Morphodynamics and tidal flow asymmetry of the Huanghe River Estuary
-
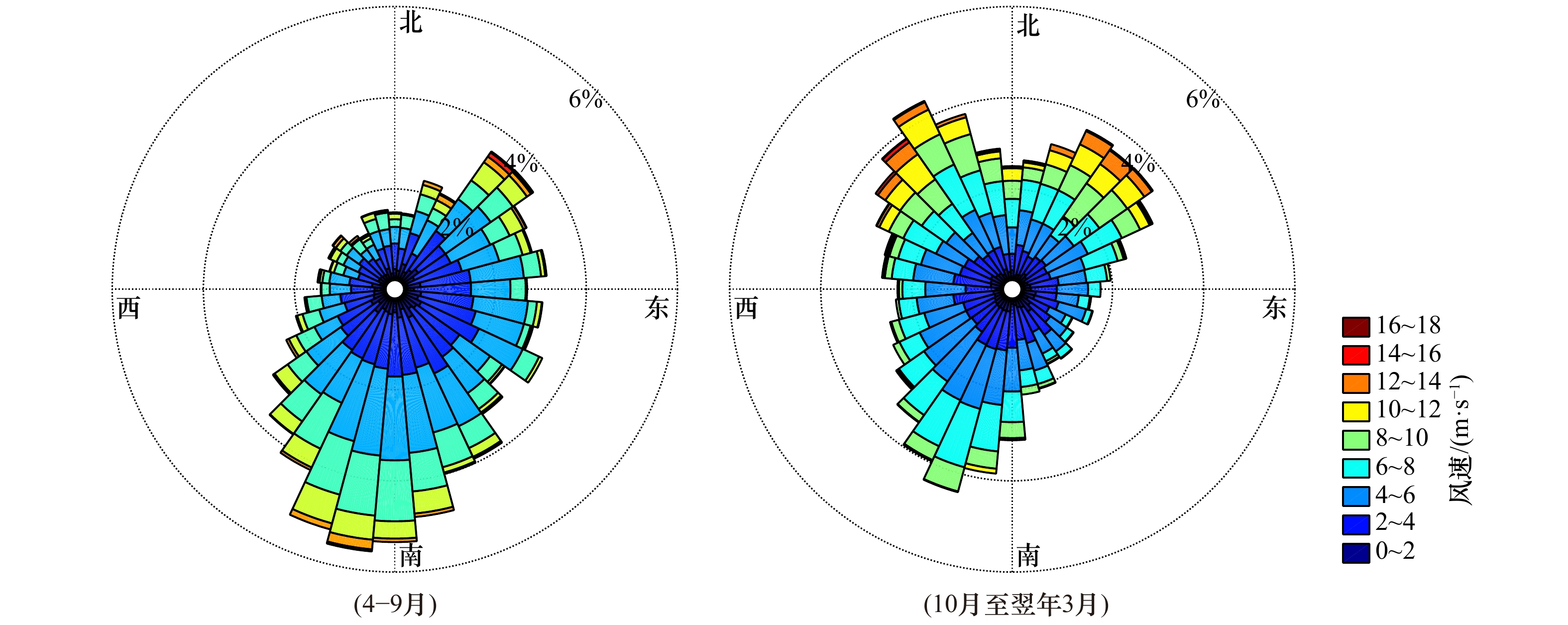
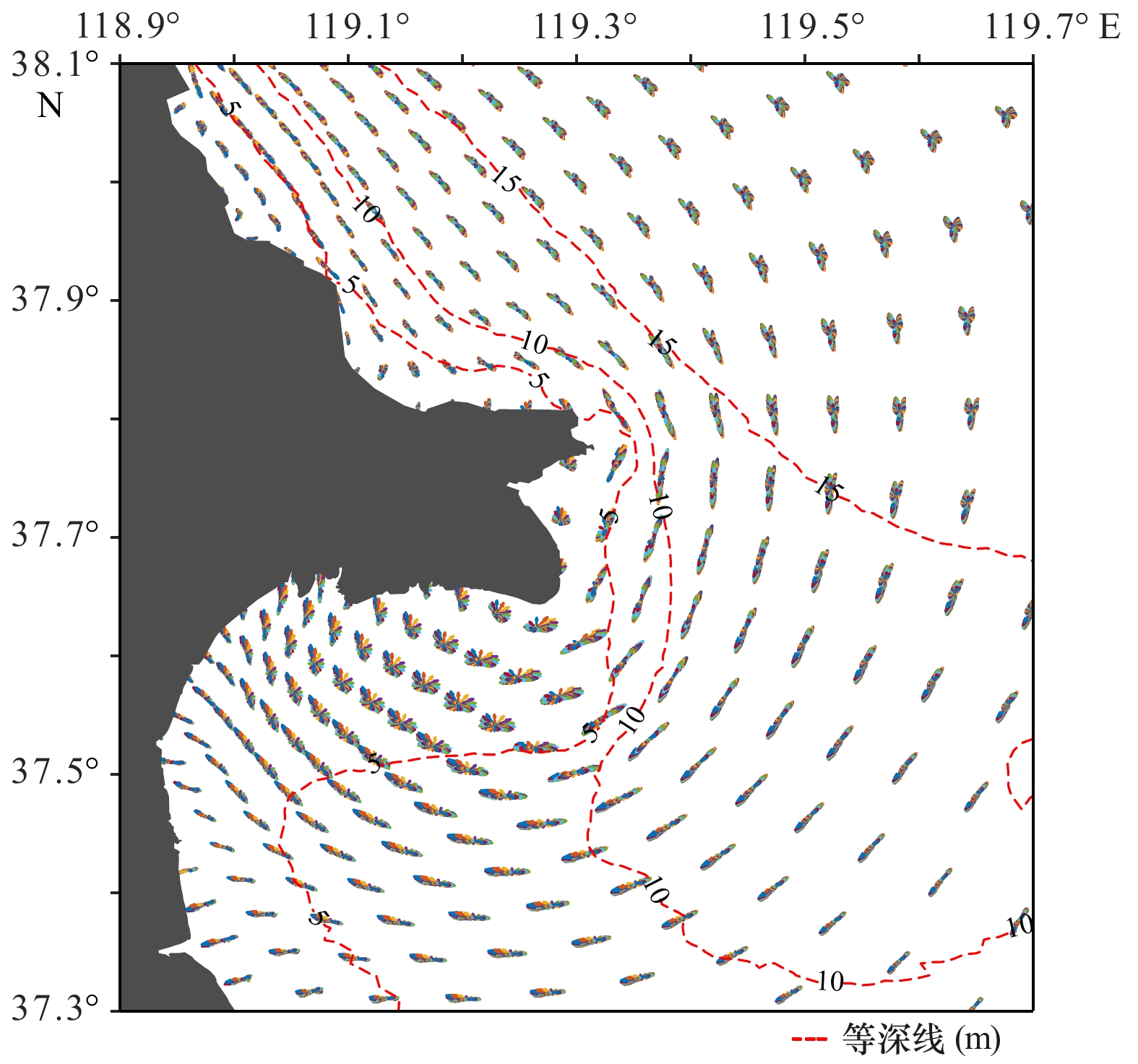
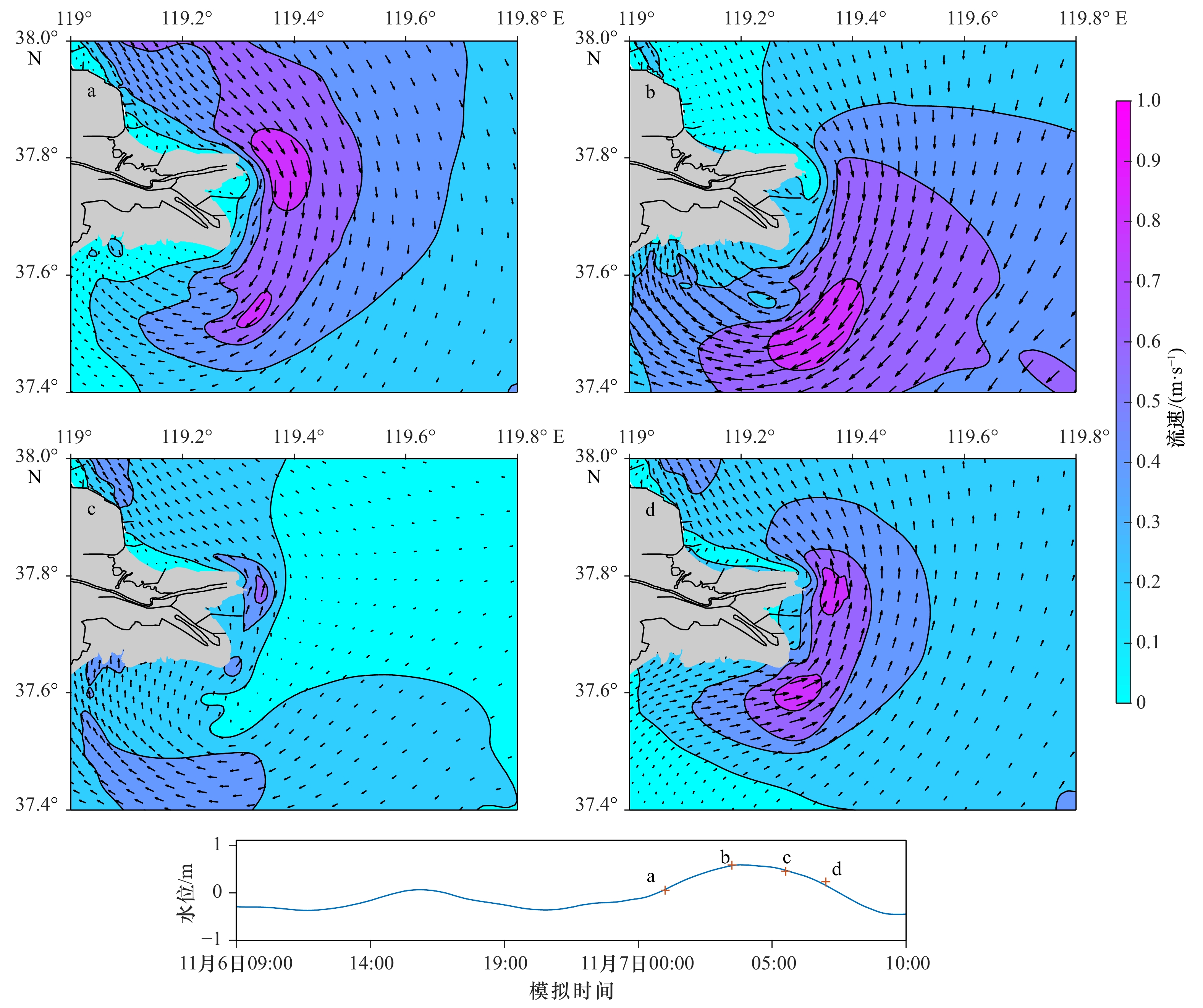
摘要: 涨落潮不对称是河口滨海区流场的重要特征,在泥沙输运和地貌演变过程中扮演着重要的角色。本文基于实测水深地形、沉积物粒度、水文泥沙观测等资料,分析了黄河口滨海区的冲淤变化、泥沙输运和沉积物特征。同时,本文利用Delft 3D模型模拟了黄河口滨海区的流场,并计算了不同条件下涨落潮流速的不对称分布,结合上述分析,探讨了黄河口滨海区冲淤演变的动力机制。结果表明:现行黄河口至莱州湾滨海区相间分布多个淤积和侵蚀中心;黄河口滨海区存在显著的涨落潮流速不对称现象,现行河口外为涨潮优势流分布区,并呈舌状向南部莱州湾方向伸展,而近岸和莱州湾则普遍为落潮主导;黄河口滨海区的冲淤变化很大程度上受涨落潮流速不对称空间分布及涨落潮优势流转换所控制;强北风作用增强和扩展涨潮优势,促使莱州湾淤积和沉积物粗化。Abstract: The asymmetry of flood and ebb plays an important role in the process of sediment transport and geomorphological evolution, which is a significant feature of the flow field in estuaries. The erosion and accumulation, sediment transport and sediment characteristics in the Huanghe River Estuary based on the measured topography, sediment particle size, hydrological and sediment observation data were analyzed in this paper. The Delft 3D model was used to simulate the flow field in the Huanghe River Estuary, and the spatial distribution of magnitude differences between flood and ebb velocities under different conditions were calculated. Combining the above, the dynamic mechanism of erosion and accretion in coastal area of the Huanghe River Estuary was discussed. The results show that there are multiple siltation and erosion centers distributed between the active river mouth and the Laizhou Bay. There is a noticeable asymmetry of flood and ebb velocities in the area, and there is the flood dominant area off the active river mouth, extending the Laizhou Bay southward in a tongue shape, while the near shore and the Laizhou Bay are dominated by ebb. The erosion and deposition in the Huanghe River Estuary are largely controlled by the spatial distribution of flow velocity asymmetry and the conversion of dominant flow. The strong north wind strengthens and expands flood-dominance, and promotes siltation and coarsening of sediment in the Laizhou Bay.
-
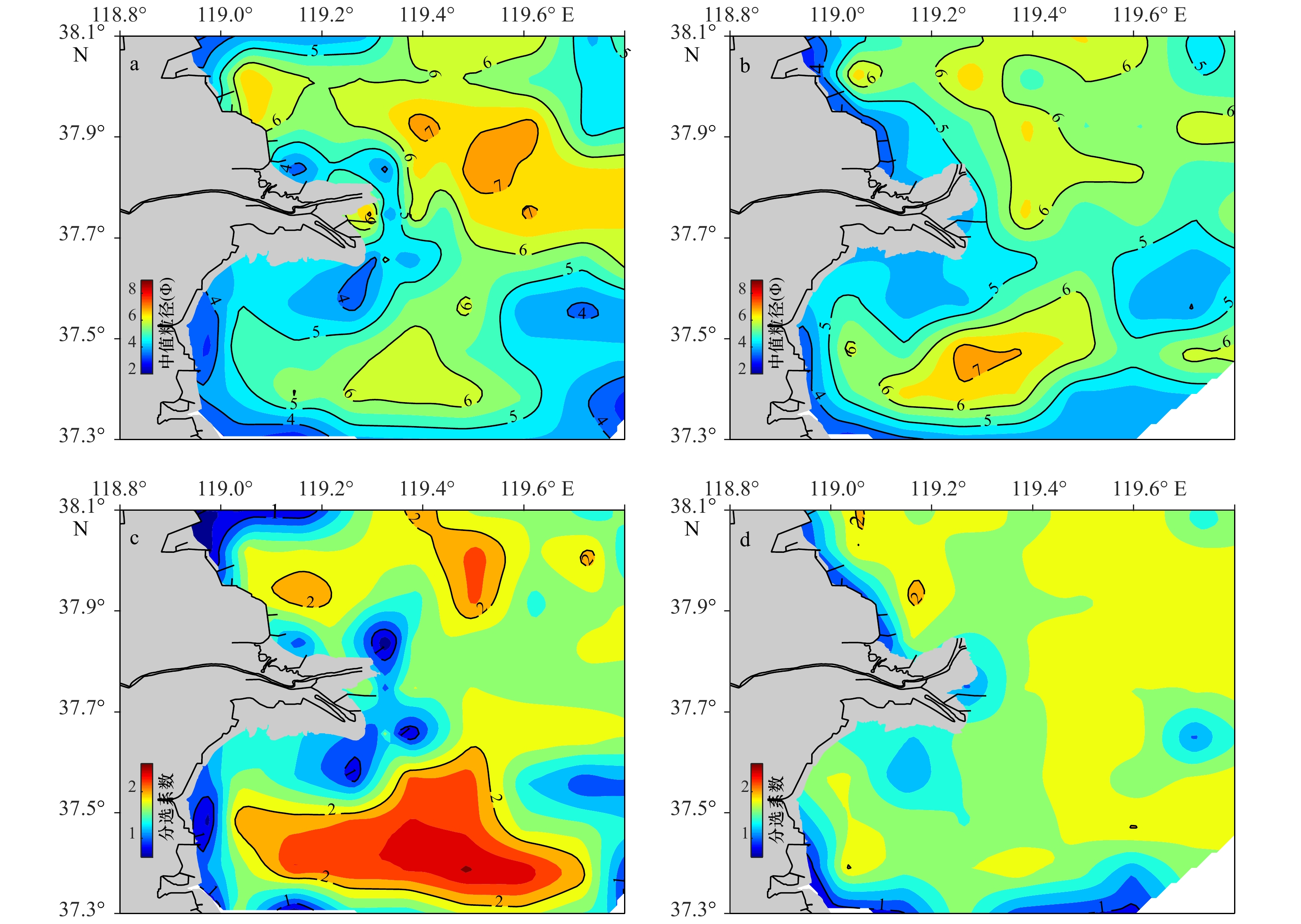
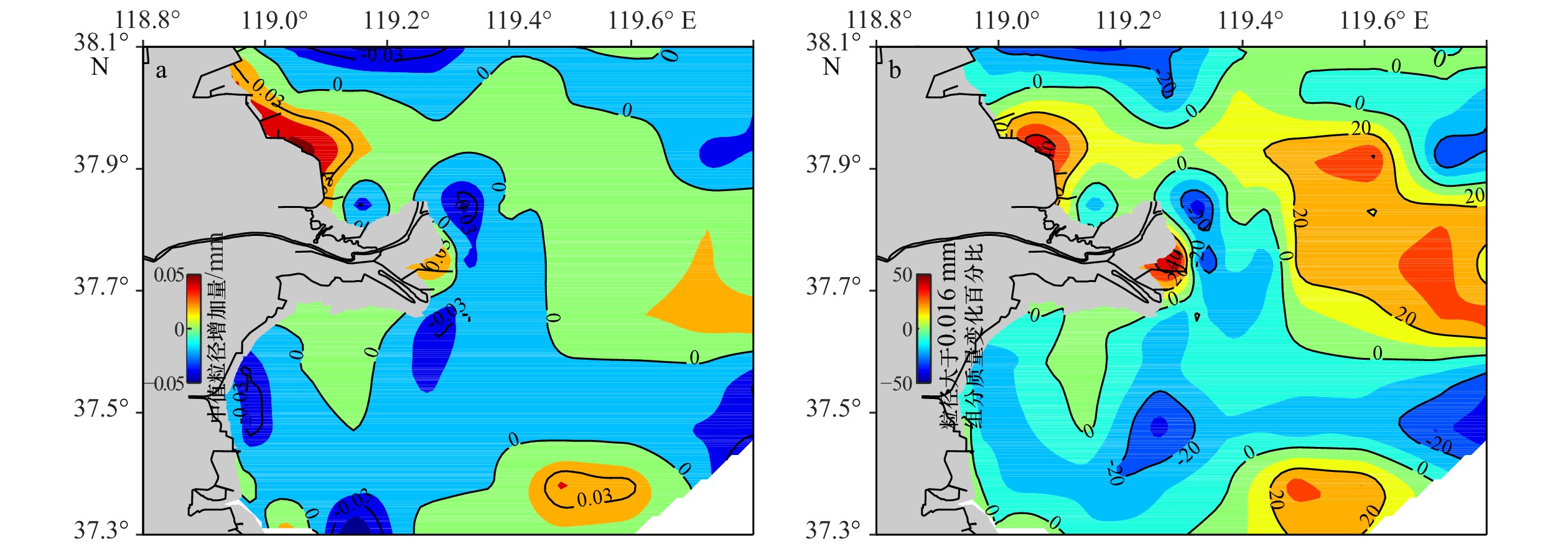
图 5 2007年和2015年黄河三角洲海域表层沉积物中值粒径、分选系数空间分布
a. 2007年中值粒径;b. 2015年中值粒径;c. 2007年分选系数;d. 2015年分选系数
Fig. 5 Spatial distribution of median grain size and sorting coefficient of surface sediment in the Huanghe River Delta in 2007 and 2015
a. Median grain size in 2007; b. median grain size in 2015; c. sorting coefficient in 2007; d. sorting coefficient in 2015
表 1 各动力项潮周期输沙量和方向
Tab. 1 Tidal-averaged suspended sediment flux and direction of each dynamic term
站位 T1 T2 T4 T5 T6 T9 平流输沙项 潮流输沙项 总输沙 A1_第1次 输沙量/(kg·m−1·s−1) 50.46 0.44 7.59 0.26 1.17 9.91 49.12 3.15 52.23 方向/(°) 304 125 176 355 159 343 303 312 304 A1_第2次 输沙量/(kg·m−1·s−1) 8.78 0.47 20.55 0.12 0.43 0.05 8.23 20.60 13.03 方向/(°) 306 143 140 123 199 306 302 140 151 A2_第2次 输沙量/(kg·m−1·s−1) 11.70 0.37 1.40 0.05 0.15 0.65 11.53 0.97 12.21 方向/(°) 273 128 291 132 233 66 271 319 275 -
[1] Hoitink A J F, Hoekstra P, Van Maren D S. Flow asymmetry associated with astronomical tides: implications for the residual transport of sediment[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2003, 108(C10): 3315. doi: 10.1029/2002JC001539 [2] Gong Wenping, Schuttelaars H, Zhang Heng. Tidal asymmetry in a funnel-shaped estuary with mixed semidiurnal tides[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 2016, 66(5): 637−658. doi: 10.1007/s10236-016-0943-1 [3] Friedrichs C T, Aubrey D G. Non-linear tidal distortion in shallow well-mixed estuaries: a synthesis[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1988, 27(5): 521−545. doi: 10.1016/0272-7714(88)90082-0 [4] Nidzieko N J. Tidal asymmetry in estuaries with mixed semidiurnal/diurnal tides[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2010, 115(C8): C08006. [5] Song Dehai, Wang Xiaohua, Kiss A E, et al. The contribution to tidal asymmetry by different combinations of tidal constituents[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2011, 116(C12): C12007. doi: 10.1029/2011JC007270 [6] De Swart H E, Zimmerman J T F. Morphodynamics of tidal inlet systems[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2009, 41(1): 203−229. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.010908.165159 [7] Winterwerp J C. Fine sediment transport by tidal asymmetry in the high-concentrated Ems River: indications for a regime shift in response to channel deepening[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 2011, 61(2/3): 203−215. [8] 陈沈良, 张国安, 陈小英, 等. 黄河三角洲飞雁滩海岸的侵蚀及机理[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2005, 25(3): 9−14.Chen Shenliang, Zhang Guoan, Chen Xiaoying, et al. Coastal erosion feature and mechanism at Feiyantan in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2005, 25(3): 9−14. [9] Yang Zuosheng, Ji Youjun, Bi Naishuang, et al. Sediment transport off the Huanghe (Yellow River) delta and in the adjacent Bohai Sea in winter and seasonal comparison[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3): 173−181. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2010.06.005 [10] 陈沈良, 谷硕, 姬泓宇, 等. 新入海水沙情势下黄河口的地貌演变[J]. 泥沙研究, 2019, 44(5): 61−67.Chen Shenliang, Gu Shuo, Ji Hongyu, et al. Processes of the Yellow River Mouth on new water and sediment condition[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2019, 44(5): 61−67. [11] Wang Nan, Li Guangxue, Qiao Lulu, et al. Long-term evolution in the location, propagation, and magnitude of the tidal shear front off the Yellow River Mouth[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2017, 137: 1−12. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2017.01.020 [12] Chen Xiaoying, Chen Shenliang, Dong Ping, et al. Temporal and spatial evolution of the coastal profiles along the Yellow River Delta over last three decades[J]. GeoJournal, 2008, 71(2/3): 185−199. [13] Uncles R J, Elliott R C A, Weston S A. Dispersion of salt and suspended sediment in a partly mixed estuary[J]. Estuaries, 1985, 8(3): 256−269. doi: 10.2307/1351486 [14] 沈健, 沈焕庭, 潘定安, 等. 长江河口最大浑浊带水沙输运机制分析[J]. 地理学报, 1995, 50(5): 411−420.Shen Jian, Shen Huanting, Pan Ding’an, et al. Analysis of transport mechanism of water and suspended sediment in the turbidity maximum of the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1995, 50(5): 411−420. [15] 吴华林, 沈焕庭, 朱建荣. 河口泥沙通量研究综述[J]. 泥沙研究, 2001(5): 73−79.Wu Hualin, Shen Huanting, Zhu Jianrong. Estuarine sediment fluxes: an overview[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2001(5): 73−79. [16] 蒋陈娟, 李九发, 吴华林, 等. 长江河口北槽水沙过程对航道整治工程的响应[J]. 海洋学报, 2013, 35(4): 129−141.Jiang Chenjuan, Li Jiufa, Wu Hualin, et al. Effects of the deep waterway project on the characteristics of hydrodynamics and sediment dynamics in the North Passage of the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2013, 35(4): 129−141. [17] 彭俊, 刘锋, 陈沈良. 黄河三角洲强侵蚀岸段海域的悬沙输运机理研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2015(5): 44−50.Peng Jun, Liu Feng, Chen Shenliang. Study on suspended sediment transport in sea area off the heavy erosion coast of the Yellow River Delta[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2015(5): 44−50. [18] 陈斌, 刘健, 高飞. 莱州湾悬沙输运机制研究[J]. 水科学进展, 2015, 26(6): 857−866.Chen Bin, Liu Jian, Gao Fei. Suspended sediment transport mechanism in Laizhou Bay[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2015, 26(6): 857−866. [19] Dyer K R. The salt balance in stratified estuaries[J]. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science, 1974, 2(3): 273−281. doi: 10.1016/0302-3524(74)90017-6 [20] Nidzieko N J, Ralston D K. Tidal asymmetry and velocity skew over tidal flats and shallow channels within a macrotidal river delta[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2012, 117(C3): C03001. [21] Xing Fei, Wang Yaping, Wang H V. Tidal hydrodynamics and fine-grained sediment transport on the radial sand ridge system in the southern Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 291−294: 192−210. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.06.006 [22] Ji Hongyu, Pan Shunqi, Chen Shenliang. Impact of river discharge on hydrodynamics and sedimentary processes at Yellow River Delta[J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 425: 106210. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106210 [23] Ralston D K, Geyer W R, Lerczak J A. Structure, variability, and salt flux in a strongly forced salt wedge estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2010, 115(C6): C06005. [24] 刘锋. 黄河口及其邻近海域泥沙输运及其动力地貌过程[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2012.Liu Feng. Sediment transport and dynamic geomorphology process in the Yellow River Estuary and its adjacent sea[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2012. [25] McLaren P, Bowles D. The effects of sediment transport on grain-size distributions[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1985, 55(4): 457−470. [26] 贾建军, 程鹏, 高抒. 利用插值试验分析采样网格对粒度趋势分析的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(3): 135−141.Jia Jianjun, Cheng Peng, Gao Shu. Comparison between grain size trends derived from irregular and regular sampling grids with the help of GIS interpolation tools[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(3): 135−141. [27] 杨晓东, 姚炎明, 蒋国俊, 等. 乐清湾悬沙输移机制分析[J]. 海洋通报, 2011, 30(1): 53−59.Yang Xiaodong, Yao Yanming, Jiang Guojun, et al. Study on the transport mechanism of suspended sediment in Yueqing Bay[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2011, 30(1): 53−59. [28] Wang Houjie, Yang Zuosheng, Li Yunhai, et al. Dispersal pattern of suspended sediment in the shear frontal zone off the Huanghe (Yellow River) mouth[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2007, 27(6): 854−871. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2006.12.002 [29] 李为华, 李九发, 时连强, 等. 黄河口泥沙特性和输移研究综述[J]. 泥沙研究, 2005(3): 76−81.Li Weihua, Li Jiufa, Shi Lianqiang, et al. Review on the researches of sediment properties and transportation rules of the Huanghe estuary, China[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2005(3): 76−81. -





 下载:
下载: