018, 36(1): 35−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2018.01.004 [5] 刘振宇, 崔廷伟, 李佳, 等. 黄河口悬浮物浓度Landsat8 OLI多波段反演研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(4): 1579−1585.Liu Zhenyu, Cui Tingwei, Li Jia, et al. Suspended particle concentration retrieval in Yellow River Estuary using multi-band of Landsat8 OLI[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(4): 1579−1585. [6] Li Peng, Ke Yinghai, Bai Junhong, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of suspended particulate matter in the Yellow River Estuary, China during the past two decades based on time-series Landsat and Sentinel-2 data[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 149: 110518. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110518 [7] Dogliotti A I, Ruddick K G, Nechad B, et al. A single algorithm to retrieve turbidity from remotely-sensed data in all coastal and estuarine waters[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2015, 156: 157−168. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.09.020 [8] Novoa S, Doxaran D, Ody A, et al. Atmospheric corrections and multi-conditional algorithm for multi-sensor remote sensing of suspended particulate matter in low-to-high turbidity levels coastal waters[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(1): 61−92. doi: 10.3390/rs9010061 [9] Ramaswamy V, Rao P S, Rao K H, et al. Tidal influence on suspended sediment distribution and dispersal in the northern Andaman Sea and Gulf of Martaban[J]. Marine Geology, 2004, 208(1): 33−42. [10] 刘猛, 沈芳, 葛建忠, 等. 静止轨道卫星观测杭州湾悬浮泥沙浓度的动态变化及动力分析[J]. 泥沙研究, 2013(1): 7−13.Liu Meng, Shen Fang, Ge Jianzhong, et al. Diurnal variation of suspended sediment concentration in Hangzhou Bay from geostationary satellite observation and its hydrodynamic analysis[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2013(1): 7−13. [11] Barnes B B, Hu C, Kovach C, et al. Sediment plumes induced by the Port of Miami dredging: Analysis and interpretation using Landsat and MODIS data[J]. Remote sensing of environment, 2015, 170: 328−339. [12] Zhang M, Dong Q, Cui T, et al. Suspended sediment monitoring and assessment for Yellow River Estuary from Landsat TM and ETM+ imagery[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 146: 136−147. [13] 刘艳霞, 黄海军, 杨晓阳. 基于遥感反演的莱州湾悬沙分布及其沉积动力分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2013, 35(6): 43−53.Liu Yanxia, Huang Haijun, Yang Xiaoyang. The transportation and deposition of suspended sediment and its dynamic mechanism analysis based on Landsat images in the Laizhou Bay[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2013, 35(6): 43−53. [14] Vanhellemont Q. Adaptation of the dark spectrum fitting atmospheric correction for aquatic applications of the Landsat and Sentinel-2 archives[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2019, 225: 175−192. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.03.010 [15] Fan Yaoshen, Chen Shenliang, Zhao Bo, et al. Monitoring tidal flat dynamics affected by human activities along an eroded coast in the Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2018, 190(7): 1−17. doi: 10.1007/s10661-018-6747-7 [16] Bi Naishuang, Yang Zuosheng, Wang Houjie, et al. Sediment dispersion pattern off the present Huanghe (Yellow River) Subdelta and its dynamic mechanism during normal river discharge period[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2010, 86(3): 352−362. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2009.06.005 [17] Ji Hongyu, Chen Shenliang, Pan Shunqi, et al. Morphological variability of the active Yellow River mouth under the new regime of riverine delivery[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 564: 329−341. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.07.014 [18] 陈沈良, 张国安, 陈小英, 等. 黄河三角洲飞雁滩海岸的侵蚀与机理[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(3): 9−14.Chen Shenliang, Zhang Guoan, Chen Xiaoying, et al. Coastal erosion feature and mechanism at Feiyantan in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2005, 25(3): 9−14. [19] Ji Hongyu, Pan Shunqi, Chen Shenliang. Impact of river discharge on hydrodynamics and sedimentary processes at Yellow River Delta[J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 425: 106210. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106210 [20] Pan Yanqun, Shen Fang, Wei Xiaodao. Fusion of Landsat-8/OLI and GOCI data for hourly mapping of suspended particulate matter at high spatial resolution: A case study in the Yangtze (Changjiang) Estuary [J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(2): 158. -




 下载:
下载: