Numerical simulation of the hydrodynamic process of rip current hazard
-
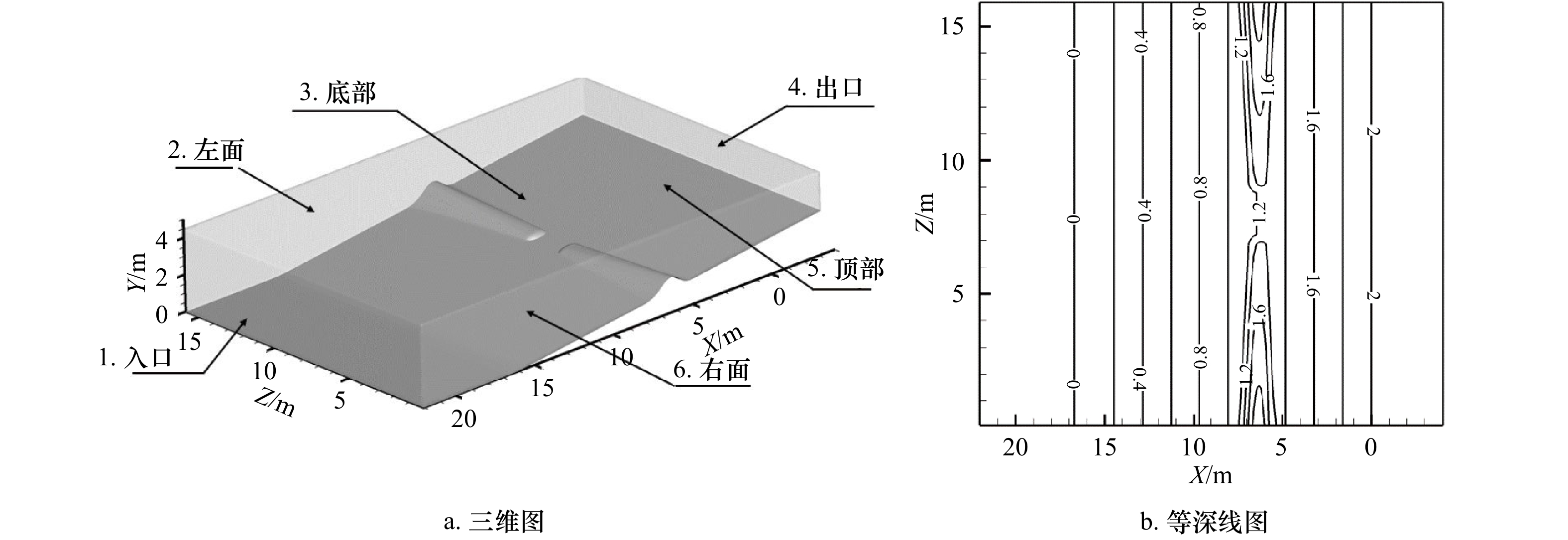
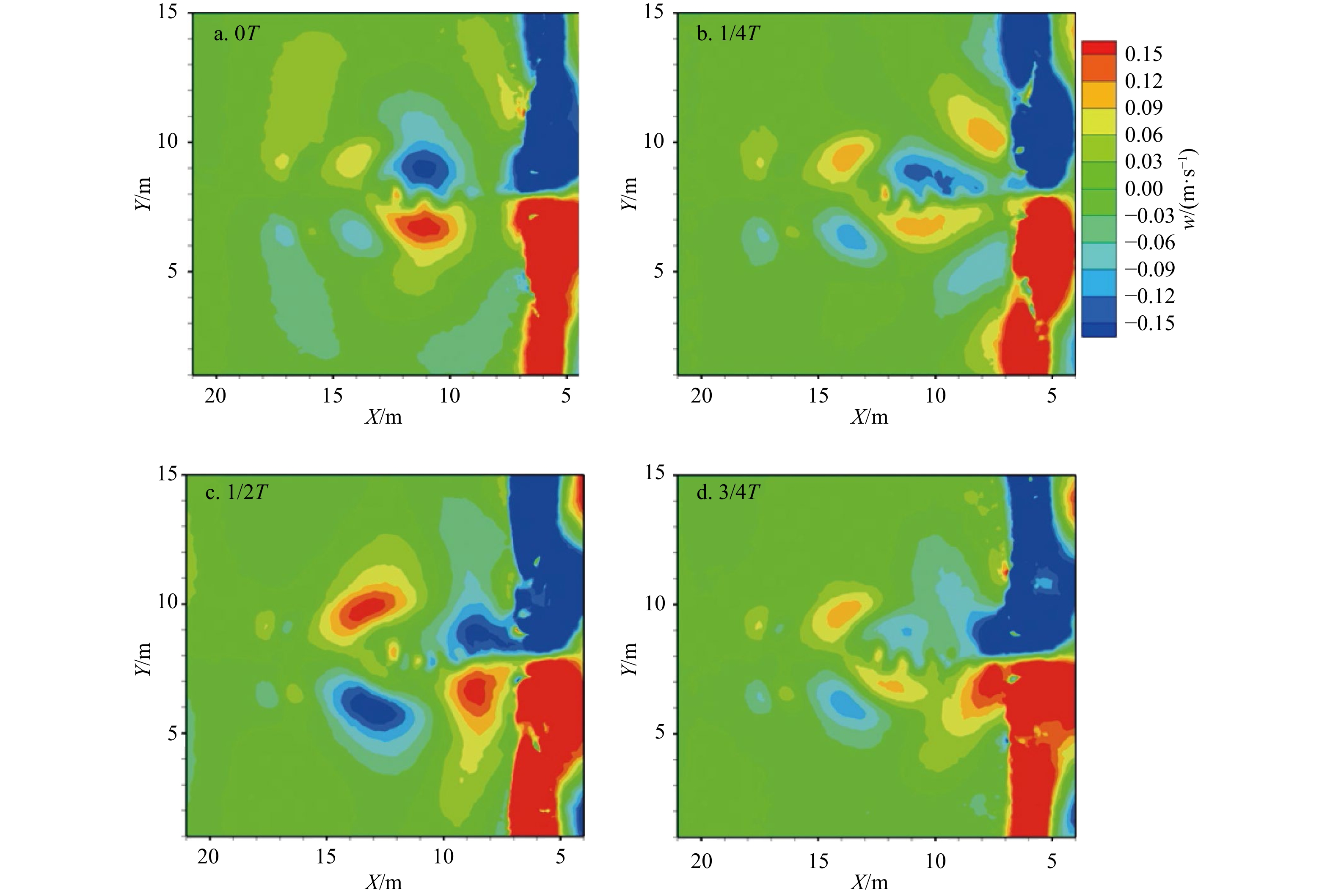
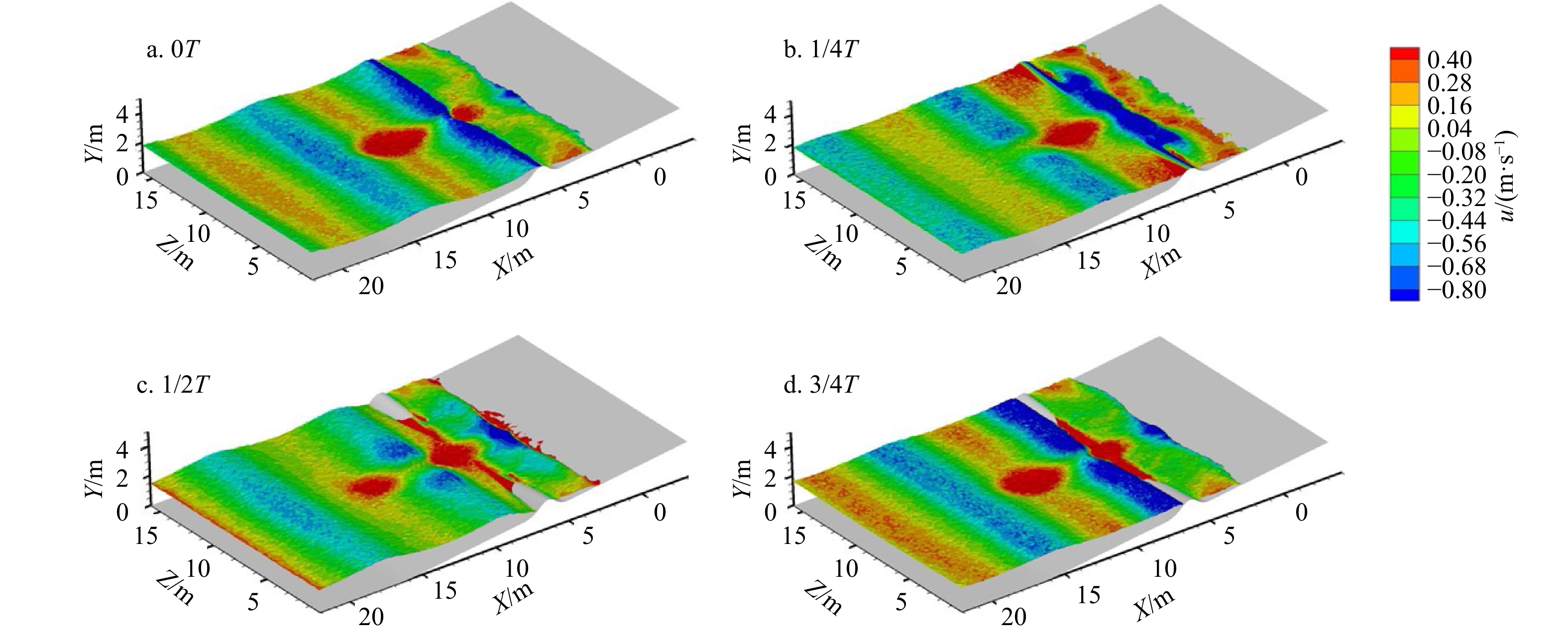
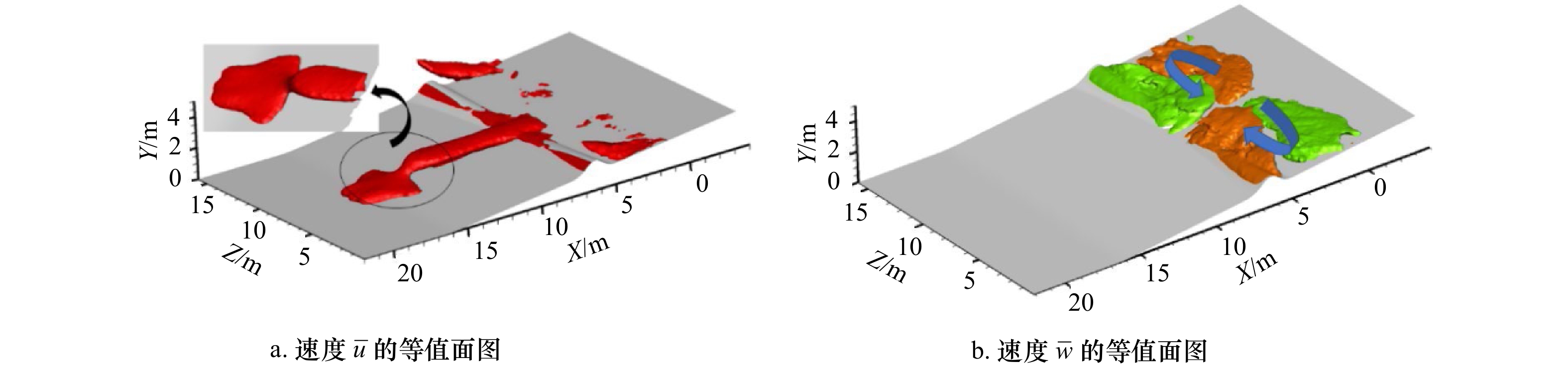
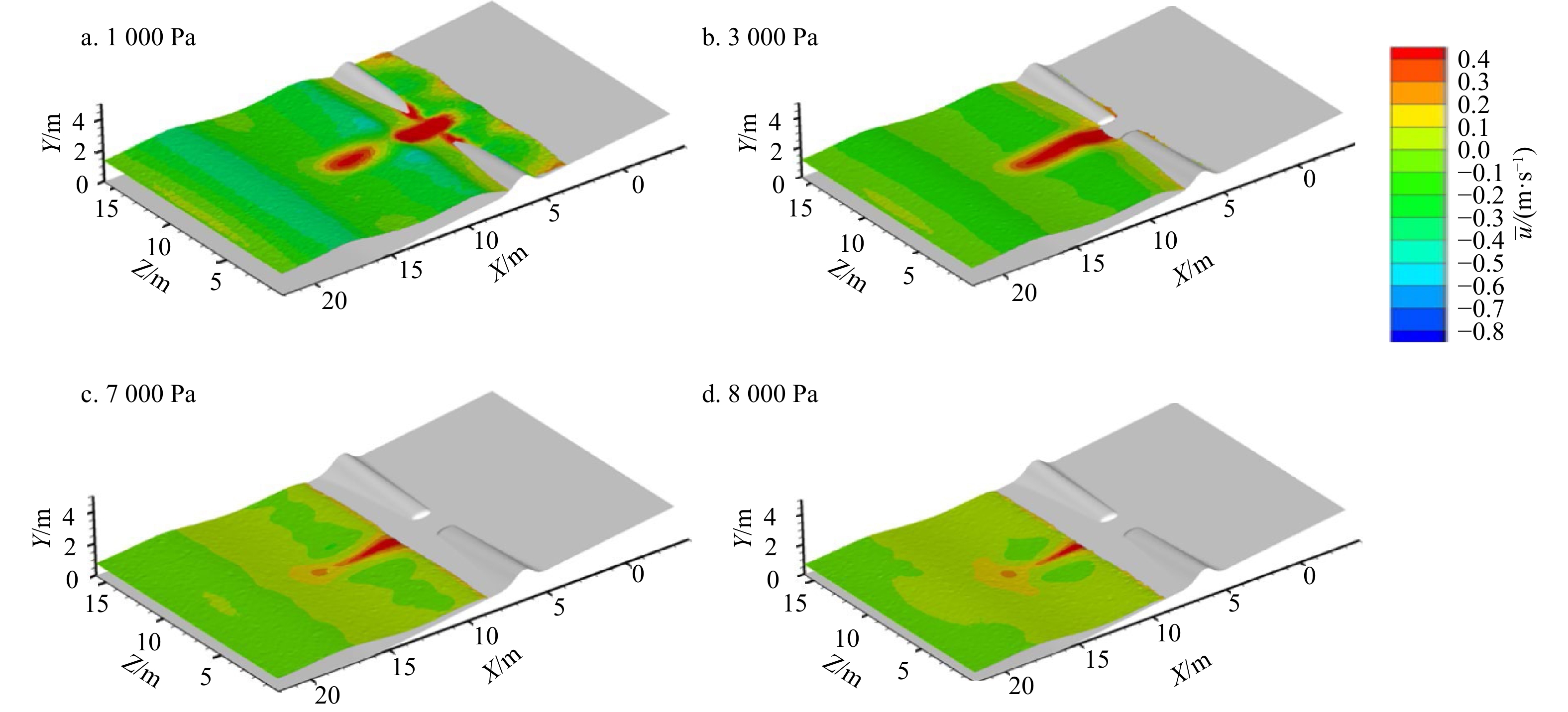
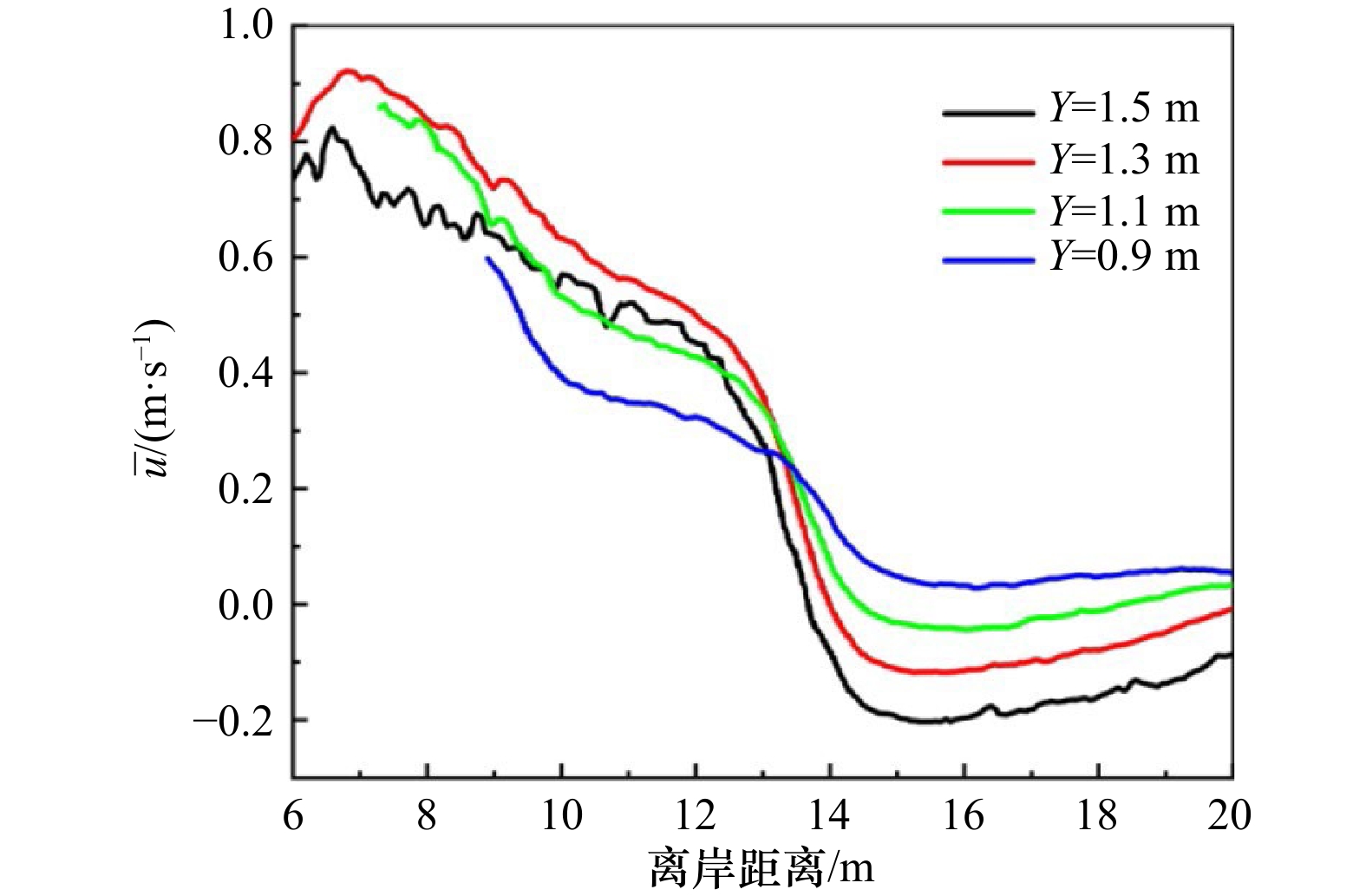
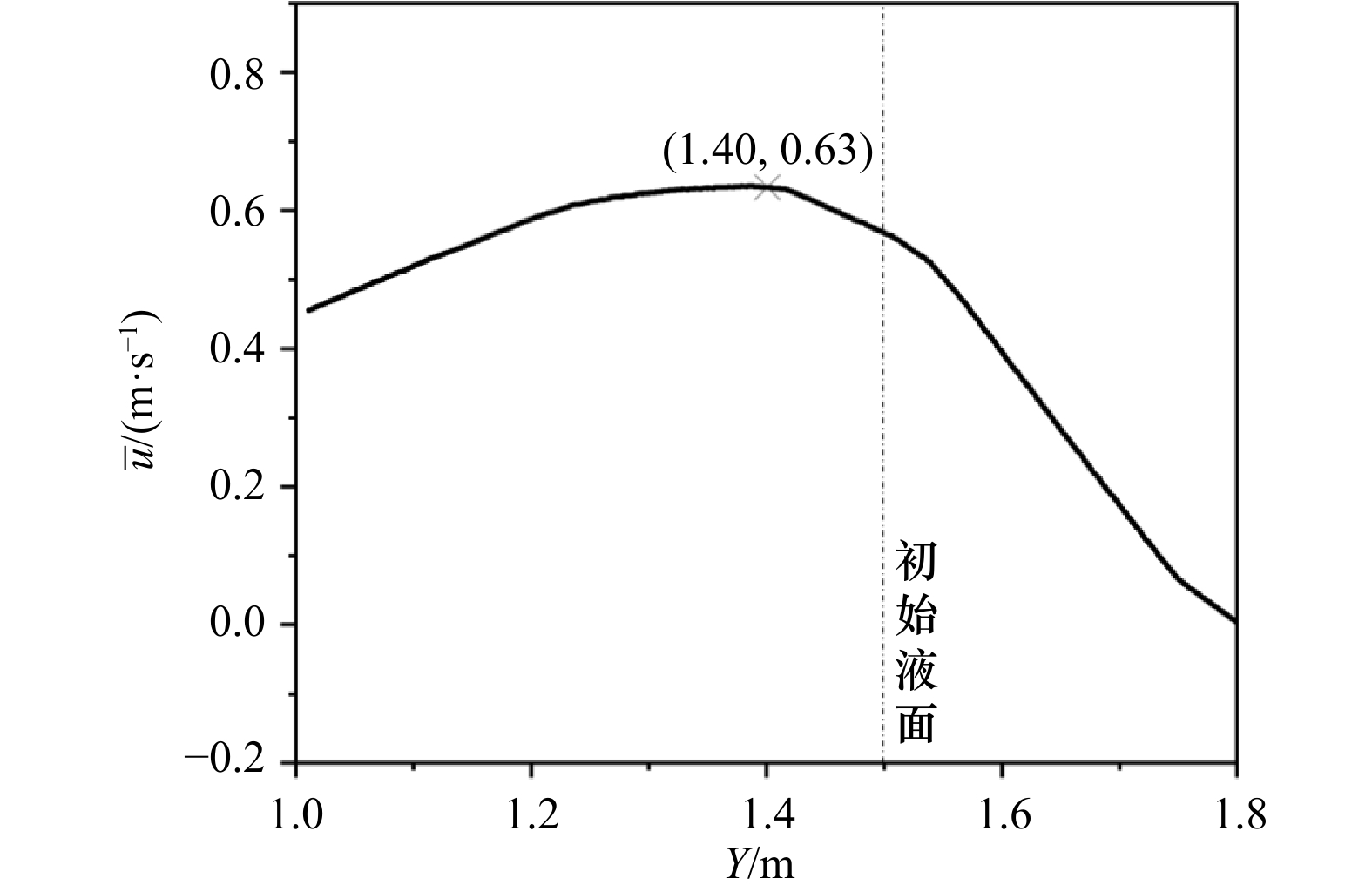
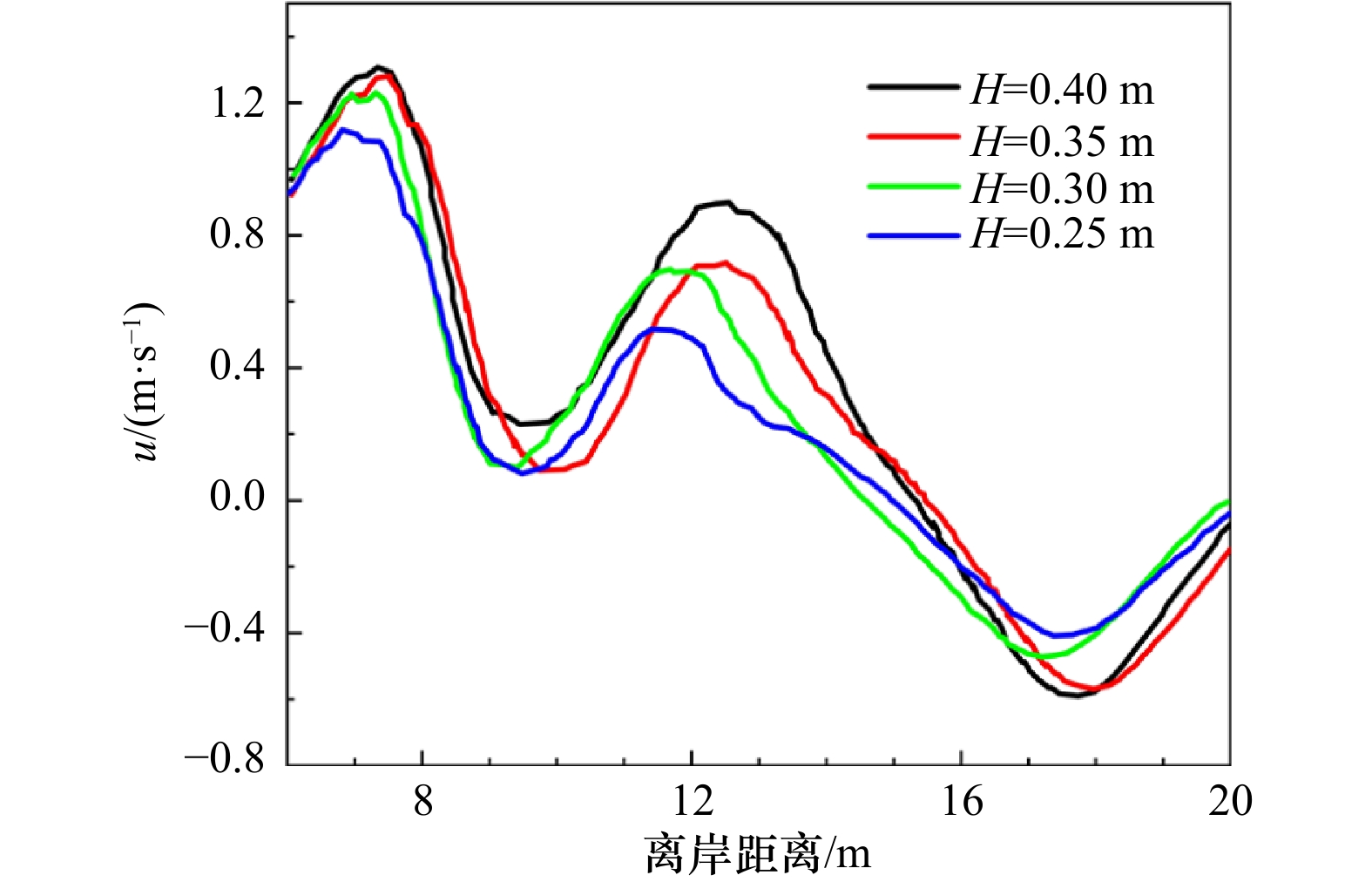
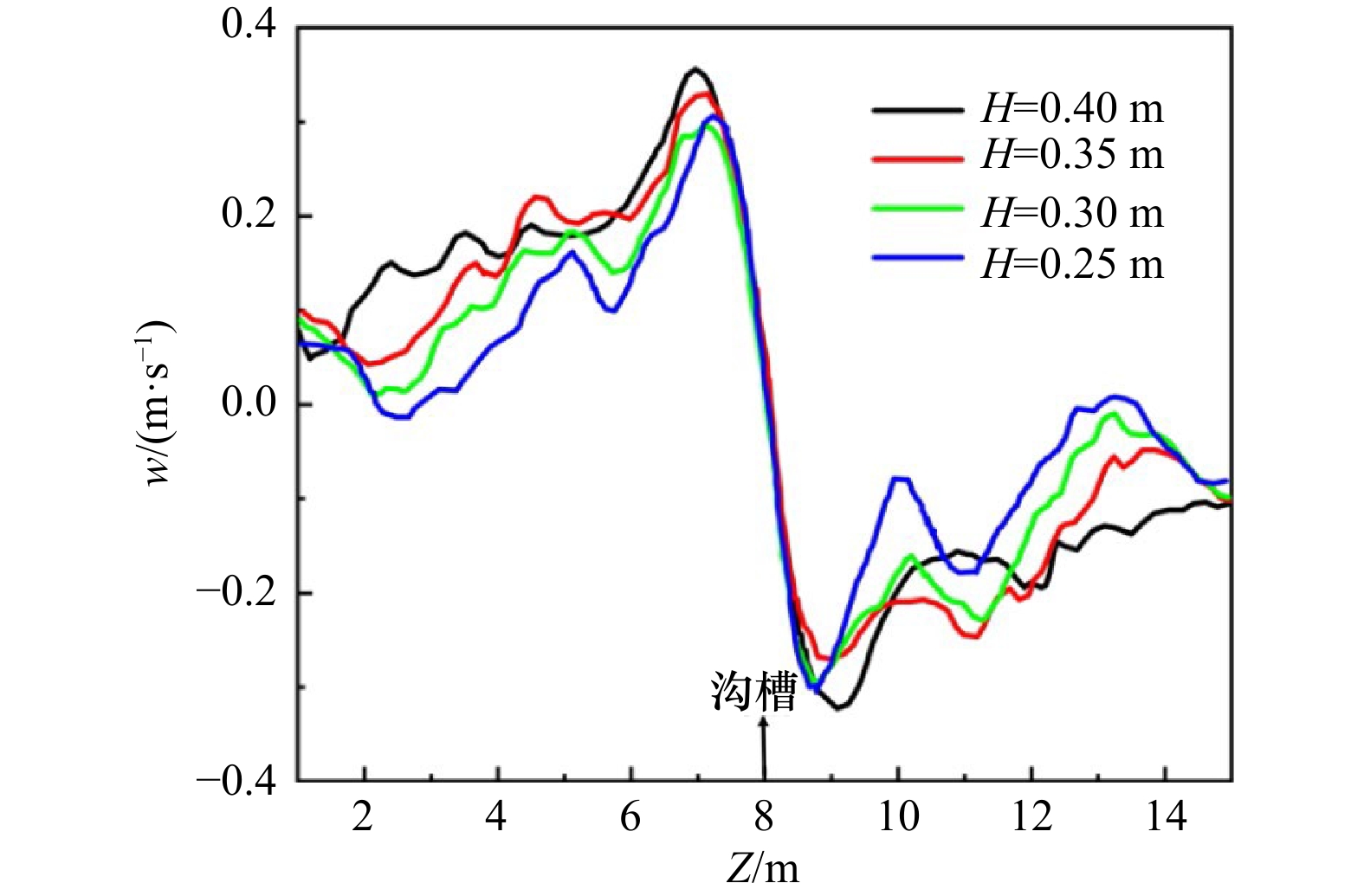
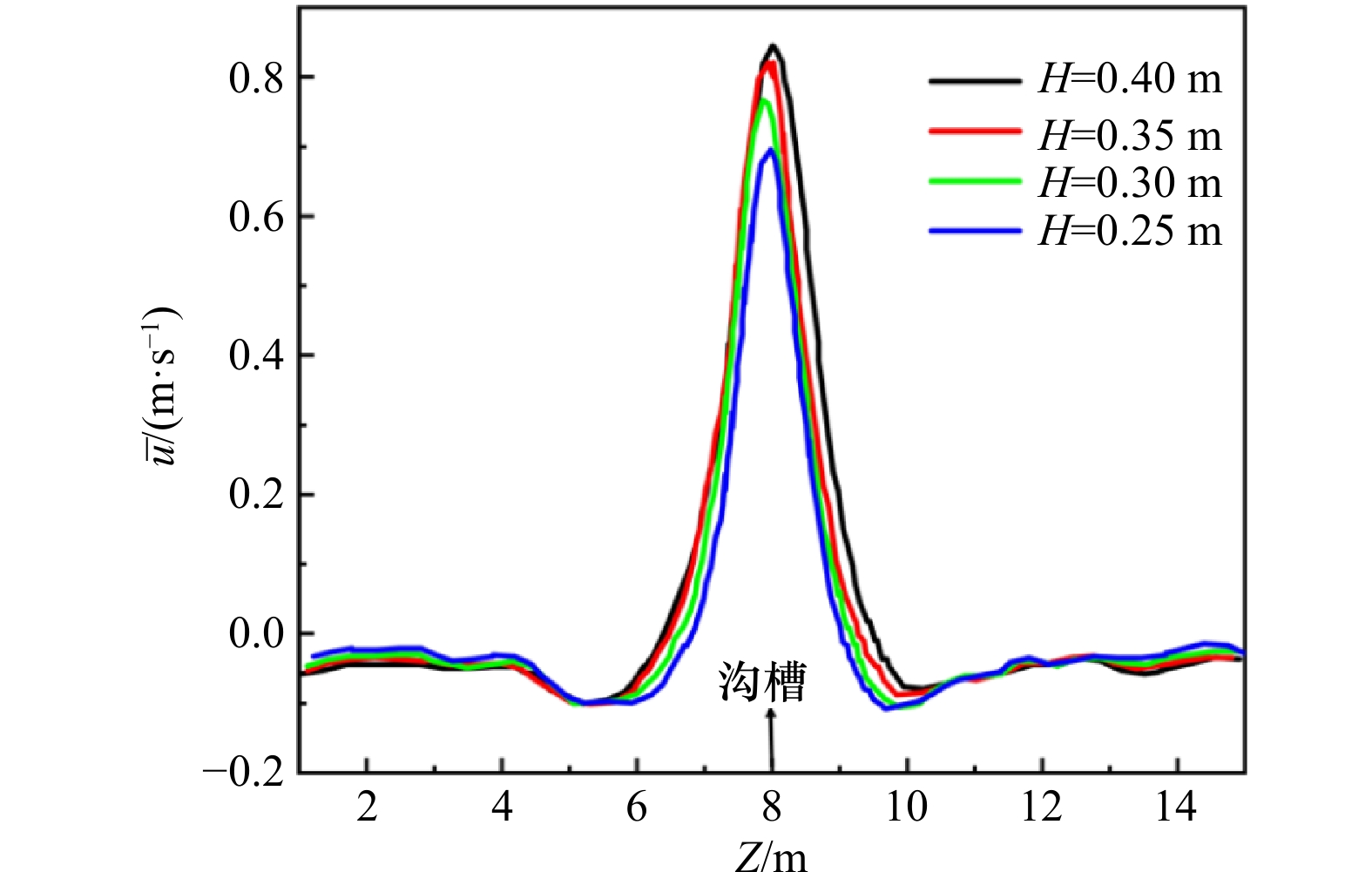
摘要: 离岸流是近岸流的重要组成部分,当波浪受到特殊海滩地形的影响,会形成一股沿着离岸方向运动的高速水流,能够迅速将人带离海岸,对海滨安全造成威胁。为了深入探究离岸流的形成机理及水动力学特性,本文基于二阶Stokes波浪理论,采用了更为光滑的变截面沙坝模型,通过流体体积法捕捉自由液面,对离岸流进行三维数值模拟探究。本文重点分析了离岸流产生时流场的瞬时速度、时均速度、压强等不同参量的分布规律,结果显示在沙坝和海岸线之间,有一对方向相反的水循环体系;对比不同流层离岸流的速度,了解到波浪与离岸流的耦合作用;并探究了入射波波高对离岸流强度及分布区域的影响,深化了对离岸流水动力学过程的认识。Abstract: Rip current is an important part of nearshore current. Affected by special beach topography, waves will form a high velocity flow moving along the offshore direction, which can quickly take people away from the shore and pose a threat to beach safety. In order to further explore the formation mechanism and hydrodynamics characteristics, three-dimensional numerical simulation of rip current was carried out. In this paper, based on the second-order Stokes wave theory, a typical sandbar model with variable cross-section is adopted and used to generate rip current. The free liquid surface is captured by volume of fluid method. The rip current flow field distribution laws of instantaneous velocity, time-averaged velocity and pressure are analyzed and made some discoveries: there is a pair of opposite water circulation systems between the bar and the shoreline. By comparing the velocity distribution of rip current a different depth, the interaction between waves and rip currents is understood. Furthermore, the influence of incident wave height on intensity and distribution of rip current is also studied, which deepens the understanding of the hydrodynamic process of rip current.
-
表 1 不同波高的Ursell数
Tab. 1 Ursell number of different wave heights
波高/m 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 Ur 5.35 6.42 7.49 8.56 -
[1] Dalrymple R A, MacMahan J H, Reniers A J H M, et al. Rip currents[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2011, 43: 551−581. doi: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-122109-160733 [2] Sonu C J. Field observation of nearshore circulation and meandering currents[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1972, 77(18): 3232−3247. doi: 10.1029/JC077i018p03232 [3] Short A D, Hogan C L. Rip currents and beach hazards: Their impact on public safety and implications for coastal management[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 1994(12): 197−209. [4] 任春平, 白玉川. 规则波导斯托克斯漂移对污染物输移的影响[J]. 水科学进展, 2017, 28(4): 605−613.Ren Chunping, Bai Yuchuan. Effects of Stokes drift induced by regular waves on pollutant transport[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2017, 28(4): 605−613. [5] Castelle B, Scott T, Brander R W, et al. Rip current types, circulation and hazard[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 163: 1−21. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.09.008 [6] Winter G. Rip current characteristics at the Dutch coast: Egmond aan zee[D]. Delft, The Netherlands: Delft University of Technology, 2012. [7] 孟凡昌, 李本霞. 裂流的研究综述[J]. 海洋预报, 2017, 34(1): 82−89. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2017.01.011Meng Fanchang, Li Benxia. Review on the study of the rip current[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2017, 34(1): 82−89. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2017.01.011 [8] 田海平, 伊兴睿, 王维. 警惕海滩隐形杀手——离岸流[J]. 力学与实践, 2020, 42(3): 381−387. doi: 10.6052/1000-0879-19-413Tian Haiping, Yi Xingrui, Wang Wei. Beware of the beach hidden killer—rip current[J]. Mechanics in Engineering, 2020, 42(3): 381−387. doi: 10.6052/1000-0879-19-413 [9] 王彦, 邹志利. 海岸裂流的研究进展及其展望[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(5): 170−176.Wang Yan, Zou Zhili. Progress and prospect of rip currents[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(5): 170−176. [10] Shepard F P, Emery K O, La Fond E C. Rip currents: A process of geological importance[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1941, 49(4): 337−369. doi: 10.1086/624971 [11] Longuet-Higgins M S, Stewart R W. Radiation stresses in water waves: a physical discussion, with applications[J]. Deep-Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1964, 11(4): 529−562. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(64)90001-4 [12] Liu P, Dalrymple R. Bottom frictional stresses and longshore currents due to waves with large angles of incidence[J]. Journal of Marine Research, 1978, 36(2): 357−375. [13] Haas K A, Svendsen I A, Haller M C, et al. Quasi-three-dimensional modeling of rip current systems[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2003, 108(C7): 3217. doi: 10.1029/2002JC001355 [14] 房克照, 邹志利, 刘忠波. 沙坝海岸上裂流的数值模拟[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 2011, 26(4): 479−486.Fang Kezhao, Zou Zhili, Liu Zhongbo. Numerical simulation of rip current generated on a barred beach[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2011, 26(4): 479−486. [15] 王彦, 邹志利. 叠加波浪有槽缓坡沙坝地形裂流试验[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2015, 23(6): 1166−1173.Wang Yan, Zou Zhili. Experimental study of rip currents by intersecting wave on barred beach of mild slopes with rip channel[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2015, 23(6): 1166−1173. [16] Wang Hong, Zhu Shouxian, Li Xunqiang, et al. Numerical simulations of rip currents off arc-shaped coastlines[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2018, 37(3): 21−30. doi: 10.1007/s13131-018-1197-1 [17] Hirt C W, Nichols B D. Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1981, 39(1): 201−225. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(81)90145-5 [18] Haller M C, Dalrymple R A, Svendsen I A. Experimental modeling of a rip current system[C]// Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Ocean Wave Measurement and Analysis. Virginia Beach, VA: ASCE, 1997: 750−764. [19] Chen Qin, Dalrymple R A, Kirby J T, et al. Boussinesq modeling of a rip current system[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1999, 104(C9): 20617−20637. doi: 10.1029/1999JC900154 [20] Ursell F. The long-wave paradox in the theory of gravity waves[J]. Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 1953, 49(4): 685−694. doi: 10.1017/S0305004100028887 [21] 房克照, 尹继伟, 邹志利. 单沟槽沙坝海岸的裂流实验研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 2013, 28(3): 363−369.Fang Kezhao, Yin Jiwei, Zou Zhili. Experiment study on rip current of barred beach with a single channel[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2013, 28(3): 363−369. -





 下载:
下载: