Application of Hilbert-Huang transform method in fine illustrating shallow marine sediment system
-
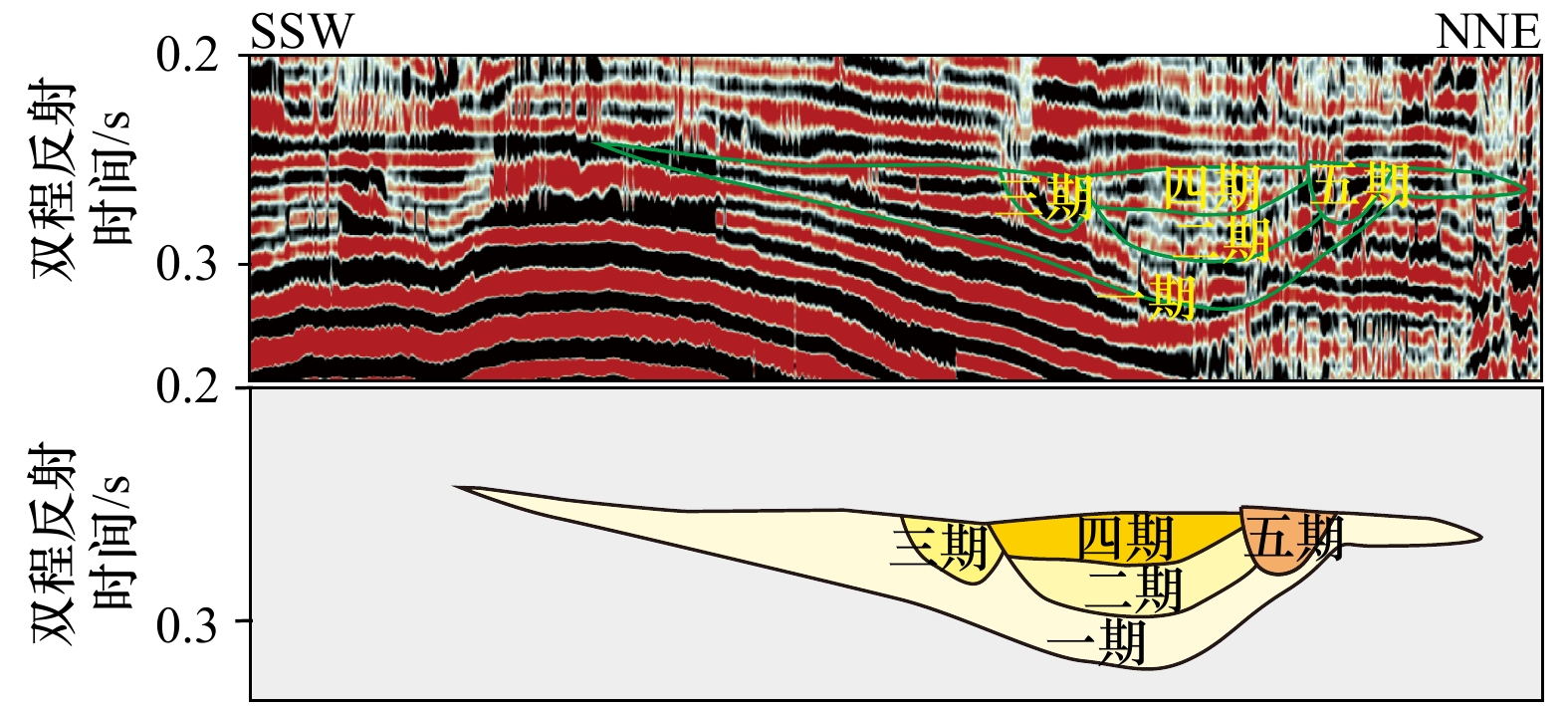
摘要: 位于马来盆地与西纳土纳盆地交汇处的研究区上新统−更新统发育复杂的浅海、海陆过渡相水下分支河道体系,常规的地震资料无法进行精细识别刻画。通过对叠后地震资料进行希尔伯特−黄变换,提取了地震资料高频分量,提高了地震资料的分辨率,有效识别了薄层砂泥岩交互特征和细微沉积体。通过对高频分量进行瞬时属性提取,明确了目的层段水下分支河道的平面展布特征。与常规叠后地震属性相比,经过希尔伯特−黄变换后的叠后地震资料提取的瞬时属性显示了更多沉积体系的细节特征,为水下分支河道的内部结构、发育期次、切割关系等时空演化研究提供了更高分辨率的地震数据。Abstract: The complex subaqueous channel system of shallow and transition facies is developed in the Pliocene-Pleistocene strata at the conjunction area of Malay Basin and West Natuna Basin, and can not be characterized in detail by conventional seismic data. By applying Hilbert-Huang transform to post-stack seismic data, the high frequency components of seismic data were extracted, the resolution of seismic data was improved, and the interaction characteristics of thin layer sand and mudstone and small sedimentary bodies were identified effectively. Through the instantaneous attribute extraction of the high frequency component, the plane distribution characteristics of the underwater branch channels in the target interval are defined. Compared with conventional post-stack seismic attributes, the instantaneous attributes extracted from post-stack seismic data after Hilbert-Huang transform show more detailed features of sedimentary system. And it provides high-resolution seismic data for the study of spatio-temporal evolution of underwater branch channels, such as internal structure, development period and cutting relationship.
-
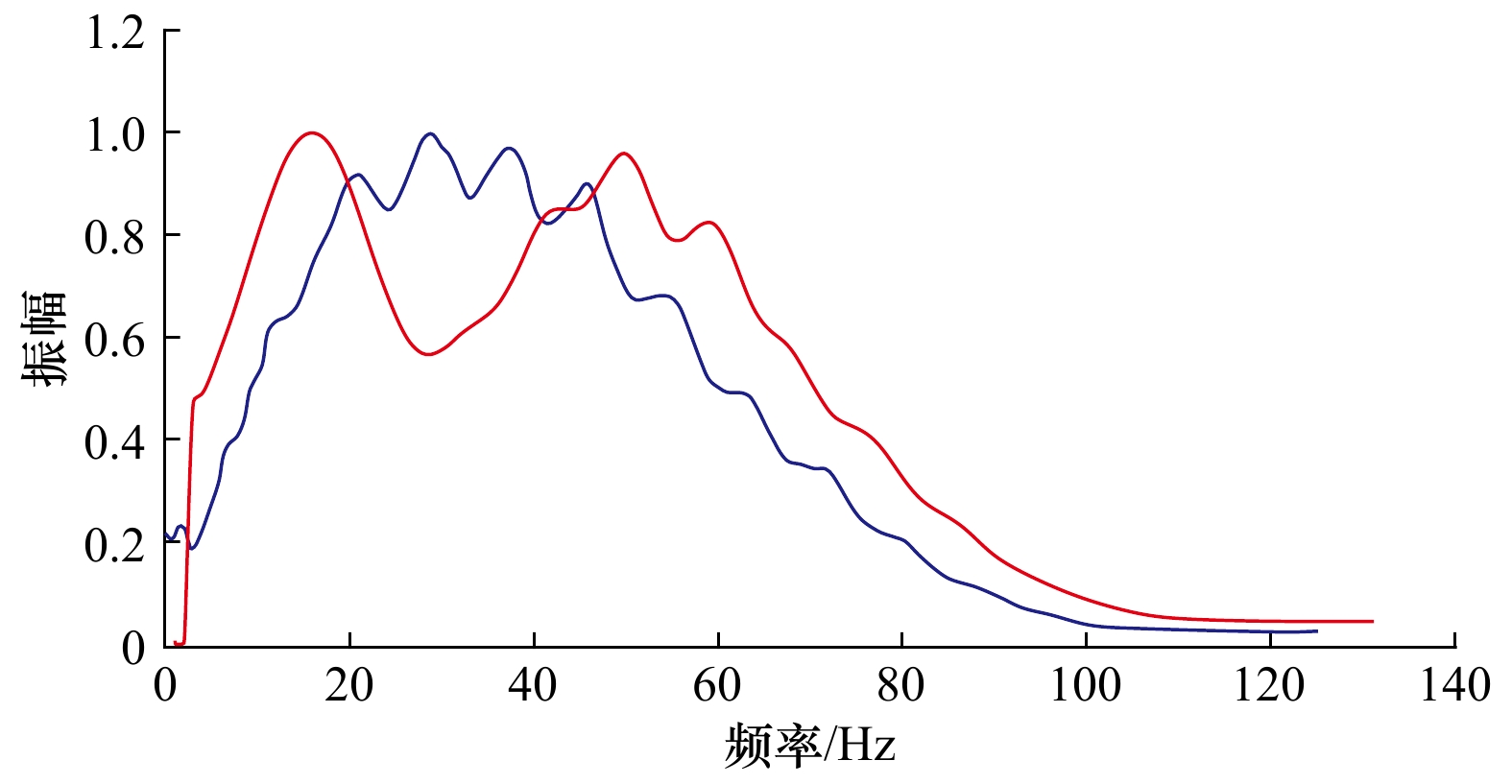
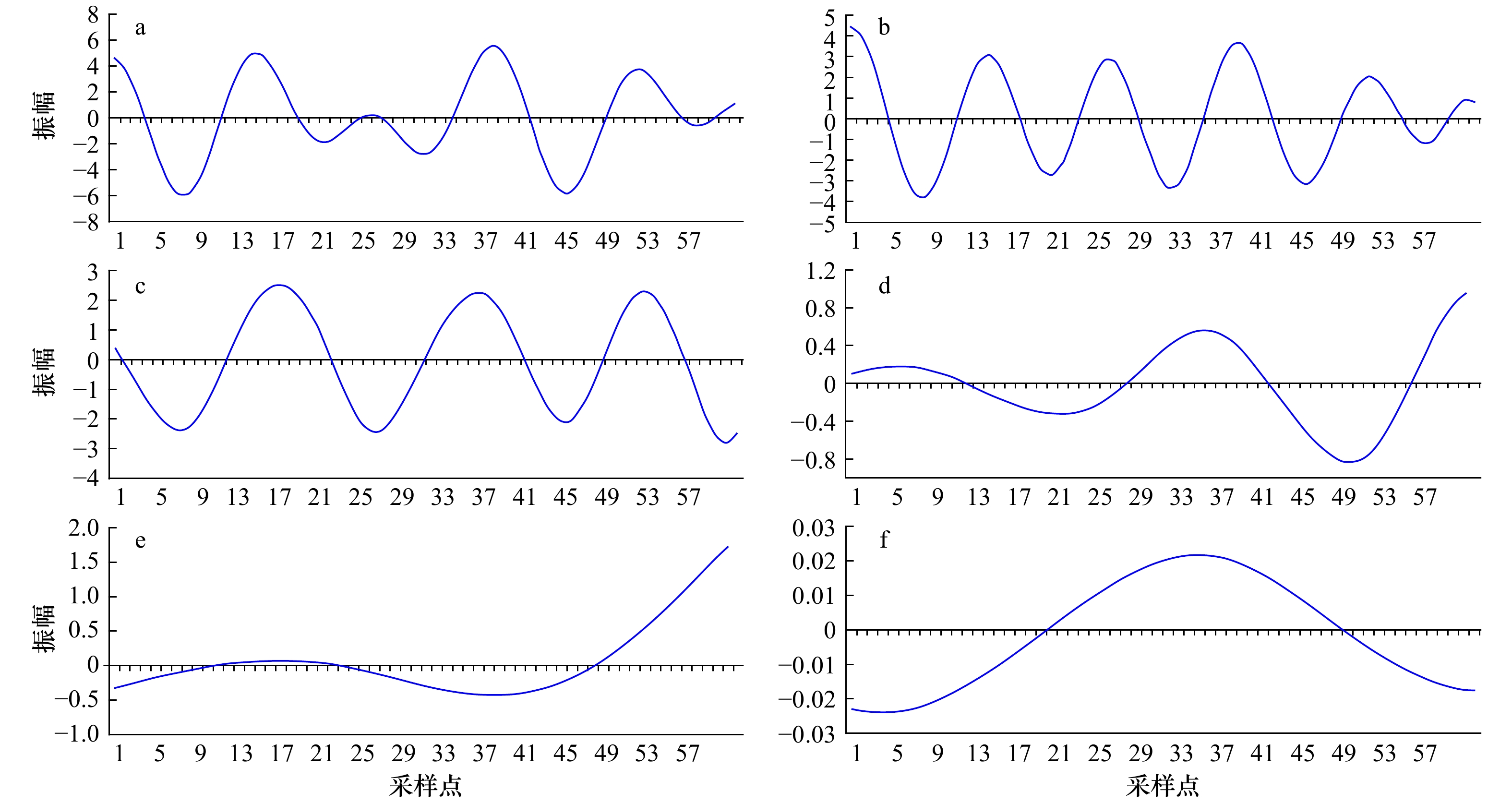
图 5 理论信号黄分解本征模态分量图
a. 理论原始信号;b. 黄分解第一本征模态分量;c. 黄分解第二本征模态分量;d. 黄分解第三本征模态分量;e. 黄分解第四本征模态分量;f. 残余分量
Fig. 5 Eigenmode component diagram of theoretical signal Huang transform
a. Theoretical original signal; b. the first eigenmode component of Huang transform; c. the second eigenmode component of Huang transform; d. the third eigenmode component of Huang transform; e. the fourth eigenmode component of Huang transform; f. residual component
-
[1] 黄光南. 希尔伯特−黄变换及其在地震资料分析处理中的应用[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2009.Huang Guangnan. Hilbert−Huang transform and application of it in seismic data analysis and processing[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2009. [2] 李辉峰, 杨蕾. 泌阳凹陷孙岗地区水下分流河道地震识别及预测[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2012, 33(6): 654−656.Li Huifeng, Yang Lei. Seismic recognition and prediction of underwater distributary channels in Sungang area of Biyang sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2012, 33(6): 654−656. [3] 颜中辉, 方刚, 徐华宁, 等. 希尔伯特谱白化方法在海洋地震资料高分辨率处理中的应用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 38(4): 212−220.Yan Zhonghui, Fang Gang, Xu Huaning, et al. The application of Hilbert spectral whitening method to high resolution processing of marine seismic data[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 38(4): 212−220. [4] 杨凯, 刘伟. 基于希尔伯特−黄变换的地震资料高分辨率处理[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2015, 12(1): 22−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2015.01.005Yang Kai, Liu Wei. The marine seismic data high resolution processing based on Hilbert−Huang transform[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2015, 12(1): 22−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2015.01.005 [5] 颜中辉, 王赟, 李攀峰, 等. 基于希尔伯特−黄变换的多分量地震去噪方法研究及应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(6): 2846−2854. doi: 10.6038/pg20150652Yan Zhonghui, Wang Yun, Li Panfeng, et al. Research and application of multi-component seismic denoising based on Hilbert−Huang transform[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(6): 2846−2854. doi: 10.6038/pg20150652 [6] 李延, 顾汉明. 基于改进的希尔伯特−黄变换的岩性油藏识别方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2015, 50(2): 341−345.Li Yan, Gu Hanming. Lithologic reservoir identification based on the improved Hilbert−Huang transform[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2015, 50(2): 341−345. [7] 曹思远, 邴萍萍, 路交通, 等. 利用改进希尔伯特−黄变换进行地震资料时频分析[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2013, 48(2): 246−254.Cao Siyuan, Bing Pingping, Lu Jiaotong, et al. Seismic data time-frequency analysis by the improved Hilbert−Huang transform[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2013, 48(2): 246−254. [8] Huang N E. Computer implemented empirical mode decomposition method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for two-dimensional signals[P]. US: US6311130B1, 2011−10−30. [9] Huang N E, Shen Zheng, Long S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceeding of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903−995. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193 [10] Huang N E, Wu M L C, Long S R, et al. A confidence limit for the empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectral analysis[J]. Proceeding of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2003, 459(2037): 2317−2345. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2003.1123 [11] 梁岳, 顾汉明, 姚知铭. 改进的希尔伯特−黄变换在储层预测中的应用[J]. 石油物探, 2016, 55(4): 606−615. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2016.04.016Liang Yue, Gu Hanming, Yao Zhiming. The application of improved Hilbert−Huang transform in reservoir prediction[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2016, 55(4): 606−615. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2016.04.016 [12] 冯红武, 王建昌. 希尔伯特−黄变换在地震信号时频分析中的应用研究[J]. 高原地震, 2018, 30(4): 11−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-586X.2018.04.003Feng Hongwu, Wang Jianchang. Applied research on Hilbert−Huang transform in time-frequency analysis of seismic signal[J]. Plateau Earthquake Research, 2018, 30(4): 11−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-586X.2018.04.003 [13] 倪仕琪, 王志欣, 宋继叶, 等. 南海西南部西纳土纳盆地油气成藏组合分析与资源潜力评价[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(5): 130−143.Ni Shiqi, Wang Zhixin, Song Jiye, et al. Analysis and resource evaluation of hydrocarbon plays in the West Natuna Basin, southwestern part of the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(5): 130−143. [14] 倪仕琪, 王志欣, 刘凤鸣, 等. 印度尼西亚西纳土纳盆地油气地质特征与分布规律[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(2): 26−34.Ni Shiqi, Wang Zhixin, Liu Fengming, et al. Geological characteristics and distribution pattern of petroleum in West Natuna Basin, Indonesia[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(2): 26−34. [15] 毕素萍, 张寿庭, 夏朝辉, 等. 西纳土纳盆地K区块反转构造与油气成藏[J]. 中国海上油气, 2016, 28(4): 24−29.Bi Suping, Zhang Shouting, Xia Zhaohui, et al. Inversion structures and their controls on hydrocarbon accumulation in Block K, West Natuna Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2016, 28(4): 24−29. [16] 毕素萍, 潘懋, 夏朝辉, 等. 南海西南部西纳土纳盆地中部走滑构造带分段性及对油气控制作用[J]. 地质论评, 2016, 62(3): 770−778.Bi Suping, Pan Mao, Xia Zhaohui, et al. Strike slip structures segmentation and its control of hydrocarbon accumulation in middle part of the West Natuna Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2016, 62(3): 770−778. [17] 毕素萍, 张寿庭, 张铭, 等. 印尼西纳土纳盆地Muda组河流体系分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2016, 16(7): 134−138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.07.020Bi Suping, Zhang Shouting, Zhang Ming, et al. Fluvial system analysis of Muda formation in West Natuna Basin, Indonesia[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2016, 16(7): 134−138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.07.020 [18] 刘海. 东、西纳土纳盆地石油地质特征及对比研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012.Liu Hai. Contrast and research of petroleum geological characteristics: West and East Natuna Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2012. [19] Meirita M F. Structural and depositional evolution, KH field, West Natuna Basin, offshore Indonesia[D]. Texas: Texas A&M University, 2004. [20] McClay K, Bonora M, Comrie-Smith N, et al. Geometries and kinematics of inversion tectonics, West Natuna Sea Basin, Indonesia[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2000, 84(9): 1463. [21] Shoup R C, Morley R J, Swiecicki T, et al. Tectono-stratigraphic framework and tertiary paleogeogeography of Southeast Asia; gulf of Thailand to south Vietnam shelf[J]. Houston Geological Society Bulletin, 2013, 55(6): 27, 29, 31, 33, 35, 37, 39. [22] Du Bois E P. Review of principal hydrocarbon-bearing basins of the South China Sea area[J]. Energy, 1981, 6(11): 1113−1140. doi: 10.1016/0360-5442(81)90029-3 [23] Burton D, Wood L J. Seismic geomorphology and tectonostratigraphic fill of half grabens, West Natuna Basin, Indonesia[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2010, 94(11): 1695−1712. doi: 10.1306/06301010003 [24] Ngah K, Madon M, Tjia H D. Role of pre-Tertiary fractures in formation and development of the Malay and Penyu basins[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1996, 106(1): 281−289. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1996.106.01.18 [25] Ginger D C, Ardjakusumah W O, Hedley R J, et al. Inversion history of the West Natuna Basin: examples from the Cumi-Cumi PSC[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Convention Proceedings. Jakarta: Indonesian Petroleum Association, 1993: 635−658. [26] Doust H, Sumner H S. Petroleum systems in rift basins-a collective approach in Southeast Asian basins[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 2007, 13(2): 127−144. doi: 10.1144/1354-079307-746 [27] Hakim M R, Naiola M Y Y, Simangunsong Y R A, et al. Hydrocarbon play of West Natuna Basin and challenge for new exploration related to structural setting and stratigraphic succession[C]//Proceedings of 32nd Annual Convention Proceedings. Jakarta: Indonesian Petroleum Association, 2008, IPA08-SG-039. [28] Manur H, Jacques J M. Deformational characteristics of the West Natuna Basin with regards to its remaining exploration potential[C]//Proceedings of 38th Annual Convention Proceedings. Jakarta: Indonesian Petroleum Association, 2014, IPA14-G-193. [29] Tjia H D, Liew K K. Changes in tectonic stress field in northern Sunda Shelf basins[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1996, 106(1): 291−306. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1996.106.01.19 [30] Tapponnier P, Lacassin R, Leloup P H, et al. The Ailao Shan/Red River metamorphic belt: Tertiary left-lateral shear between Indochina and South China[J]. Nature, 1990, 343(6257): 431−437. doi: 10.1038/343431a0 [31] 肖剑, 柳斌, 郭亚龙, 等. 基于希尔伯特变换的干涉仪信号处理[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2010, 32(1): 80−83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1194.2010.01.019Xiao Jian, Liu Bin, Guo Yalong, et al. Signal processing of microwave interferometer based on Hilbert transform[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2010, 32(1): 80−83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1194.2010.01.019 [32] 杨培杰, 印兴耀, 张广智. 希尔伯特−黄变换地震信号时频分析与属性提取[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(5): 1585−1590. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2007.05.037Yang Peijie, Yin Xingyao, Zhang Guangzhi. Seismic signal time-frequency analysis and attributes extraction based on HHT[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007, 22(5): 1585−1590. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2007.05.037 [33] 侯斌, 桂志先, 胡敏, 等. 基于希尔伯特−黄变换的地震信号时频谱分析[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 2009, 32(4): 248−251, 290.Hou Bin, Gui Zhixian, Hu Min, et al. Time-frequency spectral analysis of seismic data based on Hilbert−Huang transform[J]. Progress in Exploration Geophysics, 2009, 32(4): 248−251, 290. -





 下载:
下载: