A fine classification method for sea ice based on random forest combining texture feature and NDVI
-
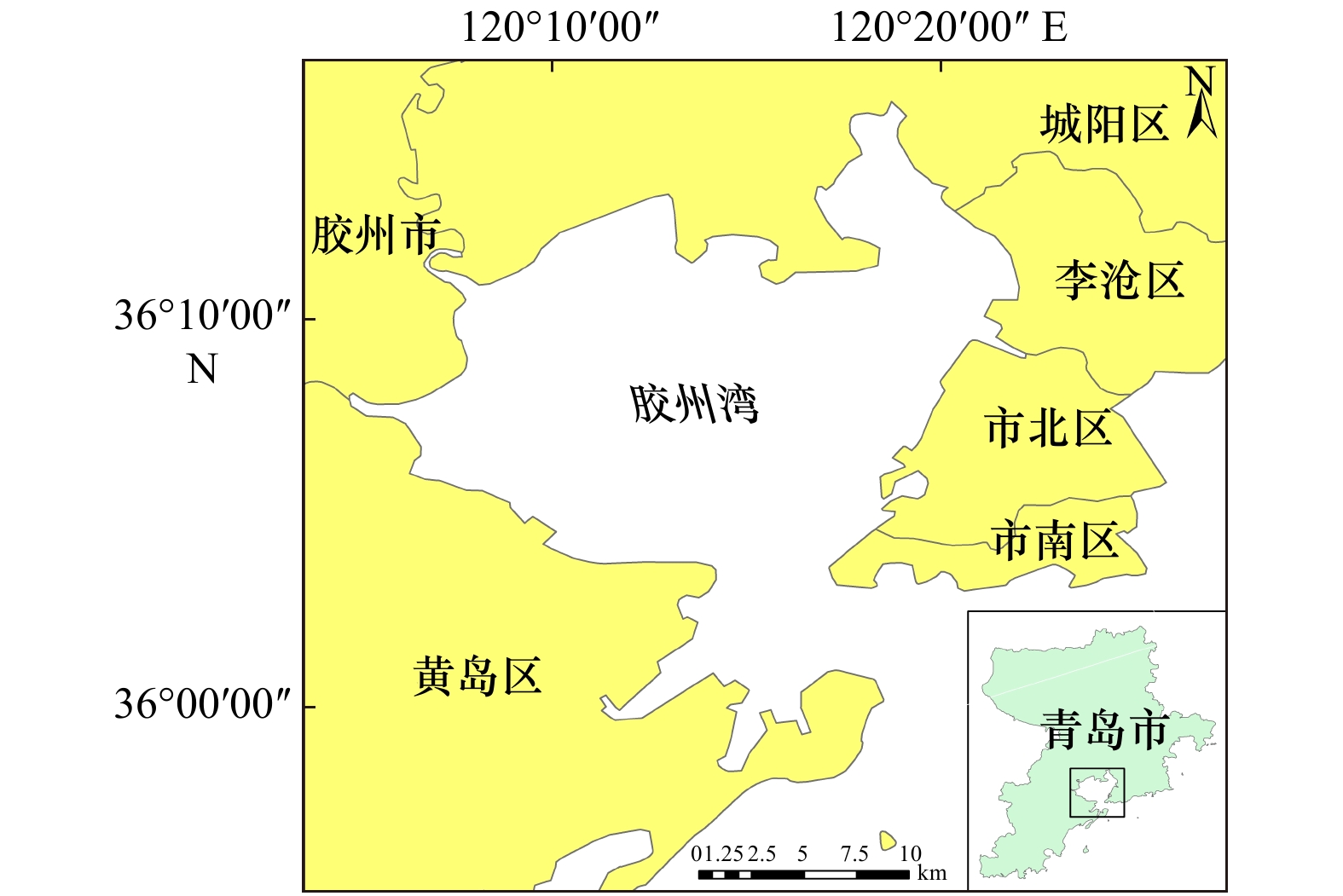
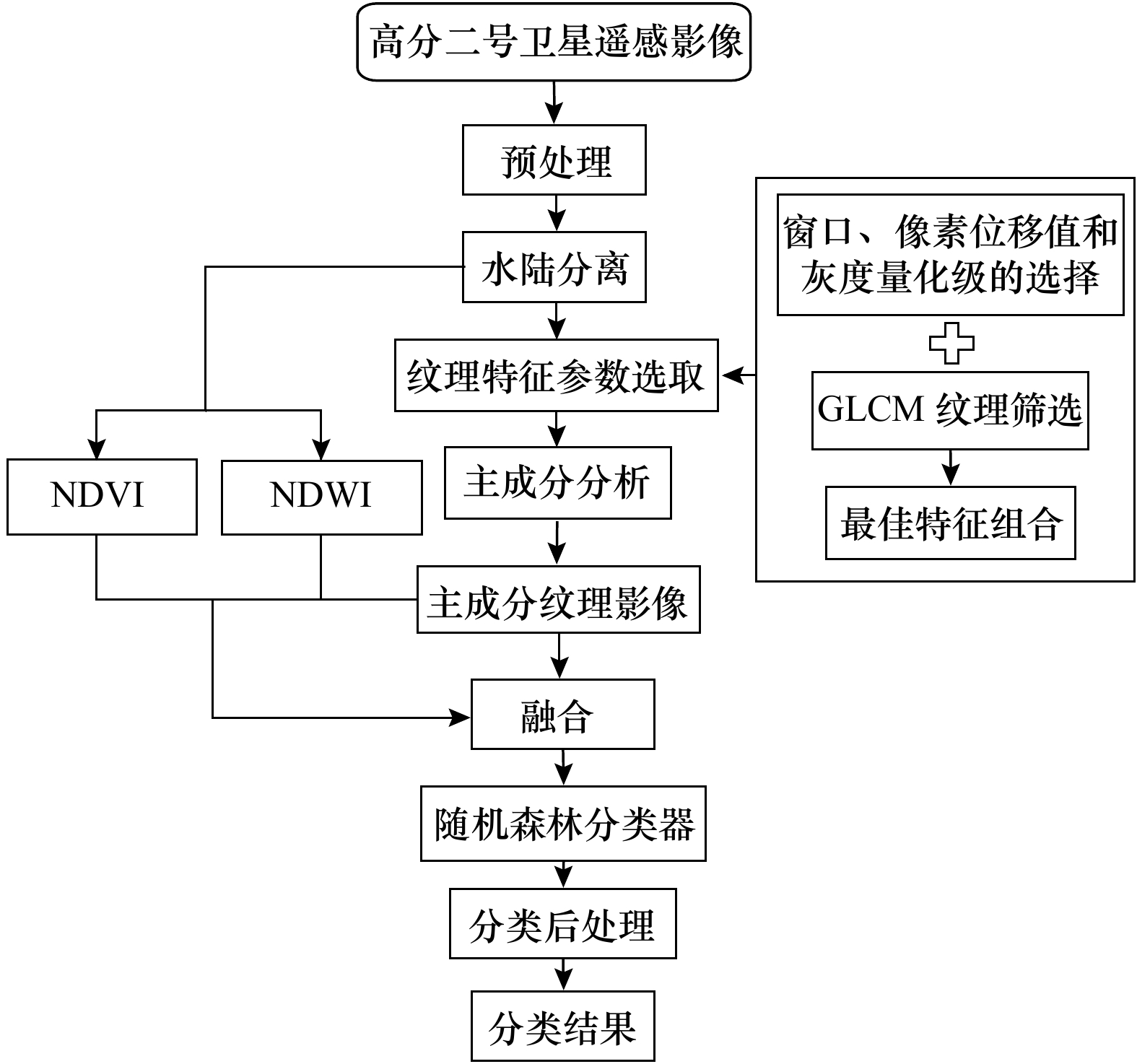
摘要: 海冰的精准分类对于掌握海冰生长发育状况,保障航海安全等具有重要意义。由于受数据源和分类方法等影响,使得海冰分类精度提高受限。本文面向高空间分辨率的光学遥感影像,提出了一种融合纹理特征和归一化差分植被指数(NDVI)的海冰精准分类方法,运用随机森林分类器构建海冰分类方法。以青岛胶州湾为实验区,高分二号(GF-2)为实验数据,进行了海冰类型提取,并与其他分类方法进行对比。结果显示:针对GF-2高分辨率光学遥感数据,融合纹理特征和NDVI的随机森林方法,相比于传统的随机森林、支持向量机、自动决策树和融合纹理特征的最大似然分类方法,总体分类精度分别提高13.70%、11.60%、19.22%、29.37%。Kappa系数分别提高0.16、0.13、0.22、0.44。相比于融合纹理特征和归一化水指数(NDWI)的随机森林方法,总体分类精度提高了9.67%,Kappa系数提高了0.09。这表明本文构建的海冰分类方法可有效提高海冰分类精度,为海冰的精确分类提供了一种有效的技术手段。Abstract: The accurate classification of sea ice is of great significance for mastering the growth and development of sea ice and ensuring the safety of navigation. Due to the influence of data sources and classification methods, the improvement of sea ice classification accuracy is limited. In this paper, for high spatial resolution optical remote sensing images, an accurate sea ice classification method based on texture features and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) was proposed, and a random forest classifier was used to construct a sea ice classification method. Taking Jiaozhou Bay of Qingdao as the experimental area and GF-2 as the experimental data, the sea ice types were extracted and compared with other classification methods. The results show that for GF-2 high-resolution optical remote sensing data, compared with the traditional random forest, support vector machine, automatic classification and regression tree methods and maximum likelihood classification method of combining texture features, the overall classification accuracy was improved by 13.70%, 11.60%, 19.22% and 29.37%, respectively. The Kappa coefficient was increased by 0.16, 0.13, 0.22 and 0.44, respectively. Compared with the random forest method based on texture features and normalized difference water index, the overall classification accuracy was improved by 9.67% and Kappa coefficient was increased by 0.09. It shows that the sea ice classification method constructed in this paper can effectively improve the accuracy of sea ice classification, and provide an effective technical means for the accurate classification of sea ice.
-
Key words:
- sea ice classification /
- GF-2 image /
- random forest /
- texture feature /
- NDVI
-
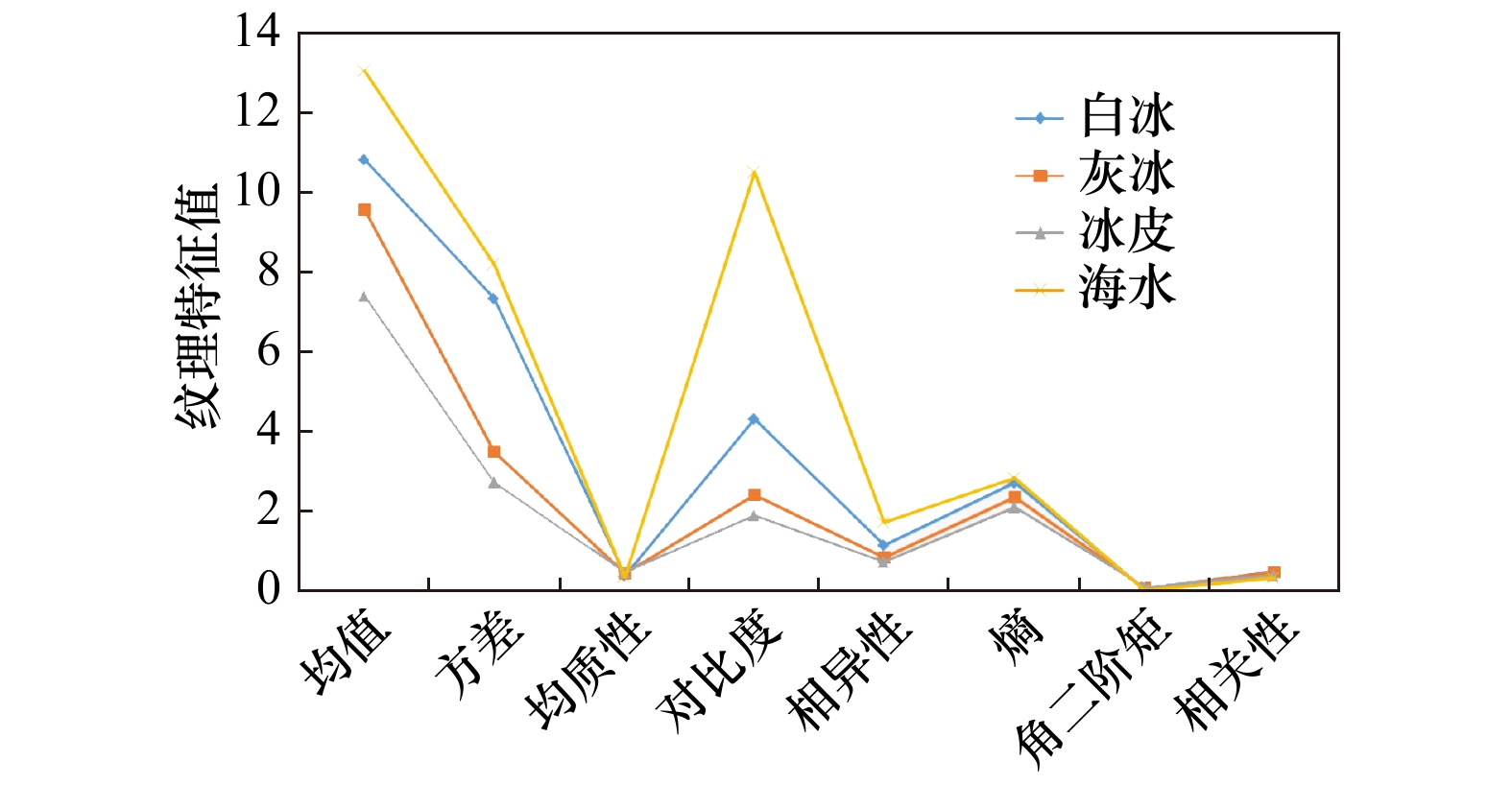
表 1 主成分分析结果
Tab. 1 Results of principal component analysis
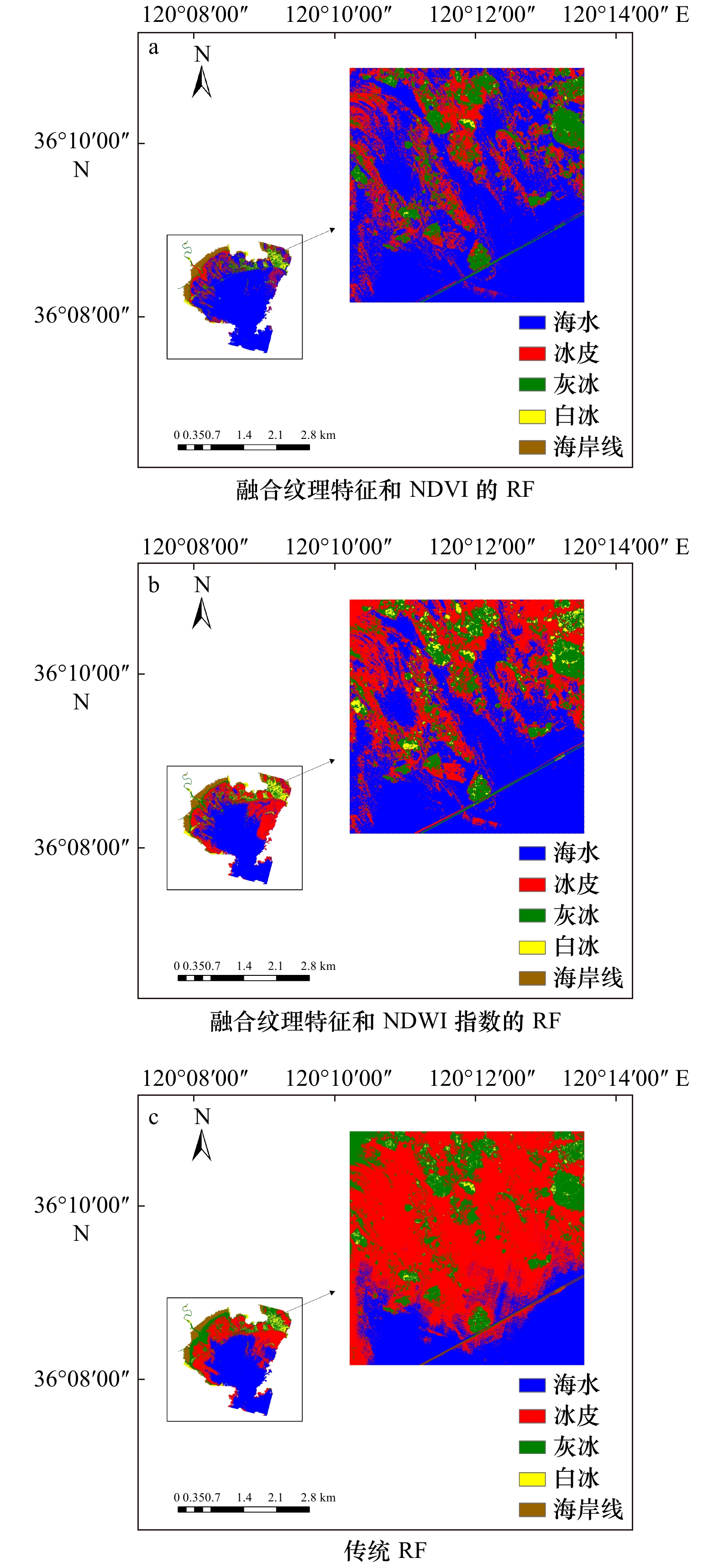
PC 特征值 累计特征值百分比/% 特征值百分比/% 1 3.848 8 96.22 96.22 2 0.146 7 99.89 3.67 3 0.004 2 99.99 0.10 4 0.000 4 100.00 0.01 表 2 不同分类算法精度
Tab. 2 Accuracy of different classification algorithms
方法 海冰
类别制图
精度/%用户
精度/%总体
精度/%Kappa
系数融合纹理特征和
NDVI的RF冰皮 26.50 10.36 84.68 0.73 灰冰 94.83 44.84 白冰 92.34 99.88 海水 84.76 94.08 融合纹理特征和
NDWI的RF冰皮 89.33 20.98 75.01 0.64 灰冰 86.96 42.21 白冰 92.62 90.45 海水 62.45 98.24 传统RF 冰皮 97.20 22.66 70.98 0.57 灰冰 96.15 9.78 白冰 98.76 100.00 海水 58.56 99.78 SVM 冰皮 92.91 15.20 73.08 0.60 灰冰 88.35 28.57 白冰 98.54 100.00 海水 60.88 99.17 CART 冰皮 99.23 14.85 65.46 0.51 灰冰 99.58 14.55 白冰 98.70 100.00 海水 57.58 99.92 融合纹理特征的ML 冰皮 90.17 13.18 55.31 0.29 灰冰 67.95 59.58 白冰 100.00 54.24 海水 55.24 67.33 -
[1] Su Hua, Wang Yunpeng, Xiao Jie, et al. Improving MODIS sea ice detectability using gray level co-occurrence matrix texture analysis method: A case study in the Bohai Sea[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2013, 85: 13−20. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.07.010 [2] Han Yanling, Wei Cong, Zhou Ruyan, et al. Combining 3D-CNN and squeeze-and-excitation networks for remote sensing sea ice image classification[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020, 2020: 8065396. [3] Zhang Lu, Liu Huiying, Gu Xinwei, et al. Sea ice classification using TerraSAR-X ScanSAR data with removal of scalloping and interscan banding[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(2): 589−598. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2889798 [4] Lohse J, Doulgeris A P, Dierking W. An optimal decision-tree design strategy and its application to sea ice classification from SAR imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(13): 1574. doi: 10.3390/rs11131574 [5] Liu Huiying, Guo Huadong, Zhang Lu. SVM-Based sea ice classification using textural features and concentration from RADARSAT-2 dual-pol ScanSAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(4): 1601−1613. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2365215 [6] Han Yanling, Gao Yi, Zhang Yun, et al. Hyperspectral sea ice image classification based on the spectral-spatial-joint feature with deep learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(18): 2170. doi: 10.3390/rs11182170 [7] 李宝辉, 侯一筠, 孙从容, 等. “北京一号”小卫星图像在渤海海冰监测中的应用[J]. 海洋学报, 2013, 35(4): 201−207.Li Baohui, Hou Yijun, Sun Congrong, et al. The application of “Beijing No. 1” satellite monitoring sea ice images in the Bohai Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2013, 35(4): 201−207. [8] 王姝力, 王志勇, 王磊. 基于Landsat-8和Sentinel-1A辽东湾海冰分类研究[J]. 北京测绘, 2019, 33(12): 1486−1492.Wang Shuli, Wang Zhiyong, Wang Lei. Study of sea ice classification of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-1A in Liaodong Bay[J]. Beijing Surveying and Mapping, 2019, 33(12): 1486−1492. [9] 韩彦岭, 李鹏, 张云, 等. 主动学习与半监督技术相结合的海冰图像分类[J]. 遥感信息, 2019, 34(2): 15−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2019.02.003Han Yanling, Li Peng, Zhang Yun, et al. Combining active learning with semi-supervised learning for sea ice image classification[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2019, 34(2): 15−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2019.02.003 [10] 张明, 吕晓琪, 张晓峰, 等. 结合纹理特征的SVM海冰分类方法研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(11): 149−156.Zhang Ming, Lü Xiaoqi, Zhang Xiaofeng, et al. Research on SVM sea ice classification based on texture features[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(11): 149−156. [11] 屈猛, 庞小平, 赵羲, 等. 利用多源遥感数据识别波弗特海冰间水道[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(6): 917−924.Qu Meng, Pang Xiaoping, Zhao Xi, et al. Detection of sea ice lead in Beaufort Sea based on multisensory remote sensing images[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(6): 917−924. [12] Haralick R M, Shanmugam K, Dinstein I. Textural features for image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1973, SMC-3(6): 610−621. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1973.4309314 [13] Hill M J. Vegetation index suites as indicators of vegetation state in grassland and savanna: An analysis with simulated SENTINEL 2 data for a North American transect[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2013, 137: 94−111. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2013.06.004 [14] Lei Ruibo, Zhang Zhanhai, Matero I, et al. Reflection and transmission of irradiance by snow and sea ice in the central Arctic Ocean in summer 2010[J]. Polar Research, 2012, 31(1): 17325. doi: 10.3402/polar.v31i0.17325 [15] Gerland S, Winther J G, Børre Ørbæk J, et al. Physical properties, spectral reflectance and thickness development of first year fast ice in Kongsfjorden, Svalbard[J]. Polar Research, 1999, 18(2): 275−282. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-8369.1999.tb00304.x [16] 陈前, 郑利娟, 李小娟, 等. 基于深度学习的高分遥感影像水体提取模型研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2019, 35(4): 43−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2019.04.007Chen Qian, Zheng Lijuan, Li Xiaojuan, et al. Water body extraction from high-resolution satellite remote sensing images based on deep learning[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2019, 35(4): 43−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2019.04.007 [17] Koutsias N, Mallinis G, Karteris M. A forward/backward principal component analysis of Landsat-7 ETM+ data to enhance the spectral signal of burnt surfaces[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2009, 64(1): 37−46. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2008.06.004 [18] Rodriguez-Galiano V F, Ghimire B, Rogan J, et al. An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2012, 67: 93−104. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2011.11.002 [19] 李鹏, 普思寻, 李振洪, 等. 2000年以来胶州湾海岸线光学与SAR多源遥感变化监测研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2020, 45(9): 1485−1492.Li Peng, Pu Sixun, Li Zhenhong, et al. Coastline change monitoring of Jiaozhou Bay from multi-source SAR and optical remote sensing images since 2000[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(9): 1485−1492. [20] Huang Wei, Sun Shunrong, Jiang Haibin, et al. GF-2 satellite 1m/4 m camera design and In-Orbit commissioning[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2018, 27(6): 1316−1321. doi: 10.1049/cje.2018.09.018 [21] Lohse J, Doulgeris A P, Dierking W. Incident angle dependence of Sentinel-1 texture features for sea ice classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(4): 552. doi: 10.3390/rs13040552 [22] 罗丽程. 基于Sentinel-1数据的北极海冰提取及分类研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海技术物理研究所), 2018.Luo Licheng. Research on the extraction and classification of Arctic sea ice based on Sentinel-1 data[D]. Shanghai: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2018. -




 下载:
下载: