Experimental investigation of breaking waves impacting a vertical pile in a large model scale
-
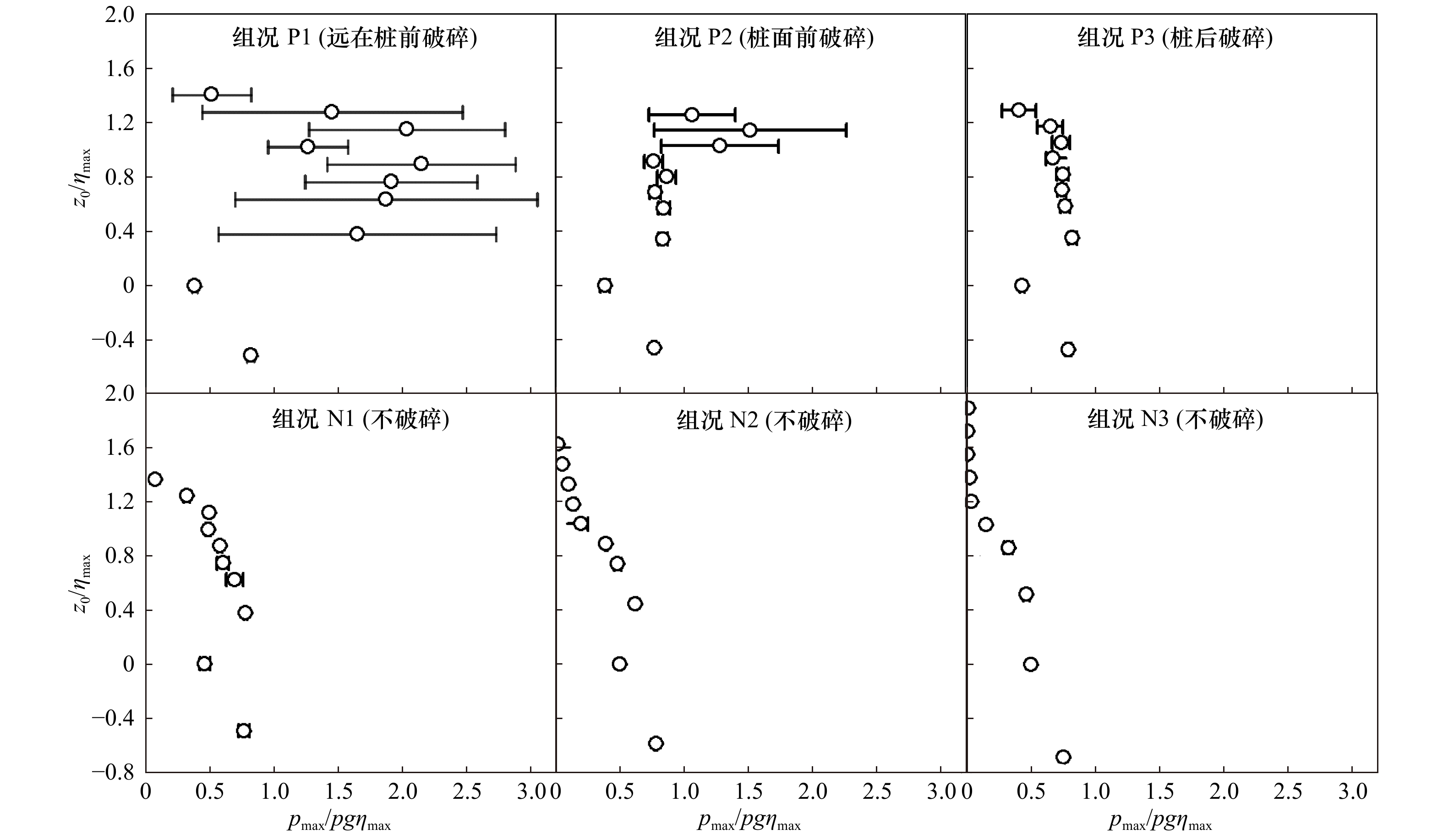
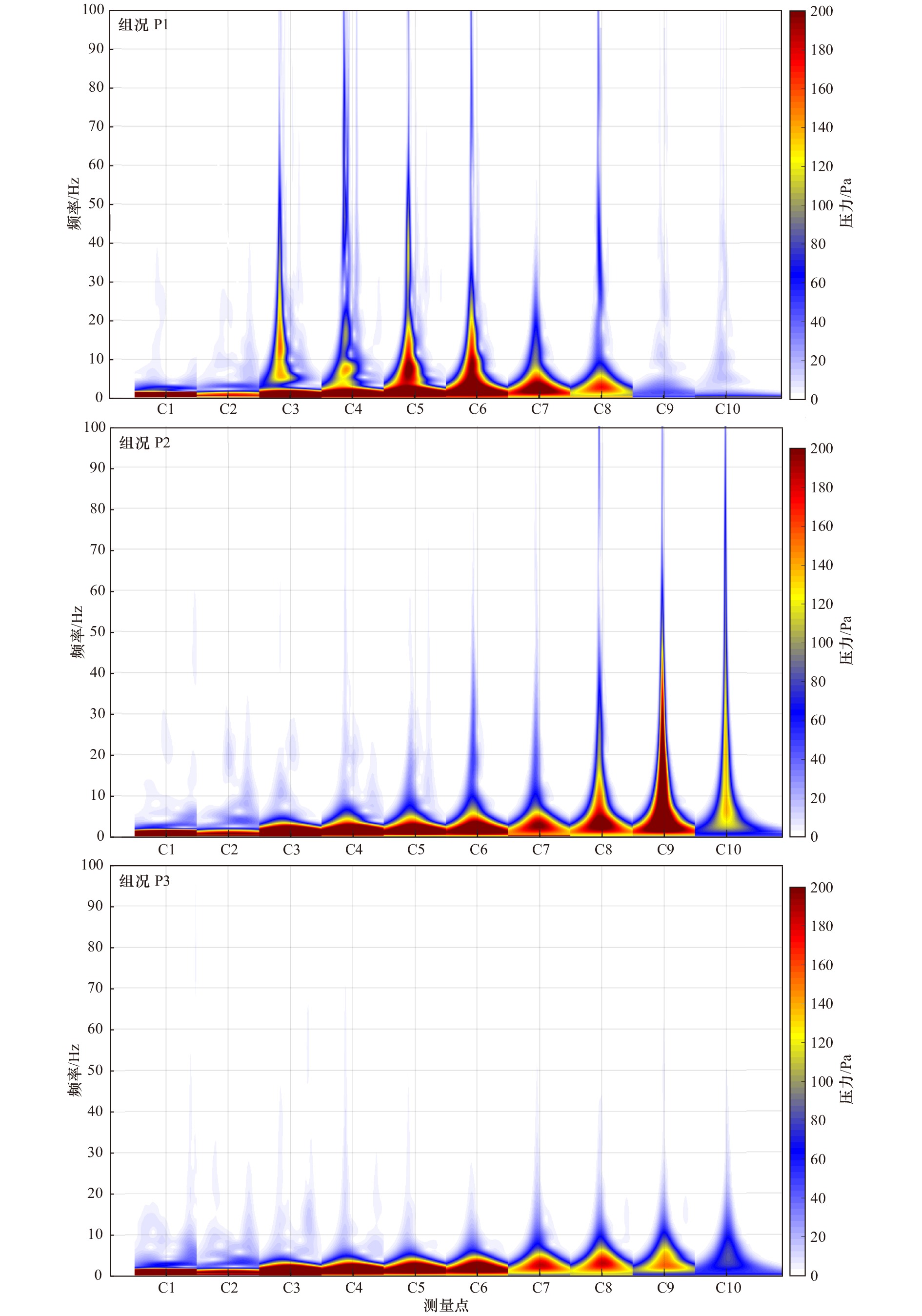
摘要: 波浪破碎是海洋中最常见的现象之一,其能够对海洋中的结构物产生巨大的波浪力作用。本文在大比尺波浪水槽通过聚焦波的方法生成了极端波浪和不同破碎阶段的破碎波浪,并对其冲击桩柱过程中的点压力进行了测量,进而采用连续小波变换的方法,对桩柱上点压力的分布及大小进行了细致分析。结果表明,多次重复试验下,相比非破碎极端波浪,破碎极端波浪产生的点压力离散性更强;波浪破碎程度越大,测点位置越靠近波峰,则点压力离散程度越大;破碎波的最大点压力出现在1.2倍的最大波面附近,且其大小可达3倍的最大静水压力;基于点压力小波谱,不同破碎阶段破碎波产生冲击作用不同,对于波浪作用桩柱前波浪已经发生破碎的情况,其冲击区域更大,点压力分布更复杂;而对于桩面破碎的情况,其造成的波浪总力更大。Abstract: Wave breaking is the most prominent feature of the ocean surface and it induces huge loads on structures. In this study, laboratory experiments in a large model scale are carried out to study wave forces on a vertical pile induced by breaking waves and non-breaking extreme waves, and to get insight the magnitude and the distribution of the wave forces, pressure transducers are installed in the face of the tested pile. The results show that in repeated experiments the wave pressures induced by the breaking waves present a wider variance compared with non-breaking waves; as the breaking density at the pile increases and the measuring point gets closer to wave crest, the variance of pressures increases; the maximum measured pressures can reach three times of the maximum hydrostatic pressure and occur at around 1.2 times of the maximum water surface. Based on the continuous wavelet spectrums of the wave pressures, different breaking phases show different characteristics: when the wave breaks far in front of the pile, its spectrum has a high frequency range with a wider vertical distribution, indicting more complicated pressures; when the wave breaks at the front of the pile, the wave force reaches a highest value.
-
Key words:
- large scale experiments /
- breaking waves /
- pile /
- wave force
-
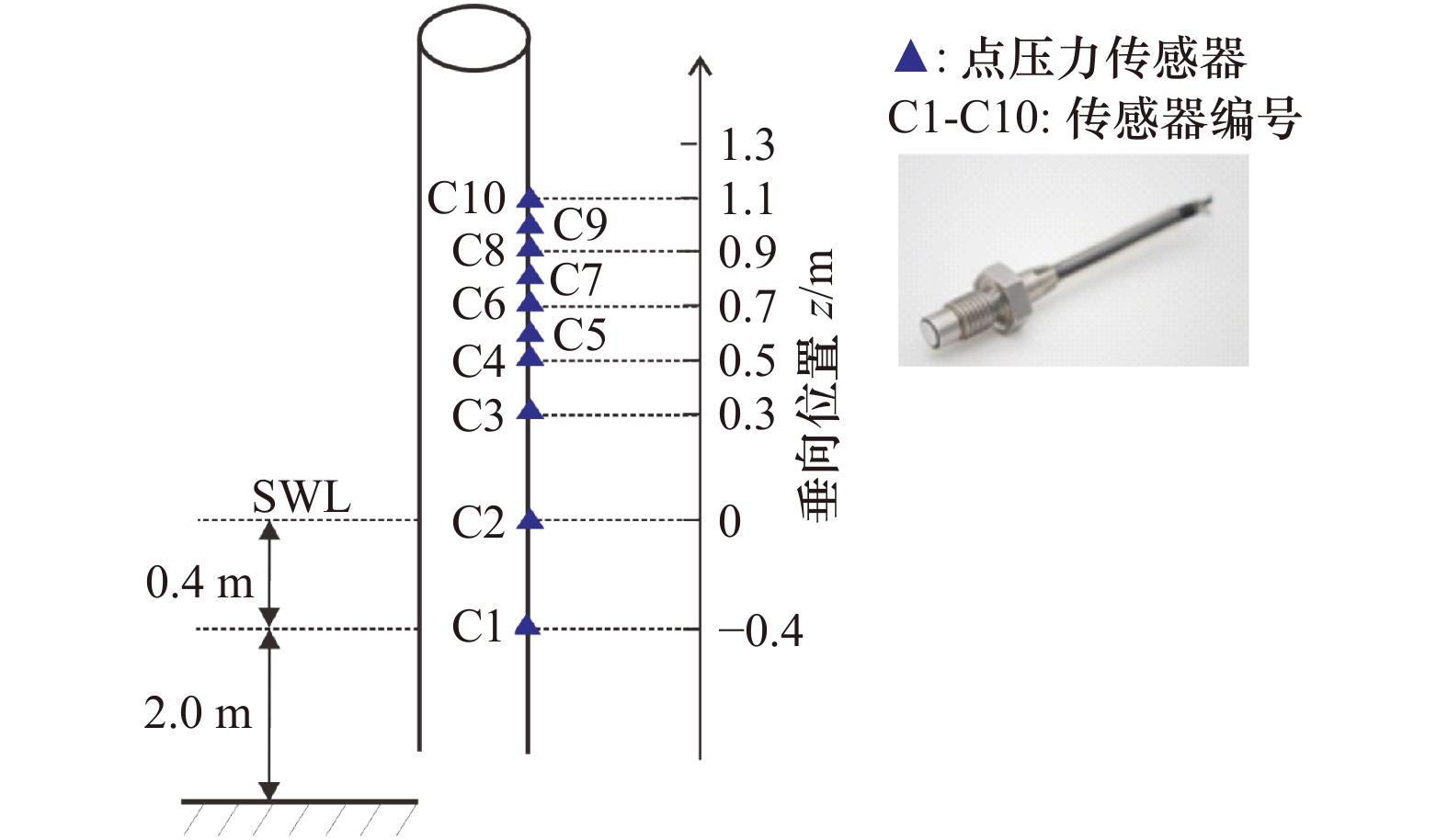
表 1 试验组况
Tab. 1 List of all the cases
组况名称 理论聚焦位置xf/m 线性聚焦波幅 A/m 是否破碎 波浪破碎相对桩柱位置 测量最大波面/m 平均值$ {\bar \eta _{\max }} $ 标准差 标准差/平均值 组况P1 242 1.15 破碎 桩柱前方破碎 0.778 0.046 5.9% 组况P2 243 1.15 破碎 桩柱面前破碎 0.871 0.038 4.4% 组况P3 246 1.15 破碎 桩柱后方破碎 0.850 0.020 2.3% 组况N1 246 1.10 未破碎 − 0.806 0.036 4.5% 组况N2 246 0.90 未破碎 − 0.677 0.016 2.4% 组况N3 246 0.70 未破碎 − 0.581 0.006 1.0% -
[1] 刘殿勇. 弱三维波浪破碎的实验研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2018.Liu Dianyong. Experimental investigation of weakly three-dimensional wave breaking[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2018. [2] Wienke J, Oumeraci H. Breaking wave impact force on a vertical and inclined slender pile-theoretical and large-scale model investigations[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2005, 52(5): 435−462. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2004.12.008 [3] 赫岩莉, 马玉祥, 马小舟, 等. 有限水深下独立波群的能量变化试验研究[J]. 海洋工程, 2019, 37(1): 56−63, 74.He Yanli, Ma Yuxiang, Ma Xiaozhou, et al. Experimental investigation on energy evolution of single wave group at finite water depth[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2019, 37(1): 56−63, 74. [4] Chan E S, Cheong H F, Tan B C. Laboratory study of plunging wave impacts on vertical cylinders[J]. Coastal Engineering, 1995, 25(1/2): 87−107. [5] Ma Yuxiang, Tai Bing, Dong Guohai, et al. Experimental study of plunging solitary waves impacting a vertical slender cylinder[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 202: 107197. [6] Tai Bing, Ma Yuxiang, Niu Xuyang, et al. Experimental investigation of impact forces induced by plunging breakers on a vertical cylinder[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 189: 106362. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106362 [7] Dias F, Ghidaglia J M. Slamming: Recent progress in the evaluation of impact pressures[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2018, 50(1): 243−273. doi: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-010816-060121 [8] Bredmose H, Bullock G N, Hogg A J. Violent breaking wave impacts. Part 3. Effects of scale and aeration[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2015, 765: 82−113. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2014.692 [9] 董玉山. LNG液舱晃荡冲击比尺效应的实验研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2015.Dong Yushan. Experimental investigation of scaling effects on sloshing impact in LNG tanks[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2015. [10] Bogaert H. An experimental investigation of sloshing impact physics in membrane LNG tanks on floating structures[D]. Delft: Delft University of Technology, 2018. [11] Hofland B, Kaminski M L, Wolters G. Large scale wave impacts on a vertical wall[J]. Coastal Engineering Proceedings, 2011, 1(32): 15. [12] Hildebrandt A. Hydrodynamics of breaking waves on offshore wind turbine structures[D]. Hannover: Leibniz Universität Hannover, 2013. [13] 陈松贵, 郑金海, 王泽明, 等. 珊瑚岛礁护岸对礁坪上极端波浪传播特性的影响[J]. 水利水运工程学报, 2019(6): 59−68. doi: 10.12170/201906007Chen Songgui, Zheng Jinhai, Wang Zeming, et al. Experimental study on impact of revetments on extreme wave propagation characteristics on coral reefs[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2019(6): 59−68. doi: 10.12170/201906007 [14] 耿宝磊, 郑宝友, 孟祥玮, 等. 天科院大比尺波浪水槽的建设与应用前景[J]. 水道港口, 2014, 35(4): 415−421. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2014.04.026Geng Baolei, Zheng Baoyou, Meng Xiangwei, et al. Construction and application prospect of the large scale wave flume in TIWTE[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2014, 35(4): 415−421. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2014.04.026 [15] Liu Dianyong, Ma Yuxiang, Dong Guohai, et al. An experimental study of weakly three-dimensional non-breaking and breaking waves[J]. European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids, 2015, 52: 206−216. doi: 10.1016/j.euromechflu.2015.03.007 [16] Paulsen B T, de Sonneville B, van der Meulen M, et al. Probability of wave slamming and the magnitude of slamming loads on offshore wind turbine foundations[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2019, 143: 76−95. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2018.10.002 [17] Ma Yuxiang, Dong Guohai, Perlin M, et al. Higher-harmonic focused-wave forces on a vertical cylinder[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2009, 36(8): 595−604. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2009.02.009 -





 下载:
下载: