Laboratory study on parameterization of ice floe melt rate at ice-air and ice-water interfaces
-
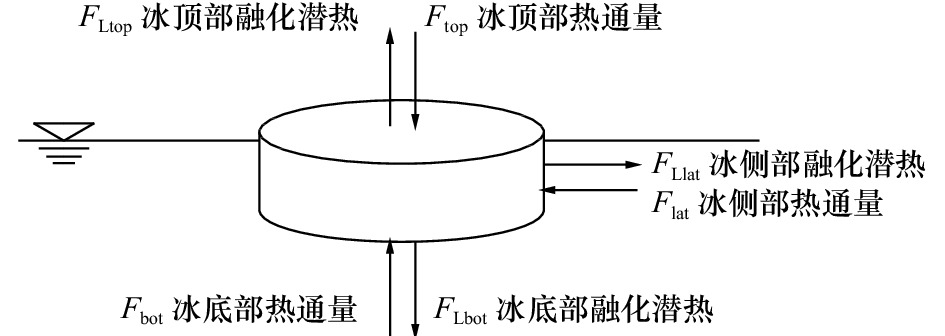
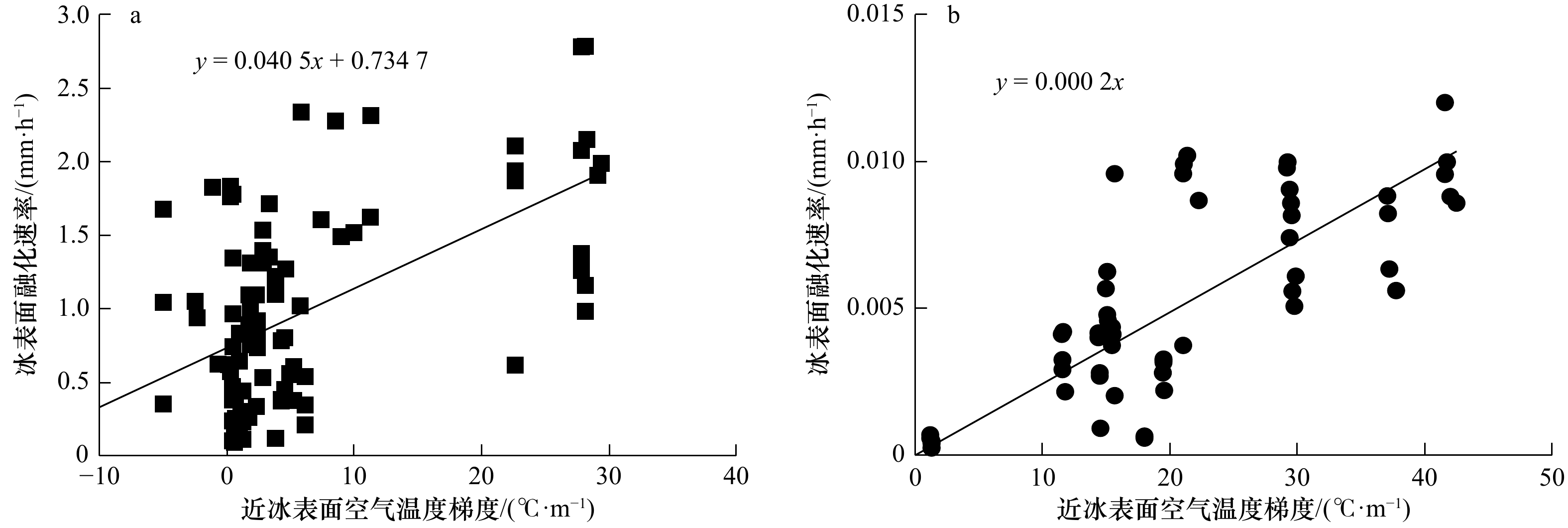
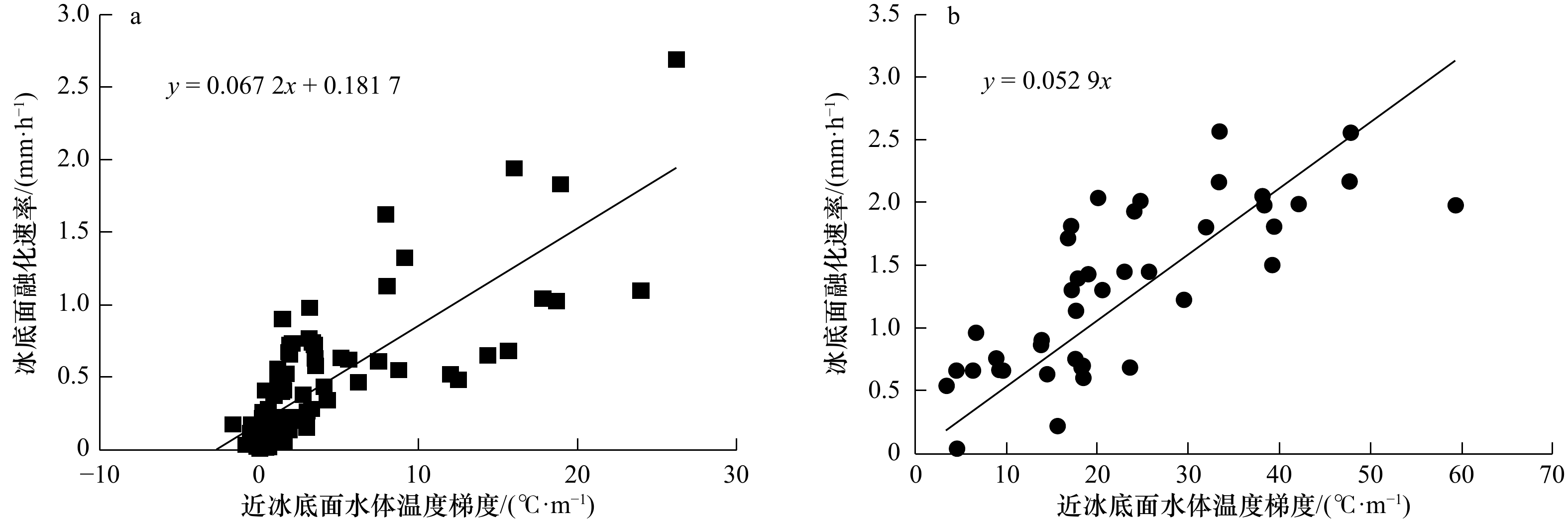
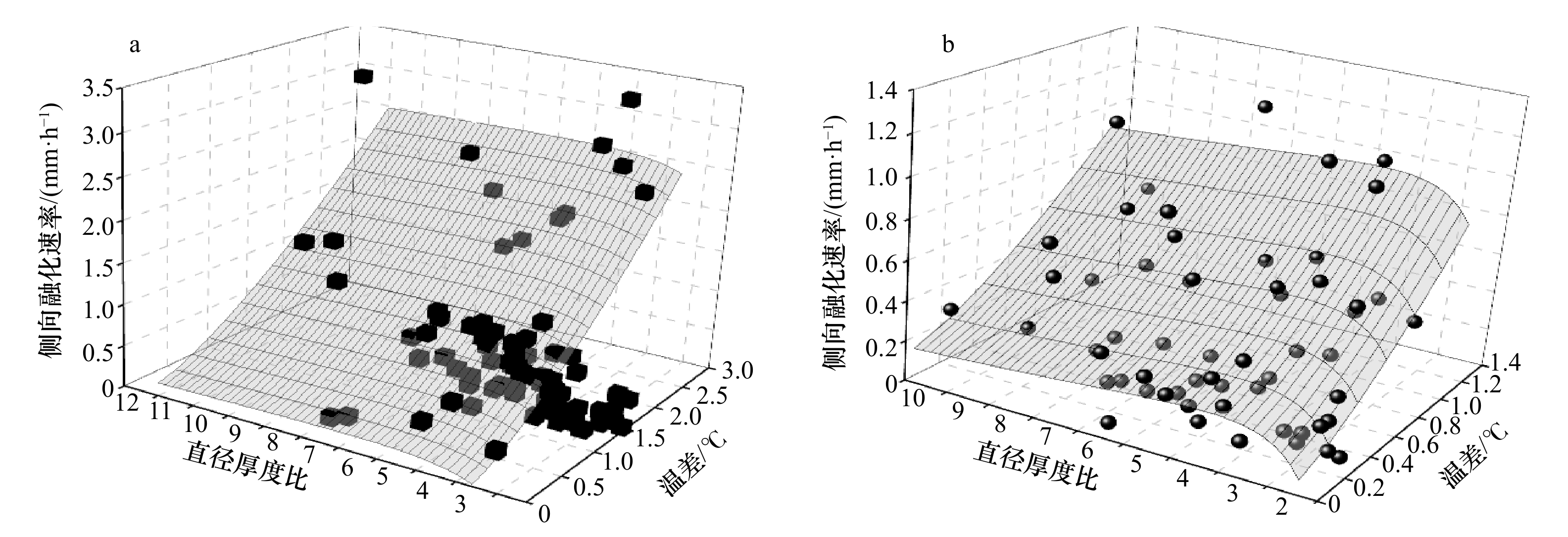
摘要: 融冰季节时天然浮冰表面、底面和侧向融化共存,三者融化速率是底面大于侧向,侧向大于表面。而且浮冰尺寸越小,侧向速率占比越高。为了解决将小尺度浮冰块尺度指标计入融化参数化方案,在低温环境实验室无辐射、无流速、控制气温和水温条件下对天然海冰和人工冻结淡水冰的圆盘试样,开展了不同初始水温和不同初始直径的圆盘试样融化过程实验,获得了圆盘试样直径、厚度和质量融化过程。依据这些实验数据,构建试样直径厚度比这一新指标,通过物理分析和数学统计手段,建立了海冰和淡水冰试样表面、底面融化速率同温度梯度,侧向融化速率和温差以及直径厚度比的关系式。这些关系式能够应用于天然直径100 m范围内浮冰的融化参数化方案,期望能解决北冰洋海冰和入海口近岸淡水冰夏季融化季节能量和质量平衡数值模拟的需求。Abstract: During the ice melting season, the surface, bottom and lateral melting of natural ice floes coexist, and the melting rate of the three is that the melting rate of the bottom is greater than the lateral, and the lateral is greater than the surface. And the smaller the ice floe size, the higher the proportion of lateral velocity. In order to solve the problem of including the small-scale ice floe scale indicators into the melting parameterization plan, in the low-temperature environment laboratory without radiation, no flow rate, controlled air temperature and water temperature, the disk samples of natural sea ice and artificially frozen fresh water ice were carried out. Experiments on the melting process of disc samples with different initial water temperatures and different initial diameters were carried out. Obtain the disc sample diameter, thickness and mass melting process. Based on these experimental data, a new indicator of sample diameter-to-thickness ratio was constructed. Through physical analysis and mathematical statistics, the melting rate of the surface and bottom surface of the sea ice and freshwater ice sample was established with the temperature gradient, the lateral melting rate, temperature difference, and diameter. The relationship between the thickness ratio. These relationships can be applied to the melting parameterization scheme of floating ice within a natural diameter range of 100 m. It is expected to solve the demand for numerical simulation of the energy and mass balance of the summer melting season of Arctic sea ice and coastal freshwater ice at the sea estuary.
-
Key words:
- Arctic sea ice /
- lateral melting /
- parameterization /
- laboratory study
-
表 1 各试样实验前初始尺寸参数
Tab. 1 Preliminary parameters of ice specimens
参数 海冰 淡水冰 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 设计初始水温/ ℃ –0.5 –0.5 –0.5 –0.5 –0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 初始平均直径/mm 68.94 92.95 124.51 154.45 185.85 68.16 90.91 119.96 154.84 191.90 初始厚度/mm 32.59 34.48 35.95 35.54 34.47 30.85 30.66 30.73 30.22 30.87 设计初始水温/ ℃ 0 0 0 0 0 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 初始平均直径/mm 69.41 88.61 122.77 154.15 191.62 67.86 89.43 119.08 153.19 192.50 初始厚度/mm 36.64 36.67 35.69 31.69 36.77 31.00 31.19 30.30 29.60 31.23 设计初始水温/ ℃ 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 初始平均直径/mm 68.77 97.42 122.98 154.53 194.45 67.45 90.42 118.91 153.01 191.00 初始厚度/mm 31.92 41.90 36.03 36.11 39.48 30.91 30.40 30.59 30.57 31.47 设计初始水温/ ℃ 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 初始平均直径/mm 69.64 88.08 124.36 152.82 193.82 67.61 89.52 120.03 153.19 191.03 初始厚度/mm 38.82 37.27 35.66 40.46 38.05 30.89 30.21 30.46 30.90 30.57 设计初始水温/ ℃ 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 初始平均直径/mm 66.95 94.93 126.87 155.86 193.29 初始厚度/mm 28.78 32.86 35.29 32.54 34.07 -
[1] 柯长青, 王蔓蔓. 基于CryoSat-2数据的2010−2017年北极海冰厚度和体积的季节与年际变化特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(11): 1−13.Ke Changqing, Wang Manman. Seasonal and interannual variation of thinkness and volume of the Arctic sea ice based on CryoSat-2 during 2010−2017[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(11): 1−13. [2] 王蔓蔓, 柯长青, 邵珠德. 基于CryoSat-2卫星测高数据的北极海冰体积估算方法[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(3): 135−144.Wang Manman, Ke Changqing, Shao Zhude. Arctic sea ice volume estimation method based on CryoSat-2 satellite altimeter data[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(3): 135−144. [3] Kwok R, Spreen G, Pang S. Arctic sea ice circulation and drift speed: Decadal trends and ocean currents[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2013, 118(5): 2408−2425. doi: 10.1002/jgrc.20191 [4] Li Zhijun, Li Runling, Wang Zipan, et al. Upper limits for chlorophyll a changes with brine volume in sea ice during the austral spring in the Weddell Sea, Antarctica[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2016, 35(2): 68−75. doi: 10.1007/s13131-015-0740-6 [5] Screen J A, Simmonds I. The central role of diminishing sea ice in recent Arctic temperature amplification[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7293): 1334−1337. doi: 10.1038/nature09051 [6] Mager D. Climate change, conflicts and cooperation in the Arctic: Easier access to hydrocarbons and mineral resources?[J]. The International Journal of Marine and Coastal Law, 2009, 24(2): 347−354. doi: 10.1163/157180809X421798 [7] 王松, 苏洁, 储敏, 等. BCC_CSM对北极海冰的模拟: CMIP5和CMIP6历史试验比较[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(5): 49−64.Wang Song, Su Jie, Chu Min, et al. Comparison of simulation results of the Arctic sea ice by BCC_CSM: CMIP5 and CMIP6 historical experiments[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(5): 49−64. [8] Wang Qingkai, Lu Peng, Leppäranta M, et al. Physical properties of summer sea ice in the Pacific Sector of the Arctic during 2008−2018[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2020, 125(9): e2020JC016371. [9] Lu Peng, Li Zhijun. A method of obtaining ice concentration and floe size from shipboard oblique sea ice images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(7): 2771−2780. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2042962 [10] Huang Wenfeng, Lu Peng, Lei Ruibo, et al. Melt pond distribution and geometry in high Arctic sea ice derived from aerial investigations[J]. Annals of Glaciology, 2016, 57(73): 105−118. doi: 10.1017/aog.2016.30 [11] Hall R T, Rothrock D A. Photogrammetric observations of the lateral melt of sea ice floes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1987, 92(C7): 7045−7048. doi: 10.1029/JC092iC07p07045 [12] Perovich D K, Grenfell T C, Richter-Menge J A, et al. Thin and thinner: Sea ice mass balance measurements during SHEBA[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2003, 108(C3): 8050. [13] 雷瑞波, 李志军, 程斌, 等. 夏季北冰洋浮冰−水道热力学特征现场观测研究[J]. 极地研究, 2010, 22(3): 286−295.Lei Ruibo, Li Zhijun, Cheng Bin, et al. Observations on the thermodynamics mechanism of the floe-lead system in the Arctic Ocean during summer[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2010, 22(3): 286−295. [14] 王庆凯, 李志军, 曹晓卫, 等. 实测冰−水侧向界面热力学融化速率[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2016, 14(6): 81−86.Wang Qingkai, Li Zhijun, Cao Xiaowei, et al. Analysis of measured thermodynamic melting rate of lateral interface between ice and water[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2016, 14(6): 81−86. [15] 王庆凯, 方贺, 李志军, 等. 湖冰侧、底部融化现场观测与热力学分析[J]. 水利学报, 2018, 49(10): 1207−1215.Wang Qingkai, Fang He, Li Zhijun, et al. Field investigations on lateral and bottom melting of lake ice and thermodynamic analysis[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2018, 49(10): 1207−1215. [16] 艾润冰, 谢涛, 刘彬贤, 等. 基于气温的浮冰侧向融化速率参数化方案实验研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(5): 150−158.Ai Runbing, Xie Tao, Liu Binxian, et al. An experimental study on parametric scheme of lateral melting rate of ice layer based on temperature[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(5): 150−158. [17] Tsamados M, Feltham D, Petty A, et al. Processes controlling surface, bottom and lateral melt of Arctic sea ice in a state of the art sea ice model[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2015, 373(2052): 20140167. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2014.0167 [18] 刘骥平, 雷瑞波, 宋米荣, 等. 适应极地快速变化海冰模式的研发与挑战[J]. 大气科学学报, 2021, 44(1): 12−25.Liu Jiping, Lei Ruibo, Song Mirong, et al. Development and challenge of sea ice model adapting to rapid polar sea ice changes[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2021, 44(1): 12−25. [19] Zhao Jinping, Gao Guoping, Jiao Yutian. Warming in Arctic intermediate and deep waters around Chukchi Plateau and its adjacent regions in 1999[J]. Science in China Series D (Earth Sciences), 2005, 48(8): 1312−1320. doi: 10.1360/02yd0504 [20] Parkinson C L, Washington W M. A large-scale numerical model of sea ice[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1979, 84(C1): 311−337. doi: 10.1029/JC084iC01p00311 [21] Perovich D K. On the summer decay of a sea ice cover[D]. Seattle: University of Washington, 1983. [22] Maykut G A, Perovich D K. The role of shortwave radiation in the summer decay of a sea ice cover[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1987, 92(C7): 7032−7044. doi: 10.1029/JC092iC07p07032 [23] Steele M. Sea ice melting and floe geometry in a simple ice-ocean model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1992, 97(C11): 17729−17738. doi: 10.1029/92JC01755 [24] 陈晓东, 王安良, Knut H, 等. 海冰盐度影响下冰水热力过程的试验研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2019, 38(1): 38−46.Chen Xiaodong, Wang Anliang, Knut H, et al. Study of the influence of sea ice salinity on the thermodynamics[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2019, 38(1): 38−46. [25] Li Zhijun, Wang Xin, Li Qingshan, et al. Study on nitrobenzene ratio in water-ice system under different conditions[J]. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 2008, 51(11): 2013−2020. doi: 10.1007/s11431-008-0136-3 [26] 赵进平, 史久新, 金明明, 等. 楚科奇海融冰过程中的海水结构研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 2010, 25(2): 154−162.Zhao Jinping, Shi Jiuxin, Jin Mingming, et al. Water mass structure of the Chukchi Sea during ice melting period in the Summer of 1999[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2010, 25(2): 154−162. [27] Overduin P P, Kane D L, Van Loon W K P. Measuring thermal conductivity in freezing and thawing soil using the soil temperature response to heating[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2006, 45(1): 8−22. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2005.12.003 [28] 秦恺, 张瑜, 高郭平, 等. 北冰洋入海径流变化状况及其与近岸海冰关系[J]. 极地研究, 2019, 31(4): 371−382.Qin Kai, Zhang Yu, Gao Guoping, et al. Variation of Arctic Ocean runoff and its correlation with coastal sea ice[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2019, 31(4): 371−382. -




 下载:
下载: