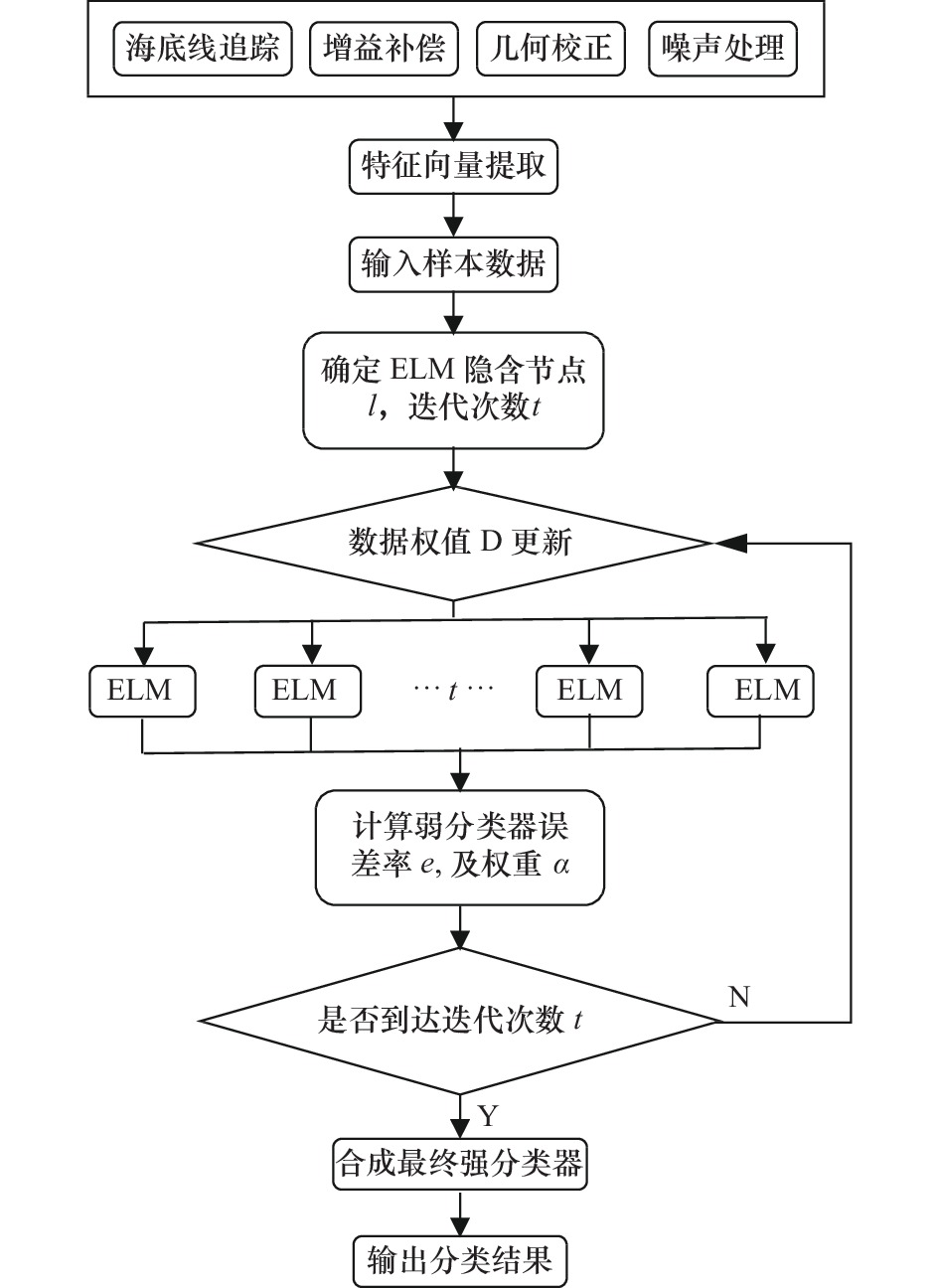
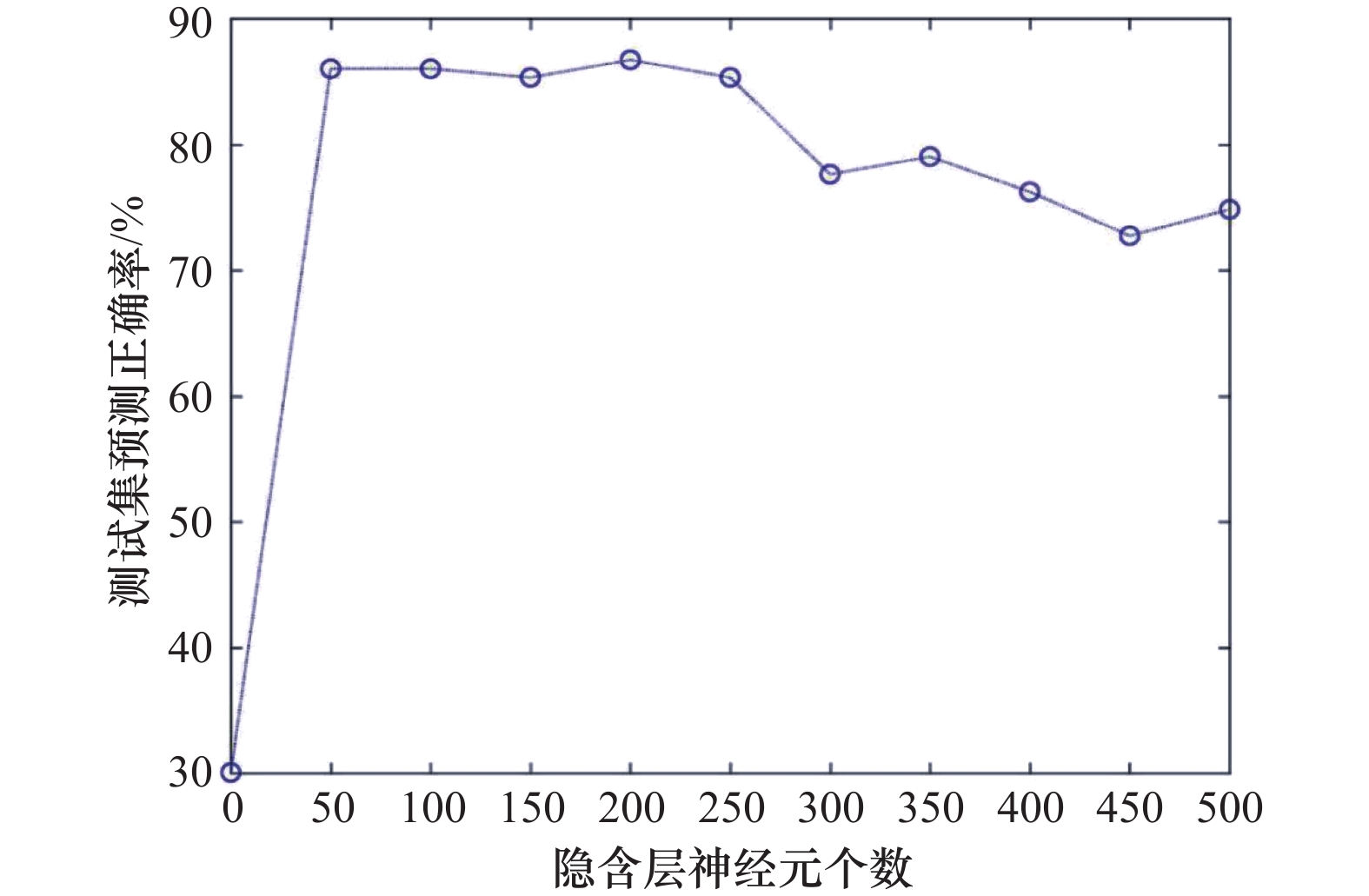
ELM-AdaBoost method of acoustic seabed sediment classification
-
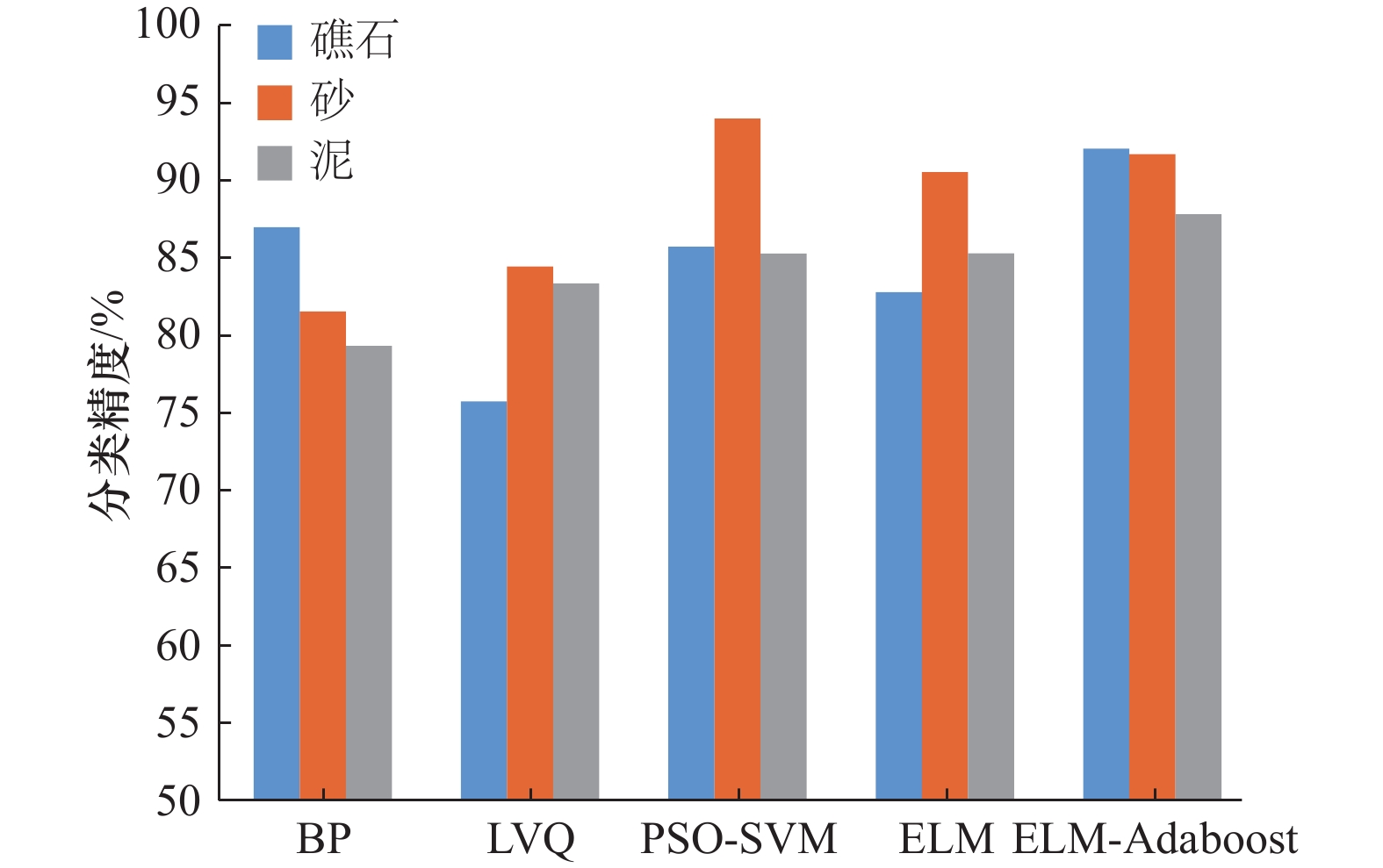
摘要: 基于自适应增强算法(AdaBoost)结合极限学习机(ELM),通过迭代、调整、优化ELM分类器之间的权值,从而构建了具有强鲁棒性、高精度的ELM-AdaBoost强分类器,增强了现有的ELM分类器的稳定性。以珠江口海区侧扫声呐图像为实验数据,对礁石、砂、泥3类典型底质进行分类识别,该方法的平均分类精度超过90%,优于单一ELM分类器的平均分类精度85.95%,也优于LVQ、BP等传统分类器,且在分类所耗时间上也远少于传统分类器。实验结果表明,本文构建的ELM-AdaBoost方法可有效应用于海底声学底质分类,可满足实时底质分类的需求。Abstract: Based on the adaptive boosting algorithm (AdaBoost) combined with the extreme learning machine (ELM), the strong classifier of ELM-AdaBoost with strong robustness and high precision is thus constructed by iterating, adjusting, and optimizing the weights between each ELM classifier. ELM-AdaBoost method can enhance the stability of the existing ELM classifier. In this paper, the data collected by side scan sonar in the Zhujiang River Estuary was used to classify and identify three types of typical sediments as rock, sand, and mud. The average classification accuracy of new method exceeds 90%, which is better than the average classification accuracy of a single ELM classifier of 85.95%. It is also superior to other traditional classifiers (i.e. LVQ and BP) and it takes much less time to classify than traditional classifiers. The experimental result shows that the proposed ELM-AdaBoost method can be effectively applied to the classification and identification of seabed sediment and can meet the needs of real-time classification of seabed sediment.
-
表 1 礁石、砂和泥3种底质的特征向量
Tab. 1 Characteristic vectors of three types of seabed sediment of rock, sand, and mud
均值 标准差 对比度 相关系数 能量 熵 礁石 0.765 7 0.153 4 1.621 2 0.326 1 0.121 6 0.616 4 0.724 2 0.180 2 3.750 0 0.032 8 0.087 6 0.577 1 0.726 6 0.142 0 1.681 8 0.358 7 0.097 6 0.603 5 0.675 0 0.155 9 2.659 1 0.194 7 0.062 1 0.574 6 0.562 7 0.230 5 6.053 0 0.127 9 0.040 3 0.472 6 砂 0.848 8 0.104 7 1.015 1 0.235 8 0.159 9 0.694 7 0.812 5 0.112 1 1.659 1 0.066 4 0.103 1 0.615 4 0.768 6 0.127 6 2.560 6 –0.089 4 0.097 7 0.570 8 0.760 8 0.114 5 1.712 1 0.023 6 0.107 1 0.625 6 0.798 6 0.109 1 1.825 7 –0.164 6 0.118 0 0.602 6 泥 0.535 9 0.298 0 3.257 6 0.702 6 0.033 6 0.587 0 0.279 7 0.252 5 3.151 5 0.604 3 0.106 6 0.664 4 0.408 7 0.302 3 4.204 5 0.572 0 0.035 2 0.563 0 0.512 7 0.288 2 3.454 5 0.654 4 0.039 4 0.586 9 0.630 8 0.220 0 2.598 5 0.598 7 0.045 6 0.597 9 表 2 5种分类器的分类性能对比表
Tab. 2 Comparison of classification performance of five classifiers
分类器 训练样本平均精度/% 底质类型 测试平均精度/% 所有测试样本平均精度/% 完成分类所耗平均时间/s BP 89.80 礁石 86.88 82.52 5 砂 81.44 泥 79.23 LVQ 76.83 礁石 75.66 81.09 298 砂 84.35 泥 83.26 PSO-SVM 93.87 礁石 85.62 88.22 447 砂 93.85 泥 85.18 ELM 93.68 礁石 82.70 85.95 0.11 砂 90.41 泥 85.19 ELM -AdaBoost 93.56 礁石 91.92 90.40 0.37 砂 91.58 泥 87.70 -
[1] 周兴华, 陈永奇. 多波束声纳数据的底质分类[C]// 我国专属经济区和大陆架勘测研究专项学术交流会论文集. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2002: 1-7.Zhou Xinghua, Chen Yongqi. A review of seafloor sediment classification using multibeam sonar data[C]// Collected Works of Exploration in Exclusive Economic Zone and Shelf Area of China. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2002: 1−7. [2] 吴自银, 郑玉龙, 初凤友, 等. 海底浅表层信息声探测技术研究现状及发展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2005, 20(11): 1210−1217. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2005.11.007Wu Ziyin, Zheng Yulong, Chu Fengyou, et al. Research status and prospect of sonar-detecting techniques near submarine[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2005, 20(11): 1210−1217. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2005.11.007 [3] Alexandrou D, Pantzartzis D. Seafloor classification with neural networks[C]//Conference Proceedings on Engineering in the Ocean Environment. Washington: IEEE, 1990: 24−26. [4] 阳凡林, 刘经南, 赵建虎, 等. 基于遗传算法的BP网络实现海底底质分类[J]. 测绘科学, 2006, 31(2): 111−114. doi: 10.3771/j.issn.1009-2307.2006.02.038Yang Fanlin, Liu Jingnan, Zhao Jianhu, et al. Seabed classification using BP neural network based on GA[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2006, 31(2): 111−114. doi: 10.3771/j.issn.1009-2307.2006.02.038 [5] 唐秋华, 刘保华, 陈永奇, 等. 基于改进BP神经网络的海底底质分类[J]. 海洋测绘, 2009, 29(5): 40−43,56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2009.05.012Tang Qiuhua, Liu Baohua, Chen Yongqi, et al. Seabed classification with improved BP neural network[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2009, 29(5): 40−43,56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2009.05.012 [6] 陈佳兵, 吴自银, 赵荻能, 等. 基于粒子群优化算法的PSO-BP海底声学底质分类方法[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(9): 51−57.Chen Jiabing, Wu Ziyin, Zhao Dineng, et al. Back propagation neural network classification of sediment seabed acoustic sonar images based on particle swarm optimization algorithms[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(9): 51−57. [7] 贺清碧. BP神经网络及应用研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通学院, 2004.He Qingbi. Back propagation neural network and applications[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2004. [8] Chakraborty B, Kodagali V, Baracho J. Sea-floor classification using multibeam echo-sounding angular backscatter data: A real-time approach employing hybrid neural network architecture[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2003, 28(1): 121−128. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2002.808211 [9] 唐秋华, 周兴华, 丁继胜, 等. 学习向量量化神经网络在多波束底质分类中的应用研究[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2006, 31(3): 229−232.Tang Qiuhua, Zhou Xinghua, Ding Jisheng, et al. Seafloor classification from multibeam backscatter data using learning vector quantization neural network[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2006, 31(3): 229−232. [10] 熊明宽, 吴白银, 李守军, 等. 基于SVM的海底声纳图像底质识别[J]. 海洋通报, 2012, 31(4): 409−414.Xiong Mingkuan, Wu Ziyin, Li Shoujun, et al. Seafloor sonar sediment image recognition with the Support Vector Machine[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2012, 31(4): 409−414. [11] 郭军, 马金凤. 基于粒子群优化算法的SVM神经网络在海底底质分类中的应用[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2012, 35(12): 66−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2012.12.021Guo Jun, Ma Jinfeng. Support vector machine neural network based on particle swarm optimization in seafloor classification[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2012, 35(12): 66−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2012.12.021 [12] 马飞虎, 鄂栋臣, 赵建虎, 等. 基于ISODATA算法的海底底质分类[J]. 测绘信息与工程, 2008, 33(6): 43−45.Ma Feihu, E Dongchen, Zhao Jianhu, et al. Seabed classification based on ISODATA algorithm[J]. Journal of Geomatics, 2008, 33(6): 43−45. [13] 吕良, 金绍华, 边刚, 等. K-均值聚类算法在多波束底质分类中的应用[J]. 海洋测绘, 2018, 38(3): 64−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2018.03.016Lü Liang, Jin Shaohua, Bian Gang, et al. The application of K-means clustering analysis algorithm in multibeam seafloor classification[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2018, 38(3): 64−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2018.03.016 [14] Marsh I, Brown C. Neural network classification of multibeam backscatter and bathymetry data from Stanton Bank (Area IV)[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2009, 70(10): 1269−1276. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2008.07.012 [15] 唐秋华, 刘保华, 陈永奇, 等. 基于自组织神经网络的声学底质分类研究[J]. 声学技术, 2007, 26(3): 380−384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3630.2007.03.006Tang Qiuhua, Liu Baohua, Chen Yongqi, et al. Acoustic seafloor classification using self organizing map neural network[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2007, 26(3): 380−384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3630.2007.03.006 [16] 郭军, 马金凤. 基于K-L变换的自组织竞争神经网络在海底底质分类中的应用[J]. 测绘工程, 2013, 22(1): 51−54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7949.2013.01.014Guo Jun, Ma Jinfeng. Self-organization competition neural network based on K-L transform in seafloor classification[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 2013, 22(1): 51−54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7949.2013.01.014 [17] 赵芳, 索岩, 彭子然. 基于蚁群优化与独立特征集的遥感图像实时分类算法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2020, 37(2): 573−577.Zhao Fang, Suo Yan, Peng Ziran. Real-time classification algorithm of remote sensing images based on ant colony optimization algorithm and independent feature sets[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2020, 37(2): 573−577. [18] 吴自银, 阳凡林, 罗孝文, 等. 高分辨率海底地形地貌——探测与处理理论技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017.Wu Ziyin, Yang Fanlin, Luo Xiaowen, et al. High-Resolution Submarine Topography−−Theory and Technology for Surveying and Post-Processing[M]. Beijing: Science Press , 2017. [19] Ji Xue, Yang Bisheng, Tang Qiuhua. Acoustic seabed classification based on multibeam echosounder backscatter data using the PSO-BP-AdaBoost Algorithm: A case study from Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2021, 46(2): 509−519. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2020.2989853 [20] 边冰, 赵明政. 基于深度极限学习机的水质预测研究[J]. 华北理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 42(1): 51−57.Bian Bing, Zhao Mingzheng. Study on water quality prediction based on deep extreme learning machine[J]. Journal of North China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 42(1): 51−57. [21] 吴军, 王士同, 赵鑫. 正负模糊规则系统、极限学习机与图像分类[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2011, 16(8): 1408−1417. doi: 10.11834/jig.100621Wu Jun, Wang Shitong, Zhao Xin. Positive and negative fuzzy rule system, extreme learning machine and image classification[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2011, 16(8): 1408−1417. doi: 10.11834/jig.100621 [22] Huang Guangbin, Zhu Qinyu, Siew C K. Extreme learning machine: A new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks[C]//2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Budapest: IEEE, 2005: 25−29. [23] Freund Y, Schapire R E. A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting[J]. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 1995, 55(1): 119−139. [24] 唐秋华, 周兴华, 丁继胜, 等. 多波束反向散射强度数据处理研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2006, 28(2): 51−55.Tang Qiuhua, Zhou Xinghua, Ding Jisheng, et al. Study on processing of multibeam backscatter data[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2006, 28(2): 51−55. [25] 李庆武, 霍冠英, 周妍. 声呐图像处理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015.Li Qingwu, Huo Guanying, Zhou Yan. Sonar Image Processing[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015. [26] 刘丽, 匡纲要. 图像纹理特征提取方法综述[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2009, 14(4): 622−635. doi: 10.11834/jig.20090409Liu Li, Kuang Gangyao. Overview of image textural feature extraction methods[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2009, 14(4): 622−635. doi: 10.11834/jig.20090409 [27] Haralick R M, Shanmugam K, Dinstein I. Textural features for image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1973, SMC-3(6): 610−621. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1973.4309314 [28] Wu Ziyin, Milliman J D, Zhao Dineng, et al. Geomorphologic changes in the lower Pearl River Delta, 1850−2015, largely due to human activity[J]. Geomorphology, 2018, 314: 42−54. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.05.001 [29] Wu Ziyin, Saito Y, Zhao Dineng, et al. Impact of human activities on subaqueous topographic change in Lingding Bay of the Pearl River Estuary, China during 1955−2013[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 37742. doi: 10.1038/srep37742 [30] Wu Ziyin, Milliman J D, Zhao Dineng, et al. Recent geomorphic change in LingDing Bay, China, in response to economic and urban growth on the Pearl River Delta, Southern China[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2014, 123: 1−12. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2014.10.009 [31] 熊明宽, 吴自银, 李守军, 等. 基于遗传小波神经网络的海底声学底质识别分类[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(5): 90−97.Xiong Mingkuan, Wu Ziyin, Li Shoujun, et al. Wavelet neural network identification and classification of sediment seabed sonar images based on genetic algorithms[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(5): 90−97. -




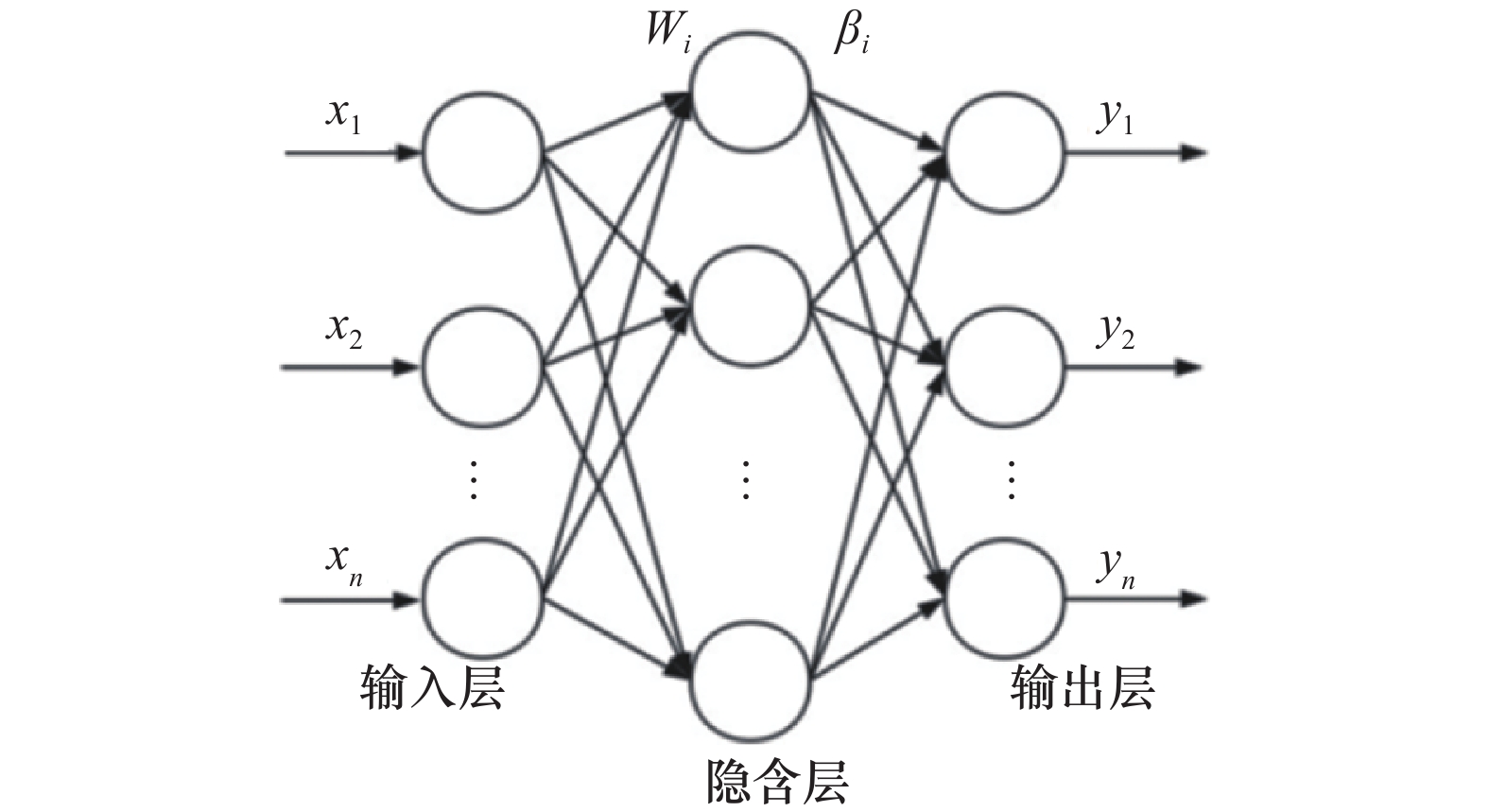
 下载:
下载: