Spatial distribution and its controlling mechanism of surface sediments in the Yazhou Bay, Hainan Island
-
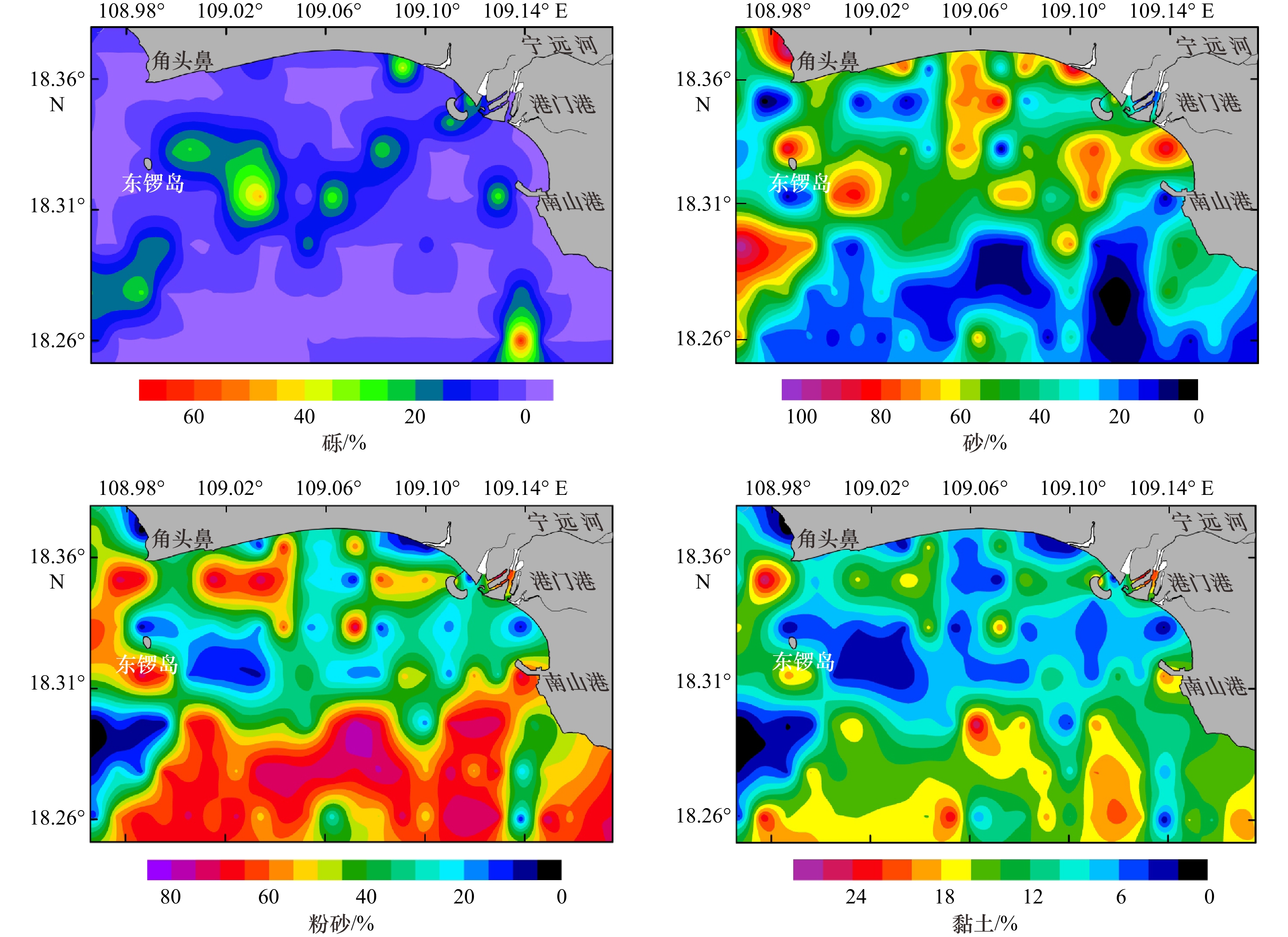
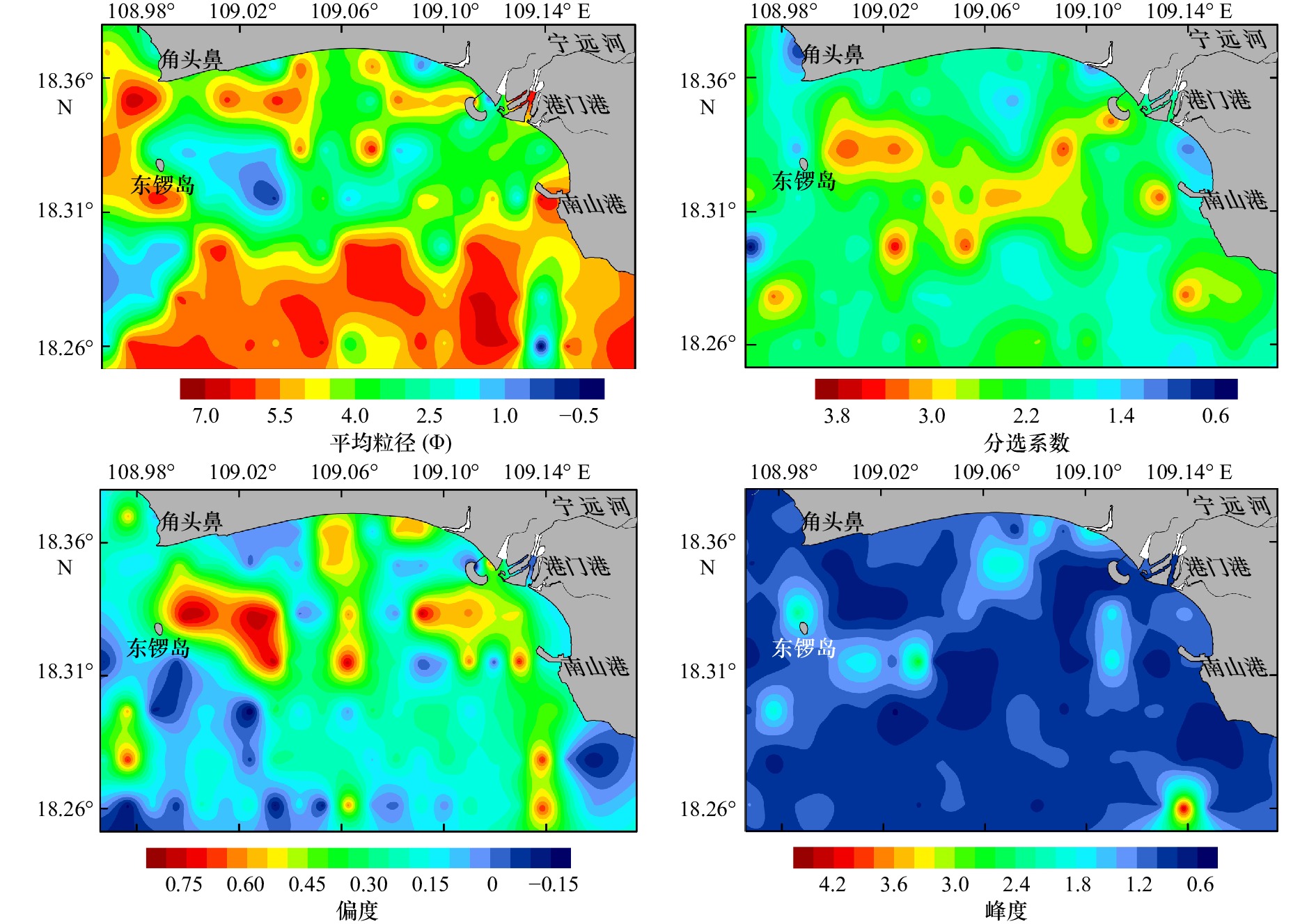
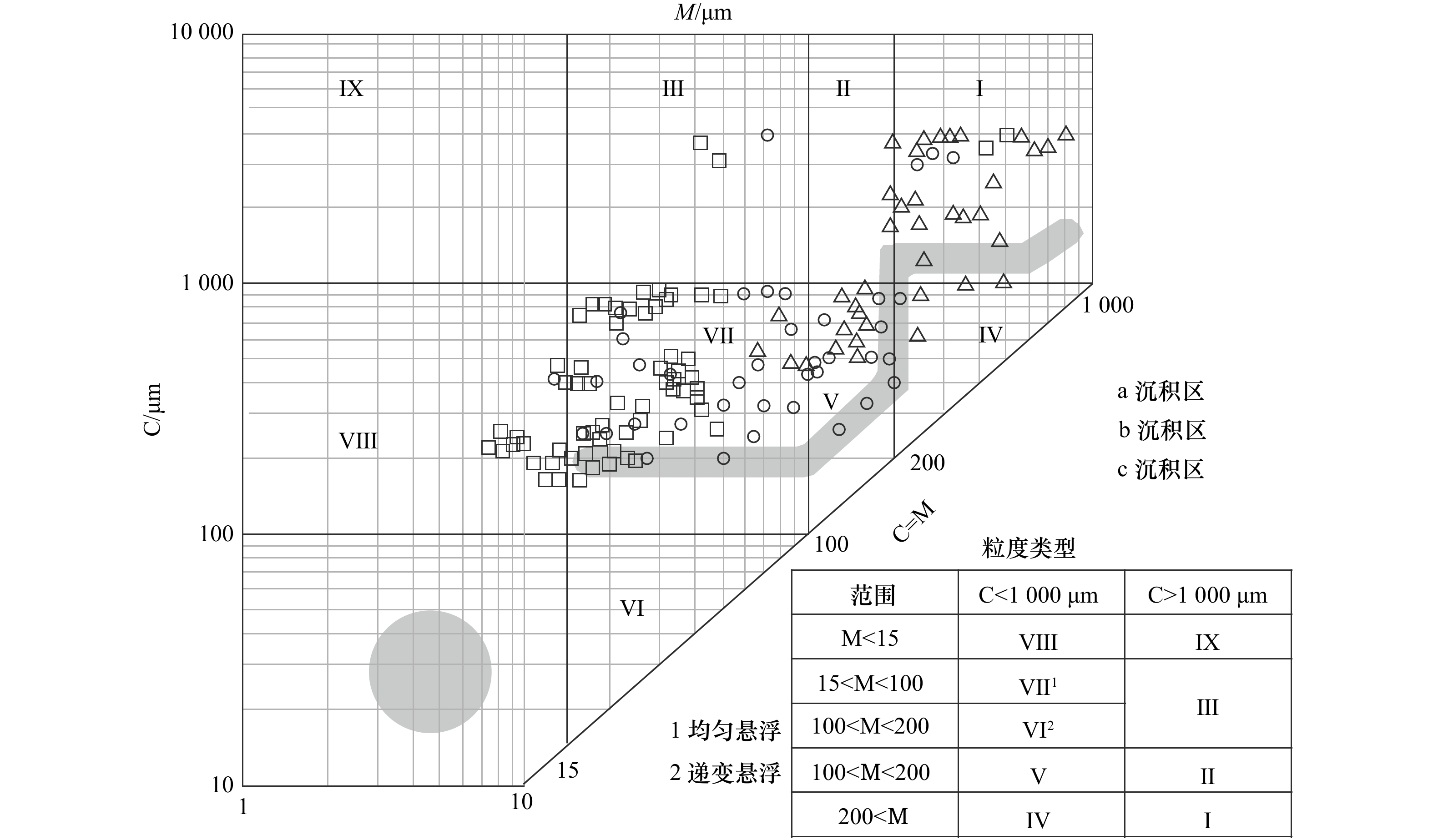
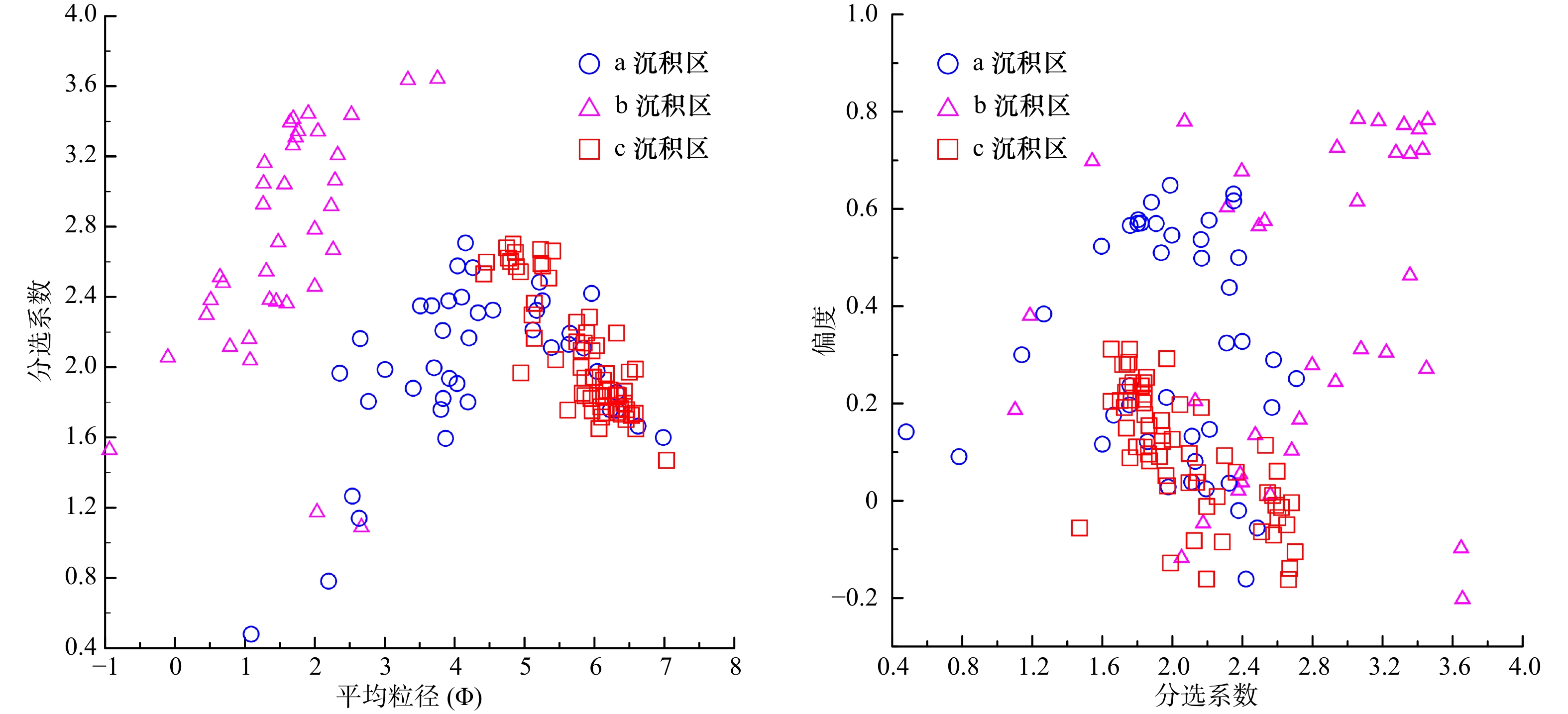
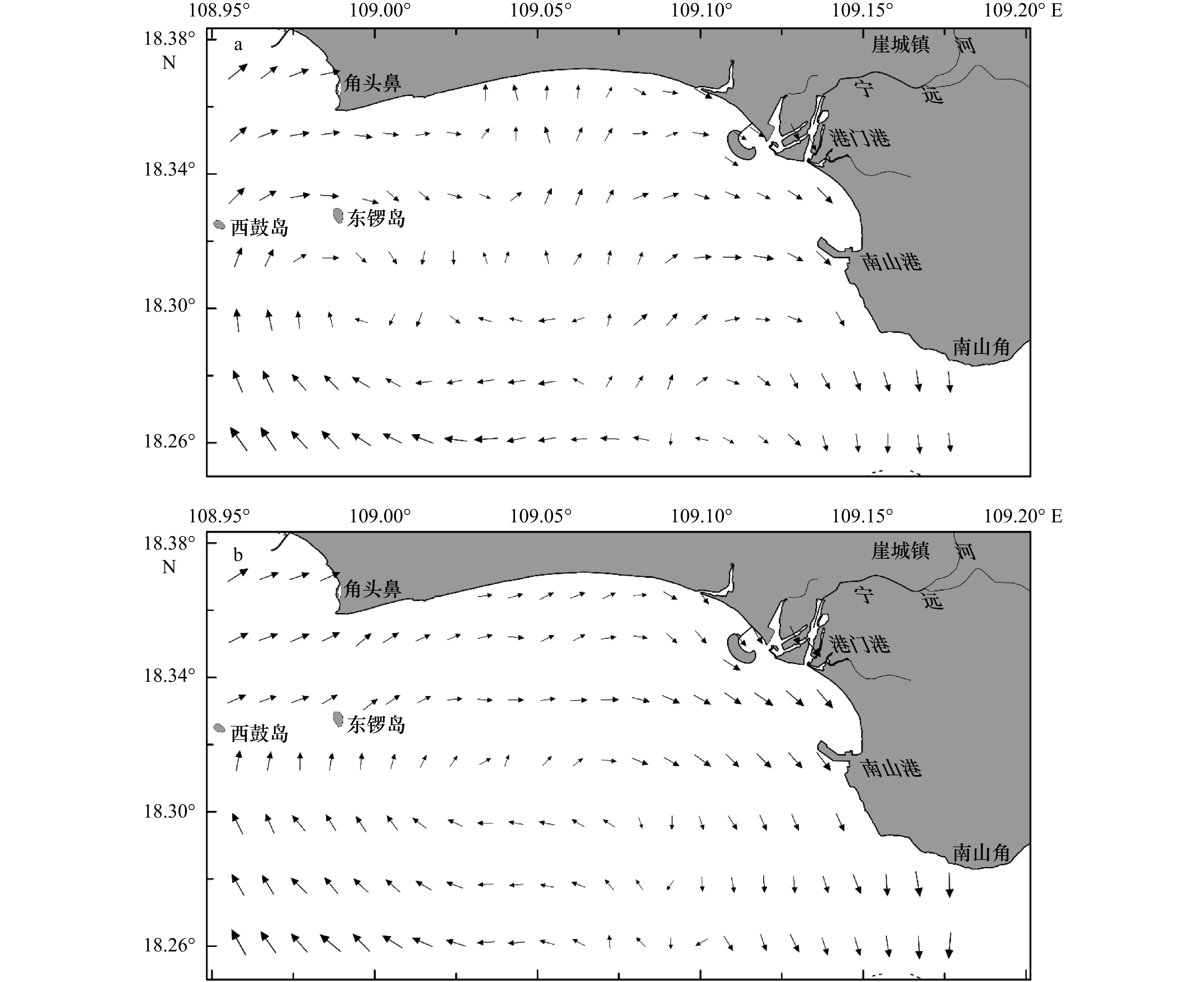
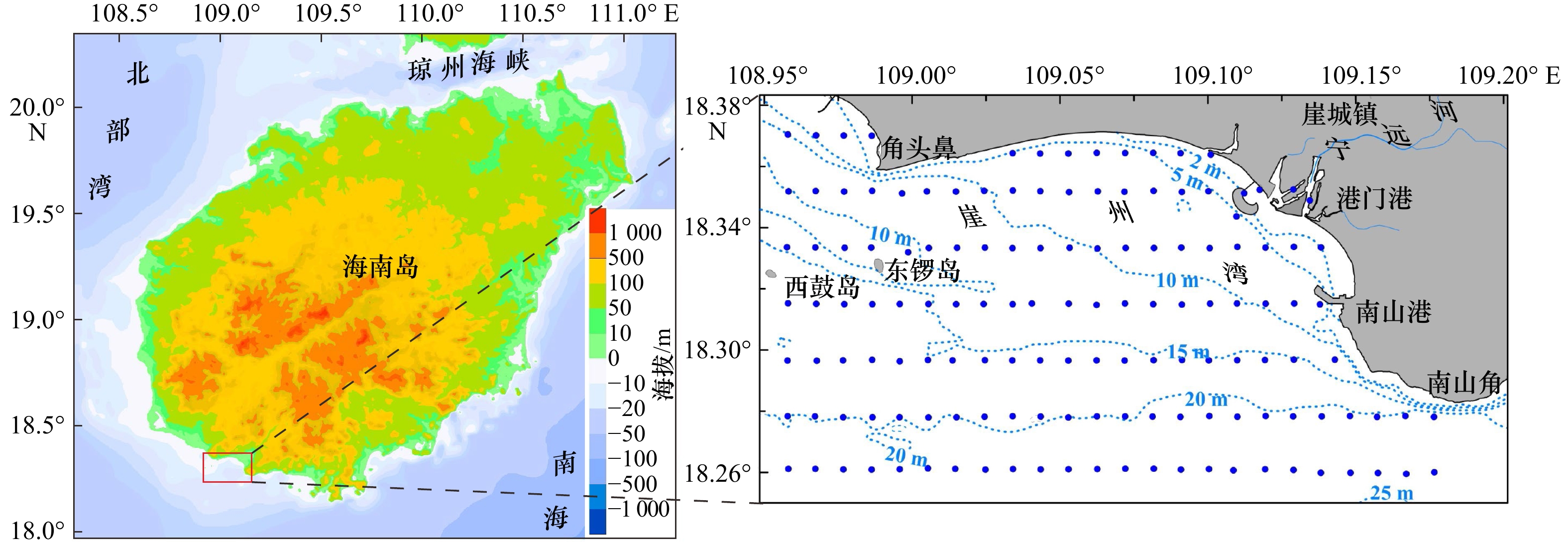
摘要: 基于崖州湾海域141个表层沉积物粒度分析数据,研究表层沉积物的粒级组分、粒度参数及其沉积动力环境特征。结果表明,研究区底质类型主要有泥质砂质砾、砾质泥质砂、砂、粉砂质砂、砂质粉砂和粉砂6种,砂质粉砂分布最为广泛;粒径总体趋势表现为自北向南由细变粗再变细的NEE条带状分布特征,分选系数总体偏高,反映了该区复杂的物源和水动力条件。运用Flemming三角图式,结合粒度象、研究区物源、水动力条件及地形特征,将研究区划分为3个沉积环境:近岸主要受控于波浪掀沙和搬运作用,粒径较细,表现为波控沉积特征;中部主要受控于径流、波浪和潮流共同作用,粒径粗,分选差,表现为河口沉积特征;南部主要受控于潮流输沙作用,波浪作用减弱,粒径细,分选相对较好,表现为相对低能的沉积环境。沉积物输移趋势分析显示研究区中西部为一沉积物汇聚中心,近岸侵蚀物质、宁远河输运物质以及外海潮流输运物质均向该处运移。Abstract: Based on the 141 surface sediments collected from the Yazhou Bay, Hainan Island, the distribution characteristics of grain size components, grain size parameters and sediment types were analyzed. The results indicate that the samples can be classified into 6 types as argillaceous arenaceous gravel, gravelly argillaceous sand, sand, silty sand, arenaceous silt and silt in the study area. In particular, the arenaceous silt is most widely distributed. The grain size diameters increase and then decrease, showing a banding distribution from north to south. The separation coefficient is generally high, which indicates the complex sediment sources and hydrodynamic conditions in this area. Base on Flemming ternary diagram, combined with sediment sources, hydrodynamic conditions and topographic features, the study area is divided into three sedimentary districts from north to south: the nearshore zone which showing the characteristics of wave-controlled deposition is mostly impacted by wave winnowing and transport, and the grain size is relatively small; the central Yazhou Bay zone is a high-energy coarse grained sand area, mainly controlled by the combined action of runoff, wave and tidal current; relatively, the southern zone is mainly affected by tidal current load, where the wave action is weakened, the sediment is the finest and deposited in a lower energy environment. In addition, the analysis of sediment transport trend shows that the midwest part of the study area is a depositional center, the silt of coastal erosion, Ningyuan River and offshore tidal current transport are carried to this area.
-
表 1 粒度参数定性描述
Tab. 1 Qualitative description of grain size parameters
标准偏差 偏度 峰度 分选极好 <0.35 极负偏 –1~–0.3 很平坦 <0.67 分选好 0.35~0.50 负偏 –0.3~–0.1 平坦 0.67~0.90 分选较好 0.50~0.71 近对称 –0.1~0.1 中等 0.90~1.11 分选中等 0.71~1.00 正偏 +0.1~0.3 尖锐 1.11~1.56 分选较差 1.00~2.00 极正偏 >0.3 很尖锐 1.56~3.00 分选差 2.00~4.00 非常尖锐 >3.00 分选极差 >4.00 -
[1] 徐志伟, 汪亚平, 李炎, 等. 多元统计及物源分析支持的北部湾东部海域沉积物输运趋势[J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(3): 67−78.Xu Zhiwei, Wang Yaping, Li Yan, et al. Sediment transport patterns in the eastern Beibu Gulf based on grain-size multivariate statistics and provenance analysis[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2010, 32(3): 67−78. [2] 杨阳, 高抒, 周亮, 等. 海南新村港潟湖表层沉积物粒度特征及其沉积环境[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(1): 94−105.Yang Yang, Gao Shu, Zhou Liang, et al. Grain size distribution of surface sediments and sedimentary environment in the lagoon of Xincun, Hainan Island[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(1): 94−105. [3] 刘志杰, 公衍芬, 周松望, 等. 海洋沉积物粒度参数3种计算方法的对比研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2013, 35(3): 179−188.Liu Zhijie, Gong Yanfen, Zhou Songwang, et al. A comparative study on the grain-size parameters of marine sediments derived from three different computing methods[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2013, 35(3): 179−188. [4] 王伟伟, 付元宾, 李树同, 等. 渤海中部表层沉积物分布特征与粒度分区[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(3): 478−485.Wang Weiwei, Fu Yuanbin, Li Shutong, et al. Distribution on surface sediment and sedimentary divisions in the middle part of Bohai sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(3): 478−485. [5] 胡恭任, 于瑞莲, 余伟河. 泉州湾潮间带表层沉积物稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 环境化学, 2011, 30(12): 2086−2091.Hu Gongren, Yu Ruilian, Yu Weihe. Geochemistry of rare-earth elements in surface sediments of inter-tidal zone of Quanzhou Bay[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 30(12): 2086−2091. [6] 蔡观强, 邱燕, 彭学超, 等. 南海西南海域表层沉积物中微量元素Ba的地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(3): 560−569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.03.021Cai Guanqiang, Qiu Yan, Peng Xuechao, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Barium in surface sediments from the southwestern area of South China Sea[J]. Geoscience, 2010, 24(3): 560−569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2010.03.021 [7] 刘建国, 陈忠, 颜文, 等. 南海表层沉积物中细粒组分的稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2010, 35(4): 563−571. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.072Liu Jianguo, Chen Zhong, Yan Wen, et al. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements in the fine-grained fraction of surface sediment from South China Sea[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010, 35(4): 563−571. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.072 [8] 毛龙江, 张永战, 张振克, 等. 海南岛三亚湾现代沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(4): 17−22.Mao Longjiang, Zhang Yongzhan, Zhang Zhenke, et al. Characteristics of sedimentary environments in Sanya Bay of Hainan Island[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(4): 17−22. [9] 王琦, 朱而勤, 张建华, 等. 海南岛三亚湾表层沉积中的自生铁矿物组合[J]. 地质学报, 1985, 59(4): 293−303, 366.Wang Qi, Zhu Erqin, Zhang Jianhua, et al. The assemblage of authigenic iron minerals in superficial sediments of the Sanya Bay, Hainan Island[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 1985, 59(4): 293−303, 366. [10] 刘建波, 刘洁, 陈春华, 等. 三亚湾表层沉积物中重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2012, 37(7): 106−109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2012.07.028Liu Jianbo, Liu Jie, Chen Chunhua, et al. Pollution characteristic and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in surface sediment of Sanya Bay[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2012, 37(7): 106−109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2012.07.028 [11] 吴伟中, 韦刚健, 谢露华, 等. 三亚湾海水中Sr/Ca、Mg/Ca变化及对珊瑚微量元素温度计的响应[J]. 海洋科学, 2014, 38(3): 46−55. doi: 10.11759/hykx20120706003Wu Weizhong, Wei Gangjian, Xie Luhua, et al. Variations of Sr/Ca, Mg/Ca ratios in seawater of the Sanya Bay and response of coral trace element thermometer[J]. Marine Sciences, 2014, 38(3): 46−55. doi: 10.11759/hykx20120706003 [12] 孙倩文, 黄康有, 谢德豪, 等. 海南岛三亚湾全新世以来沉积特征与古环境演变[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 58(3): 13−21.Sun Qianwen, Huang Kangyou, Xie Dehao, et al. On the sedimentary environment change since Holocene in the Sanya Bay, Hainan Island[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2019, 58(3): 13−21. [13] 韩孝辉, 薛玉龙, 何其江, 等. 三亚东锣岛沙滩恢复可能性探讨[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2016, 33(1): 52−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2016.01.008Han Xiaohui, Xue Yulong, He Qijiang, et al. On the possibility of restoration of the sand beach of Dongluo Island in Sanya City[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2016, 33(1): 52−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2016.01.008 [14] 王颖. 海南岛海岸环境特征[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2002, 18(3): 1−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2002.03.001Wang Ying. Features of Hainan Island coastal environment[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2002, 18(3): 1−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2002.03.001 [15] McManus J. Grain size determination and interpretation[M]//Tucker M. Techniques in Sedimentology. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1988. [16] Folk R L, Andrews P B, Lewis D W. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 1970, 13(4): 937−968. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1970.10418211 [17] Shepard F P. Nomenclature based on sand-silt-clay ratios[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1954, 24(3): 151−158. [18] Flemming B W. A revised textural classification of gravel-free muddy sediments on the basis of ternary diagrams[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2000, 20(10/11): 1125−1137. [19] Passega R. Grain size representation by CM patterns as a geologic tool[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1964, 34(4): 830−847. doi: 10.1306/74D711A4-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D [20] Gao S, Collins M B, Lanckneus J, et al. Grain size trends associated with net sediment transport patterns: An example from the Belgian continental shelf[J]. Marine Geology, 1994, 121(3/4): 171−185. [21] 吴敏. 海南岛周边海域环境变化的粘土矿物学研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2007.Wu Min. Clay mineralogical study on environmental change of Hainan Island offshore[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2007. [22] 金秉福. 粒度分析中偏度系数的影响因素及其意义[J]. 海洋科学, 2012, 36(2): 129−135.Jin Bingfu. Influencing factors and significance of the skewness coefficient in grain size analysis[J]. Marine Sciences, 2012, 36(2): 129−135. [23] 卢连战, 史正涛. 沉积物粒度参数内涵及计算方法的解析[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2010, 35(6): 54−60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2010.06.013Lu Lianzhan, Shi Zhengtao. Analysis for sediment grain size parameters of connotations and calculation method[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2010, 35(6): 54−60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2010.06.013 [24] Folk R L, Ward W C. Brazos River bar: A study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1957, 27(1): 3−26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D [25] 高抒. 沉积物粒径趋势分析: 原理与应用条件[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(5): 826−836.Gao Shu. Grain size trend analysis: Principle and applicability[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(5): 826−836. [26] 李琰, 于洪军, 易亮, 等. 渤海南部Lz908孔海陆交互沉积的粒度特征及其对沉积环境的指示[J]. 海洋科学, 2014, 38(5): 107−113. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130120003Li Yan, Yu Hongjun, Yi Liang, et al. Grain-size characteristics and its sedimentary significance of coastal sediments of the borehole Lz908 in the south Bohai Sea (the Laizhou Bay), China[J]. Marine Sciences, 2014, 38(5): 107−113. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130120003 [27] 高抒, 周亮, 李高聪, 等. 海南岛全新世海岸演化过程与沉积记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(1): 1−17. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.01Gao Shu, Zhou Liang, Li Gaocong, et al. Processes and sedimentary records for Holocene coastal environmental changes, Hainan Island: An overview[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(1): 1−17. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.01 [28] Asselman N E M. Grain-size trends used to assess the effective discharge for floodplain sedimentation, River Waal, the Netherlands[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1999, 69(1): 51−61. doi: 10.2110/jsr.69.51 [29] 俞慕耕, 刘金芳. 南海海流系统与环流形势[J]. 海洋预报, 1993, 10(2): 13−17.Yu Mugeng, Liu Jinfang. Current system and circulation in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Forecasts, 1993, 10(2): 13−17. [30] McCave I N. Grain-size trends and transport along beaches: Example from eastern England[J]. Marine Geology, 1978, 28(1/2): M43−M51. [31] McLaren P, Bowles D. The effects of sediment transport on grain-size distributions[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1985, 55(4): 457−470. [32] Le Roux J P. An alternative approach to the identification of net sediment transport paths based on grain-size trends[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1994, 94(1/2): 97−107. [33] 贾建军, 高抒, 薛允传. 图解法与矩法沉积物粒度参数的对比[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2002, 33(6): 577−582. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.06.002Jia Jianjun, Gao Shu, Xue Yunchuan. Grain-size parameters derived from graphic and moment methods: A comparative study[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2002, 33(6): 577−582. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2002.06.002 -




 下载:
下载: