Improved estimation method of retreat onset dates based on sea ice concentration
-
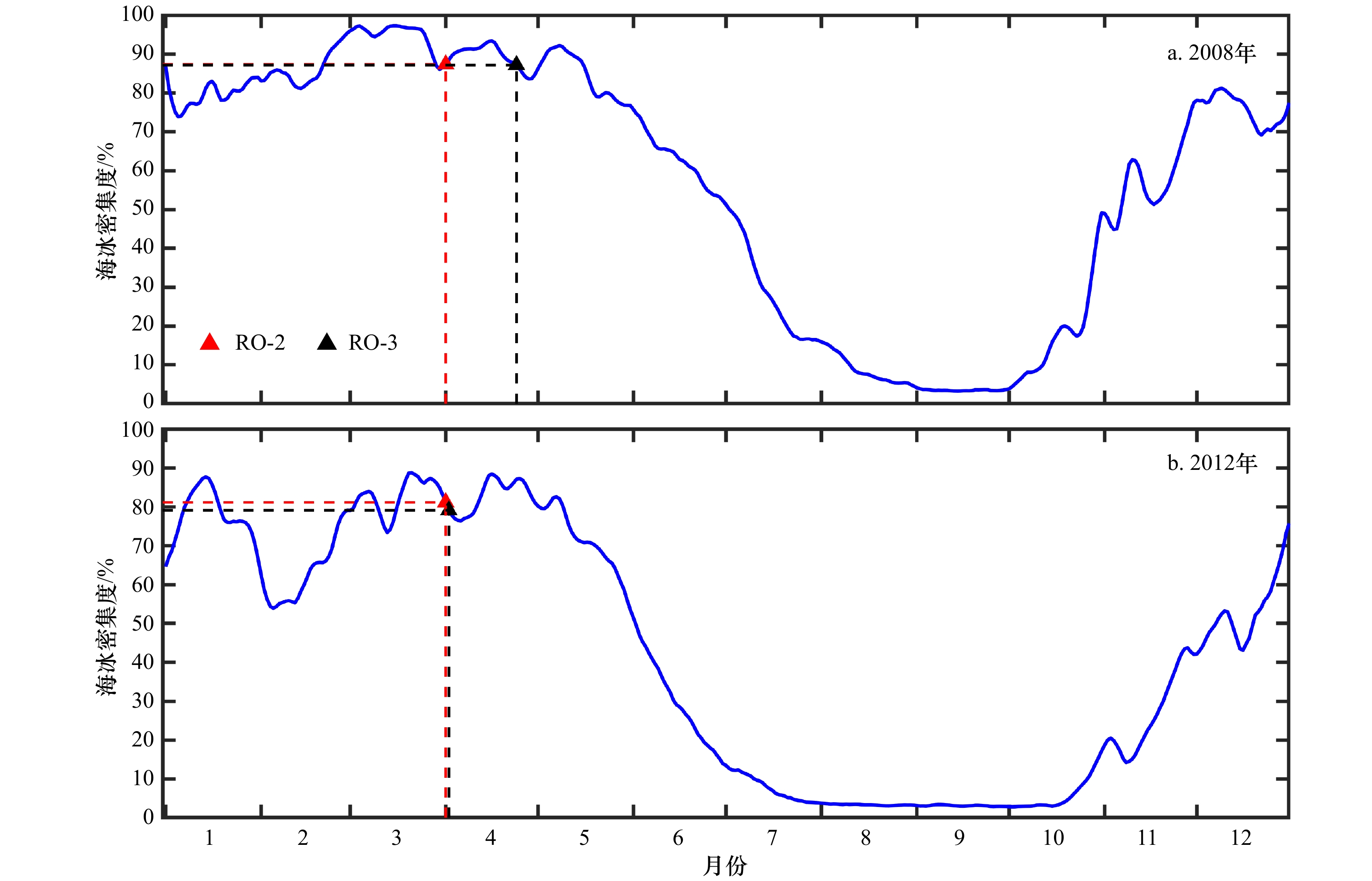
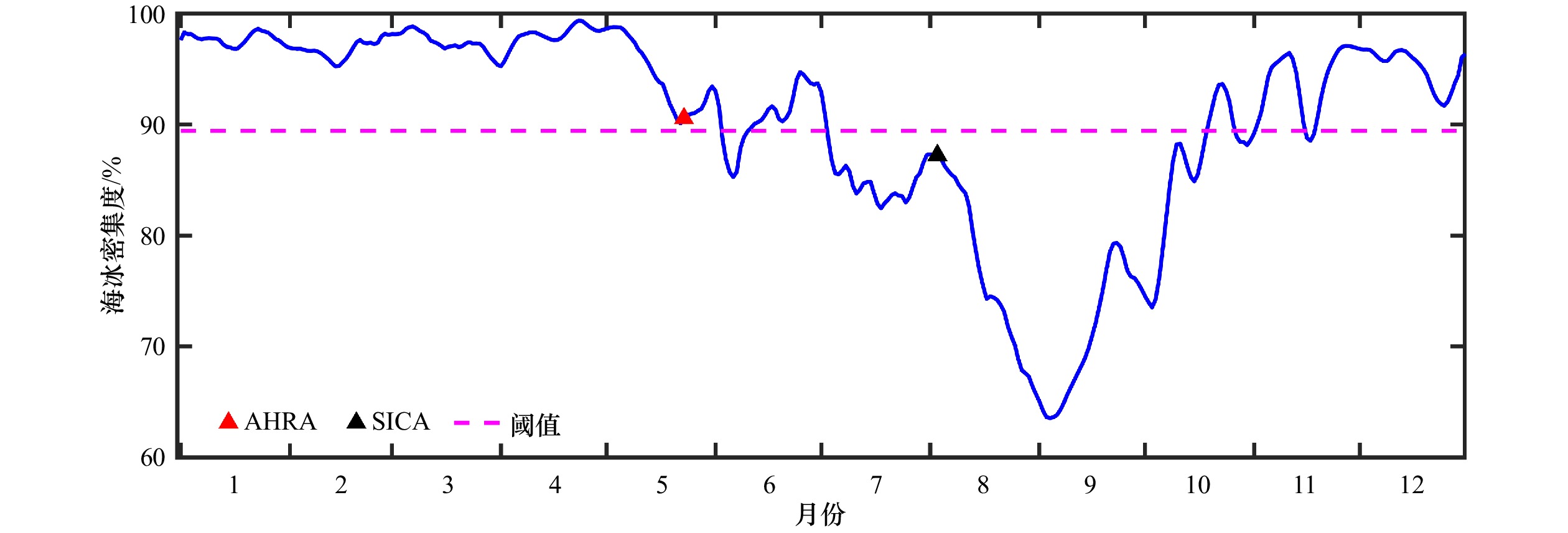
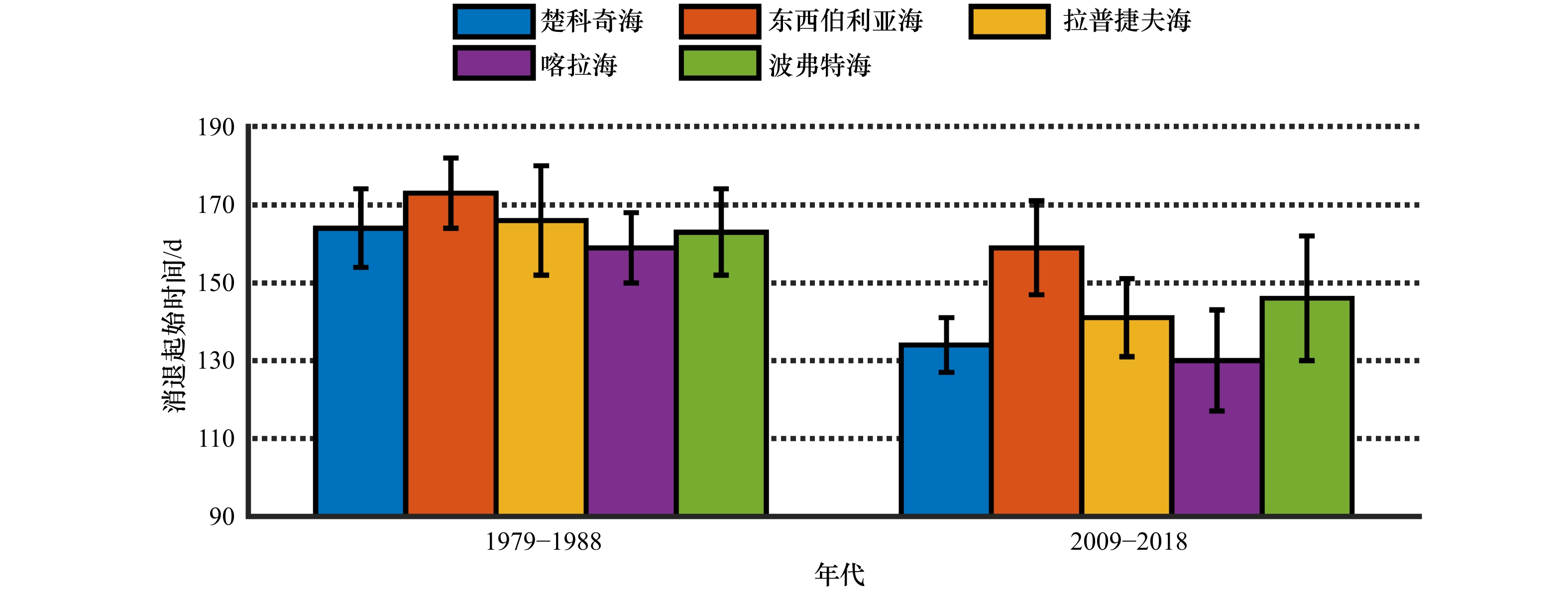
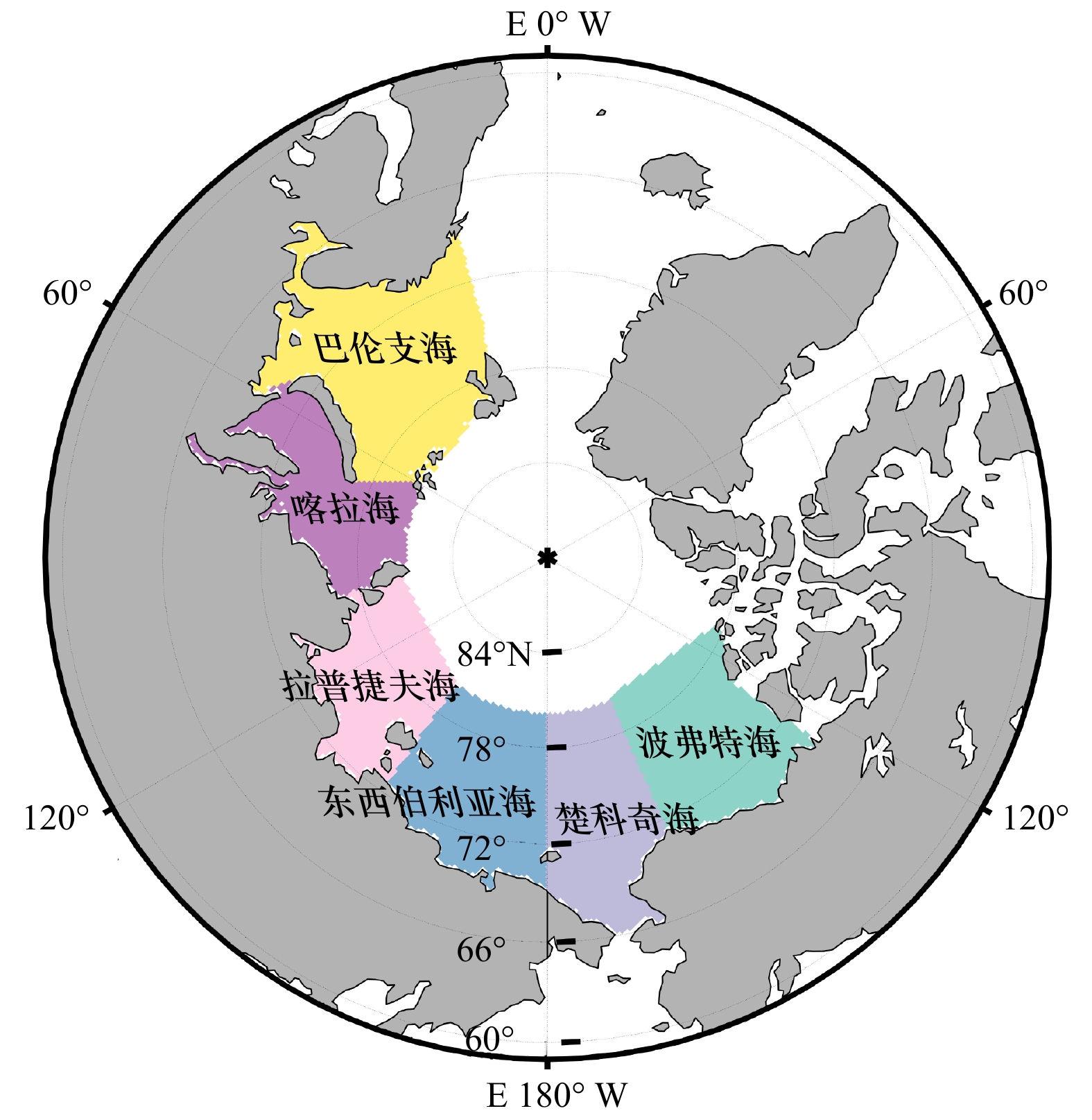
摘要: 海冰融化过程以正反馈的形式影响着海洋的热量吸收,对北极生态环境的变化和经济活动的开展起着重要作用。基于1979–2018年北冰洋逐日海冰密集度数据,本文综合考虑不同海域海冰冰况等因素,对北冰洋边缘海海冰消退起始时间的判别方法进行了改进。通过不同的方案对比分析表明,改进后的方法能够反映不同海域、不同年份冰情的变化;并且可消除一些天气扰动现象的干扰,避免过早地判别消退起始时间。应用本方法分析发现北冰洋各边缘海消退起始时间存在提前的趋势,与融化起始时间的提前趋势较为一致。但是不同海域提前程度存在明显差异,喀拉海和楚科奇海提前消退的趋势最强,达到了9 d/(10 a),而东西伯利亚海消退提前趋势最弱,只有4 d/(10 a),区域间的差异逐渐增大。海冰消退起始时间存在显著的年际差异,各边缘海的标准差均在15 d左右,近10年中消退最早与最晚之间的差值最大可达50 d,出现在波弗特海。Abstract: The melting of sea ice affects the ocean heat absorption in the form of positive feedback, and plays an important role in the changes of the Arctic environment and economic activities in the Arctic region. Based on the daily sea ice concentration data of the Arctic Ocean from 1979 to 2018, the estimation method of sea ice retreat onset dates in the Arctic marginal sea was improved by comprehensively considering the factors such as sea ice conditions and so on in different seas. Comparative analyses of different methods show that this improved method can reflect the changes of ice conditions in different sea areas and different years, and can eliminate some influences of weather disturbance on the estimation of retreat onset, so as to avoid premature estimation results. By using this method, it is found that the retreat onset dates of every Arctic marginal sea are generally advanced. The advanced trends of retreat onset dates are generally the same as advanced trends of melt onset dates. However, different sea areas have different degrees of advancement. The Kara Sea and the Chukchi Sea have the strongest trend of early retreating, reaching 9 d/(10 a), while the East Siberian Sea has the weakest trend, only 4 d/(10 a). The difference of retreat onset dates gradually increases between these regions. There are significant interannual variations in the retreat onset dates, the standard deviations of each marginal sea are about 15 d. In the past decade, the difference between the earliest and the latest retreating reaches 50 d, which appeared in the Beaufort Sea.
-
表 1 1979−2017年SICA判别的消退起始时间与AHRA方法的平均值与趋势对比
Tab. 1 Mean and trend differences of retreat onset dates estimated by SICA and AHRA during 1979−2017
海域 平均值/d 趋势/(d·(10 a)−1) AHRA SICA AHRA SICA 楚科奇海 137±13 147±15 –8* –9* 东西伯利亚海 148±14 165±16 –9* –4* 拉普捷夫海 143±12 153±18 –7* –8* 喀拉海 126±14 140±16 –9* –9* 波弗特海 148±10 157±17 –7* –7* 注:*表示变化趋势通过95%置信度检查。时间从1月1日起算。 -
[1] Belchansky G I, Douglas D C, Platonov N G. Duration of the Arctic sea ice melt season: Regional and interannual variability, 1979–2001[J]. Journal of Climate, 2004, 17(1): 67−80. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<0067:DOTASI>2.0.CO;2 [2] Lindsay R, Schweiger A. Arctic sea ice thickness loss determined using subsurface, aircraft, and satellite observations[J]. The Cryosphere, 2015, 9(1): 269−283. doi: 10.5194/tc-9-269-2015 [3] Comiso J C. Large decadal decline of the Arctic multiyear ice cover[J]. Journal of Climate, 2012, 25(4): 1176−1193. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00113.1 [4] 赵进平, 史久新, 王召民, 等. 北极海冰减退引起的北极放大机理与全球气候效应[J]. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(9): 985−995.Zhao Jinping, Shi Jiuxin, Wang Zhaomin, et al. Arctic amplification produced by sea ice retreat and its global climate effects[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2015, 30(9): 985−995. [5] Overland J E, Wood K R, Wang M Y. Warm Arctic-cold continents: Climate impacts of the newly open Arctic sea[J]. Polar Research, 2011, 30(1): 15787. doi: 10.3402/polar.v30i0.15787 [6] 黄季夏, 张天媛, 曹云锋, 等. 北极海冰消融情景下东北航道通航性能演变分析[J]. 地理学报, 2021, 76(5): 1051−1064. doi: 10.11821/dlxb202105001Huang Jixia, Zhang Tianyuan, Cao Yunfeng, et al. The evolution of navigation performance of Northeast Passage under the scenario of Arctic sea ice melting[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2021, 76(5): 1051−1064. doi: 10.11821/dlxb202105001 [7] Lei Ruibo, Tian-Kunze X, Leppäranta M, et al. Changes in summer sea ice, albedo, and portioning of surface solar radiation in the Pacific sector of Arctic Ocean during 1982–2009[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2016, 121(8): 5470−5486. doi: 10.1002/2016JC011831 [8] Curry J A, Schramm J L, Ebert E E. Sea ice-albedo climate feedback mechanism[J]. Journal of Climate, 1995, 8(2): 240−247. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1995)008<0240:SIACFM>2.0.CO;2 [9] Stroeve J, Notz D. Changing state of Arctic sea ice across all seasons[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2018, 13(10): 103001. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aade56 [10] Stroeve J C, Crawford A D, Stammerjohn S. Using timing of ice retreat to predict timing of fall freeze-up in the Arctic[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(12): 6332−6340. doi: 10.1002/2016GL069314 [11] Drobot S D, Anderson M R. An improved method for determining snowmelt onset dates over Arctic sea ice using scanning multichannel microwave radiometer and Special Sensor Microwave/Imager data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2001, 106(D20): 24033−24049. doi: 10.1029/2000JD000171 [12] Markus T, Stroeve J C, Miller J. Recent changes in Arctic sea ice melt onset, freezeup, and melt season length[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2009, 114(C12): C12024. doi: 10.1029/2009JC005436 [13] Anderson M R. Determination of a melt-onset date for Arctic sea-ice regions using passive-microwave data[J]. Annals of Glaciology, 1997, 25: 382−387. doi: 10.3189/S0260305500014324 [14] Bliss A C, Miller J A, Meier W N. Comparison of passive microwave-derived early melt onset records on Arctic sea ice[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(3): 199. doi: 10.3390/rs9030199 [15] 朱大勇, 赵进平, 史久新. 北极楚科奇海海冰面积多年变化的研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2007, 29(2): 25−33.Zhu Dayong, Zhao Jinping, Shi Jiuxin. Study on the multi-year variations of sea ice cover of Chukchi Sea in Arctic Ocean[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2007, 29(2): 25−33. [16] 马靖凯, 陶树豪, 杜凌, 等. 北极太平洋扇区海冰融冻期的年代际变化[J]. 气候变化研究快报, 2019, 8(3): 302−311. doi: 10.12677/CCRL.2019.83034Ma Jingkai, Tao Shuhao, Du Ling, et al. Decadal variation of sea ice melting-frozen season in the Pacific sector of the Arctic[J]. Climate Change Research Letters, 2019, 8(3): 302−311. doi: 10.12677/CCRL.2019.83034 [17] Onarheim I H, Eldevik T, Smedsrud L H, et al. Seasonal and regional manifestation of Arctic sea ice loss[J]. Journal of Climate, 2018, 31(12): 4917−4932. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0427.1 [18] Meier W N, Fetterer F, Savoie M, et al. NOAA/NSIDC Climate Data Record of Passive Microwave Sea Ice Concentration, Version 3[Z]. Boulder, Colorado, USA: National Snow and Ice Data Center, 2019. [19] Comiso J C, Nishio F. Trends in the sea ice cover using enhanced and compatible AMSR-E, SSM/I, and SMMR data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2008, 113(C2): C02S07. [20] Ogi M, Rigor I G, McPhee M G, et al. Summer retreat of Arctic sea ice: Role of summer winds[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35(24): L24701. doi: 10.1029/2008GL035672 [21] Bliss A C, Anderson M R. Snowmelt onset over Arctic sea ice from passive microwave satellite data: 1979–2012[J]. The Cryosphere, 2014, 8(6): 2089−2100. doi: 10.5194/tc-8-2089-2014 [22] Bliss A C, Anderson M R. Daily area of snow melt onset on Arctic sea ice from passive microwave satellite observations 1979–2012[J]. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(11): 11283−11314. doi: 10.3390/rs61111283 [23] Steele M, Bliss A C, Peng G, et al. Arctic Sea Ice Seasonal Change and Melt/Freeze Climate Indicators from Satellite Data, Version 1[Z]. Boulder, Colorado, USA: National Snow and Ice Data Center, 2018. [24] El Naggar S, Garrity C, Ramseier R O. The modelling of sea ice melt-water ponds for the high Arctic using an airborne line scan camera, and applied to the Satellite Special Sensor Microwave/Imager (SSM/I)[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1998, 19(12): 2373−2394. doi: 10.1080/014311698214785 [25] Maksym T. Arctic and Antarctic sea ice change: Contrasts, commonalities, and causes[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2019, 11: 187−213. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010816-060610 [26] 朱大勇, 赵进平, 史久新. 2003年与1999年楚科奇海海冰的差异及其发生原因[J]. 极地研究, 2005, 17(1): 11−22.Zhu Dayong, Zhao Jinping, Shi Jiuxin. Differences of sea ice distribution in Chukchi Sea and their dynamic mechanism in 1999 and 2003[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2005, 17(1): 11−22. [27] Kapsch M L, Skific N, Graversen R G, et al. Summers with low Arctic sea ice linked to persistence of spring atmospheric circulation patterns[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2019, 52(3): 2497−2512. -




 下载:
下载: