Characterization and reconstruction of meso-structure of gas-bearing soils at different storage pressures
-
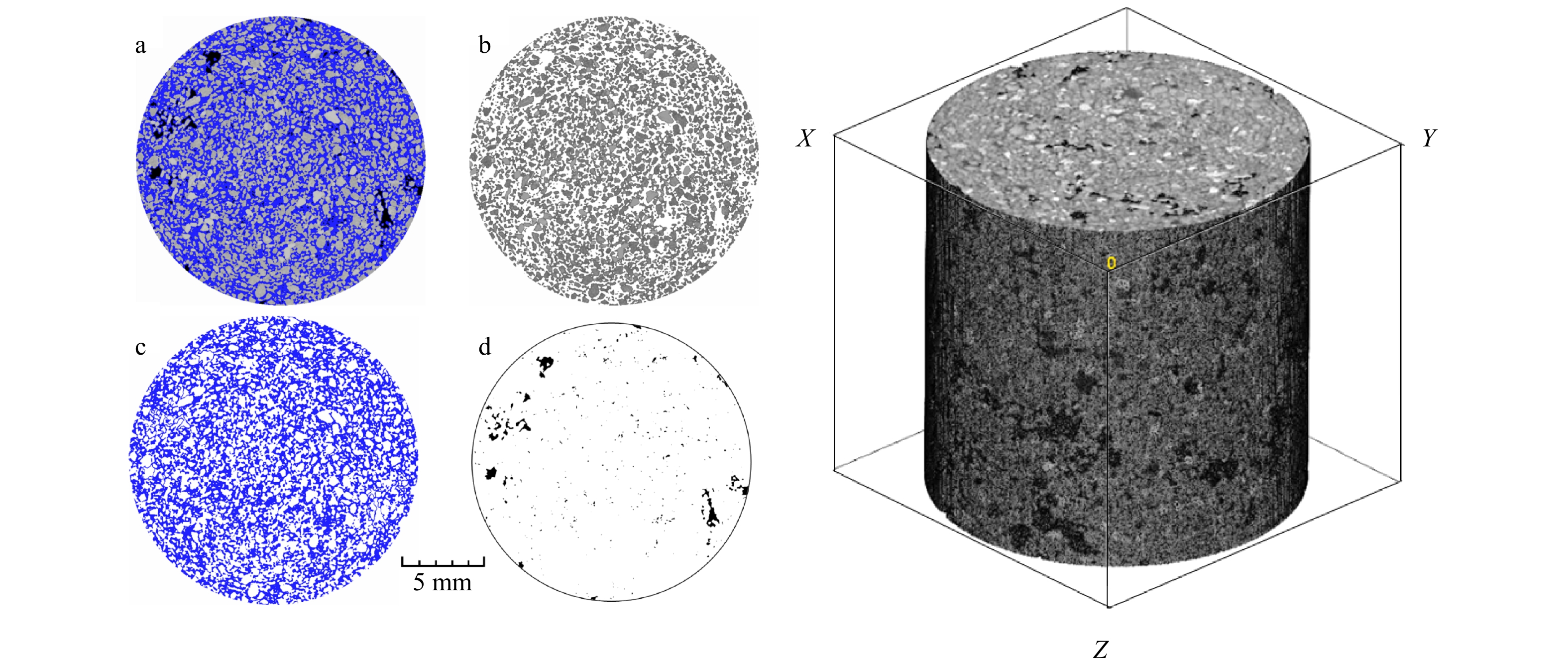
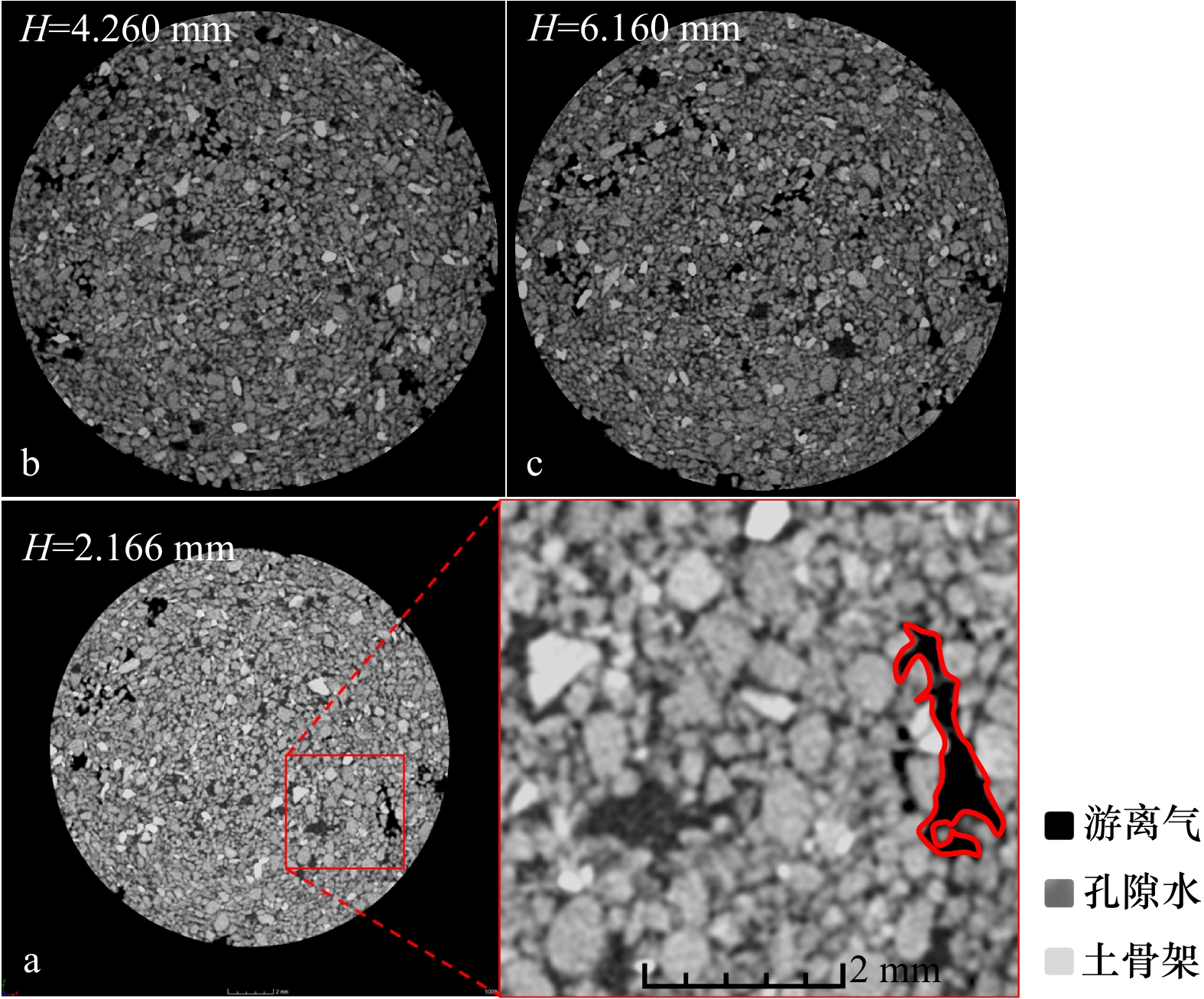
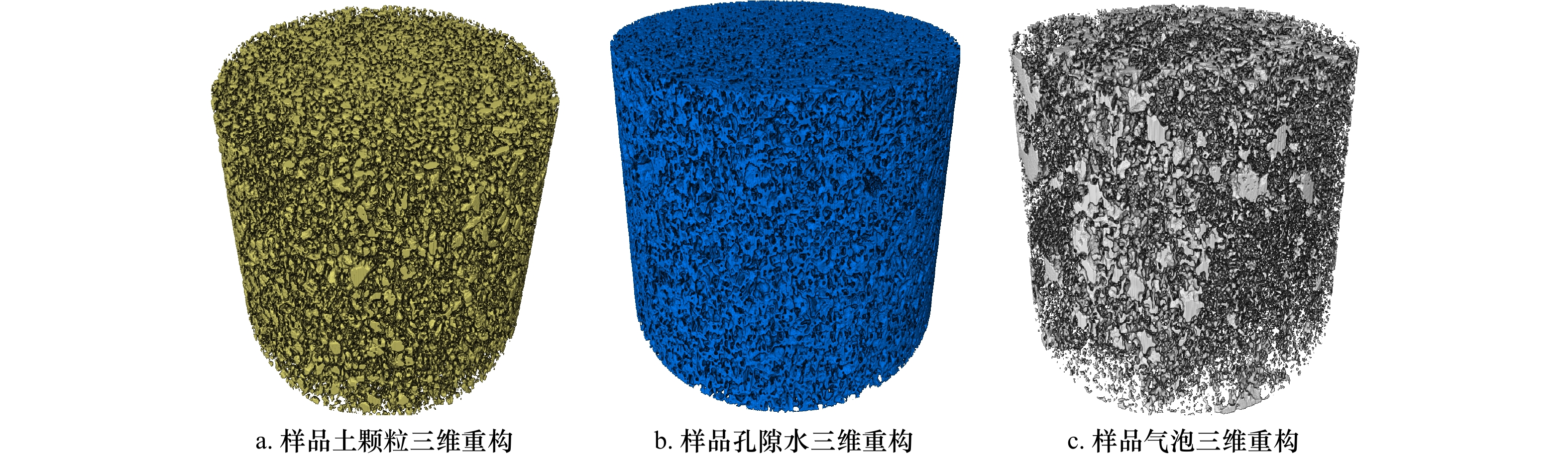
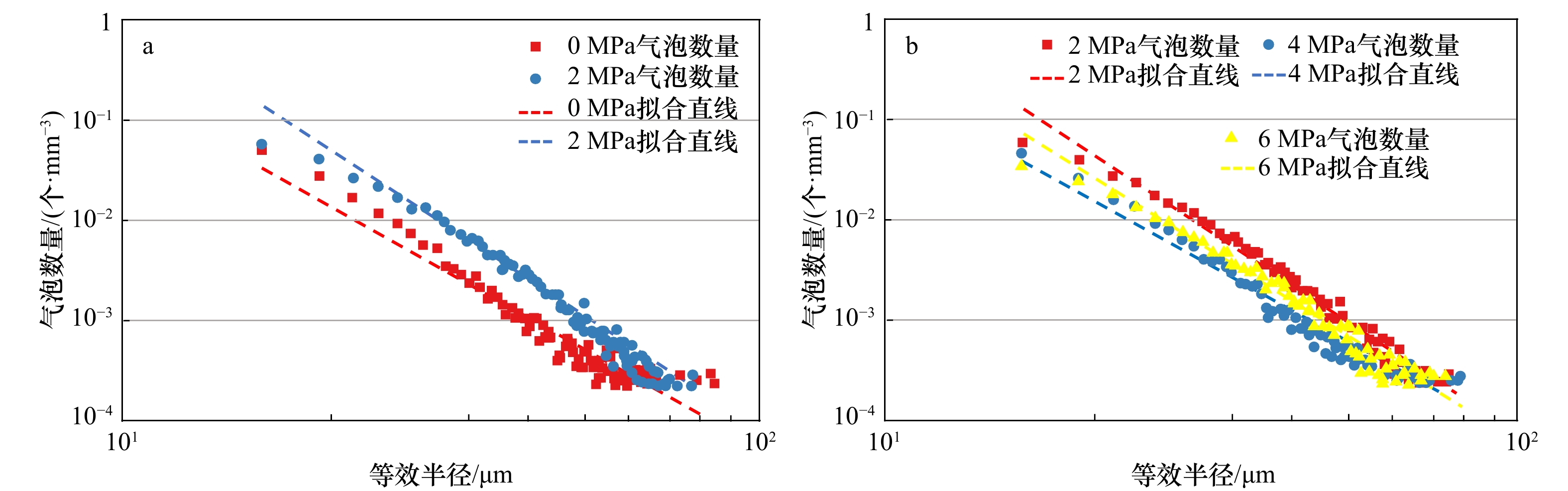
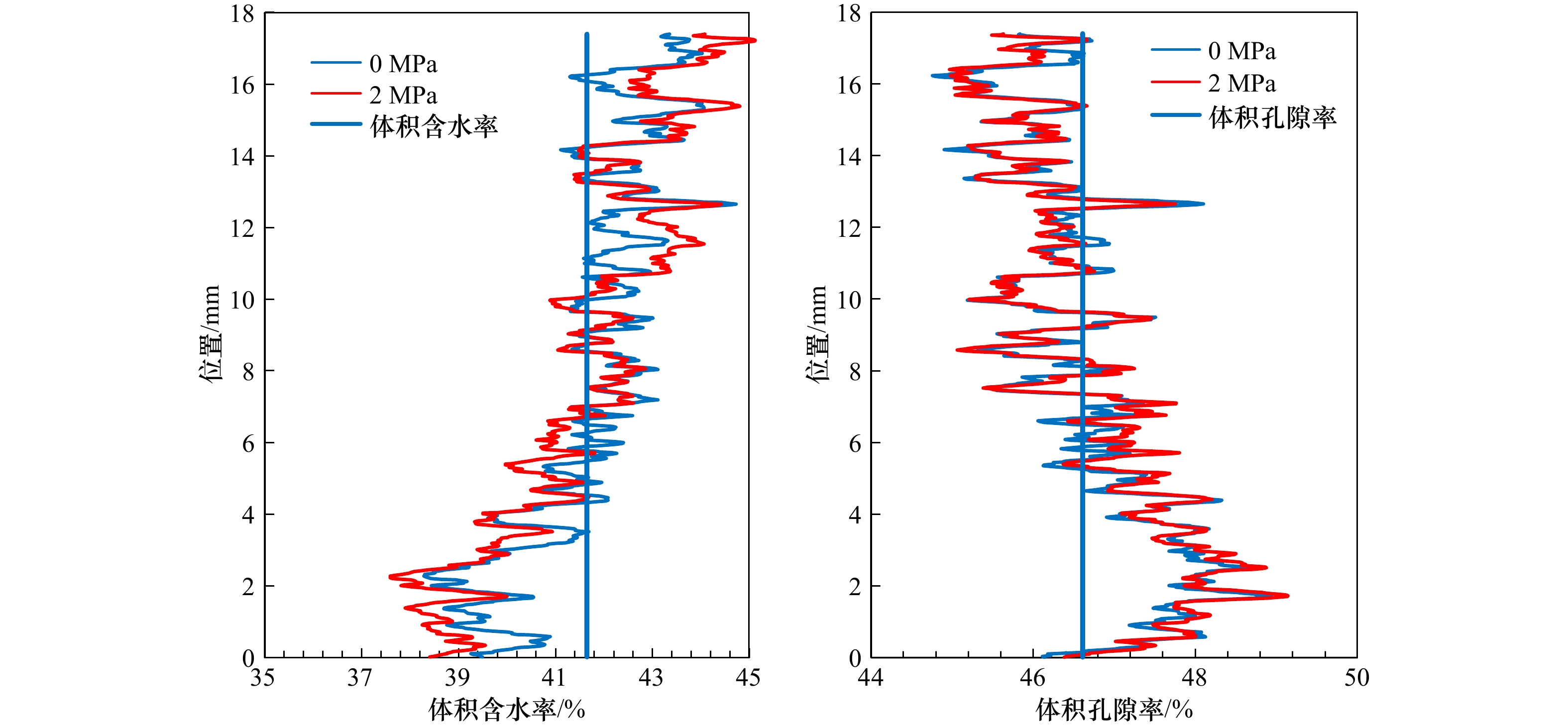
摘要: 含气土的储藏气压与细观结构表征是研究浅层气地质灾害的关键因素。利用工业CT扫描测试系统,采用立式旋转扫描,微焦点X射线光源的位置固定,样品沿XY平面方向匀速旋转1周,设定旋转步长为0.3°/s,对反应釜内含气样品注气加压至2 MPa、4 MPa、6 MPa,充分考虑样品成像最佳分辨率、最佳探测范围等因素的影响。结果表明,CT扫描获得的切片图像与重构图像具有良好的实验效果;加压注气到2 MPa时,小气泡灰度值增加;加压到6 MPa时气体整体灰度值增加明显;增压过程中气泡数量随着气泡半径增加而减少;加压注气过程会导致固−液−气三相物质局部变化,表现为孔隙气、孔隙水的体积变化幅度整体大于土骨架,微观局部位置会有较大的升高或降低。当不同位置的气体含量上升且占据主导地位时,会驱动着孔隙水的减少与土骨架的移动。Abstract: The storage pressure and reconstruction of the mesostructure of gas-bearing sediments are key factors in the study of shallow gas geohazards. Using an industrial CT scanning test system, vertical rotational (SR) scanning is used, with the position of the microfocus X-ray source fixed and the sample rotated at a constant speed of 360° along the XY plane, with a set rotation step of 0.3° per second, the gas-bearing samples in the reactor are pressurized to 2 MPa, 4 MPa, and 6 MPa, taking into account the best resolution of the sample imaging, the best detection range and other. The results show that the slices and reconstructed images obtained from the CT scan have good experimental results; the greyscale values of small bubbles increase when pressurized to 2 MPa; the overall greyscale values of gas increase significantly when pressurized to 6 MPa; the number of bubbles decrease with increasing bubble radius during the pressurization process; the pressurization process lead to local changes in the solid-liquid-gas phase, which show that the volume of pore gas and pore water changes more than that of the soil skeleton. The overall change is greater than that of the soil skeleton, and the microscopic local location will have a greater rise or decrease. When the gas content at different locations rises and dominates, it will drive the reduction of pore water and the movement of the soil skeleton.
-
Key words:
- gas bearing sediments /
- gas reservoir pressure /
- microstructure /
- CT scan
-
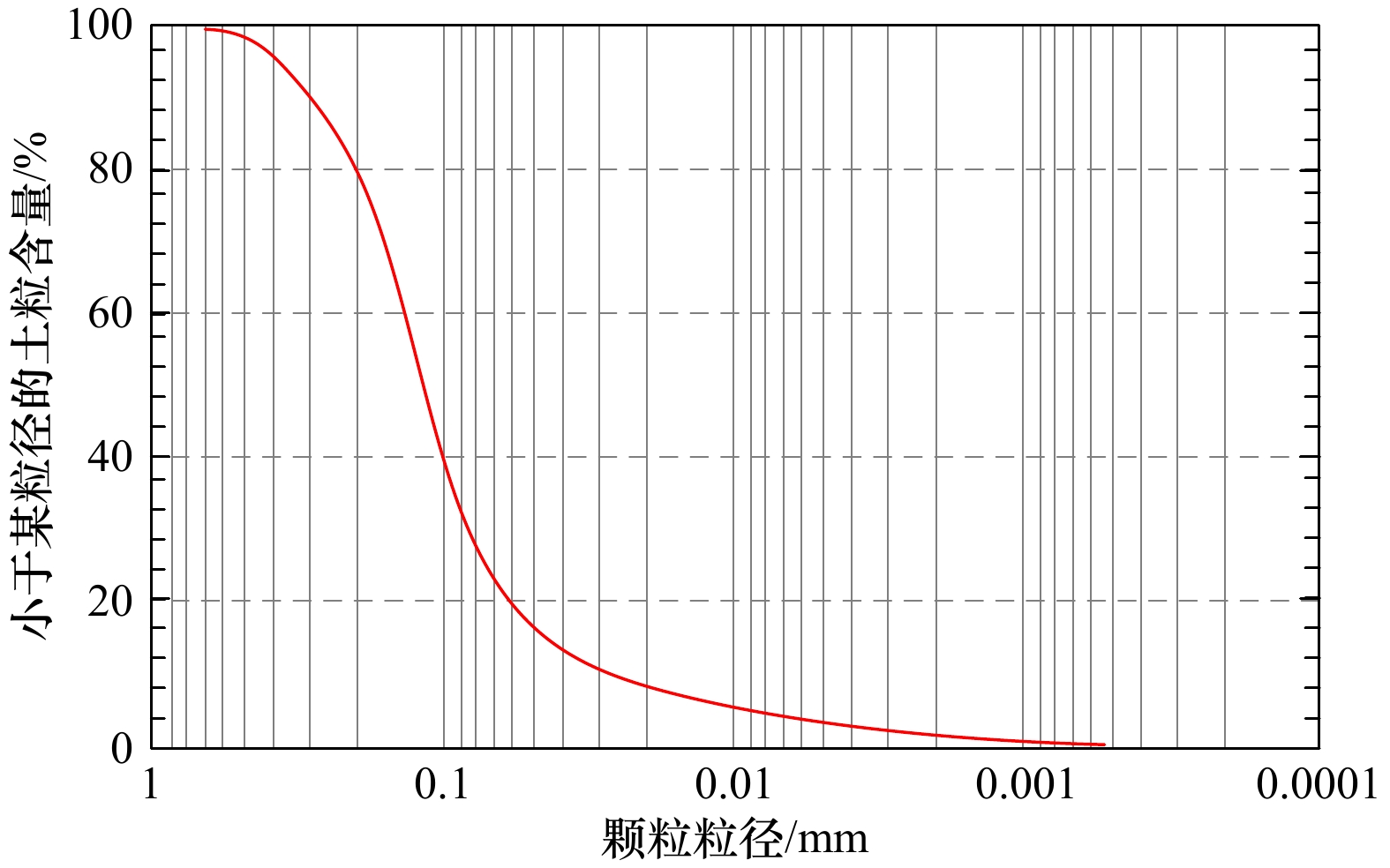
表 1 实验砂土基本物理性质指标
Tab. 1 Basic physical properties of experimental sand
粒径/mm 比重/(g·cm−3) 含水率/% 孔隙度/% 饱和度/% <0.7 2.62 40 45 88.9 表 2 不同气藏压力下表观含气量
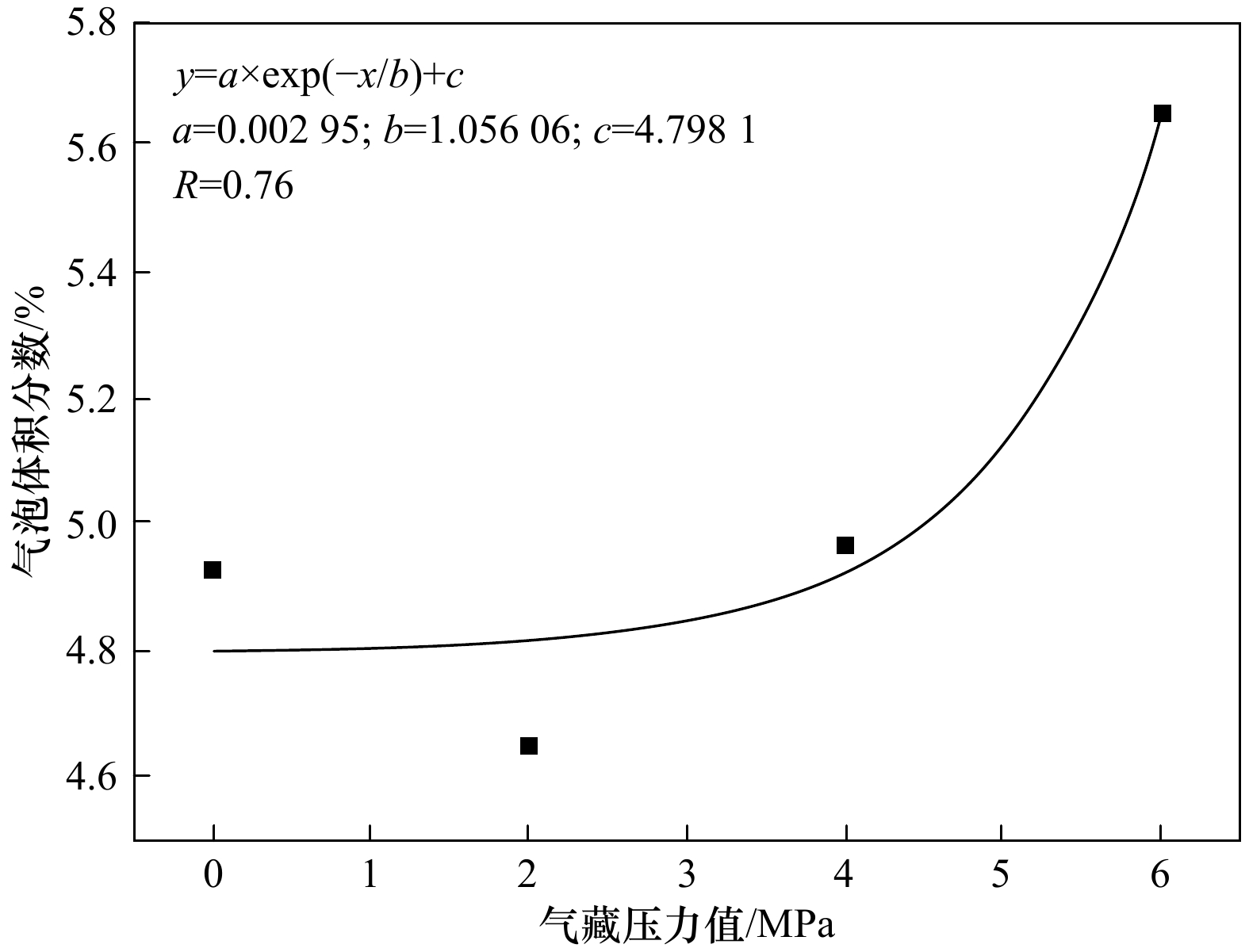
Tab. 2 Apparent gas content under different gas reservoir pressures
气藏压力值/MPa 气泡数量/个 气泡体积分数/% 0 11 499 4.93 2 16 391 4.65 4 10 164 4.97 6 11 966 5.66 -
[1] Fleischer P, Orsi T, Richardson M, et al. Distribution of free gas in marine sediments: a global overview[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2001, 21(2): 103−122. doi: 10.1007/s003670100072 [2] 李萍, 杜军, 刘乐军, 等. 我国近海海底浅层气分布特征[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2010, 21(1): 69−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.01.015Li Ping, Du Jun, Liu Lejun, et al. Distribution characteristics of the shallow gas in Chinese offshore seabed[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2010, 21(1): 69−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.01.015 [3] Robb G B N, Leighton T G, Dix J K, et al. Measuring bubble populations in gassy marine sediments: a review[C]//Proceedings of the Institute of Acoustics Spring Conference 2006: Futures in Acoustics: Today’s Research-Tomorrow’s Careers. UK: University of Southampton, 2006. [4] Gardner T. Modeling signal loss in surficial marine sediments containing occluded gas[J]. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2003, 113(3): 1368−1378. doi: 10.1121/1.1542731 [5] Jackson D R, Richardson M D. High-Frequency Seafloor Acoustics[M]. New York: Springer, 2007. [6] Anderson A L, Abegg F, Hawkins J A, et al. Bubble populations and acoustic interaction with the gassy floor of Eckernförde Bay[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1998, 18(14/15): 1807−1838. [7] Warner G S, Nieber J L, Moore I D, et al. Characterizing macropores in soil by computed tomography[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1989, 53(3): 653−660. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1989.03615995005300030001x [8] Sham W K. The undrained shear strength of soils containing large gas bubbles[D]. Belfast: Queen’s University of Belfast, 1989. [9] Wheeler S J. The undrained shear strength of soils containing large gas bubbles[J]. Geotechnique, 1988, 38(3): 399−413. doi: 10.1680/geot.1988.38.3.399 [10] Sultan N, De Gennaro V, Puech A. Mechanical behaviour of gas-charged marine plastic sediments[J]. Geotechnique, 2012, 62(9): 751−766. doi: 10.1680/geot.12.OG.002 [11] Best A I, Tuffin M D J, Dix J K, et al. Tidal height and frequency dependence of acoustic velocity and attenuation in shallow gassy marine sediments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2004, 109(B8): B08101. [12] Kim G Y, Narantsetseg B, Kim J W, et al. Physical properties and micro-and macro-structures of gassy sediments in the inner shelf of SE Korea[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 344: 170−180. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.01.049 [13] Hong Y, Wang L Z, Ng C W W, et al. Effect of initial pore pressure on undrained shear behaviour of fine-grained gassy soil[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2017, 54(11): 1592−1600. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2017-0015 [14] Thomas S, Hill A J, Clare M A, et al. Understanding engineering challenges posed by natural hydrocarbon infiltration and the development of authigenic carbonate[C]//Offshore Technology Conference. Houston, Texas, USA: Offshore Technology Conference, 2011. [15] Duffy S M, Wheeler S J, Bennell J D. Shear modulus of kaolin containing methane bubbles[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1994, 120(5): 781−796. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1994)120:5(781) [16] 张巍, 梁小龙, 唐心煜, 等. 显微CT扫描南京粉砂空间孔隙结构的精细化表征[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(4): 683−689. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201704013Zhang Wei, Liang Xiaolong, Tang Xinyu, et al. Fine characterization of spatial pore structure of Nanjing silty sand using micro-CT[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(4): 683−689. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201704013 [17] Liu L, Wilkinson J, Koca K, et al. The role of sediment structure in gas bubble storage and release[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2016, 121(7): 1992−2005. doi: 10.1002/2016JG003456 [18] Zhang Fengshou, Zhu Haiyan, Zhou Hangguo, et al. Discrete-element-method/computational-fluid-dynamics coupling simulation of proppant embedment and fracture conductivity after hydraulic fracturing[J]. SPE Journal, 2017, 22(2): 632−644. doi: 10.2118/185172-PA [19] 邢磊, 焦静娟, 刘雪芹, 等. 渤海海域浅层气分布及地震特征分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2017, 47(11): 70−78.Xing Lei, Jiao Jingjuan, Liu Xueqin, et al. Distribution and seismic reflection characteristics of shallow gas in Bohai Sea[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(11): 70−78. -





 下载:
下载: