Comparative analysis on numerical simulation of the impacts of different beach nourishment schemes on beach profile
-
摘要: 大量工程实践表明,海滩养护是当前抵御海岸侵蚀的常见措施。通过人为地向海滩补充沙源,以达到海岸防护、修复沙滩等目的。本文建立了XBeach一维海滩剖面演变数值模型,并与物理模型试验结果进行对比验证;计算常浪条件下不同方案补沙后海滩剖面达到平衡状态的速率;通过对比补沙工况与未补沙工况的风暴后剖面,分析风暴作用下的防护效果。结果发现,补沙量较大时,沙坝向海侧位置补沙在常浪条件下补沙效率高于滩肩补沙,在风暴条件下防护效果优于滩肩补沙。此次研究对于在实际海滩养护过程中节约施工成本、提高施工效率有着重要意义,同时对于评估沙滩养护工程效果有一定的参考价值。Abstract: Numerous engineering projects show that beach nourishment is a common method against coastal erosion. Beach nourishment is an artificial process of adding sediment to a beach to increase beach width and protect it from erosion. In this paper, a 1D numerical model for beach profile was established and verified by the results of physical model experiment. In addition, the rates of profile change to equilibrium profile on different positions and different sand volume schemes were calculated, and the efficiency was compared and analyzed. To analyze the protection effects of beach nourishment, the profiles in nourishment schemes and no nourishment schemes after storm condition were compared. It turned out that when the nourishment volume was large the efficiency of bar nourishment under the calm condition was higher than of berm nourishment, and the nourishment effect under the storm condition was better. This study has important implications to save construction costs and raise working efficiency during the practical nourishment engineering. In the meantime, it sheds light on evaluating the effect of beach nourishment.
-
Key words:
- beach nourishment /
- equilibrium profile /
- XBeach /
- numerical model /
- nourishment efficiency
-
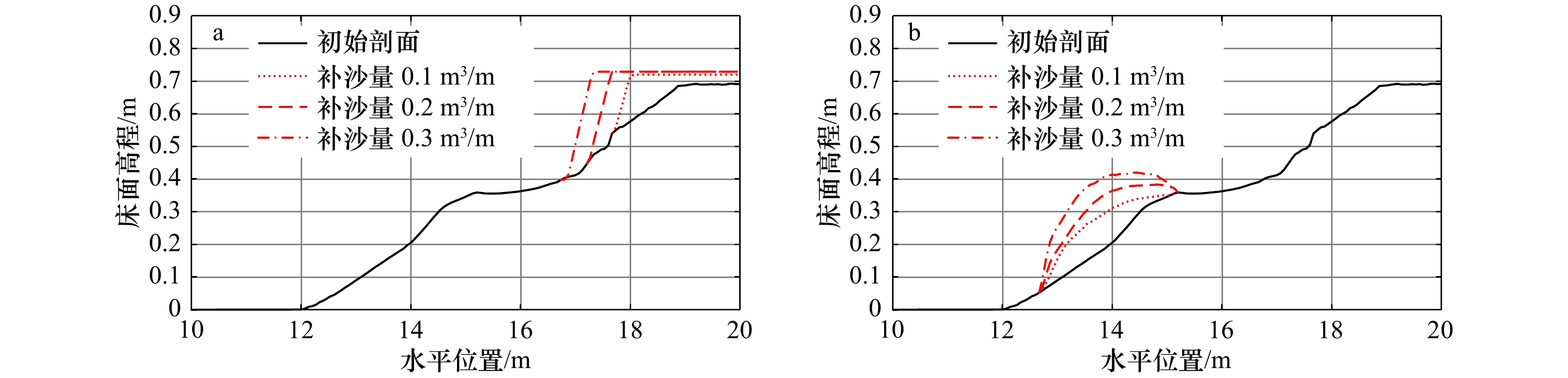
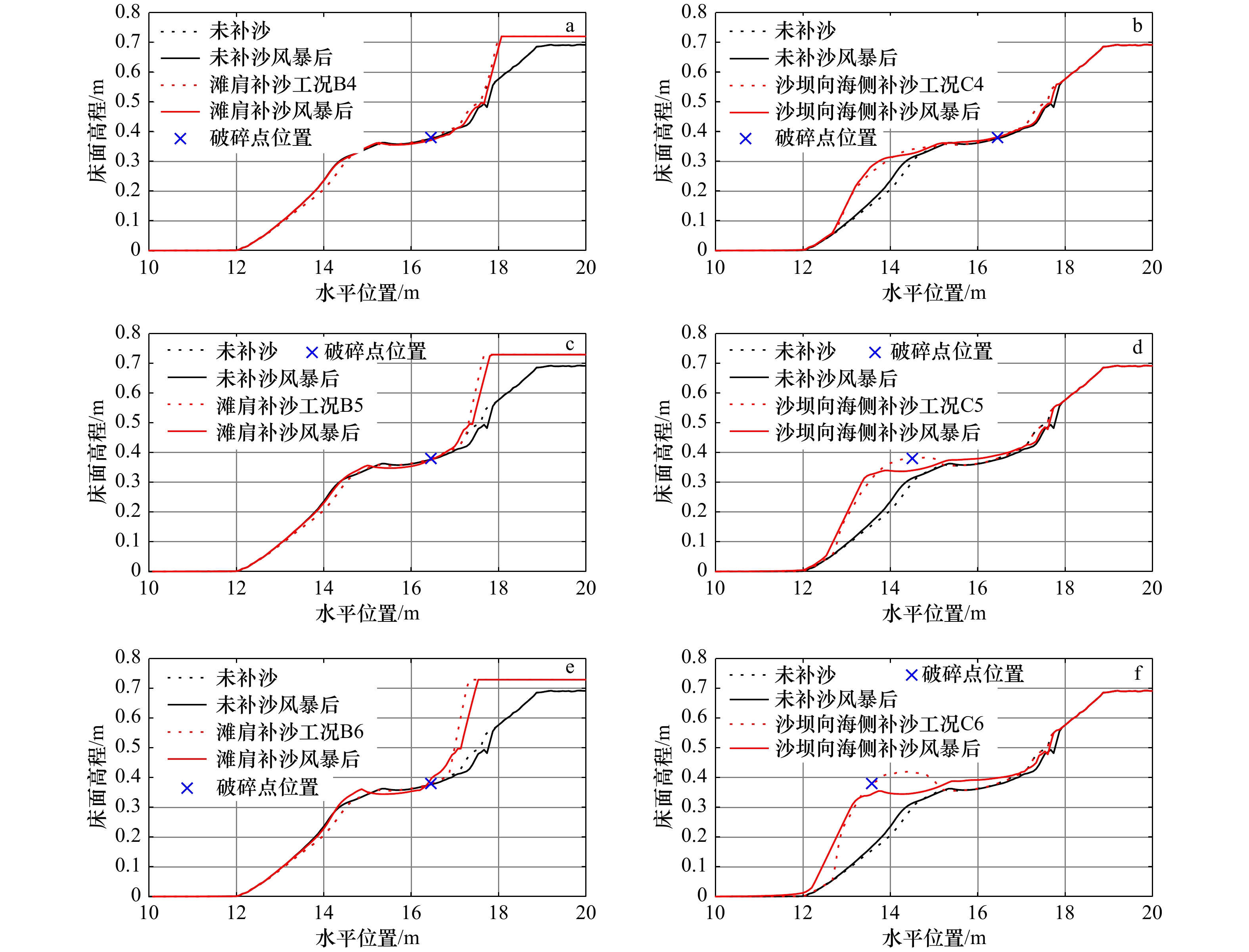
图 8 风暴作用下人工补沙剖面变化
a. 滩肩补沙(0.1 m3/m);b. 沙坝向海侧补沙(0.1 m3/m);c. 滩肩补沙(0.2 m3/m);d. 沙坝向海侧补沙(0.2 m3/m);e. 滩肩补沙(0.3 m3/m);f. 沙坝向海侧补沙(0.3 m3/m)
Fig. 8 Changes of artificial beach profile under storm
a. Berm nourishment (0.1 m3/m); b. bar nourishment to the seaward (0.1 m3/m); c. berm nourishment (0.2 m3/m); d. berm nourishment to the seaward (0.2 m3/m); e. berm nourishment (0.3 m3/m); f. bar nourishment to the seaward (0.3 m3/m)
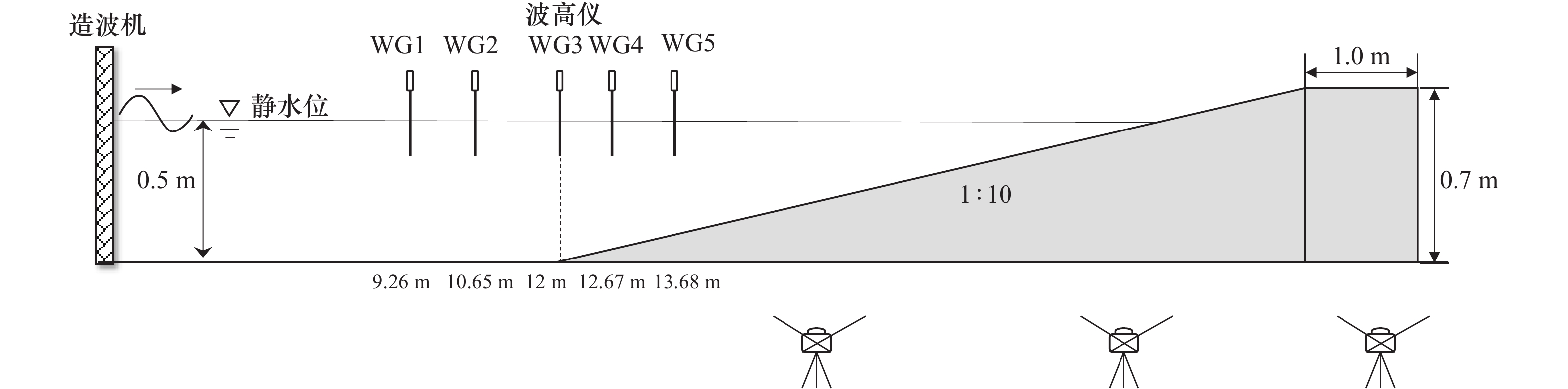
表 1 人工沙滩稳定性试验验证工况
Tab. 1 Validation cases of artificial beach stability test
工况 试验水深/m 初始坡度 波浪类型 平均波高H/m 周期/s 滩肩宽度/m 作用时间T/h 一 0.5 1∶10 规则波 0.14 1.5 1.0 8 二 0.5 1∶10 规则波 0.14 1.8 1.0 8 三 0.5 1∶10 规则波 0.17 1.5 1.0 8 表 2 数值模型误差统计
Tab. 2 Error statistics of the numerical model
工况 BSS R2 SCI 一 0.972 0.978 0.081 二 0.951 0.968 0.107 三 0.986 0.993 0.061 表 3 数值模拟工况
Tab. 3 Numerical simulation cases
补沙位置 工况 波浪类型 波高/m 周期/s 补沙量/(m3·m−1) 模拟时间/h 剖面类型 模拟条件 未补沙 A1 规则波 0.08 2.0 0 8 过渡型 常浪 A2 不规则波 0.15 1.5 0 0.5 侵蚀型 风暴 滩肩 B1 规则波 0.08 2.0 0.1 8 过渡型 常浪 B2 规则波 0.08 2.0 0.2 8 过渡型 常浪 B3 规则波 0.08 2.0 0.3 8 过渡型 常浪 B4 不规则波 0.15 1.5 0.1 0.5 侵蚀性 风暴 B5 不规则波 0.15 1.5 0.2 0.5 侵蚀性 风暴 B6 不规则波 0.15 1.5 0.3 0.5 侵蚀性 风暴 沙坝向海侧 C1 规则波 0.08 2.0 0.1 8 过渡型 常浪 C2 规则波 0.08 2.0 0.2 8 过渡型 常浪 C3 规则波 0.08 2.0 0.3 8 过渡型 常浪 C4 不规则波 0.15 1.5 0.1 0.5 侵蚀型 风暴 C5 不规则波 0.15 1.5 0.2 0.5 侵蚀型 风暴 C6 不规则波 0.15 1.5 0.3 0.5 侵蚀型 风暴 注:规则波对应平均波高,不规则波对应有效波高。 表 4 模拟工况0~8 h内RMSE值变化率(单位:10−2 m/h)
Tab. 4 The change rate of RMSE value within 8 hours of simulation cases (unit: 10−2 m/h)
补沙量/(m3·m−1) 补沙位置 0~1 h 1~2 h 2~3 h 3~4 h 4~5 h 5~6 h 6~7 h 7~8 h 0.1 滩肩 0.10 0.12 0.07 0.07 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 沙坝向海侧 0.08 0.09 0.07 0.06 0.06 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.2 滩肩 0.24 0.22 0.18 0.14 0.09 0.10 0.03 0.01 沙坝向海侧 0.49 0.46 0.28 0.22 0.18 0.14 0.12 0.01 0.3 滩肩 0.34 0.22 0.08 0.20 0.15 0.09 0.07 0.01 沙坝向海侧 2.02 0.93 0.47 0.33 0.27 0.21 0.17 0.01 表 5 风暴后海滩边缘水平位置变化(单位:m)
Tab. 5 Changes of horizontal position of beach edge after storm (unit: m)
补沙位置 工况 Y=0.43 m Y=0.47 m Y=0.50 m 未补沙 A2 −0.20 −0.17 −0.14 滩肩 B4 −0.10 −0.07 −0.07 B5 +0.09 +0.09 −0.10 B6 +0.40 +0.37 +0.18 沙坝向海侧 C4 −0.14 −0.14 −0.07 C5 −0.07 −0.14 −0.11 C6 0 −0.06 −0.11 注:“+”代表向海扩宽;“−”代表向陆缩窄。 表 6 风暴后水下凹槽处床面高程变化(单位:m)
Tab. 6 Changes of bed elevation at underwater trough after storm (unit: m)
补沙位置 工况 X=15.5 m X=16.0 m X=16.4 m 未补沙 A2 +0.005 +0.004 −0.003 滩肩 B4 +0.001 −0.004 −0.008 B5 −0.008 −0.009 −0.005 B6 −0.011 −0.009 −0.006 沙坝向海侧 C4 +0.007 +0.006 +0.002 C5 +0.019 +0.017 +0.012 C6 +0.033 +0.029 +0.020 注:“+”代表高程增加;“−”代表高程减小。 -
[1] 李震, 雷怀彦. 中国砂质海岸分布特征与存在问题[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2006, 22(6): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2006.06.001Li Zhen, Lei Huaiyan. Distribution and existing problems of sandy coast in China[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2006, 22(6): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2006.06.001 [2] Luijendijk A, Hagenaars G, Ranasinghe R, et al. The state of the world’s beaches[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 6641. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24630-6 [3] Vousdoukas M I, Ranasinghe R, Mentaschi L, et al. Sandy coastlines under threat of erosion[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2020, 10(3): 260−263. doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-0697-0 [4] Bruun P. Sea-level rise as a cause of shore erosion[J]. Journal of the Waterways and Harbors Division, 1962, 88(1): 117−130. doi: 10.1061/JWHEAU.0000252 [5] 吴建, 拾兵. 近岸补沙养护海滩研究综述[J]. 海洋科学, 2011, 35(8): 108−112.Wu Jian, Shi Bing. A review of the shoreface nourishment for beach protection[J]. Marine Sciences, 2011, 35(8): 108−112. [6] 庄振业, 王永红, 包敏, 等. 海滩养护过程和工程技术[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 39(5): 1019−1024.Zhuang Zhenye, Wang Yonghong, Bao Min, et al. Beach nourishment process and engineering technology[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2009, 39(5): 1019−1024. [7] 董丽红, 梁书秀, 孙昭晨. 海滩养护理论与试验研究进展[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2012, 29(5): 44−51.Dong Lihong, Liang Shuxiu, Sun Zhaochen. Research progress of beach conservation theory and experiment[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2012, 29(5): 44−51. [8] 姚国权. 欧, 美, 日的人造海滩[J]. 海洋信息, 1999(4): 27−28.Yao Guoquan. Artificial beach in Europe, America and Japan[J]. Marine Information, 1999(4): 27−28. [9] 胡广元, 庄振业, 高伟. 欧洲各国海滩养护概观和启示[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2008, 24(12): 29−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2008.12.007Hu Guangyuan, Zhuang Zhenye, Gao Wei. Overview and enlightenment of beach nourishment in Europe[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2008, 24(12): 29−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2008.12.007 [10] 莫文渊, 纪桂红, 谢琳, 等. 三亚三美湾和鹿回头湾人工沙滩设计[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2014, 30(3): 34−37.Mo Wenyuan, Ji Guihong, Xie Lin, et al. Artificial sand beaches design in Sanmei Bay and Luhuitou Bay, Sanya[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2014, 30(3): 34−37. [11] 谢世楞. 桂林洋海滩整治工程概况[J]. 港工技术, 1993(1): 1−8.Xie Shileng. Beach improvement works at Guilinyang[J]. Port Engineering Technology, 1993(1): 1−8. [12] 曹惠美, 蔡锋, 陈峰. 厦门滨海沙滩的养护与海洋旅游业发展的探讨[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2009, 26(7): 58−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2009.07.012Cao Huimei, Cai Feng, Chen Feng. The conservation of coastal beaches and development of marine tourism of Xiamen City[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2009, 26(7): 58−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2009.07.012 [13] Larson M, Kraus N C, Wise R A. Equilibrium beach profiles under breaking and non-breaking waves[J]. Coastal Engineering, 1999, 36(1): 59−85. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3839(98)00049-0 [14] Dean R G. Equilibrium beach profiles: US Atlantic and Gulf coasts, Department of Civil Engineering[R]. Newark: University of Delaware, 1977. [15] 李志强, 陈子燊. 海滩平衡剖面形态研究进展[J]. 海洋通报, 2002, 21(5): 82−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2002.05.012Li Zhiqiang, Chen Zishen. Progress in the studies on beach profile shapes[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2002, 21(5): 82−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2002.05.012 [16] 蔡锋, 刘根. 我国海滩养护修复的发展与技术创新[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2019, 38(4): 452−463.Cai Feng, Liu Gen. Beach nourishment development and technological innovations in China: an overview[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2019, 38(4): 452−463. [17] Roelvink D, Reniers A, Van Dongeren A, et al. Modelling storm impacts on beaches, dunes and barrier islands[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2009, 56(11/12): 1133−1152. [18] Harley M D, Armaroli C, Ciavola P. Evaluation of XBeach predictions for a real-time warning system in Emilia-Romagna, Northern Italy[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2011, SI 64(2): 1861−1865. [19] Roelvink D, Van Dongeren A, Mccall R, et al. Xbeach technical reference: kingsday release[R]. The Netherlands: UNESCO-IHE Institute for Water Education & Delft University of Technology, 2015. [20] 孙波, 孙林云, 陈雄波. 人工育滩的近岸补沙方法[C]//第十二届中国海岸工程学术讨论会论文集. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2005: 509-512.Sun Bo, Sun Linyun, Chen Xiongbo. Nearshore sediment supplement method for artificial beach nourishment[C]//China Symposium on Coastal Engineering. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2005: 509−512. [21] 杨燕雄, 杨雯, 邱若峰, 等. 人工近岸沙坝在海滩养护中的应用——以北戴河养滩工程为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(2): 23−30.Yang Yanxiong, Yang Wen, Qiu Ruofeng, et al. Application of artificial submerged sandbars to beach nourishment—A case from Beidaihe beach[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2013, 29(2): 23−30. [22] Sunamura T, Horikawa K. Two-dimensional beach transformation due to waves[C]//14th International Conference on Coastal Engineering. Copenhagen: ASCE, 1973: 920−938. [23] Hanson H, Brampton A, Capobianco M, et al. Beach nourishment projects, practices, and objectives—a European overview[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2002, 47(2): 81−111. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3839(02)00122-9 [24] Collins J I, Wier W. Probabilities of Wave Characteristics in the Surf Zone[R]. [S.I.: s.n.], 1969. -




 下载:
下载: