Centennial scale environmental changes in the elemental geochemistry of tidal flat sediments in the northern Jiangsu radial sand ridges
-
摘要: 苏北辐射沙洲是分布于江苏岸外的典型沉积堆积体,受长江、黄河泥沙供给和近岸潮流动力的共同影响,发育了典型的粉砂淤泥质潮滩,沉积物元素可以记录潮滩环境变化的重要信息。在辐射沙洲岸滩采集了3个短柱沉积物岩芯,建立可靠的年代框架,采用高分辨率XRF元素扫描仪进行地球化学元素测试,选用XRF信号强度高的14种元素进行聚类和相关性方法提取环境信息,研究过去百年尺度人类活动和海岸环境变化下的苏北辐射沙洲岸滩沉积环境变化。结果表明,该区典型潮滩剖面岩芯沉积物中Si、Ca、As和Fe元素相对含量较高,且自北向南其含量不断增加,Mn、Ba、Cu和Zn元素含量较低,在所有剖面含量变化不大。在垂向上,Si、Ca和Fe元素变化趋势一致,而Ni、Zn和S元素在不同柱状岩芯中呈现与Si、Ca和Fe相反的变化趋势。相关关系和聚类分析显示,Si、Ca和Fe元素之间具有较高的相关性,即具有近似的地球化学行为和一致的物质来源;与元素Ni、Cu和Zn呈负相关,暗示了这几种元素与前者具有不同的地球化学行为。苏北辐射沙洲潮滩沉积物沉积环境发生了明显变化且在不同区域呈现不同的变化规律,物质来源、水动力环境、人类活动等因素是导致沉积环境变化的主要原因。Abstract: The radial sand ridges is a typical sedimentary accumulation body distributed off the coast of Jiangsu Province. Under the influence of the sediment supply of the Changjiang River and the Huanghe River as well as the coastal tidal current, the typical silty-muddy tidal flats are developed, and the sediment elements can record the important information of the environmental changes of the tidal flats. Three short core samples were collected in the tidal flat of radial sand ridges to establish a reliable chronological framework and geochemical element testing, and 14 elements with high X-ray fluorescence (XRF) core scanner analysis signal strength were selected for clustering and correlation method to extract environmental information. The sedimentary environment changes of the northern Jiangsu radial sand ridges under the influence of human activities and coastal environment changes in the past 100 years were studied. The results indicate that the contents of Si, Ca and Fe in the core sediments of typical tidal flat profile in this area are relatively high, and the contents of Si, Ca and Fe increasing from north to south, while the contents of Mn, Ba, Cu and Zn are low, and the little changes in contents at all profiles changes. In terms of vertical change, Si, Ca and Fe have the same vertical change trend, while Ni, Zn and S have the opposite change trend with Si, Ca and Fe in different sediment cores. Correlation and clustering analysis show that Si, Ca and Fe have high correlation, that is, they have similar geochemical behavior and consistent material source. In addition, it is negatively correlated with elements Ni, Cu and Zn, suggesting that these elements have different geochemical behaviors with the former. The sedimentary environment changes of the tidal flat are obvious and show different patterns in different regions in the northern Jiangsu radial sand ridges, and the material source, hydrodynamic environment and human activities are the main reasons leading to the change of the sedimentary environment.
-
Key words:
- tidal flats /
- sediment /
- element geochemistry /
- X-ray fluorescence /
- northern Jiangsu radial sand ridges
-
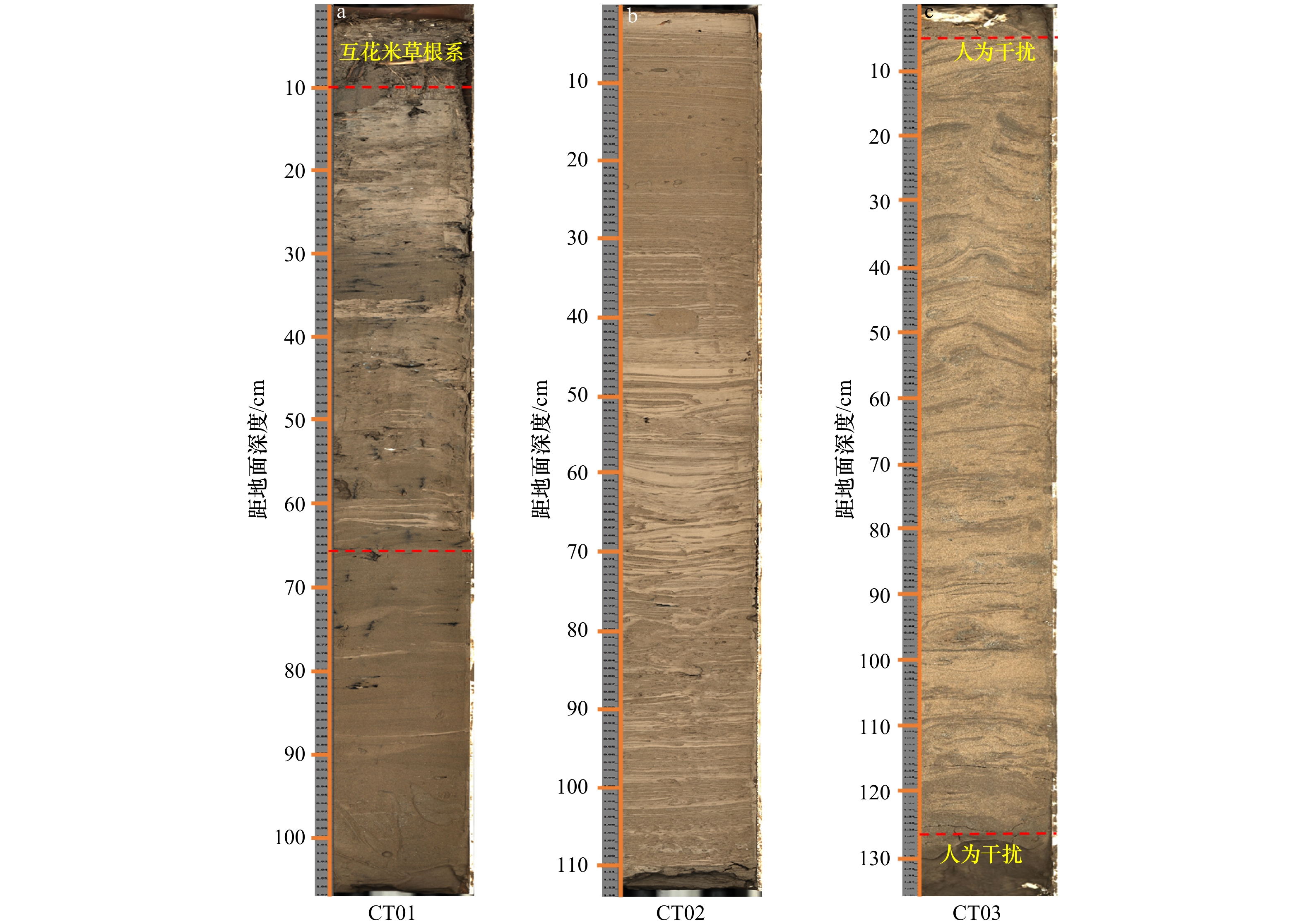
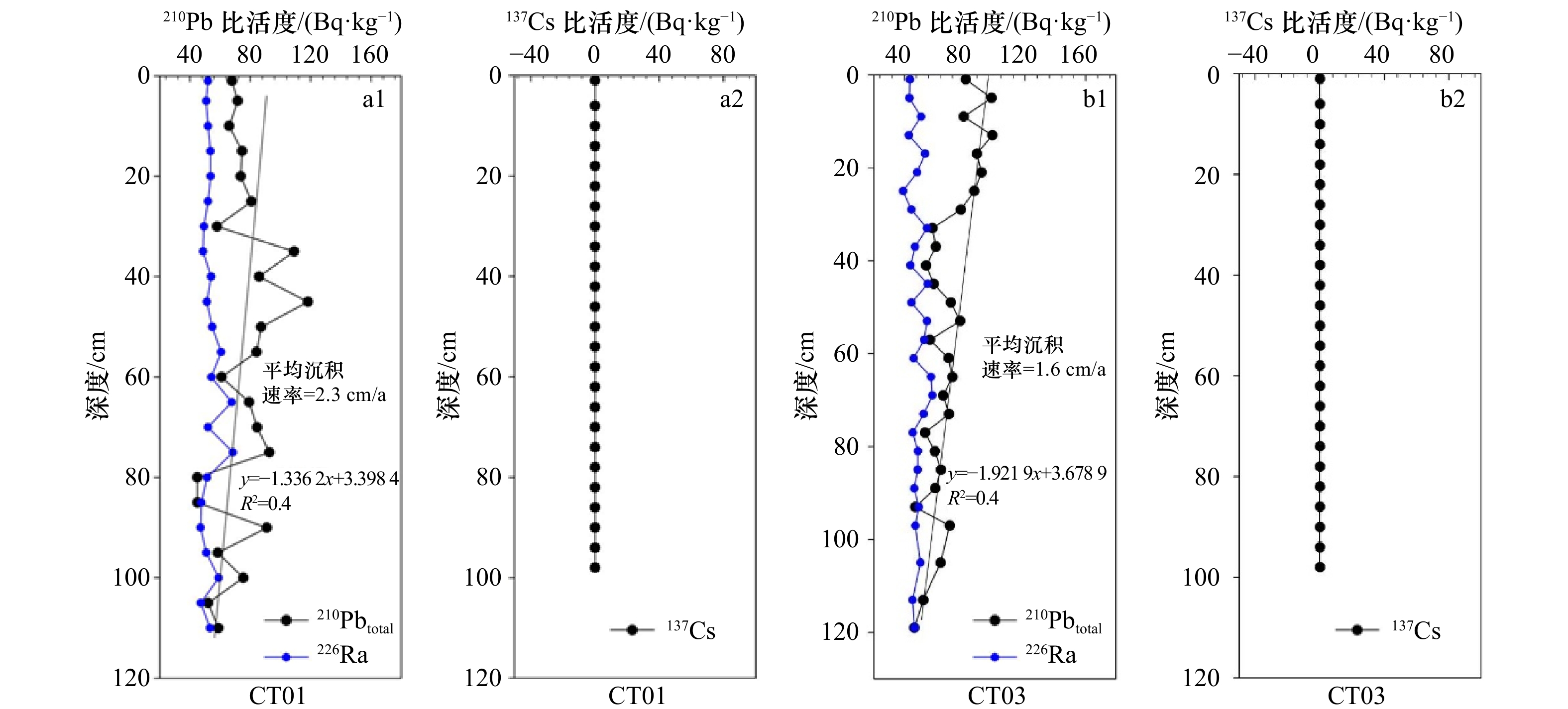
表 1 苏北辐射沙洲岸滩柱状岩芯沉积物站位信息
Tab. 1 The information of core sediments samples station in tidal flat in the northern Jiangsu radial sand ridges
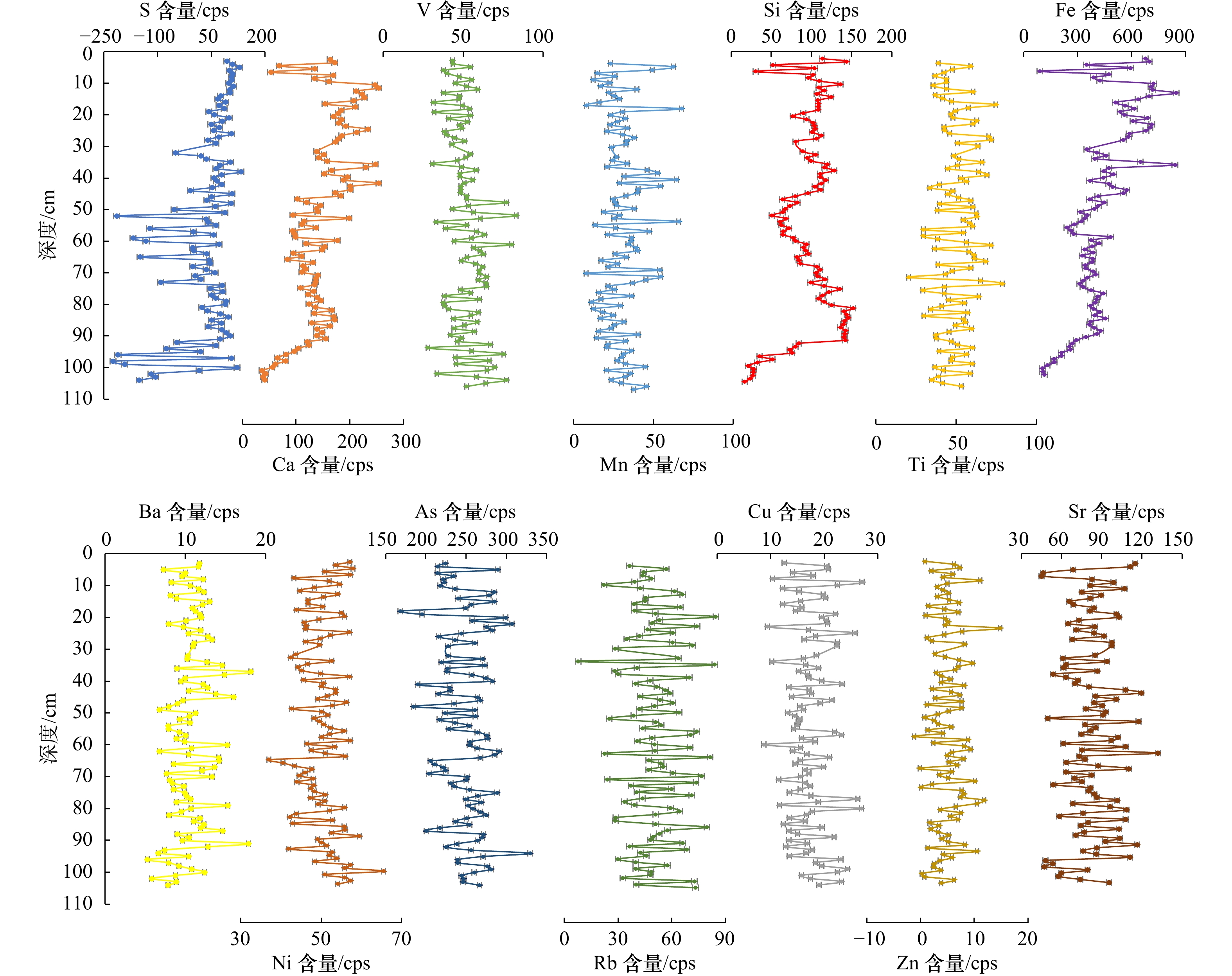
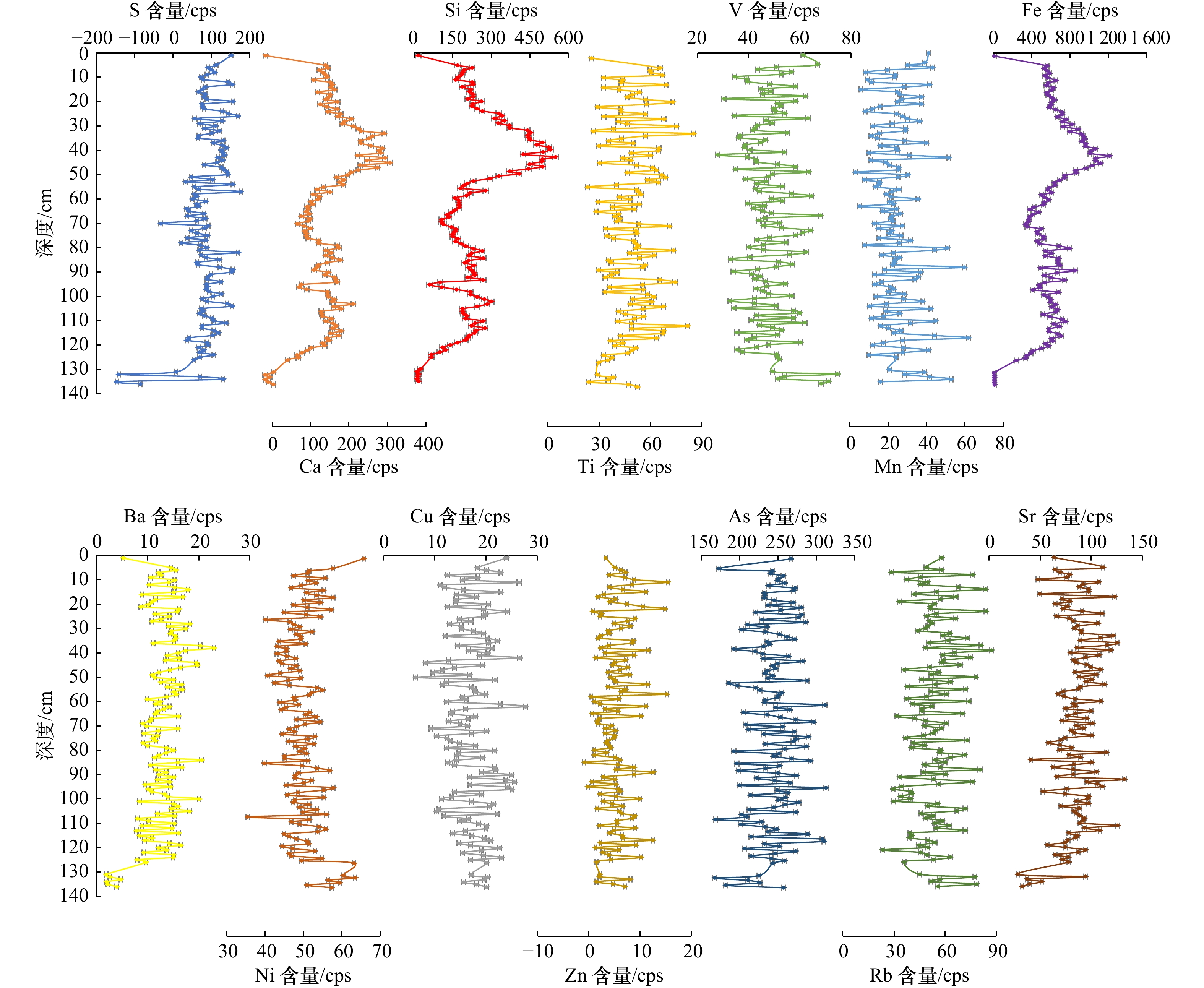
岩芯编号 取样地点 纬度 经度 CT01 射阳河口 33.772°N 120.526 55°E CT02 川东港 33.076 566°N 120.867°E CT03 海安 32.648 6°N 120.986°E 表 2 苏北辐射沙洲岸滩沉积物元素含量
Tab. 2 The element content of core sediments in tidal flat in the northern Jiangsu radial sand ridges
元素 射阳河口潮滩 川东港互花米草滩 海安近岸潮滩 最小值/cps 最大值/cps 平均值/cps 标准
偏差变异
系数最小值/cps 最大值/cps 平均值/cps 标准
偏差变异
系数最小值/cps 最大值/cps 平均值/cps 标准
偏差变异
系数Si 16.76 151.80 95.41 31.99 0.34 172.94 560.33 246.00 75.10 0.31 11.49 549.54 235.09 122.1 0.52 S −224.6 132.56 34.76 82.32 2.37 16.73 147.06 75.40 34.94 0.46 −146.7 176.34 87.08 48.81 0.56 Ca 36.45 253.78 144.92 49.86 0.34 206.21 636.93 285.80 62.13 0.22 12.75 337.83 176.28 65.69 0.37 Ti 19.17 77.24 48.59 11.59 0.24 28.33 88.94 58.27 12.65 0.22 22.33 84.53 48.05 13.25 0.28 V 27.85 83.24 51.80 10.94 0.21 21.97 74.40 45.63 9.39 0.21 27.91 74.59 48.28 9.07 0.19 Mn 6.85 66.61 29.36 12.52 0.43 3.68 50.18 25.73 10.42 0.41 6.19 65.04 27.83 11.37 0.41 Fe 88.52 847.36 425.82 161.3 0.38 601.70 1793.6 887.94 187.26 0.21 5.57 1213.5 604.23 230.8 0.38 Ba 5.27 18.16 10.64 2.46 0.23 6.62 22.55 13.66 3.01 0.22 1.92 22.98 12.88 3.78 0.29 Ni 36.79 65.28 50.07 4.90 0.10 33.09 53.30 43.83 4.23 0.10 34.33 64.57 48.69 4.87 0.10 Cu 8.72 27.03 17.27 3.87 0.22 4.08 26.28 16.01 4.00 0.25 6.28 27.71 17.22 4.27 0.25 Zn −0.83 15.15 5.31 2.94 0.55 −0.91 18.71 5.68 3.78 0.67 −0.72 15.63 5.54 3.30 0.59 As 168.18 329.38 248.10 28.25 0.11 186.12 351.51 240.38 28.98 0.12 167.67 312.54 243.35 29.83 0.12 Rb 7.68 84.77 50.46 15.29 0.30 30.70 101.78 58.92 14.21 0.24 21.84 85.56 52.30 13.11 0.25 Sr 45.09 132.00 82.47 18.44 0.22 53.18 136.33 91.92 15.60 0.17 28.04 132.26 85.01 19.35 0.23 表 3 射阳河口互花米草滩岩芯沉积物中元素相关性
Tab. 3 The element correlation of core sediments in the Spartina alterniflora tidal flat of Sheyang Estuary
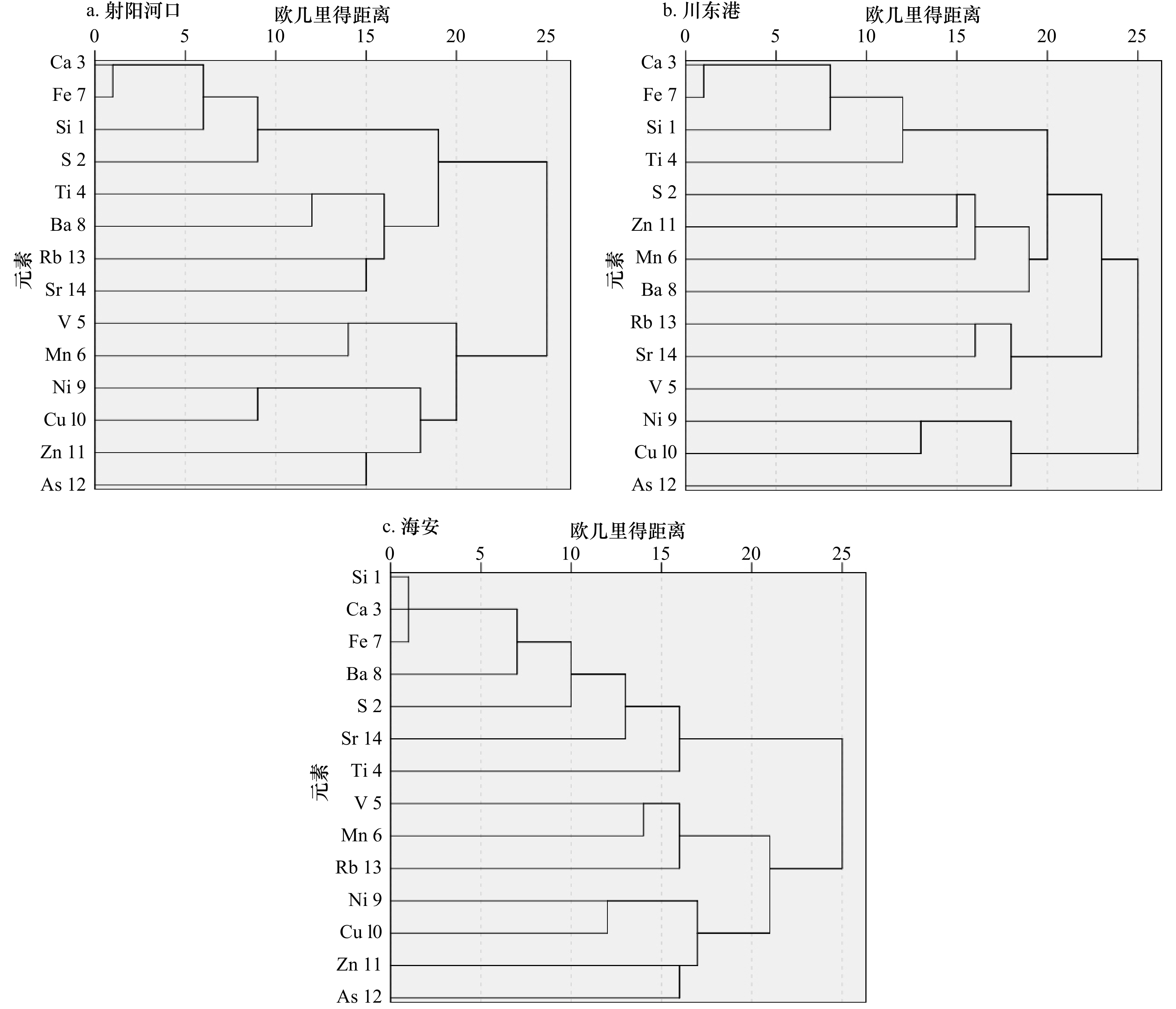
相关性 Si S Ca Ti V Mn Fe Ba Ni Cu Zn As Rb Sr 平均粒径 Si 1 S 0.52** 1 Ca 0.63** 0.43** 1 Ti 0.04 −0.03 0.17 1 V −0.24* −0.45** −0.26** −0.05 1 Mn −0.13 −0.12 −0.05 0.04 0.15 1 Fe 0.55** 0.45** 0.85** 0.22* −0.28** −0.02 1 Ba 0.37** 0.21* 0.38** 0.25* −0.15 −0.01 0.34** 1 Ni −0.27** −0.06 −0.29** −0.12 −0.08 0.10 −0.23* −0.08 1 Cu −0.19 −0.07 −0.15 −0.15 0.01 0.02 −0.08 −0.22* 0.39** 1 Zn 0.14 0.10 0.10 0.09 −0.17 −0.09 0.12 0.04 −0.08 0.10 1 As −0.09 −0.05 −0.09 −0.03 0.14 −0.17 −0.08 −0.21* 0.08 0.05 0.12 1 Rb 0.02 −0.10 0.02 0.11 −0.09 0.04 0.01 0.03 0.05 −0.12 −0.09 −0.04 1 Sr 0.20* 0.08 0.22* 0.05 −0.10 −0.02 0.18 0.10 0.17 0.02 0.04 −0.12 0.09 1 平均粒径 −0.10 −0.25 −0.59** −0.03 0.12 −0.18 −0.65** −0.09 0.17 0.06 0.08 0.14 0.08 0.13 1 注:**表示在0.01级别(双尾),相关性显著;*表示在0.05级别(双尾),相关性显著。 表 4 川东港互花米草滩岩芯沉积物中元素相关性
Tab. 4 The element correlation of core sediments in the Spartina alterniflora tidal flat of the Chuangdong Gang
相关性 Si S Ca Ti V Mn Fe Ba Ni Cu Zn As Rb Sr 平均粒径 Si 1 S 0.41** 1 Ca 0.74** 0.33** 1 Ti 0.34** 0.05 0.36** 1 V −0.02 −0.13 −0.10 0.07 1 Mn 0.09 0.14 0.02 −0.05 −0.15 1 Fe 0.50** 0.15 0.87** 0.31** −0.15 −0.02 1 Ba 0.29** 0.19* 0.12 0.08 −0.12 0.03 −0.01 1 Ni −0.04 0.06 −0.27** −0.16 −0.02 −0.07 −0.31** 0.11 1 Cu −0.12 0.07 −0.14 −0.10 0.05 −0.10 −0.12 −0.08 0.25** 1 Zn 0.26** 0.20* 0.25** 0.05 −0.17 0.14 0.15 −0.01 −0.09 0.09 1 As 0.01 0.07 0.02 −0.02 −0.11 −0.09 0.04 −0.05 0.17 0.06 0.13 1 Rb 0.08 −0.08 0.12 −0.08 0.03 0.06 0.08 0.04 −0.15 −0.02 −0.05 −0.25** 1 Sr −0.02 −0.00 0.02 −0.10 0.06 −0.01 −0.02 −0.14 −0.06 0.06 −0.11 −0.10 0.12 1 平均粒径 0.217* 0.02 −0.04 −0.08 0.16 0.17 −0.22* 0.13 0.02 −0.08 −0.06 −0.03 0.05 −0.03 1 注:**表示在0.01级别(双尾),相关性显著;*表示在0.05级别(双尾),相关性显著。 表 5 海安岸外潮滩岩芯沉积物中元素相关性
Tab. 5 The element correlation of core sediments in the Haian tidal flat
相关性 Si S Ca Ti V Mn Fe Ba Ni Cu Zn As Rb Sr 平均粒径 Si 1 S 0.45** 1 Ca 0.94** 0.43** 1 Ti 0.17 0.16 0.20* 1 V −0.19* −0.13 −0.21* 0.11 1 Mn 0.01 0.04 −0.02 0.10 0.06 1 Fe 0.88** 0.40** 0.89** 0.15 −0.24** 0.02 1 Ba 0.38** 0.17 0.41** −0.15 −0.19* 0.07 0.40** 1 Ni −0.35** −0.10 −0.31** −0.08 0.10 −0.01 −0.28** −0.10 1 Cu −0.10 0.00 −0.07 0.06 −0.12 0.06 0.06 0.01 0.23* 1 Zn 0.04 0.07 0.03 −0.05 −0.01 0.08 0.07 0.09 0.07 0.14 1 As −0.08 −0.16 −0.10 −0.06 0.13 0.04 −0.07 −0.11 0.13 0.06 0.05 1 Rb 0.33** 0.17 0.30** 0.04 −0.06 −0.03 0.29** 0.23** −0.18 −0.03 −0.11 −0.19* 1 Sr 0.31** 0.11 0.30** 0.14 0.06 0.00 0.29** 0.06 0.00 0.02 −0.05 −0.15 0.26** 1 平均粒径 0.09 0.04 0.01 0.05 0.00 −0.09 0.03 −0.12 −0.16 −0.09 −0.18* −0.14 −0.04 −0.02 1 注:**表示在0.01级别(双尾),相关性显著;*表示在0.05级别(双尾),相关性显著。 -
[1] 王颖, 朱大奎, 周旅复, 等. 南黄海辐射沙脊群沉积特点及其演变[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1998, 28(5): 385−393.Wang Ying, Zhu Dakui, Zhou Lüfu, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and evolution of radiative sand ridge group in the South Yellow Sea[J]. Science in Chia (Series D), 1998, 28(5): 385−393. [2] Murray N J, Clemens R S, Phinn S R, et al. Tracking the rapid loss of tidal wetlands in the Yellow Sea[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2014, 12(5): 267−272. doi: 10.1890/130260 [3] Li Xing, Zhang Xin, Qiu Chuanyin, et al. Rapid loss of tidal flats in the Yangtze River delta since 1974[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(5): 1636. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051636 [4] Zhao Chuanpeng, Qin Chengzhi, Teng Jiakun. Mapping large-area tidal flats without the dependence on tidal elevations: a case study of Southern China[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 159: 256−270. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.11.022 [5] Sagar S, Roberts D, Bala B, et al. Extracting the intertidal extent and topography of the Australian coastline from a 28 year time series of Landsat observations[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2017, 195: 153−169. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.04.009 [6] 王颖. 黄海陆架辐射沙脊群[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002.Wang Ying. Radiative Sandy Ridge Field on Continental Shelf of the Yellow Sea[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Press, 2002. [7] 任美锷. 江苏省海岸带和海涂资源综合调查报告[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1986.Ren Mei’e. Comprehensive Survey Report on Coastal Zone and Marine Resources of Jiangsu Province[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1986. [8] Zhang R S, Chen C J. Evolution of Jiangsu Offshore Banks (Radial Offshore Tidal Sands) and Probability of Tiaozini Sands Merged into Mainland[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1992: 56−64. [9] Gao Shu. Modeling the preservation potential of tidal flat sedimentary records, Jiangsu coast, eastern China[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2009, 29(16): 1927−1936. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2008.12.010 [10] 金宇豪, 丁贤荣, 葛小平. 基于MSS/ETM影像辐射沙脊群沙脊地貌遥感演变分析[J]. 地理空间信息, 2015, 13(6): 79−81, 88.Jin Yuhao, Ding Xianrong, Ge Xiaoping. Sand ridge geomorphic remote sensing evolution analysis of radial sand ridges based on MSS/ETM[J]. Geospatial Information, 2015, 13(6): 79−81, 88. [11] 李岚, 丁贤荣, 葛小平, 等. 辐射沙脊群蒋家沙西段地貌演变特征[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(4): 366−370.Li Lan, Ding Xianrong, Ge Xiaoping, et al. Geomorphic evolution characteristics of western segment of Jiangjiasha in radial sand ridge group area[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2015, 43(4): 366−370. [12] 李清, 殷勇. 南黄海辐射沙脊群里磕脚11DT02孔沉积相分析及环境演化[J]. 地理研究, 2013, 32(10): 1843−1855.Li Qing, Yin Yong. Sedimentary facies and evolution of the Likejiao sandy ridge, in the South Yellow Sea offshore area, eastern China[J]. Geographical Research, 2013, 32(10): 1843−1855. [13] 朱大奎, 柯贤坤, 高抒. 江苏海岸潮滩沉积的研究[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 1986, 4(3): 19−27.Zhu Dakui, Ke Xiankun, Gao Shu. Tidal flat sedimentation of Jiangsu coast[J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 1986, 4(3): 19−27. [14] 王宝灿, 虞志英, 刘苍字, 等. 海州湾岸滩演变过程和泥沙流动向[J]. 海洋学报, 1980, 2(1): 79−96.Wang Baocan, Yu Zhiying, Liu Cangzi, et al. The change of coasts and beaches and the movement of longshore sediments of the Haizhou Bay[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1980, 2(1): 79−96. [15] 任美锷, 张忍顺, 杨巨海, 等. 风暴潮对淤泥质海岸的影响——以江苏省淤泥质海岸为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1983, 3(4): 1−24.Ren Mei’e, Zhang Renshun, Yang Juhai, et al. The influence of storm tide on mud plain coast−with special reference to Jiangsu Province[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1983, 3(4): 1−24. [16] 李炎, 谢钦春. 杭州湾庵东浅滩地貌演变规律[J]. 东海海洋, 1993, 11(2): 25−33.Li Yan, Xie Qinchun. Dynamical development of the Andong tidal flat in Hangzhou Bay, China[J]. Donghai Marine Science, 1993, 11(2): 25−33. [17] 李九发. 长江河口南汇潮滩泥沙输移规律探讨[J]. 海洋学报, 1990, 12(1): 75−82.Li Jiufa. Sediment transport in Nanhui tidal flat of the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1990, 12(1): 75−82. [18] 李占海. 江苏大丰潮滩沉积动力过程研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2005.Li Zhanhai. Sediment dynamic process of intertidal flats, Dafeng, Northern Jiangsu, China[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2005. [19] 王爱军, 高抒, 贾建军, 等. 江苏王港盐沼的现代沉积速率[J]. 地理学报, 2005, 60(1): 61−70.Wang Aijun, Gao Shu, Jia Jianjun, et al. Contemporary sedimentation rates on salt marshes at Wanggang, Jiangsu, China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2005, 60(1): 61−70. [20] 杨桂山, 施雅风, 季子修. 江苏淤泥质潮滩对海平面变化的形态响应[J]. 地理学报, 2002, 57(1): 76−84.Yang Guishan, Shi Yafeng, Ji Zixiu. The morphological response of typical mud flat to sea level change in Jiangsu coastal plain[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2002, 57(1): 76−84. [21] 高抒, 李安春. 浅海现代沉积作用研究展望[J]. 海洋科学, 2000, 24(2): 1−3.Gao Shu, Li Anchun. Research of sedimentary processes in marine environments: a prospect[J]. Marine Science, 2000, 24(2): 1−3. [22] 陈志华, 石学法, 王湘芹, 等. 南黄海B10岩心的地球化学特征及其对古环境和古气候的反映[J]. 海洋学报, 2003, 25(1): 69−77.Chen Zhihua, Shi Xuefa, Wang Xiangqin, et al. Geochemical changes in Core B10 in the southern Huanghai Sea and implications for variations in paleoenvironment and paleoclimate[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2003, 25(1): 69−77. [23] Li Xiangdong, Shen Zhenguo, Wai O W H, et al. Chemical forms of Pb, Zn and Cu in the sediment profiles of the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2001, 42(3): 215−223. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00145-4 [24] Weltje G J, Tjallingii R. Calibration of XRF core scanners for quantitative geochemical logging of sediment cores: theory and application[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 274(3/4): 423−438. [25] Boyle J F. Rapid elemental analysis of sediment samples by isotope source XRF[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2000, 23(2): 213−221. doi: 10.1023/A:1008053503694 [26] Loring D H, Asmund G. Geochemical factors controlling accumulation of major and trace elements in Greenland coastal and fjord sediments[J]. Environmental Geology, 1996, 28(1): 2−11. doi: 10.1007/s002540050072 [27] Hu Guang, Jin Zhangdong, Zhang Fei. Constraints of authigenic carbonates on trace elements (Sr, Mg) of lacustrine ostracod shells in paleoenvironment reconstruction and its mechanism[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2008, 51(5): 654−664. doi: 10.1007/s11430-008-0043-2 [28] Francus P, Lamb H, Nakagawa T, et al. The potential of high-resolution X-ray fluorescence core scanning: applications in paleolimnology[J]. PAGES News, 2009, 17(3): 93−95. doi: 10.22498/pages.17.3.93 [29] Ziegler M, Jilbert T, De Lange G J, et al. Bromine counts from XRF scanning as an estimate of the marine organic carbon content of sediment cores[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2008, 9(5): Q05009. [30] Metcalfe S E, Jones M D, Davies S J, et al. Climate variability over the last two millennia in the North American Monsoon region, recorded in laminated lake sediments from Laguna de Juanacatlán, Mexico[J]. The Holocene, 2010, 20(8): 1195−1206. doi: 10.1177/0959683610371994 [31] 刘旭英, 高建华, 白凤龙, 等. 苏北新洋港潮滩柱状沉积物粒度分布特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(4): 27−35.Liu Xuying, Gao Jianhua, Bai Fenglong, et al. Grain size information in different evolution periods of Xinyanggang tidal flat in Jiangsu Province[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(4): 27−35. [32] 王颖, 朱大奎. 中国的潮滩[J]. 第四纪研究, 1990, 10(4): 291−300.Wang Ying, Zhu Dakui. Tidal flats of China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1990, 10(4): 291−300. [33] 诸裕良, 严以新, 薛鸿超. 南黄海辐射沙洲形成发育水动力机制研究——Ⅰ. 潮流运动平面特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1998, 28(5): 403−410.Zhu Yuliang, Yan Yixin, Xue Hongchao. Hydrodynamic mechanism of the formation and development of radiative sandbars in the South Yellow Sea: I. Plane characteristics of tidal current movement[J]. Science in China (Series D), 1998, 28(5): 403−410. [34] 张忍顺, 沈永明, 陆丽云, 等. 江苏沿海互花米草(Spartina alterniflora)盐沼的形成过程[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2005, 36(4): 358−366.Zhang Renshun, Shen Yongming, Lu Liyun, et al. Formation of Spartina alterniflora salt marsh on Jiangsu coast, China[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2005, 36(4): 358−366. [35] 徐晓凤. 射阳海岸现代沉积速率及重金属污染特征[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2015.Xu Xiaofeng. Modern sedimentation rate and heavy metal pollution characteristics of Sheyang coast[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2015. [36] 刘婷, 胡宝清. 基于聚类分析的复杂网络中的社团探测[J]. 复杂系统与复杂性科学, 2007, 4(1): 28−35.Liu Ting, Hu Baoqing. Detecting community in complex networks using cluster analysis[J]. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 2007, 4(1): 28−35. [37] 胡雷芳. 五种常用系统聚类分析方法及其比较[J]. 浙江统计, 2007(4): 11−13.Hu Leifang. Five common system cluster analysis methods and their comparison[J]. Zhejiang Statistics, 2007(4): 11−13. [38] 李天斌. 宁夏天景山奥陶系马家沟组、米钵山组常量、微量元素聚类分析成果解释[J]. 岩相古地理, 1999, 19(2): 21−28.Li Tianbin. The geological interpretation on the results of cluster analysis of major and trace elements from the Ordovician Majiagou and Miboshan Formations in the Tianjing mountain area, Ningxia[J]. Sedimentary Facies and Palaeogeography, 1999, 19(2): 21−28. -





 下载:
下载: