An analysis on the propagation of the instabilities of longshore currents using wavelet coherence spectrum
-
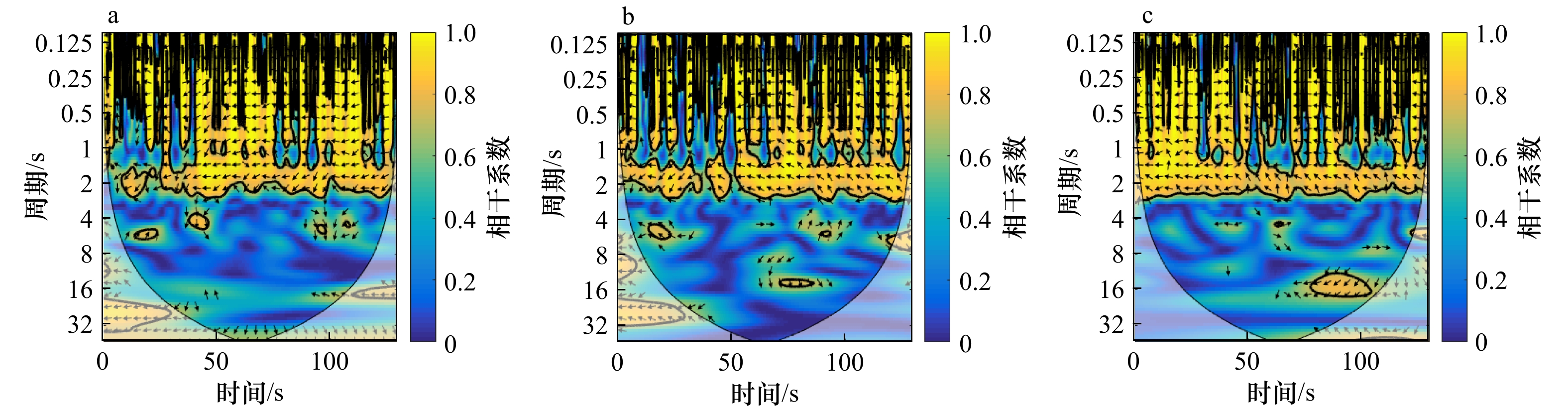
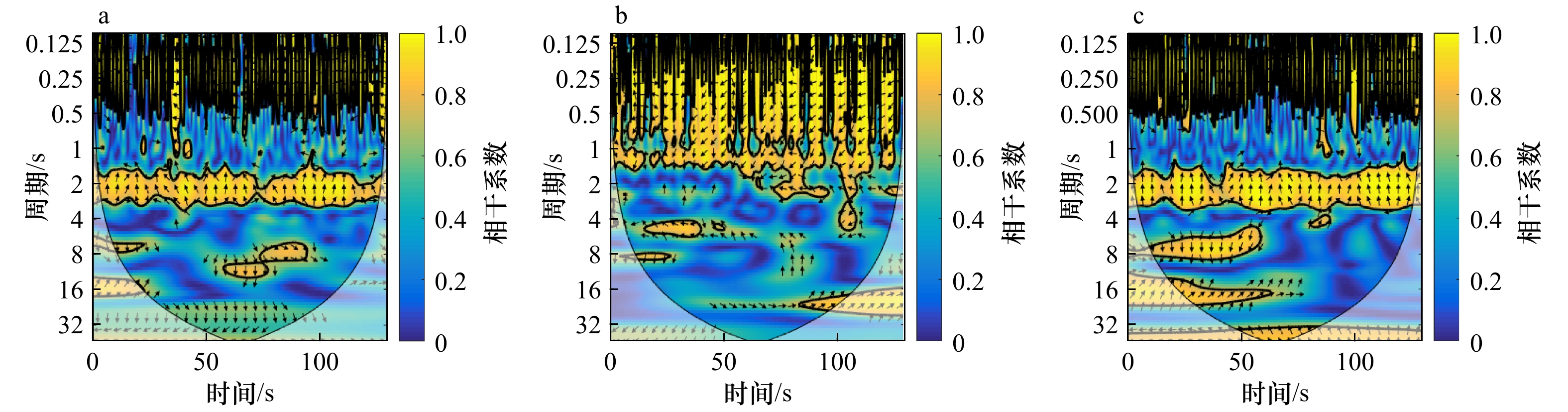
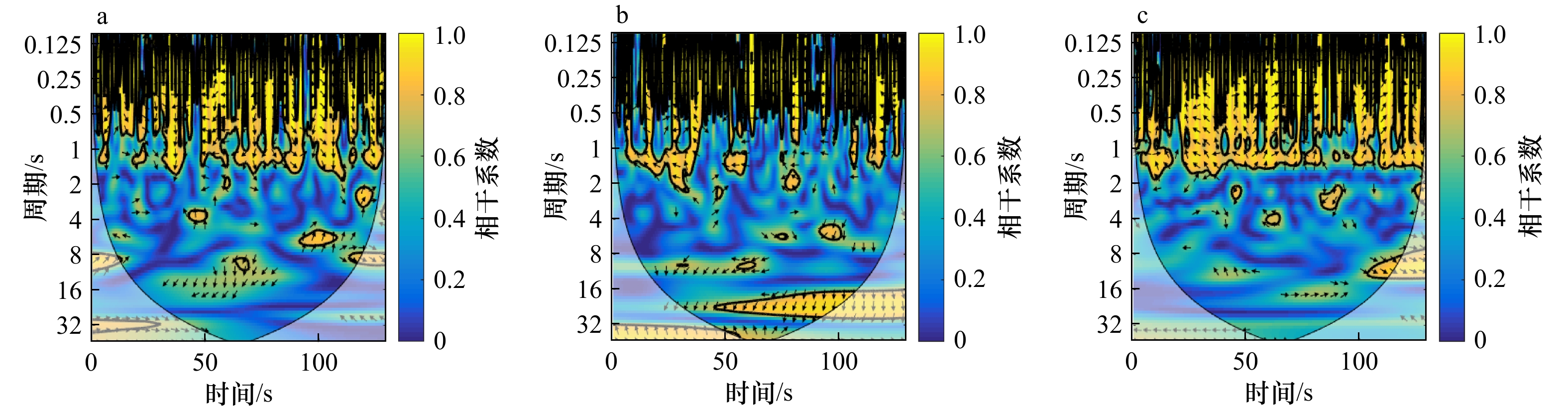
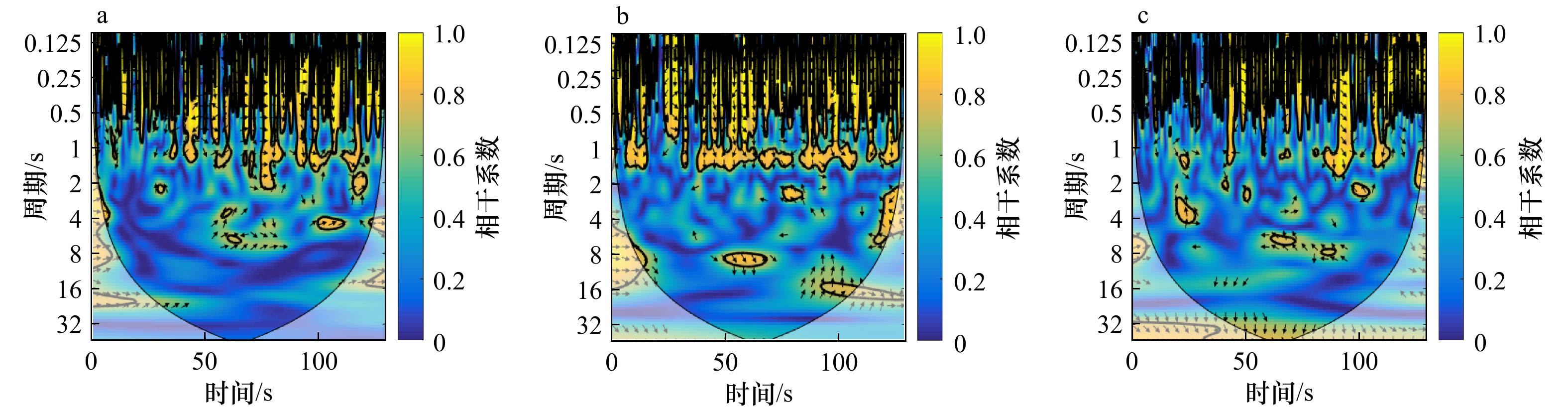
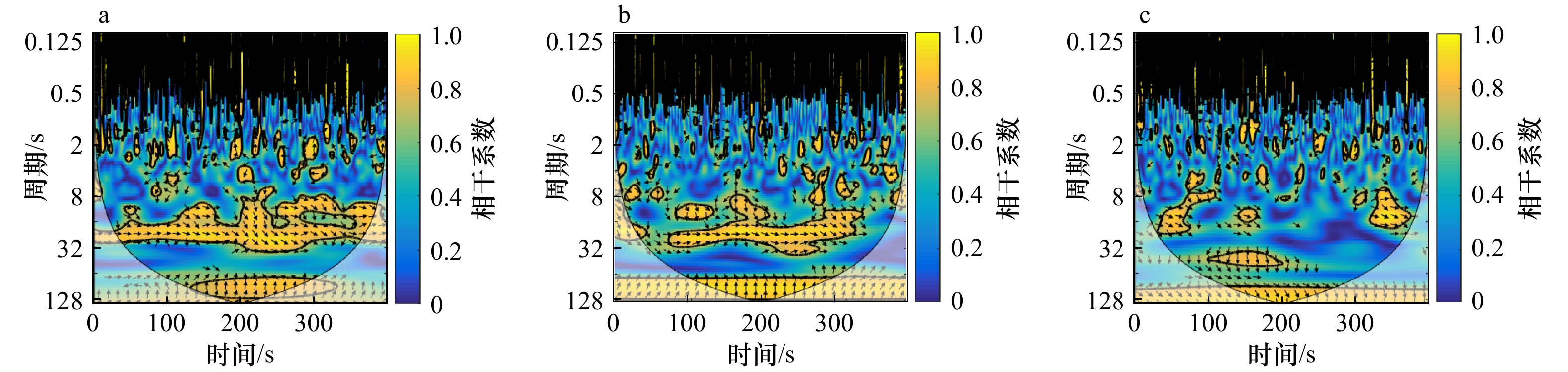
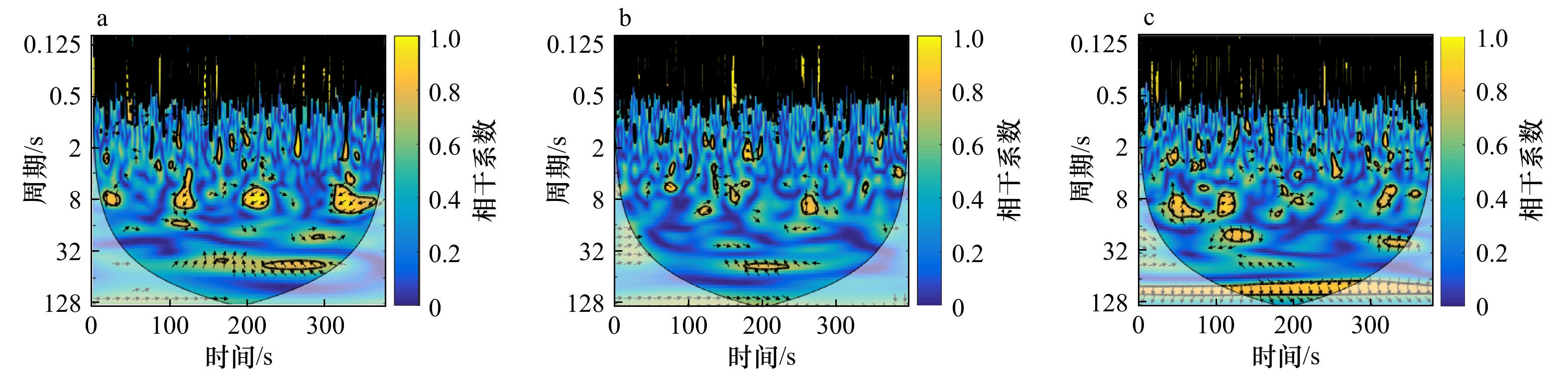
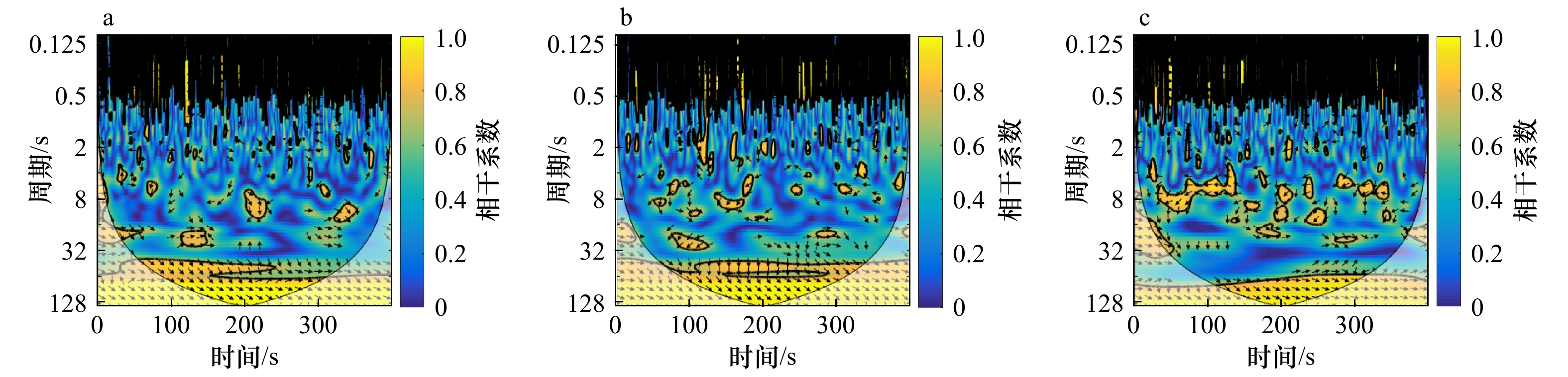
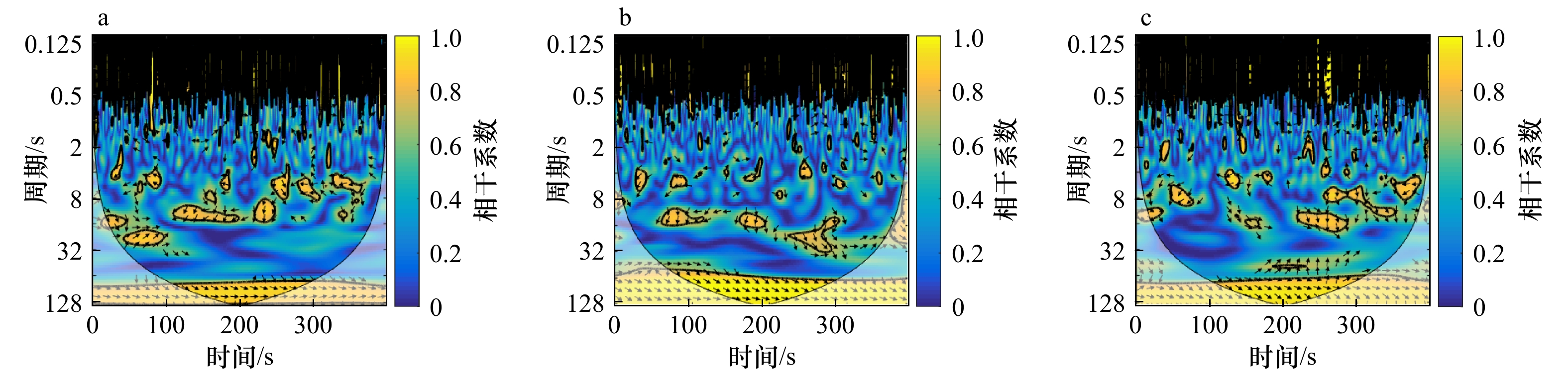
摘要: 沿岸流不稳定运动属于超低频运动,研究它的传播特性,有助于深入理解其对岸滩演变、污染物、鱼卵等输移、迁移的影响。本文基于小波相干谱对所选实验波况进行了研究,分析了规则波、随机波入射情况下沿岸流不稳定运动传播特性,并讨论了入射波高、周期、坡度等对其的影响。结果表明,不规则波更易诱导出沿岸流不稳定运动,且在不规则波情况下,不稳定运动在沿岸方向相距4 m的两个断面上产生的相位差都约为±30°,与波浪入射角相近;随着入射波高的增加,非线性随之增强,更易诱导出不稳定运动,生成的沿岸流不稳定运动周期范围将增大;入射波周期对沿岸流不稳定运动的传播特性影响较小;坡度越陡越易诱导出超低频的不稳定运动。Abstract: The instabilities of longshore currents are the far infragravity band waves. The study of its propagation characteristics will help us to understand its influence on the evolution of coastal beach and the transport and migration of pollutants, fish eggs and other organisms. Based on the wavelet coherence spectrum, this paper analyzes the propagation characteristics of the unsteady motion under regular and random waves, and discusses the influence of the wave height, period and slope on it. The results show that the irregular wave is easier to induce the unsteady motion, and the positive or negative phase difference of the unsteady motion is about 30° in the case of irregular waves, which is similar to the incident angle of waves; with the increase of the incident wave height, nonlinear effects become stronger and the period range of the unsteady motion will be wider, that is to say, it is easier to induce the unsteady motion; the incident wave period has a little effect on the propagation; the steeper the slope is, the more likely it is to induce the instabilities of longshore currents.
-
Key words:
- longshore current /
- unsteady motion /
- propagation /
- wavelet coherence /
- phase lag
-
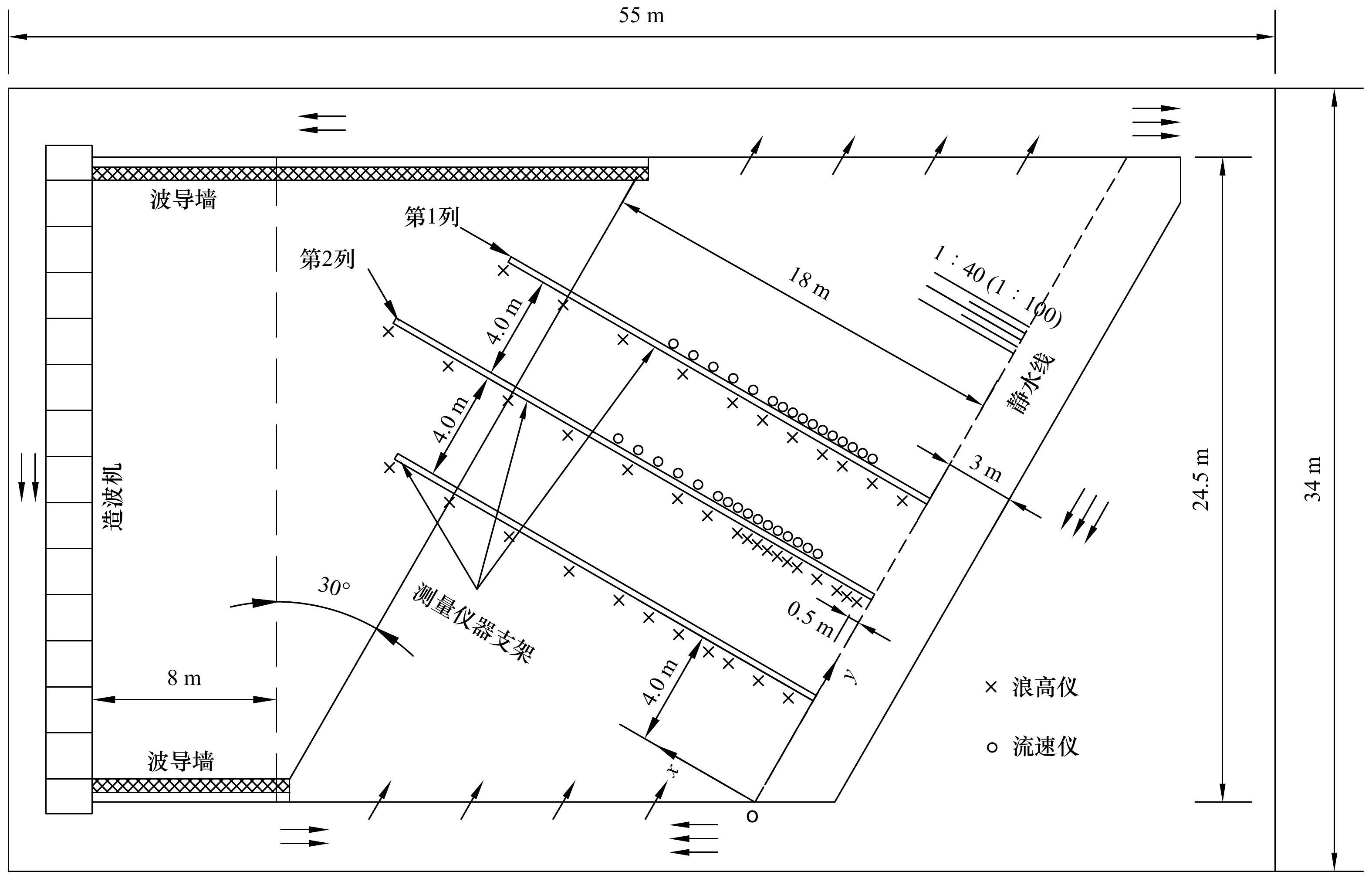
表 1 波况参数
Tab. 1 Wave parameters
入射波 波况 坡度 静水深/
cm入射
波高/cm入射波
周期/sx1/m xn/m 规则波 1 1∶40 45 5.0 1.0 2.5 2.0 3.0 2 1∶40 45 5.9 1.5 4.0 3.5 4.5 3 1∶40 45 10.5 1.5 5.0 4.5 5.5 4 1∶40 45 13.0 1.5 2.5 2.0 3.0 5 1∶40 45 5.2 2.0 4.0 3.5 4.5 随机波 6 1∶100 18 3.4 2.0 6.0 5.5 6.5 7 1∶40 45 3.6 1.0 2.5 2.0 3.0 8 1∶40 45 5.5 1.0 3.0 2.5 3.5 9 1∶40 45 7.8 1.0 4.0 3.5 4.5 10 1∶40 45 4.0 1.5 2.5 2.0 3.0 11 1∶40 45 3.7 2.0 3.0 2.5 3.5 -
[1] Shanks A L, Morgan S G, Macmahan J, et al. Persistent differences in horizontal gradients in phytoplankton concentration maintained by surf zone hydrodynamics[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 2018, 41(1): 158−176. doi: 10.1007/s12237-017-0278-2 [2] Bowen A J, Holman R A. Shear instabilities of the mean longshore current 1. Theory[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1989, 94(C12): 18023−18030. doi: 10.1029/JC094iC12p18023 [3] Özkan-Haller H T, Kirby J T. Nonlinear evolution of shear instabilities of the longshore current: A comparison of observations and computations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1999, 104(C11): 25953−25984. doi: 10.1029/1999JC900104 [4] Dodd N, Iranzo V, Caballería M. A subcritical instability of wave-driven alongshore currents[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2004, 109(C2): C02018. doi: 10.1029/2001JC00106 [5] Reniers A J H M, Battjes J A, Falqués A, et al. A laboratory study on the shear instability of longshore currents[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1997, 102(C4): 8597−8609. doi: 10.1029/96JC03863 [6] Noyes T J, Guza R T, Feddersen F, et al. Model-data comparisons of shear waves in the nearshore[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2005, 110(C5): C05019. doi: 10.1029/2004JC002541 [7] Ren Chunping, Zou Zhili, Qiu Dahong. Experimental study of the instabilities of alongshore currents on plane beaches[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2012, 59(1): 72−89. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2011.07.004 [8] 任春平, 蒋利君, 季海嘉. 沿岸流不稳定运动对边缘波影响的实验研究[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2015, 45(4): 423−433. doi: 10.1360/N092014-00028Ren Chunping, Jiang Lijun, Ji Haijia. A laboratory study of the effects of the instability of longshore currents on the edge waves[J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2015, 45(4): 423−433. doi: 10.1360/N092014-00028 [9] 沈良朵. 缓坡沿岸流不稳定性特征研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2015.Shen Liangduo. Study of the feature of longshore current and its instability on mild beach slope[D]. Daliang: Daliang University of Technology, 2015. [10] Ruiz-Merchán J, Otero L, Conde M, et al. Field observations of wave and current characteristics on a microtidal reflective beach[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2019, 35(6): 1164−1184. doi: 10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-18-00120.1 [11] Conde-Frias M, Otero L, Restrepo J C, et al. Experimental analysis of infragravity waves in two eroded microtidal beaches[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 36(5): 31−43. doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-1054-7 [12] Grinsted A, Moore J C, Jevrejeva S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series[J]. Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics, 2004, 11(5/6): 561−566. doi: 10.5194/npg-11-561-2004 [13] Wang Gang, Nguyena V T, Zheng Jinhai, et al. Disintegration of linear edge waves[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2013, 27(4): 557−562. doi: 10.1007/s13344-013-0047-3 [14] Reniers A J H M, Battjes J A. A laboratory study of longshore currents over barred and non-barred beaches[J]. Coastal Engineering, 1997, 30(1): 1−21. [15] Tang Jun, Lü Yigang, Shen Yongming, et al. Numerical study on influences of breakwater layout on coastal waves, wave-induced currents, sediment transport and beach morphological evolution[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2017, 141: 375−387. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.06.042 -




 下载:
下载: