Comparative study on the liquefaction properties of seabed silt under wave loading in the Huanghe River Delta
-
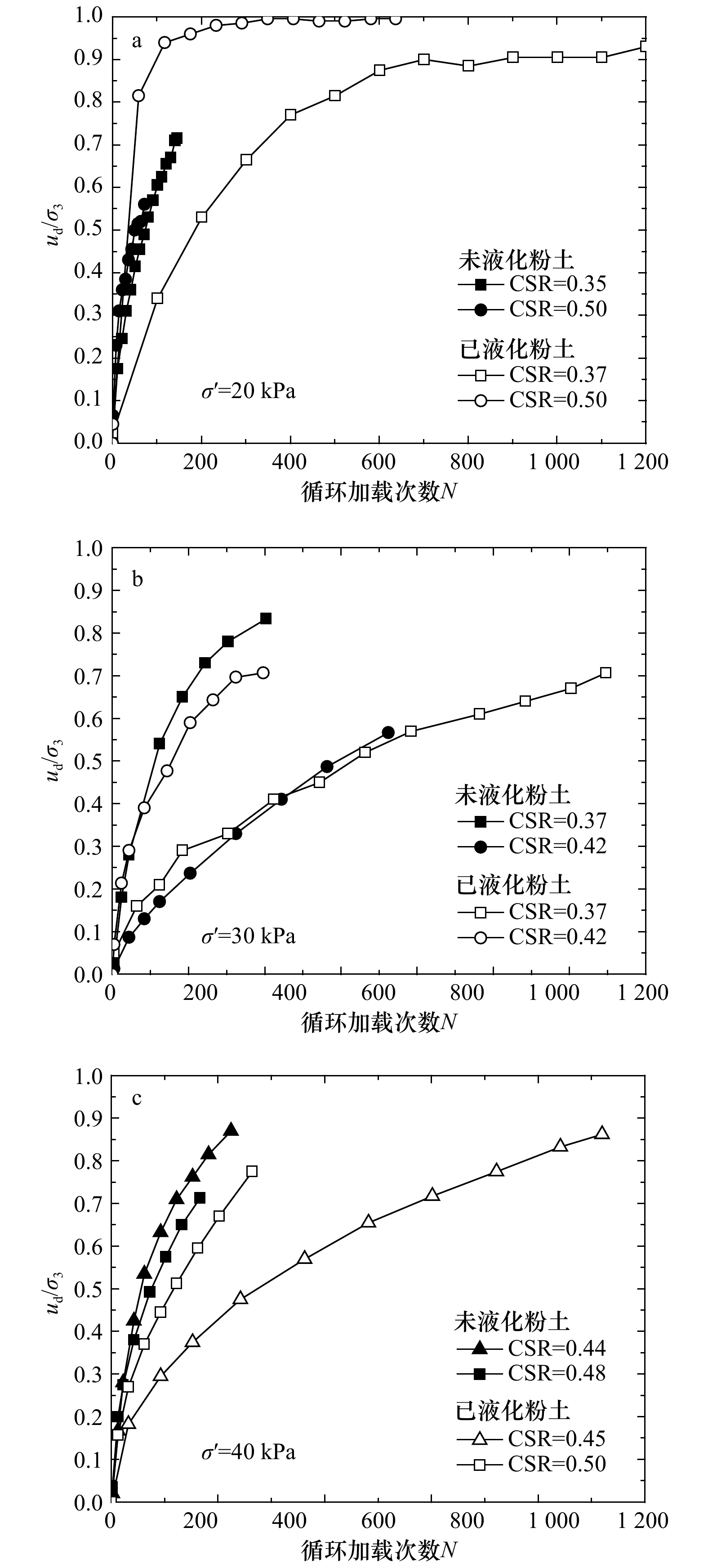
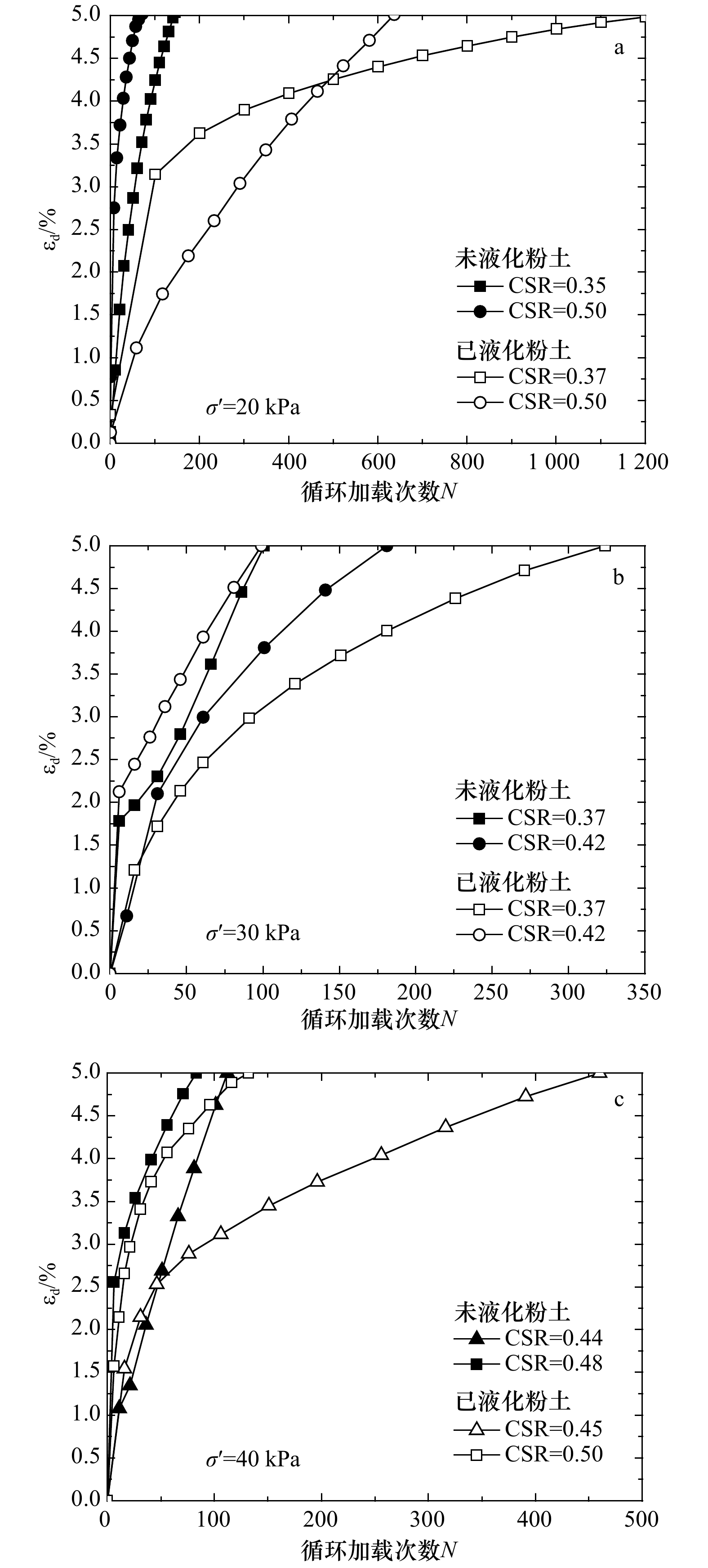
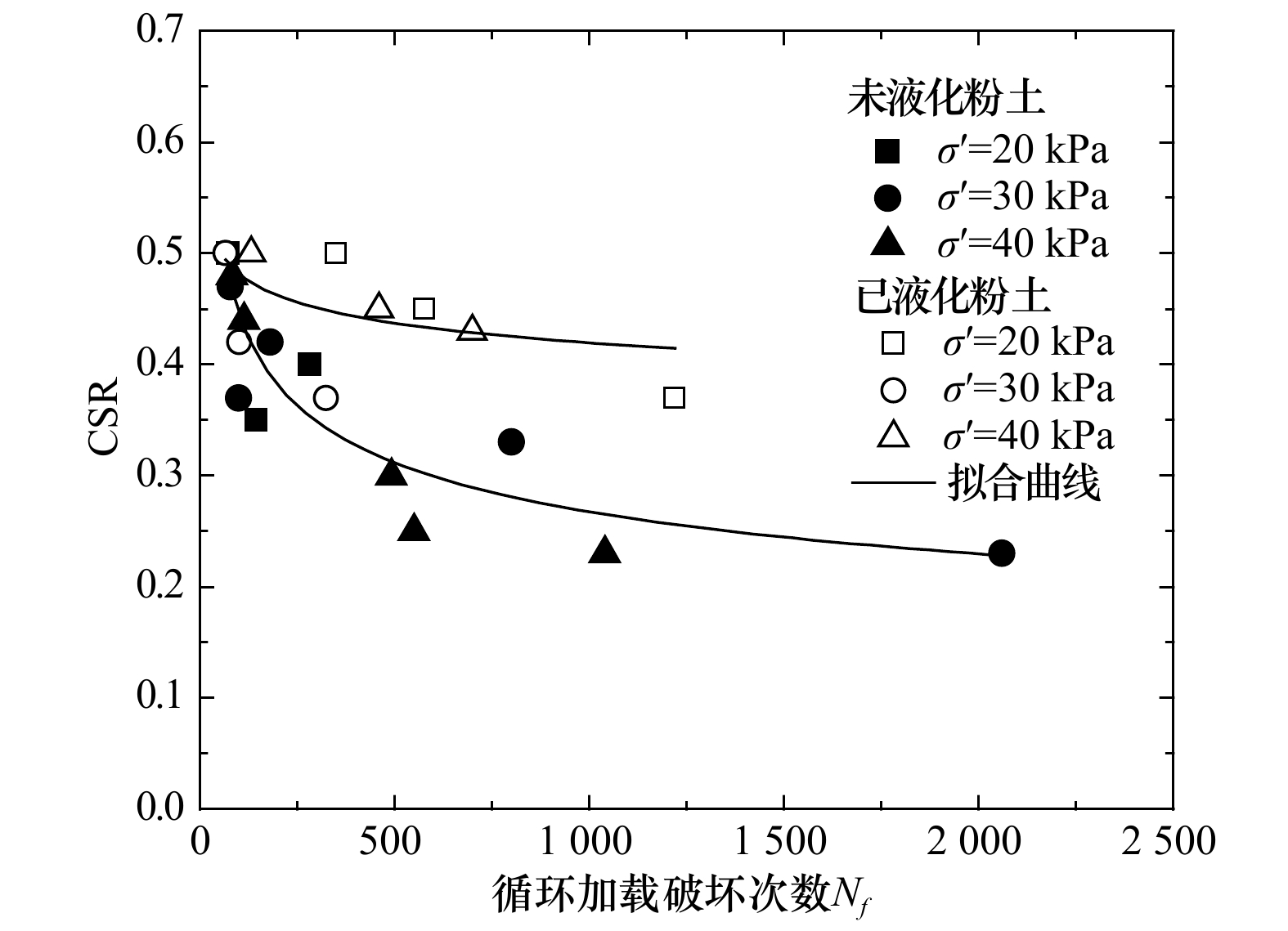
摘要: 作为一种常见的近海海底灾害地质现象,波致海床液化严重威胁着黄河三角洲地区海底工程设施的安全。粉质海床液化后,海底粉土的结构、物理和力学性质均发生了改变,研究该变化规律尤其是评估液化后海底粉土再次发生液化的可能性具有重要的理论意义和应用价值。本文利用室内动三轴仪对取自黄河三角洲已液化和未液化海底粉土开展了液化试验对比研究,讨论了已液化和未液化海底粉土在孔压增长模式和轴向动应变发展趋势方面的异同,对比分析了二者的液化势。研究结果表明:应变标准比孔压标准更适用于评估黄河三角洲地区海底粉土的液化势;孔压和动应变发展模式均表明与未液化粉土相比,已液化海底粉土再次发生液化的抗力有所提高;已液化和未液化海底粉土归一化孔压比ud/σ3与循环加载次数比N/Nf间相关关系可采用双曲线或指数函数模型进行定量化描述;未液化海底粉土的波致液化临界循环应力比约为0.20,已液化海底粉土的临界循环应力比约为0.35。研究成果有助于加深对海底粉土波致液化特性的认识,亦可为循环应力历史影响下的土体力学性质研究提供参考。Abstract: As a common submarine geological disaster, wave-induced seabed liquefaction seriously threatens the safety of subsea engineering facilities in the Huanghe River Delta. The structure, physical and mechanical properties of seabed soil after wave-induced liquefaction all have changed, so it has important theoretical significance and practical value to study on the evaluation of potential possibility of re-liquefaction of seabed soil after previous liquefaction. In this paper, a series of cyclic triaxial liquefaction tests were conducted on core samples collected from submarine non-liquefied and liquefied zone in the Huanghe River Delta, respectively. The differences between non-liquefied and liquefied seabed soil in the developing trends of pore pressure and axial dynamic strain with cycles were analyzed and discussed, and the corresponding liquefaction potentials were also comparatively evaluated. The test results show that compared to pore pressure, the strain standard is more suitable to evaluate the liquefaction potential of the seabed silt in the Huanghe River Delta. The pore pressure and dynamic axial strain development characteristics indicate that the re-liquefaction resistance of the liquefied seabed silt is improved to some extent compared with the non-liquefied silt. Furthermore, the correlations between the normalized pore pressure ratio ud/σ3 and the normalized cycle ratio N/Nf could be described quantitatively by the hyperbolic or exponential functions for liquefied and non-liquefied seabed silts. Finally, the critical cyclic stress ratio for the non-liquefied seabed silt is around 0.20 compared to 0.35 for the liquefied one in the Huanghe River Delta. The research findings will contribute to deepening the understanding of the wave-induced liquefaction mechanism of seabed silt, and also provide an example reference for the study of the mechanical properties of soil subjected to previous cyclic stress history.
-
Key words:
- Huanghe River Delta /
- seabed silt /
- re-liquefaction /
- cyclic triaxial test
-
表 1 海底粉土基本物理性质指标
Tab. 1 Physical properties of seabed silt
分类 海床以下深度/m 含水量/% 干密度/(g·cm−3) 比重 孔隙比 塑限/% 液限/% 塑性指数 未液化粉土 0.5 23.3 1.62 2.71 0.70 18.7 26.8 8.1 1.0 23.4 1.62 2.70 0.69 19.1 27.0 7.9 1.5 23.0 1.63 2.71 0.69 17.6 26.8 9.2 2.5 26.7 1.58 2.70 0.71 21.3 28.5 7.2 3.0 25.9 1.59 2.71 0.71 21.9 30.5 8.6 3.5 25.3 1.60 2.70 0.69 21.7 29.9 8.2 4.3 27.9 1.57 2.70 0.72 22.6 31.6 9.0 4.7 25.6 1.59 2.70 0.69 21.6 29.7 8.1 已液化粉土 0.5 24.5 1.61 2.70 0.70 20.6 27.6 7.0 1.0 24.2 1.61 2.70 0.70 20.6 26.3 5.7 1.5 24.9 1.61 2.70 0.69 18.6 26.1 7.5 2.5 23.4 1.62 2.70 0.66 20.6 28.1 7.5 3.0 23.9 1.62 2.70 0.67 20.6 27.9 7.3 3.5 23.6 1.62 2.71 0.67 19.7 27.7 8.0 4.3 21.9 1.64 2.70 0.64 15.9 25.2 9.3 4.7 22.1 1.64 2.71 0.65 16.7 24.5 7.8 表 2 循环应力加载方案
Tab. 2 Cyclic dynamic stress loading program
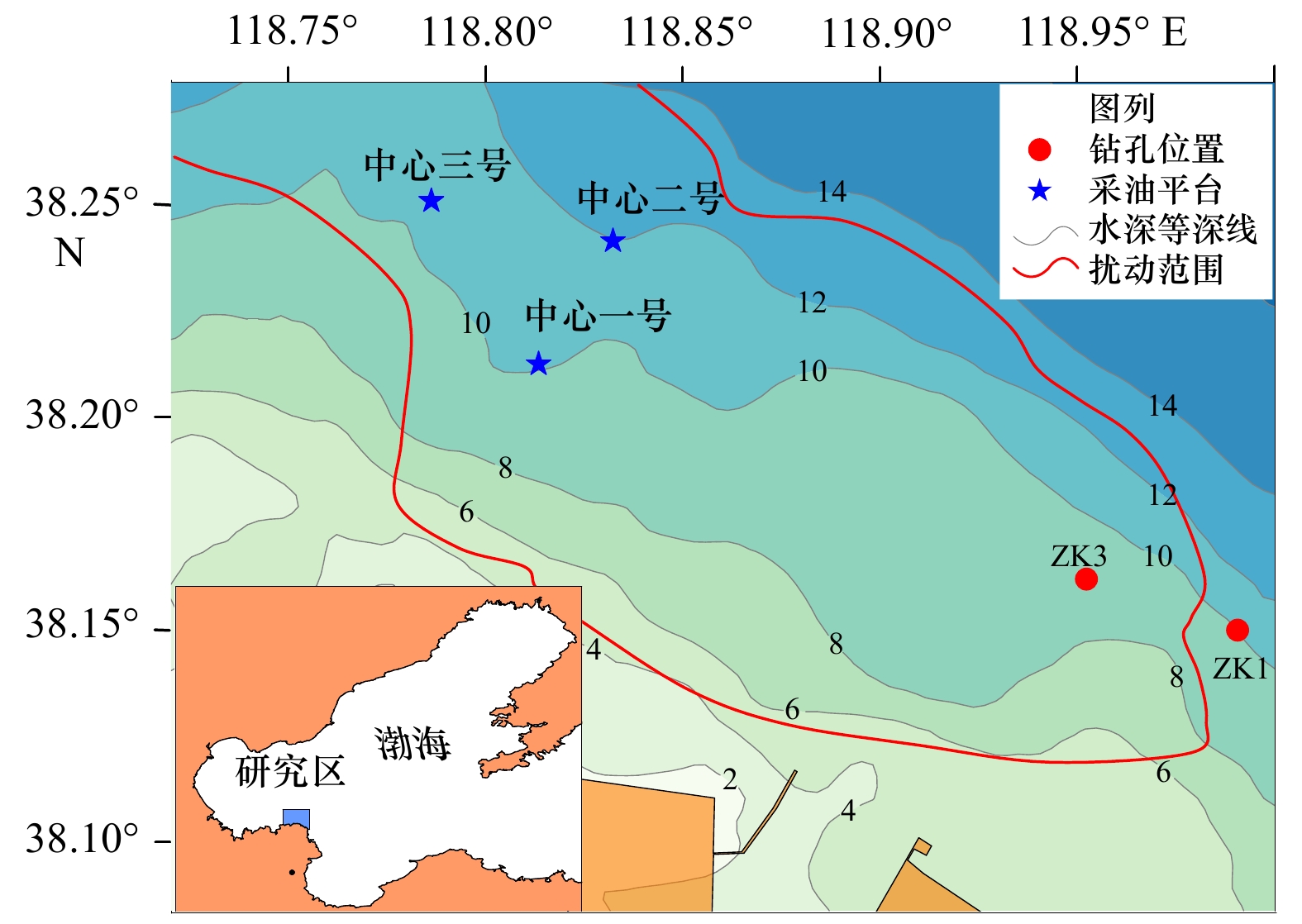
分类 钻孔编号 海床以下深度/m 固结围压/kPa 循环应力比 初始模拟波浪状态 波高/m 波长/m 水深/m 未液化粉土 ZK1 0.75~1.60 20 0.35, 0.40, 0.50 6.0 60.0 10.0 2.55~3.60 30 0.23, 0.33, 0.37, 0.42, 0.47 4.7 60.0 10.0 3.75~4.70 40 0.23, 0.25, 0.30, 0.44, 0.48 5.2 60.0 10.0 已液化粉土 ZK3 0.95~1.85 20 0.37, 0.45, 0.50 6.4 60.0 10.0 2.48~3.50 30 0.37, 0.42, 0.50 7.5 60.0 10.0 3.70~4.70 40 0.43, 0.45, 0.50 9.0 60.0 10.0 表 3 孔压发展双曲线模型拟合参数
Tab. 3 Coefficients of hyperbolic model for pore pressure development
分类 围压/kPa 模型 CSR 参数a 参数b 相关系数R2 未液化粉土 20 双曲线 0.35 0.512 0.918 0.99 0.40 0.818 0.761 0.99 0.50 0.375 1.494 0.98 30 双曲线 0.23 0.041 1.025 0.99 0.33 0.042 0.971 0.99 0.37 0.297 0.890 0.99 0.42 0.951 0.845 0.99 0.47 0.662 0.567 0.99 40 双曲线 0.23 0.133 0.973 0.99 0.25 0.154 0.955 0.99 0.30 0.394 1.149 0.99 0.44 0.275 0.890 0.99 0.48 0.365 1.090 0.99 已液化粉土 20 双曲线 0.37 0.146 0.906 0.99 0.45 0.128 1.072 0.99 0.50 0.022 0.969 0.99 30 双曲线 0.37 0.410 1.072 0.98 0.42 0.277 1.148 0.99 0.50 0.519 0.712 0.99 40 双曲线 0.43 0.577 0.427 0.99 0.45 0.292 0.913 0.99 0.50 0.410 0.952 0.98 -
[1] Milliman J D, Meade R H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1983, 91(1): 1−21. doi: 10.1086/628741 [2] 冯秀丽, 沈渭铨, 杨荣民, 等. 现代黄河口区沉积环境与沉积物工程性质的关系[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 1994(S1): 21−28.Feng Xiuli, Shen Weiquan, Yang Rongmin, et al. Relation between the geotechnical character of sediment and the sedimentary environment of the modern Huanghe Estuary area[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 1994(S1): 21−28. [3] 冯秀丽, 林霖, 庄振业, 等. 现代黄河水下三角洲全新世以来土层岩土工程参数与沉积环境之间的关系[J]. 海岸工程, 1999, 18(4): 1−7.Feng Xiuli, Lin Lin, Zhuang Zhenye, et al. The relationship between geotechnical parameters and sedimentary environment of soil layers since Holocene in modern Huanghe subaqueous delta[J]. Coastal Engineering, 1999, 18(4): 1−7. [4] 常方强, 贾永刚. 黄河口粉质土海床液化过程的现场试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2012, 45(1): 121−126.Chang Fangqiang, Jia Yonggang. In-situ test to study silt liquefaction at the subaqueous delta of Yellow River[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2012, 45(1): 121−126. [5] 刘晓磊, 贾永刚, 郑杰文. 波浪导致黄河口海床沉积物超孔压响应现场试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(11): 3055−3062.Liu Xiaolei, Jia Yonggang, Zheng Jiewen. In situ experiment of wave-induced excess pore pressure in the seabed sediment in Yellow River Estuary[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(11): 3055−3062. [6] Prior D B, Yang Z S, Bornhold B D, et al. Active slope failure, sediment collapse, and silt flows on the modern subaqueous Huanghe (Yellow River) delta[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1986, 6(2): 85−95. doi: 10.1007/BF02281644 [7] 冯秀丽, 戚洪帅, 王腾, 等. 黄河三角洲埕岛海域地貌演化及其地质灾害分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2004, 25(S1): 17−20.Feng Xiuli, Qi Hongshuai, Wang Teng, et al. Geomorphological evolution and geological disasters analysis in Chengdao sea area of the Yellow River Delta[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2004, 25(S1): 17−20. [8] 许国辉, 孙永福, 于月倩, 等. 黄河水下三角洲浅表土体的风暴液化问题[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(2): 37−42.Xu Guohui, Sun Yongfu, Yü Yueqian, et al. Storm-induced liquefaction of the surficial sediments in the Yellow River subaqueous delta[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(2): 37−42. [9] Wang Hu, Liu Hongjun. Evaluation of storm wave-induced silty seabed instability and geo-hazards: a case study in the Yellow River delta[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2016, 58: 135−145. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2016.03.013 [10] 马彬彬. 暴风浪作用下海底粉土液化研究[D]. 青岛: 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所, 2015.Ma Binbin. Liquefaction of seabed silt under storm waves[D]. Qingdao: The First Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, 2015. [11] 孙永福, 董立峰, 宋玉鹏. 黄河水下三角洲粉质土扰动土层特征及成因探析[J]. 岩土力学, 2008, 29(6): 1494−1499.Sun Yongfu, Dong Lifeng, Song Yupeng. Analysis of characteristics and formation of disturbed soil on subaqueous delta of Yellow River[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(6): 1494−1499. [12] 宋玉鹏, 孙永福, 杜星, 等. 黄河水下三角洲液化与未液化粉土的工程地质性质对比研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2019, 37(1): 55−64.Song Yupeng, Sun Yongfu, Du Xing, et al. Comparative study on the difference of engineering geological characteristics between liquefied silt and non-liquefied silt in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2019, 37(1): 55−64. [13] 许国辉, 卫聪聪, 孙永福, 等. 黄河水下三角洲浅表局部扰动地层工程特性与成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(6): 19−25.Xu Guohui, Wei Congcong, Sun Yongfu, et al. The engineering characteristics of shallow disturbed strata and analysis of their formation on the subaqueous Yellow River Delta[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(6): 19−25. [14] 王虎. 波浪作用下黄河三角洲海床失稳机制与评价方法[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015.Wang Hu. Mechanism and quantitative evaluation of wave-induced seabed instability in the Yellow River delta[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2015. [15] 王欣, 许国辉, 孙永福, 等. 黄河水下三角洲液化海底的重新层化及其试验求证[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(6): 29−40.Wang Xin, Xu Guohui, Sun Yongfu, et al. Storm-waves-induced seabed sediment liquefaction and Re-stratification on the Yellow River subaqueous delta[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(6): 29−40. [16] 张丽萍, 贾永刚, 侯伟, 等. 液化过程对海床土性质改造的波浪水槽试验[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(3): 171−180.Zhang Liping, Jia Yonggang, Hou Wei, et al. Wave flume experiment on seabed reconstruction by liquefaction[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(3): 171−180. [17] 刘晓磊, 贾永刚, 郑杰文. 现代黄河三角洲沉积物波浪动力响应研究评述[J]. 工程地质学报, 2015, 23(S1): 313−319.Liu Xiaolei, Jia Yonggang, Zheng Jiewen. A review of sediment dynamic responses to waves in the modern Yellow River delta[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2015, 23(S1): 313−319. [18] 郭莹, 王琦. 落锥法确定粉土液限和塑限的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(9): 2569−2574.Guo Ying, Wang Qi. Experimental research on fall cone test to determine liquid limit and plastic limit of silts[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(9): 2569−2574. [19] 王刚, 许国辉, 刘志钦, 等. 波致粉质土液化过程中物理力学性态变化试验研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(1): 176−183.Wang Gang, Xu Guohui, Liu Zhiqin, et al. Experimental study on the physical and mechanical characteristics changes of wave-induced liquefied silt[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(1): 176−183. [20] 常方强, 贾永刚. 波浪作用下埕岛海域粉质土海床的累积液化[J]. 华侨大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 34(4): 434−438.Chang Fangqiang, Jia Yonggang. Residual liquefaction of silt seabed induced by wave at the Chengdao sea area[J]. Journal of Huaqiao University (Natural Science), 2013, 34(4): 434−438. [21] 唐亮, 凌贤长, 徐鹏举, 等. 土体液化动力分析数值模型[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2010, 42(4): 521−524.Tang Liang, Ling Xianzhang, Xu Pengju, et al. Numerical model for dynamic analysis of soil liquefaction[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010, 42(4): 521−524. [22] 李飒, 孙兴松, 要明伦. 混黏土的粉土、粉砂室内试验液化判别标准的研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2006, 27(3): 360−364.Li Sa, Sun Xingsong, Yao Minglun. Study of liquefaction evaluation used in indoor test of silt, silty sand mixed clay[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(3): 360−364. [23] Seed H B. Soil liquefaction and cyclic mobility evaluation for level ground during earthquakes[J]. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division, 1979, 105(2): 201−255. doi: 10.1061/AJGEB6.0000768 [24] 谢定义. 土动力学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2011.Xie Dingyi. Soil Dynamics[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2011. [25] 于濂洪, 王波. 饱和粉土振动孔隙水压力的试验研究[J]. 大连大学学报, 1999, 20(4): 59−62.Yu Lianhong, Wang Bo. Study on pore water pressure of saturated and disturbed sandy loam during cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Dalian University, 1999, 20(4): 59−62. [26] 曾长女, 刘汉龙, 丰土根, 等. 饱和粉土孔隙水压力性状试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2005, 26(12): 1963−1966.Zeng Changnü, Liu Hanlong, Feng Tugen, et al. Test study on pore water pressure mode of saturated silt[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2005, 26(12): 1963−1966. [27] 曾长女, 刘汉龙, 陈育民. 细粒含量对粉土动孔压发展模式影响的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2008, 29(8): 2193−2198.Zeng Changnü, Liu Hanlong, Chen Yumin. Test study on influence of fine particle content on dynamic pore water pressure development mode of silt[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(8): 2193−2198. [28] 郑刚, 霍海峰, 雷华阳, 等. 振动频率对饱和黏土动力特性的影响[J]. 天津大学学报, 2013, 46(1): 38−43.Zheng Gang, Huo Haifeng, Lei Huayang, et al. Contrastive study on the dynamic characteristics of saturated clay in different vibration frequencies[J]. Journal of Tianjin University, 2013, 46(1): 38−43. [29] 王树英, 阳军生, Luna R. 前期动载对低塑性粉土静态和动态强度的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(2): 363−368.Wang Shuying, Yang Junsheng, Luna R. Effect of previous dynamic loading on static and dynamic strengths of low-plasticity silt[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(2): 363−368. -




 下载:
下载: