Submarine geomorphologic features and genetic mechanism in the Xuande atoll, Xisha Islands
-
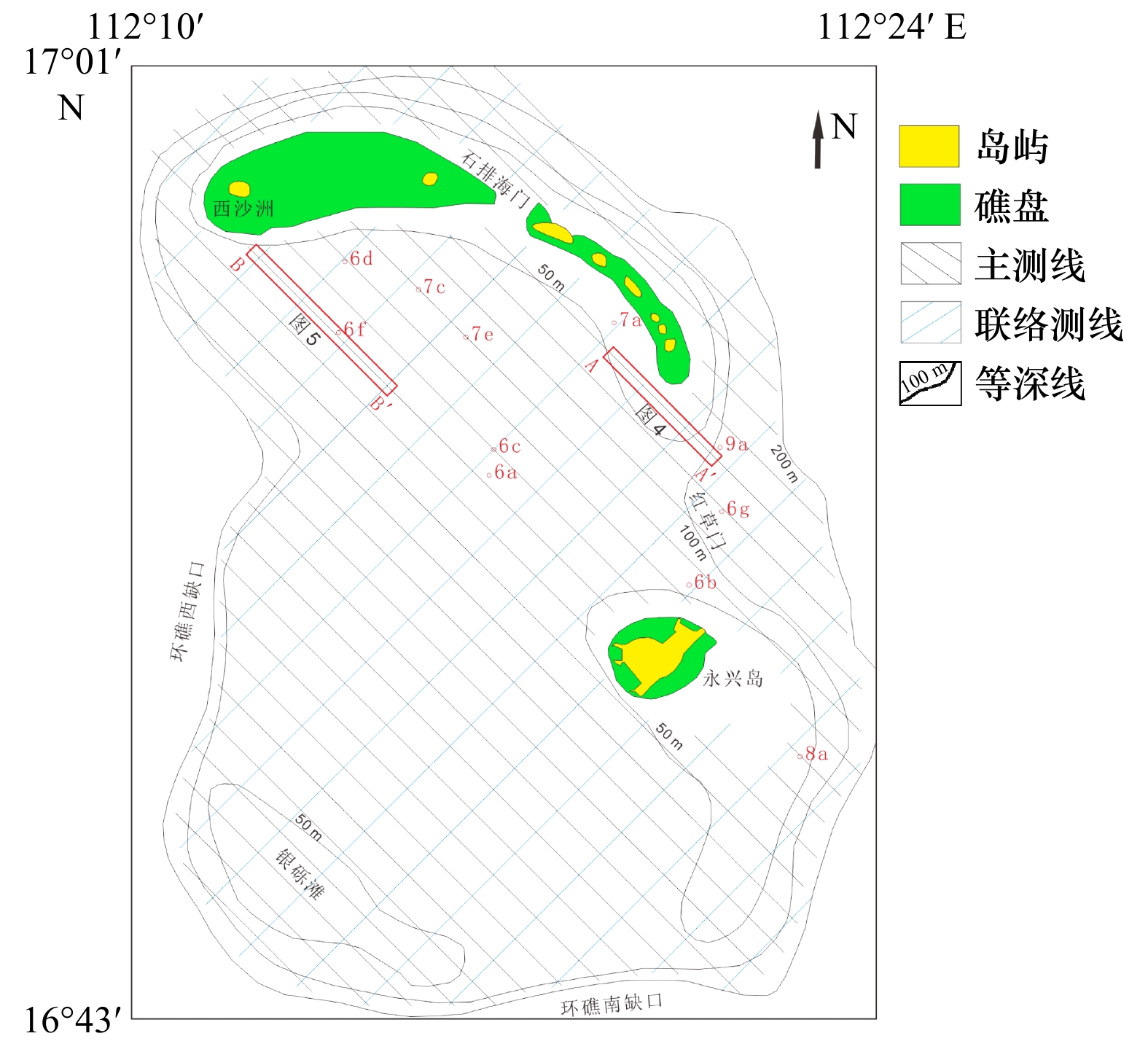
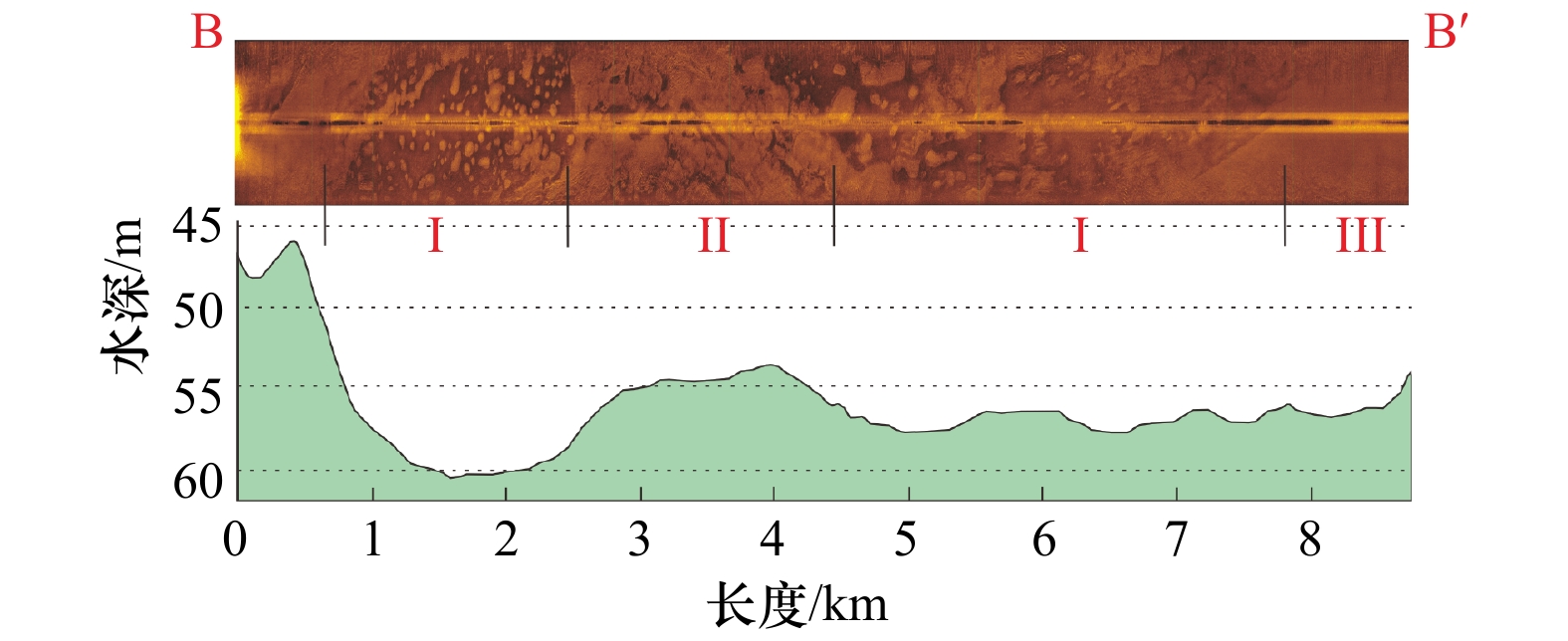
摘要: 海底地形地貌及类型分布特征对指示区域地质构造影响、海平面升降、海洋水动力等有重要意义。本文通过侧扫声呐、单波束测深、表层沉积物取样等方法,分析了西沙群岛宣德环礁精细水下地貌组合特征,并探讨了其成因机制。结果表明:(1)宣德环礁为残缺型环礁类型,中部为潟湖沉积,礁盘之间形成西沙洲口门、“红草门”、环礁西缺口和环礁南缺口等4处水深超过60 m的深水口门,并首次识别了西沙洲口门;(2)宣德环礁水下地貌类型可划分为3级11类地貌类型。研究区的沙波及槽沟等动力地貌单元显示,宣德环礁浅水区海底特征地貌由盛行季风和波浪场所控制,深水口门形成的潮汐通道水体为塑造宣德环礁潟湖区动力地貌的主要因素。研究区东南部向海坡存在6级水下阶地,通过对比南海珊瑚礁阶地特征,宣德环礁向海坡阶地成因很可能是全球海平面变化和地壳沉降的共同作用。Abstract: The submarine topographic features and distribution types of the Xuande atoll in the Xisha Islands have important indications for the influence of regional geological structure, sea level rise and fall, and ocean hydrodynamics. In order to study the submarine topography and geomorphology of the Xuande atoll, we detailed survey in the Xuande atoll of the Xisha Islands, including side scan sonar, single-beam sounding, and surface sediment sampling. The results show that: (1) Xuande atoll is a type of incomplete atoll, with lagoon deposits in the middle, and four water channels with a water depth of about 60 m had been divided, namely, the gate of the Xishazhou at the northwest of the atoll, the “Red Grass Gate” of the Nanshazhou-Yongxing, the gap on the west side of the atoll, and the gap on the south side of the atoll; (2) according to the geomorphic features, the underwater geomorphic types of the Xuande atoll are divided into 3 grades and 11 types of grades classification systems. The dynamic geomorphology units such as sand waves and grooves in the study area show that the submarine features in the shallow water area of Xuande atoll are controlled by prevailing monsoons and wave sites. The tidal channel water body formed by the deep water entrance is the main factor shaping the dynamic geomorphology of the Xuande atoll lagoon area. There are six levels of underwater terraces on the seaward slope in the southeastern part of the study area. By comparing the characteristics of the coral reef terraces in the South China Sea, the genesis of the seaward slope terraces on the Xuande atoll is likely to be a combination of global sea level changes and crustal subsidence.
-
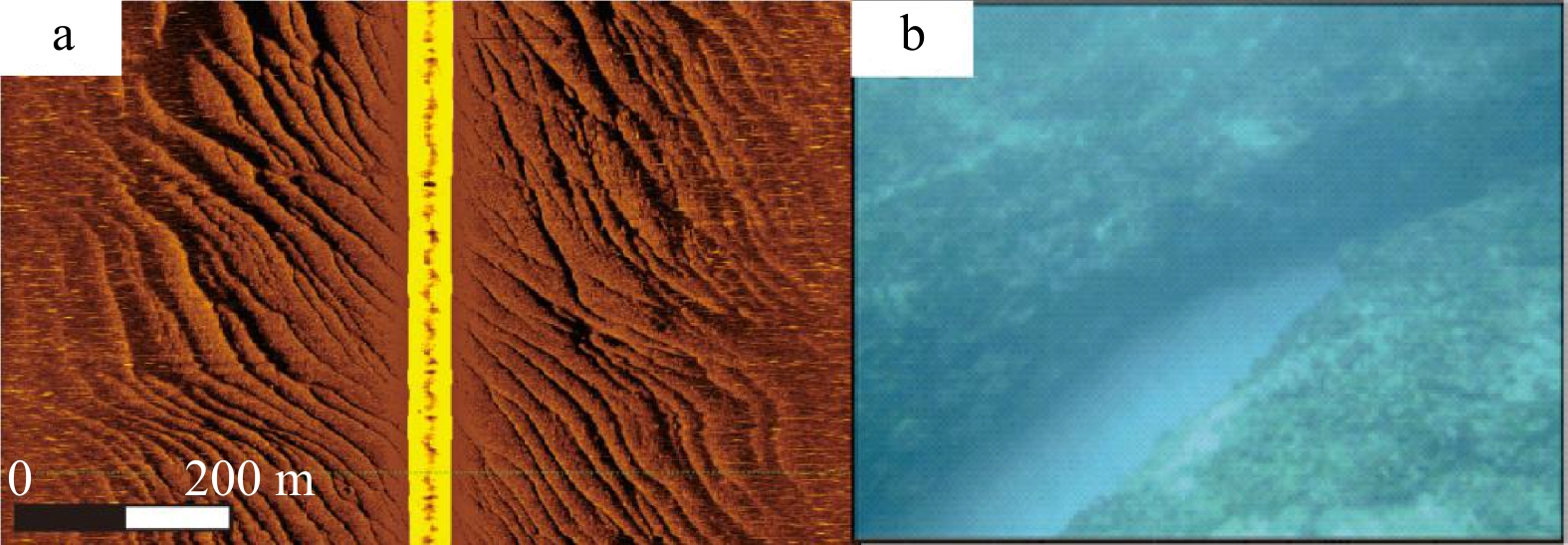
图 6 砂质海底、沙波侧扫影像及其表层沉积物(位置见图2)
a. 砂质海底侧扫影像;b−d. 砂质海底表层沉积物;f. 潟湖盆沙波侧扫影像;g. 向海坡沙波侧扫影像;e.潟湖盆沙波表层沉积物
Fig. 6 Sand seafloor, side scan image of sand wave and surface sediments (the location is shown in Fig.2)
a. Sand seabed side scan image; b−d. sand seabed surface sediments; f. lateral scan image of sand wave in lagoon basin; g. sand wave lateral image of sea slope; e. sand wave surface sediments in lagoon basin
图 7 珊瑚礁侧扫影像及其表层沉积物(位置见图2)
a. 礁前区珊瑚礁影像;b. 礁前区珊瑚礁碎块;c. 潟湖盆边缘珊瑚礁侧扫影像;d. 潟湖盆边缘珊瑚礁表层沉积物;e. 潟湖盆珊瑚礁侧扫影像;f. 潟湖盆珊瑚礁表层沉积物
Fig. 7 Side scan image of coral reef and surface sediments (the location is shown in Fig.2)
a. Coral reef image in front of the reef; b. coral reef fragments in front of the reef; c. side scan image of coral reef at the edge of lagoon basin; d. surface sediments of coral reefs at the edge of the lagoon basin; e. side scan image of coral reef in lagoon basin; f. surface sediments of coral reefs in the lagoon basin
图 8 突起脊−槽沟侧扫及水下影像(位置见图2)
a.永兴岛东南侧突起脊−槽沟侧扫影像;b. 永兴岛珊瑚礁坪前缘突起脊−槽沟水下影像[39]
Fig. 8 Protruding ridge-groove side scan and underwater image (the location is shown in Fig.2)
a. Side scan image of protruding ridge-groove on the southeast side of Yongxing Island; b. underwater image of the protruding ridge-groove on the front edge of the coral reef flat of Yongxing Island[39]
图 9 向海坡水下阶地侧扫影像及其表层沉积物(位置见图2)
a. 七连屿向海坡水下阶地侧扫影像;b. 七连屿向海坡水下阶地表层沉积物
Fig. 9 Side scan images of underwater terraces and surface sediments on the slope (the location is shown in Fig.2)
a. Side scan image of underwater terrace on Qilianyu sea slope; b. surface sediments of the underwater terraces on the Qilianyu sea slope
图 13 七连屿向海坡水下阶地侧扫影像及地形剖面
a. 七连屿向海坡六级水下阶地侧扫影像;b. 七连屿向海坡六级水下阶地地形剖面;c. 永暑礁东南礁前向海坡地形剖面[42];d. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁礁外坡地形剖面[18]
Fig. 13 Side scan image and topographic profile of underwater terraces on the seawall slope of Qilianyu Island
a. Side scan image of the sixth-level underwater terrace on the Qilianyu sea slope; b. topographic profile of the sixth-level underwater terrace on the Qilianyu sea slope; c. topographic profile of the front sea slope of the southeast reef of Yongshu Reef[42]; d. topographic profile of the outer slope of the coral reef in the Nansha Islands[18]
表 1 砂质海底沉积物粒级组分统计表
Tab. 1 Statistical of grain size composition of the sand seafloor
点位 水深/m 砾石含量/% 砂含量/% 粉砂含量/% 黏土含量/% 平均粒径/(Φ) 分选系数 偏态系数 峰态系数 b 54.54 11.60 81.73 5.43 1.24 1.06 1.90 0.05 0.86 c 55.31 11.70 82.20 4.92 1.18 1.25 1.82 −0.17 0.90 d 56.46 0.00 59.84 32.76 7.40 4.03 2.33 0.48 0.84 e 53.23 0.00 82.19 15.87 1.94 2.99 1.28 0.35 1.48 表 2 宣德环礁海底侧扫影像地貌分类
Tab. 2 Classification of landforms from side scan images of Xuande atoll
一级地貌 二级地貌 三级地貌 分类定义 微地貌特征 发育水深/m 1. 环礁顶 1.1 礁顶向海坡 1.1.1 礁前(向海侧) 礁坪礁脊线至水下礁脊线区域 槽沟、近岸浅水珊瑚礁群 <20 1.1.2 礁盘前缘 水下礁脊线至礁盘边缘线区域 沙波、宣德环礁第二级水下阶地 20~70 1.1.3 礁盘斜坡 礁盘边缘线至环礁边缘线区域 沙波、宣德环礁第三级水下阶地 70~100 1.2 潟湖 1.2.1 礁前(潟湖侧) 礁坪礁脊线至水下礁脊线区域 槽沟、近岸浅水珊瑚礁群 <20 1.2.2 潟湖坡 水下礁脊线至潟湖底斜坡区域 20~50 1.2.3 潟湖底 潟湖平坦海底 水下砂质沉积 50~60 1.3 潮汐通道 1.3.1 水下沙坝 受潮汐水道控制突入潟湖平坦海底的
砂质沉积体水下砂质沉积、浅水沙波 50~55 1.3.2 潮汐水体通道 潮流水体自环礁边缘至潟湖水下
砂质沉积体区域水下砂质沉积 50~60 1.3.3 潮汐通道深切区 潮流冲刷深切潟湖盆区域 砂质沉积反射特征的
水下珊瑚群礁55~60 2. 环礁向海
斜坡2.1 向海坡上坡 浅水平台 环礁边缘线以深平直型陡坡 100~700 2.2 向海坡下坡 深水平台 切割起伏型斜坡 >700 -
[1] 孙家淞, 周长振, 冯栋志. 从几种海底地貌类型的发育论述水动力作用的影响[J]. 海洋通报, 1984, 3(2): 54−61.Sun Jiasong, Zhou Changzhen, Feng Dongzhi. On effects of hydrodynamic processes on the development of some submarine geomorphological features[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1984, 3(2): 54−61. [2] 郭旭东, 冯文科. 据地貌声图判读研究海底地貌和底质类型[J]. 地质科学, 1978, 13(4): 373−382.Guo Xudong, Fen Wenke. A study of bottom geomorphology and submarine sediments by sonargraphic interpretation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1978, 13(4): 373−382. [3] 冯文科, 鲍才旺, 陈俊仁, 等. 南海北部海底地貌初步研究[J]. 海洋学报, 1982, 4(4): 462−472.Feng Wenke, Bao Caiwang, Chen Junreng, et al. Preliminary study on submarine relief of the northern South China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1982, 4(4): 462−472. [4] 蔡秋蓉. 南海北部海底微地貌特征与近代变化[J]. 南海地质研究, 2003(14): 77−83.Cai Qiurong. Micro-geomorphic features and their dynamic change in northern South China Sea[J]. Gresearch of Eological South China Sea, 2003(14): 77−83. [5] 陈卫民, 杨作升, 曹立华, 等. 现代长江口水下底坡上的微地貌类型及分区[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 1993(S1): 45−51.Chen Weimin, Yang Zuosheng, Cao Lihua, et al. Microgeomorphology on the subaqueous slope of the Changjiang River delta[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 1993(S1): 45−51. [6] 赵铁虎, 李春, 丛鸿文, 等. 青岛近岸海区海底地貌类型及声学特征[J]. 海洋测绘, 2005, 25(1): 40−43.Zhao Tiehu, Li Chun, Cong Hongwen, et al. Relief type and acoustic characters of inshore seabed along Qingdao[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2005, 25(1): 40−43. [7] 陈俊仁. 我国南部西沙群岛地区第四纪地质初步探讨[J]. 地质科学, 1978(1): 46−56.Chen Junren. A preliminary discussion on quaternary geology of Xisha Qundao Islands of South China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1978(1): 46−56. [8] 曾昭璇. 试论中国珊瑚礁地貌类型[J]. 热带地貌资料, 1980: 1−16.Zeng Zhaoxuan. The geomorphological types of coral reef of China[J]. Tropical Landforms, 1980: 1−16. [9] 曾昭璇, 黄少敏, 曾迪鸣. 西沙群岛石岛地貌学上诸问题[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1984, 5(4): 335−341.Zeng Zhaoxuan, Huang Shaomin, Zeng Diming. Some problems concerning geomorphology of Shidao, Xisha Islands[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1984, 5(4): 335−341. [10] 余克服, 宋朝景, 赵焕庭. 西沙群岛永兴岛地貌与现代沉积特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 1995(2): 24−31.Yu Kefu, Song Chaojing, Zhao Huanting. The characters of geomorphology and modern sediments of Yongxing Island, Xisha Islands[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 1995(2): 24−31. [11] 赵焕庭, 宋朝景, 朱袁智. 南沙群岛“危险地带”腹地珊瑚礁的地貌与现代沉积特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 1992, 12(4): 368−377.Zhao Huanting, Song Chaojing, Zhu Yuanzhi. Geomorphic and modern sedimentary features of coral reefs in the hinterland of “Dangerous Ground”, Nansha Islands[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1992, 12(4): 368−377. [12] 孙宗勋, 赵焕庭. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁动力地貌特征[J]. 热带海洋, 1996, 15(2): 53−60.Sun Zongxun, Zhao Huanting. Features of dynamic geomorphology of coral reefs in Nansha Islands[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1996, 15(2): 53−60. [13] 周胜男, 施祺, 周桂盈, 等. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁砾洲地貌特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2019, 43(6): 48−59.Zhou Shengnan, Shi Qi, Zhou Guiying, et al. Geomorphic features of coral shingle cays in the Nansha Islands[J]. Marine Sciences, 2019, 43(6): 48−59. [14] 张江勇, 黄文星, 刘胜旋, 等. 南海西沙海域甘泉海台的阶梯状地形[J]. 热带地理, 2016, 36(1): 10−18.Zhang Jiangyong, Huang Wenxing, Liu Shengxuan, et al. Terrace topographyof the Ganquan Plateau in the Xisha Area of the South China Sea[J]. Tropical Geography, 2016, 36(1): 10−18. [15] 赵焕庭, 王丽荣. 珊瑚礁形成机制研究综述[J]. 热带地理, 2016, 36(1): 1−9.Zhao Huanting, Wang Lirong. Review on the study of formation mechanism of coral reefs[J]. Tropical Geography, 2016, 36(1): 1−9. [16] 于红兵, 孙宗勋. 南沙群岛永暑礁上部向海坡地貌特征研究[J]. 海洋通报, 1999, 18(3): 49−54.Yu Hongbing, Sun Zongxun. Geomorphic features of upper seaward slope of Yongshu reef, Nansha Islands[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1999, 18(3): 49−54. [17] 王雪木, 陈万利, 薛玉龙, 等. 西沙群岛宣德环礁晚第四纪灰砂岛沉积地层[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(6): 37−45.Wang Xuemu, Chen Wanli, Xue Yulong. The Late Quaternary Carbonate sand deposits at the Xuande Atoll[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(6): 37−45. [18] 赵焕庭, 王丽荣, 宋朝景. 南海珊瑚礁地貌模型研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(9): 112−120.Zhao Huanting, Wang Lirong, Song Chaojing. Geomorphological model of coral reefs in the South China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(9): 112−120. [19] 黄荣永, 余克服, 王英辉, 等. 珊瑚礁遥感研究进展[J]. 遥感学报, 2019, 23(6): 1091−1112.Huang Rongyong, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui, et al. Progress of the study on coral reef remote sensing[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2019, 23(6): 1091−1112. [20] 周旻曦, 刘永学, 李满春, 等. 多目标珊瑚岛礁地貌遥感信息提取方法——以西沙永乐环礁为例[J]. 地理研究, 2015, 34(4): 677−690.Zhou Minxi, Liu Yongxue, Li Manchun, et al. Geomorphologic information extraction for multi-objective coral islands from remotely sensed imagery: a case study for Yongle Atoll, South China Sea[J]. Geographical Research, 2015, 34(4): 677−690. [21] 龚剑明, 朱国强, 杨娟, 等. 面向对象的南海珊瑚礁地貌单元提取[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2014, 16(6): 997−1004.Gong Jianming, Zhu Guoqiang, Yang Juan, et al. A study on the object-oriented model for geomorphic unit extraction of coral reefs in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2014, 16(6): 997−1004. [22] 左秀玲, 苏奋振, 赵焕庭, 等. 南海珊瑚礁高分辨率遥感地貌分类体系研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 2018, 37(11): 1463−1472. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.11.003Zuo Xiuling, Su Fenzhen, Zhao Huanting, et al. Development of a geomorphic classification scheme for coral reefs in the South China Sea based on high-resolution satellite images[J]. Progress in Geography, 2018, 37(11): 1463−1472. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.11.003 [23] 金翔龙. 海洋地球物理研究与海底探测声学技术的发展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(4): 1243−1249.Jin Xianglong. The development of research in marine geophysics and acoustic technology for submarine exploration[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007, 22(4): 1243−1249. [24] 吴自银, 郑玉龙, 初凤友, 等. 海底浅表层信息声探测技术研究现状及发展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2005, 20(11): 1210−1217.Wu Ziyin, Zheng Yulong, Chu Fengyou, et al. Research status and prospect of sonar-detecting techniques near submarine[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2005, 20(11): 1210−1217. [25] 王晓, 王爱学, 蒋廷臣, 等. 侧扫声呐图像应用领域综述[J]. 测绘通报, 2019(1): 1−4.Wang Xiao, Wang Aixue, Jiang Tingchen, et al. Review of application areas for side scan sonar image[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2019(1): 1−4. [26] 郭军, 冯强强, 温明明, 等. Teledyne Benthos TTV-301声学深拖系统在海底微地形地貌调查中的应用[J]. 测绘工程, 2018, 27(10): 46−51.Guo Jun, Feng Qiangqiang, Wen Mingming, et al. Research and application of the Teledyne Benthos TTV-301 deep-tow system to the microtopography seabed[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 2018, 27(10): 46−51. [27] 张同伟, 唐嘉陵, 李正光, 等. 蛟龙号载人潜水器在深海精细地形地貌探测中的应用[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 61(8): 1148−1156. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9187-3Zhang Tongwei, Tang Jialing, Li Zhengguang, et al. Use of the Jiaolong manned submersible for accurate mapping of deep-sea topography and geomorphology[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(8): 1148−1156. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9187-3 [28] Hamouda A, Soliman K, El-Gharabawy S, et al. Comparative study between acoustic signals and images for detecting seabed features[J]. The Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 2019, 45(2): 145−151. doi: 10.1016/j.ejar.2019.03.002 [29] Alves T M, Gawthorpe R L, Hunt D W, et al. Cenozoic tectono-sedimentary evolution of the western Iberian margin[J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 195(1/4): 75−108. [30] Alves T M, Cunha T, Bouriak S, et al. Surveying the flanks of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: the Atlantis Basin, North Atlantic Ocean (36°N)[J]. Marine Geology, 2004, 209(1/4): 199−222. [31] Alves T M, Lykousis V, Sakellariou D, et al. Constraining the origin and evolution of confined turbidite systems: southern Cretan margin, Eastern Mediterranean Sea (34°30−36°N)[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2007, 27(1): 41−61. doi: 10.1007/s00367-006-0051-1 [32] 邵磊, 朱伟林, 邓成龙, 等. 南海西科1井碳酸盐岩生物礁储层沉积学 年代地层与古海洋环境[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2016.Shao Lei, Zhu Weilin, Deng Chenglong, et al. Sedimentological Chronostratigraphy and Paleomarine Environment of Carbonate Reef Reservoir in Well Xike 1, South China Sea[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2016. [33] 杨胜雄, 邱燕, 朱本铎, 等. 南海地质地球物理系列图系[M]. 天津: 中国航海图书出版社, 2015.Yang Shengxiong, Qiu Yan, Zhu Benduo, et al. Atelas of Geology and Geophysics of the South China Sea[M]. Tianjin: China Navigation Publications, 2015. [34] 李亮, 何其江, 龙根元, 等. 南海宣德海域表层沉积物粒度特征及其输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(6): 140−148.Li Liang, He Qijiang, Long Genyuan, et al. Sediment grain size distribution pattern and transportation trend in the Xuande Water, South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(6): 140−148. [35] 赵焕庭, 宋朝景, 余克服, 等. 西沙群岛永兴岛和石岛的自然与开发[J]. 海洋通报, 1994, 13(5): 44−56.Zhao Huanting, Song Chaojing, Yu Kefu, et al. Nature and development of Yongxing Island and Shi Island of Xisha Islands[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1994, 13(5): 44−56. [36] Folk R L. A review of grain-size parameters[J]. Sedimentology, 1966, 6(2): 73−93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1966.tb01572.x [37] 王颖. 中国区域海洋学——海洋地貌学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2012.Wang Ying. Regional Oceanography of China Seas: Marine Geomorphology[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2012. [38] 曾昭璇, 梁景芬, 丘世钧. 中国珊瑚礁地貌研究[M]. 广州: 广东人民出版社, 1997.Zeng Zhaoxuan, Liang Jingfen, Qiu Shijun. Geomorphology of Coral Reefs in China[M]. Guangzhou: Guangdong People’s Publishing House, 1997. [39] 沈建伟, 杨红强, 王月, 等. 西沙永兴岛珊瑚礁坪的群落动态和浅水碳酸盐沉积特征[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2013, 56(9): 1471−1486. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4677-3Shen Jianwei, Yang Hongqiang, Wang Yue, et al. Coral community dynamics and shallow-water carbonate deposition of the reef-flat around Yongxing Island, the Xisha Islands[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2013, 56(9): 1471−1486. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4677-3 [40] Gischler E. Indo-pacific and Atlantic spurs and grooves revisited: the possible effects of different Holocene sea-level history, exposure, and reef accretion rate in the shallow fore reef[J]. Facies, 2010, 56(2): 173−177. doi: 10.1007/s10347-010-0218-0 [41] Rogers J S, Monismith S G, Feddersen F, et al. Hydrodynamics of spur and groove formations on a coral reef[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2013, 118(6): 3059−3073. doi: 10.1002/jgrc.20225 [42] 朱袁智, 沙庆安, 郭丽芬. 南沙群岛永暑礁新生代珊瑚礁地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997.Zhu Yuanzhi, Sha Qing’an, Guo Lifeng. Cenozoic Coral Reef Geology of the Yongshu Reef, Nansha Islands[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997. -





 下载:
下载: