Rheological characteristics and its influencing factors of dense cohesive sediments in the Huanghe River subaqueous delta
-
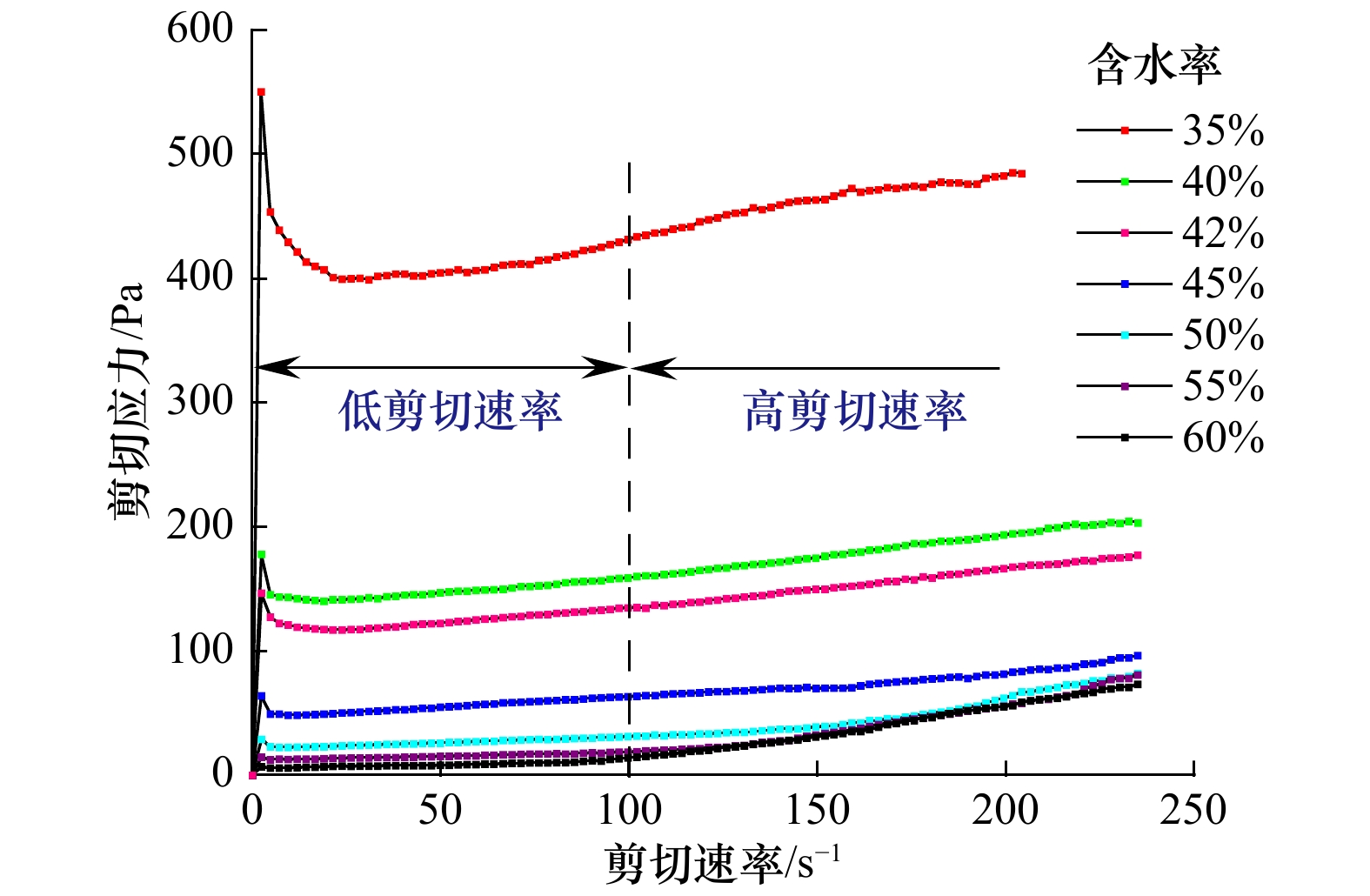
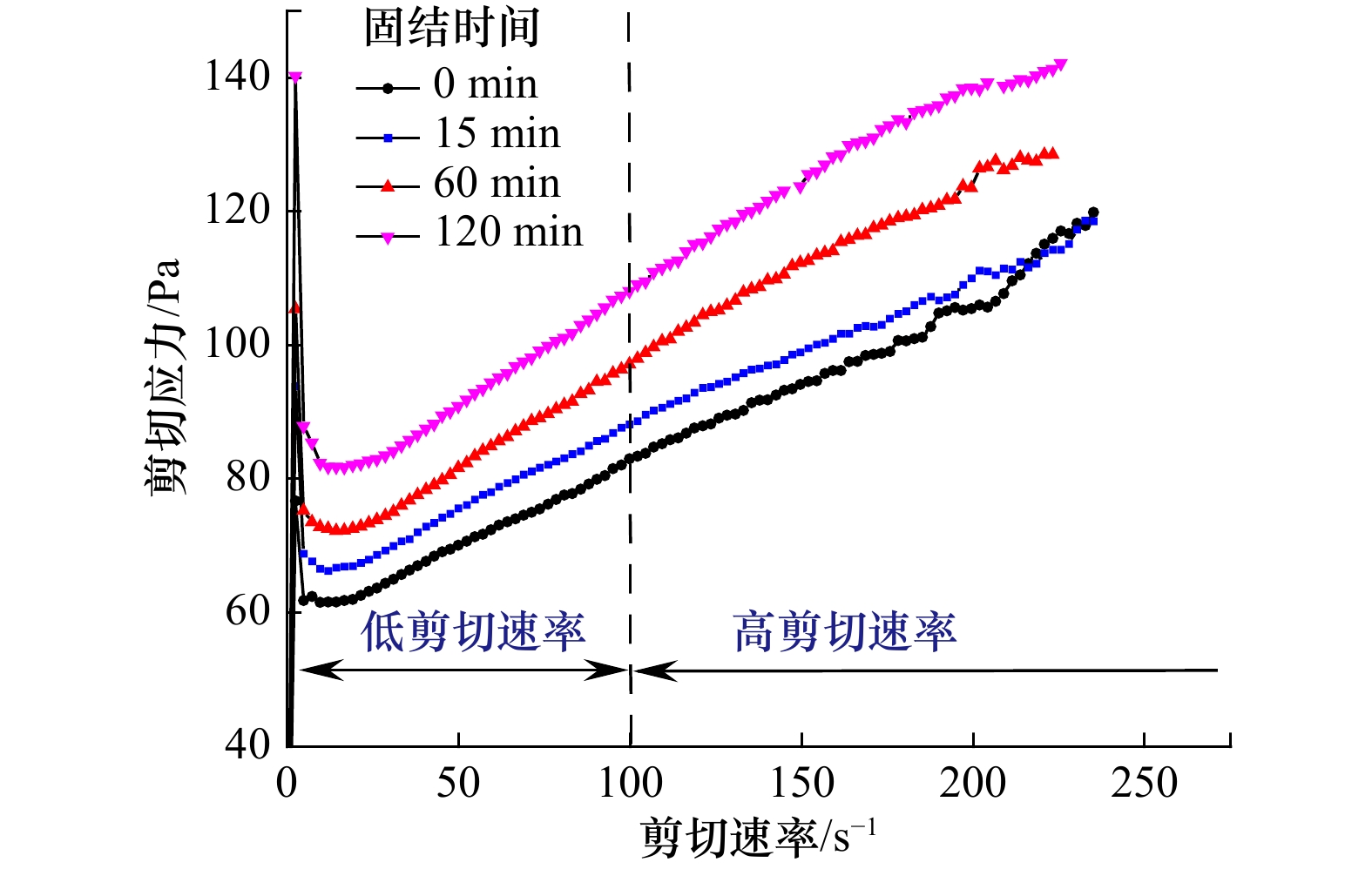
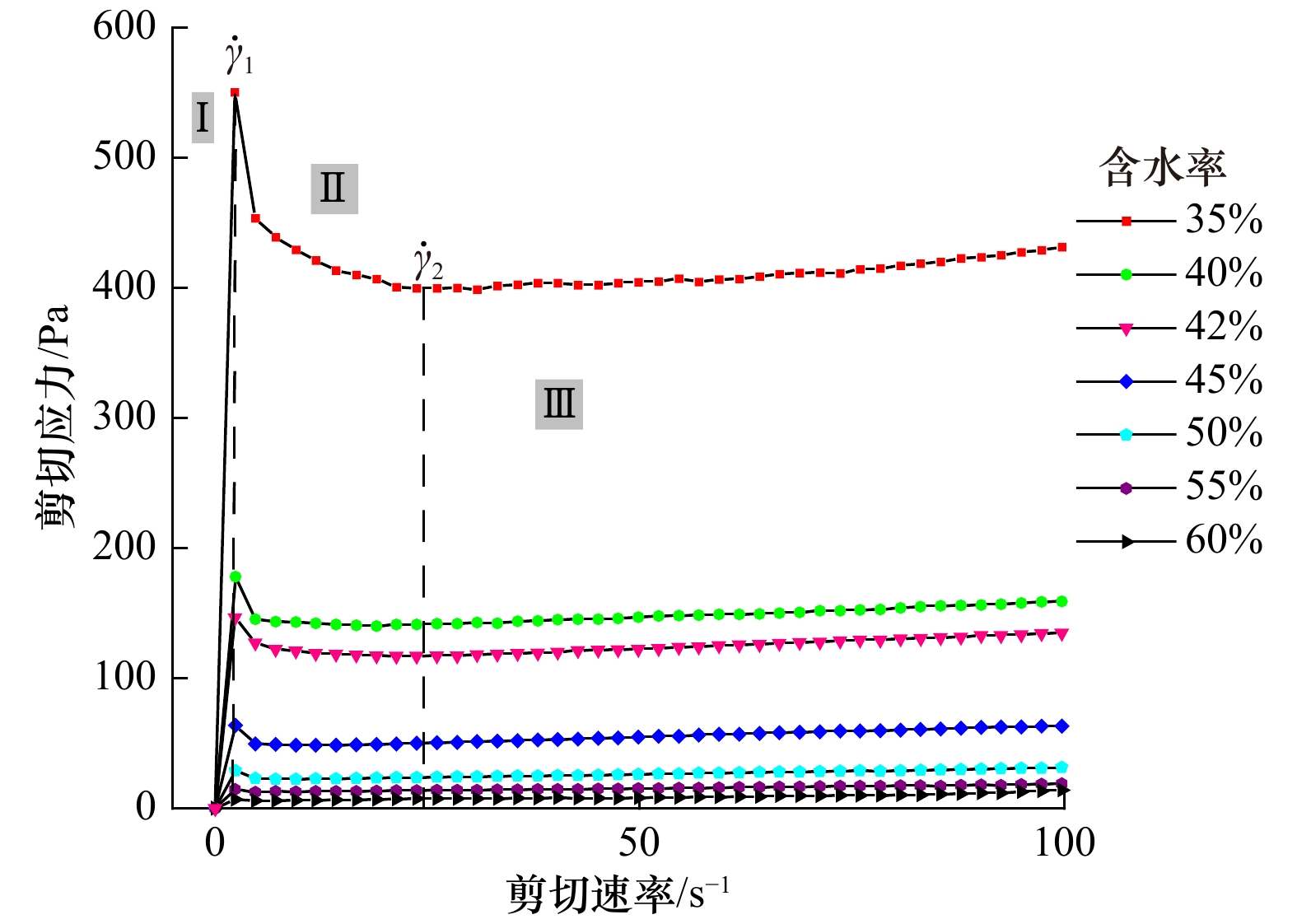
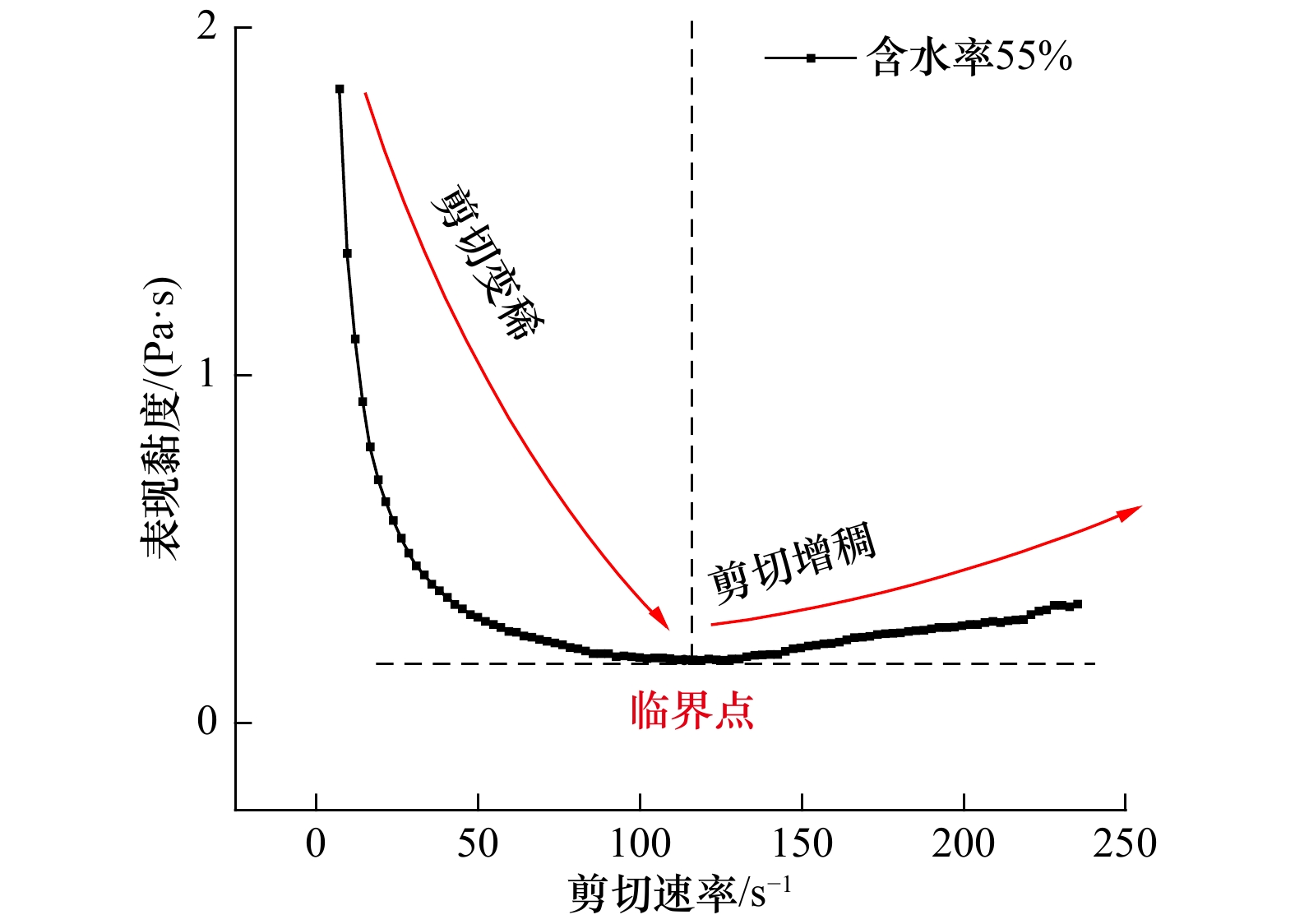
摘要: 黏性泥沙在黄河水下三角洲广泛分布,其在外部载荷作用下易引发泥沙淤积、冲刷、海床流化等问题,对港口、航道、海底管线等工程设施构成巨大威胁。利用黄河水下三角洲埕岛海域所取海底表层沉积物,制备不同固结时间和不同含水率的高浓度黏性泥沙样品。采用R/S流变仪,对所制备高浓度黏性泥沙样品进行全剪切速率下的流变试验,分析黄河水下三角洲高浓度黏性泥沙流变特性及含水率和固结时间对流变特性的影响。结果表明,高浓度黏性泥沙在剪切荷载作用下流化失稳,发生相态转化;屈服应力在固结120 min后增加了35%;含水率50%以上高浓度黏性泥沙在高剪切速率下表现出剪切增稠行为,且随含水率增加剪切增稠行为越明显;Power模型适用于含水率大于50%的高浓度黏性泥沙在高剪切速率下的流变行为。本研究可为海底黏性泥沙运动过程数值模拟与海底重力流等灾害预测提供参考。Abstract: Cohesive sediments are widely distributed in the subaqueous delta of the Huanghe River and can easily cause problems such as sedimentation, erosion and sea-bed fluidization under the action of external load, which poses a great threat to the engineering facilities such as ports, waterways and submarine pipelines. Samples of cohesive sediment with different consolidation times and different water contents were prepared by using the undisturbed cohesive sediment taken from the fluid mud development area of the Huanghe River subaqueous delta. The rheological tests were carried out under the mode of full shear rate with R/S rheometer to analyze the rheological characteristics of cohesive sediment in the Huanghe River subaqueous delta and the effects of water content and consolidation time on the rheological characteristics. The results show that the cohesive sediment flows and becomes unstable under the shear load, and the phase changes. The yield stress increased by 35% after being consolidated for 120 min. The shear thickening behavior of the cohesive sediment with 50% water content at a high shear rate was more obvious with the increase of water content. Power model is applicable to the rheological behavior of the cohesive sediment with a water content greater than 50% at high shear rate. This study can provide a reference for the numerical simulation of subaqueous cohesive sediment and the prediction of subaqueous gravity flow.
-
表 1 原状泥沙基本物理性质
Tab. 1 Physical properties of natural sediments
取样点 含水率/
%塑限/
%液限/
%塑性
指数含水率/
液限粉粒
含量/%黏粒
含量/%Q1 47.42 19.59 29.89 10.30 1.59 71.0 27.9 Q2 42.30 20.17 30.44 10.27 1.39 71.7 26.9 Q3 34.81 19.57 30.83 11.26 1.13 72.6 23.4 Q4 48.08 18.64 33.11 4.47 1.45 74.3 22.1 Q5 44.59 22.1 30.74 8.64 1.45 72.1 27.1 Q6 42.80 17.21 31.23 14.02 1.37 74.3 21.6 表 2 R/S流变仪基本参数
Tab. 2 Basic parameters of R/S rheometer
精度/% 可测量扭矩/ N·m 角分辨率/mrad 可调转速/(r·min−1) 可测剪切强度/Pa 转子型号 1 0.05~50 0.8 0.7~1 000 0~1 706 V40-20 表 3 样品信息表
Tab. 3 Information of samples
试样编号 密度/(g·cm−3) 含水率/% 固结时间/min 1 1.52 35 5 2 1.51 40 5 3 1.50 42 5 4 1.47 45 0, 15, 60, 120 5 1.44 50 5 6 1.40 55 5 7 1.37 60 5 表 4 各固结时间Bingham模型参数
Tab. 4 Bingham model parameters at different consolidation times
固结时间/min τy/Pa η0 R2 0 57.333 0.249 7 0.994 6 15 64.326 0.258 8 0.996 1 60 68.119 0.284 8 0.995 9 120 77.245 0.302 6 0.986 1 表 5 各含水率高浓度黏性泥沙流变模型参数
Tab. 5 Parameters of dense cohesive sediment rheological model
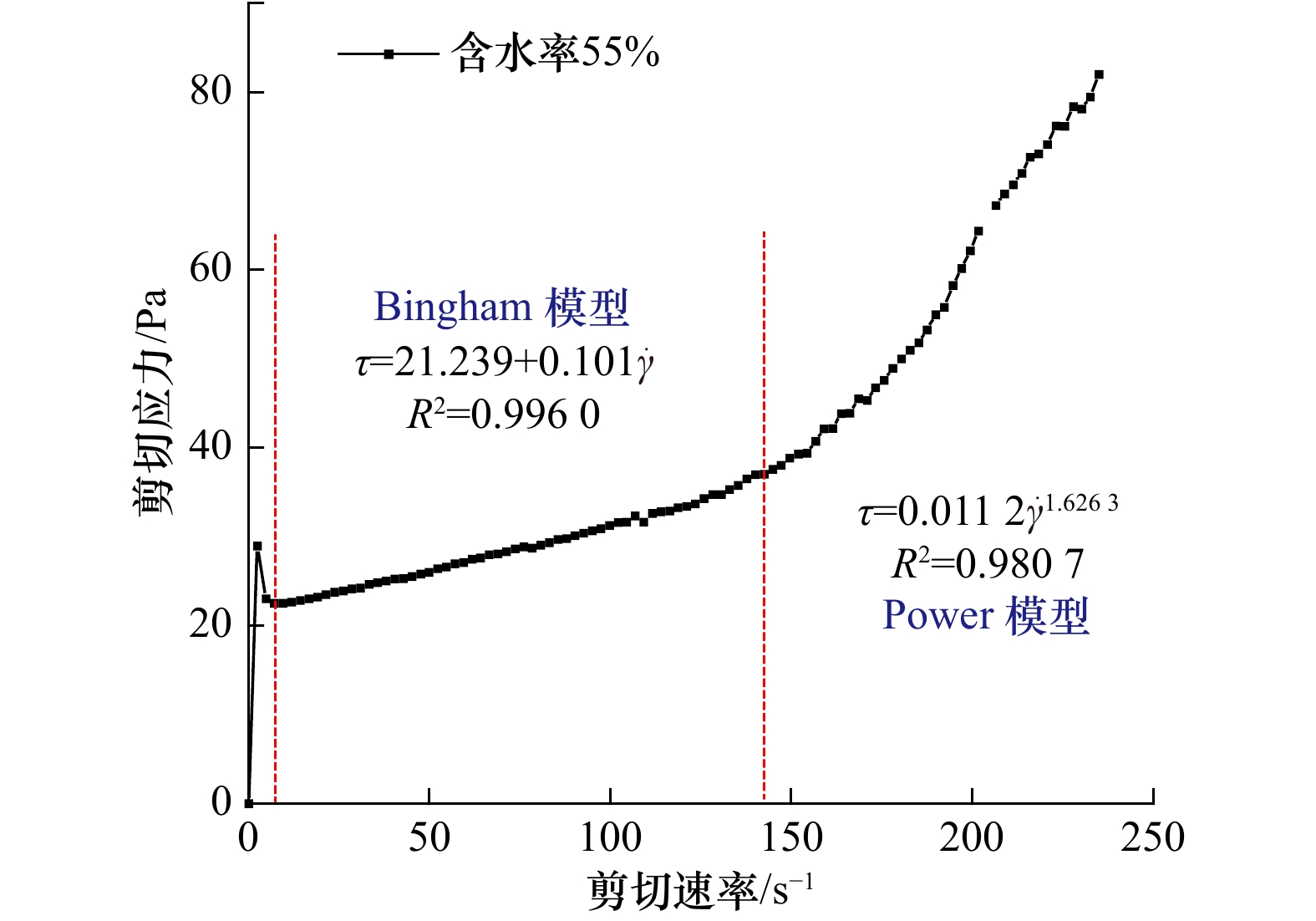
含水率/% Bingham模型 Power模型 τy η0 R2 K n R2 35 380 0.531 0.96 − − − 40 130 0.313 0.99 − − − 42 107 0.29 0.99 − − − 45 44 0.190 0.98 − − − 低剪切速率 高剪切速率 50 21 0.101 0.99 0.011 2 1.62 0.98 55 11 0.075 0.96 0.001 7 1.970 0.99 60 5 0.056 0.97 0.001 6 1.973 0.99 注:−表示无数据。 -
[1] 孙连成. 淤泥质海岸天津港工程泥沙治理与功效[J]. 水运工程, 2009(4): 10−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2009.04.003Sun Liancheng. Tianjin Port engineering sediment treatment and efficacy on silt coast[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 2009(4): 10−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2009.04.003 [2] 任美锷, 张忍顺, 杨巨海, 等. 风暴潮对淤泥质海岸的影响——以江苏省淤泥质海岸为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1983, 3(4): 1−24.Ren Mei’e, Zhang Renshun, Yang Juhai, et al. The influence of storm tide on mud plain coast—with special reference to Jiangsu Province[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1983, 3(4): 1−24. [3] 曹祖德. 浮泥特性研究进展[J]. 水道港口, 1992(1): 34−40.Cao Zude. Advances in cohesive sediment research[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 1992(1): 34−40. [4] 贾永刚, 单红仙. 黄河口海底斜坡不稳定性调查研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2000, 11(1): 1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2000.01.001Jia Yonggang, Shan Hongxian. Investigation and study of slope unstability of subaqueous delta of modern Yellow River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2000, 11(1): 1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2000.01.001 [5] 李广雪, 庄克琳, 姜玉池. 黄河三角洲沉积体的工程不稳定性[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(2): 21−26.Li Guangxue, Zhuang Kelin, Jiang Yuchi. Engineering instability of the deposition bodies in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20(2): 21−26. [6] 文明征, 王振豪, 张博文, 等. 黄河水下三角洲浮泥层分布与扰动地层调查研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2018, 26(S1): 677−683.Wen Mingzheng, Wang Zhenhao, Zhang Bowen, et al. Survey on the distribution of fluid mud and disturbed strata on subaqueous Yellow River Delta[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(S1): 677−683. [7] 胡正红, 张婧, 刘兴年, 等. 泥石流浆体流变特性影响因素试验研究[J]. 水力发电学报, 2014, 33(2): 131−136.Hu Zhenghong, Zhang Jing, Liu Xingnian, et al. Experimental study on rheological properties factors of debris flow slurry[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2014, 33(2): 131−136. [8] 戴志军, 朱文武, 李为华, 等. 近期长江口北槽河道浮泥变化及影响因素研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2005(1): 49−54, 74.Dai Zhijun, Zhu Wenwu, Li Weihua, et al. Research on recent changes of fluid mud and its impacted factors in the north passage of the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2005(1): 49−54, 74. [9] 许宝华, 王真祥. 象山港进港航道外干门浅段试挖槽浮泥观测研究[J]. 人民长江, 2009, 40(22): 67−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2009.22.024Xu Baohua, Wang Zhenxiang. Observation and research on floating mud in trial excavation section of main entrance channel of Xiangshan Port[J]. Yangtze River, 2009, 40(22): 67−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2009.22.024 [10] Yang W Y, Tan S K, Wang H K, et al. Rheological properties of bed sediments subjected to shear and vibration loads[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 2013, 140(1): 109−113. [11] Huang Zhenhua, Aode H. A laboratory study of rheological properties of mudflows in Hangzhou Bay, China[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2009, 24(4): 410−424. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6279(10)60014-5 [12] Coussot P, Piau J M. On the behavior of fine mud suspensions[J]. Rheologica Acta, 1994, 33(3): 175−184. doi: 10.1007/BF00437302 [13] 王梦寒, 王宪业, 陈思明, 等. 黏性泥沙的物理特性与起动应力的流变学分析[J]. 泥沙研究, 2018, 43(6): 8−14.Wang Menghan, Wang Xianye, Chen Siming, et al. Influences of physical properties of cohesive sediment on threshold shear stress based on rheological method[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2018, 43(6): 8−14. [14] 郭兴森, 年廷凯, 范宁, 等. 低温环境下南海海底泥流的流变试验及模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(1): 161−167.Guo Xingsen, Nian Tingkai, Fan Ning, et al. Rheological tests and model for submarine mud flows in South China Sea under low temperatures[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(1): 161−167. [15] 呼和敖德, 黄振华, 张袁备, 等. 连云港淤泥流变特性研究[J]. 力学与实践, 1994, 16(1): 21−24.Hu Heaode, Huang Zhenhua, Zhang Yuanbei, et al. Study on rheological characteristics of silt in Lianyungang[J]. Mechanics in Engineering, 1994, 16(1): 21−24. [16] 练继建, 戴丽荣, 俞波. 淤泥的几种流变模式[J]. 海河水利, 1997(4): 6−11.Lian Jijian, Dai Lirong, Yu Bo. Flow patterns of silting mud[J]. Haihe Water Resources, 1997(4): 6−11. [17] 王裕宜, 詹钱登, 严璧玉. 泥石流体的流变特性与运移特征[M]. 长沙: 湖南科学技术出版社, 2014.Wang Yuyi, Zhan Qiandeng, Yan Biyu. Debris-flow Rheology and Movement[M]. Changsha: Hunan Science & Technology Press, 2014. [18] 冯秀丽, 周松望, 林霖, 等. 现代黄河三角洲粉土触变性研究及其应用[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2004, 34(6): 1053−1056.Feng Xiuli, Zhou Songwang, Lin Lin, et al. The Thixotropy of silt in Huanghe Delta[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2004, 34(6): 1053−1056. [19] 刘涛, 张美鑫, 崔逢. 循环荷载下粉土液化流动特性拖球试验研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(3): 115−121.Liu Tao, Zhang Meixin, Cui Feng. Dragging ball test on flow characteristics of liquefied silt under cyclic loading[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(3): 115−121. [20] 刘涛, 崔逢, 张美鑫. 波浪作用下液化粉土流动特性拖球试验研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(3): 123−130.Liu Tao, Cui Feng, Zhang Meixin. Dragging ball test on flow characteristics of liquefied silt under wave loading[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(3): 123−130. [21] Einsele G. Deep-reaching liquefaction potential of marine slope sediments as a prerequisite for gravity mass flows? (Results from the DSDP)[J]. Marine Geology, 1990, 91(4): 267−279. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(90)90049-P [22] Whitehouse R, Soulsby R, Roberts W, et al. Dynamics of estuarine muds: A manual for practical applications[M]. London: Institution of Civil Engineers, 2000. [23] 杨秀娟, 贾永刚. 黄河口入海泥沙沉积固结过程长期现场观测研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(4): 671−678.Yang Xiujuan, Jia Yonggang. Long-term field observation of sediment consolidation process in Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(4): 671−678. [24] 杨闻宇. 剪切载荷作用下高浓度粘性泥沙流变特性的实验研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2014.Yang Wenyu. Experimental study on the rheological properties of dense cohesive sediments under shear loadings[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2014. -





 下载:
下载: