Simulating the evolution of a focused wave group by a Boussinesq-type model
-
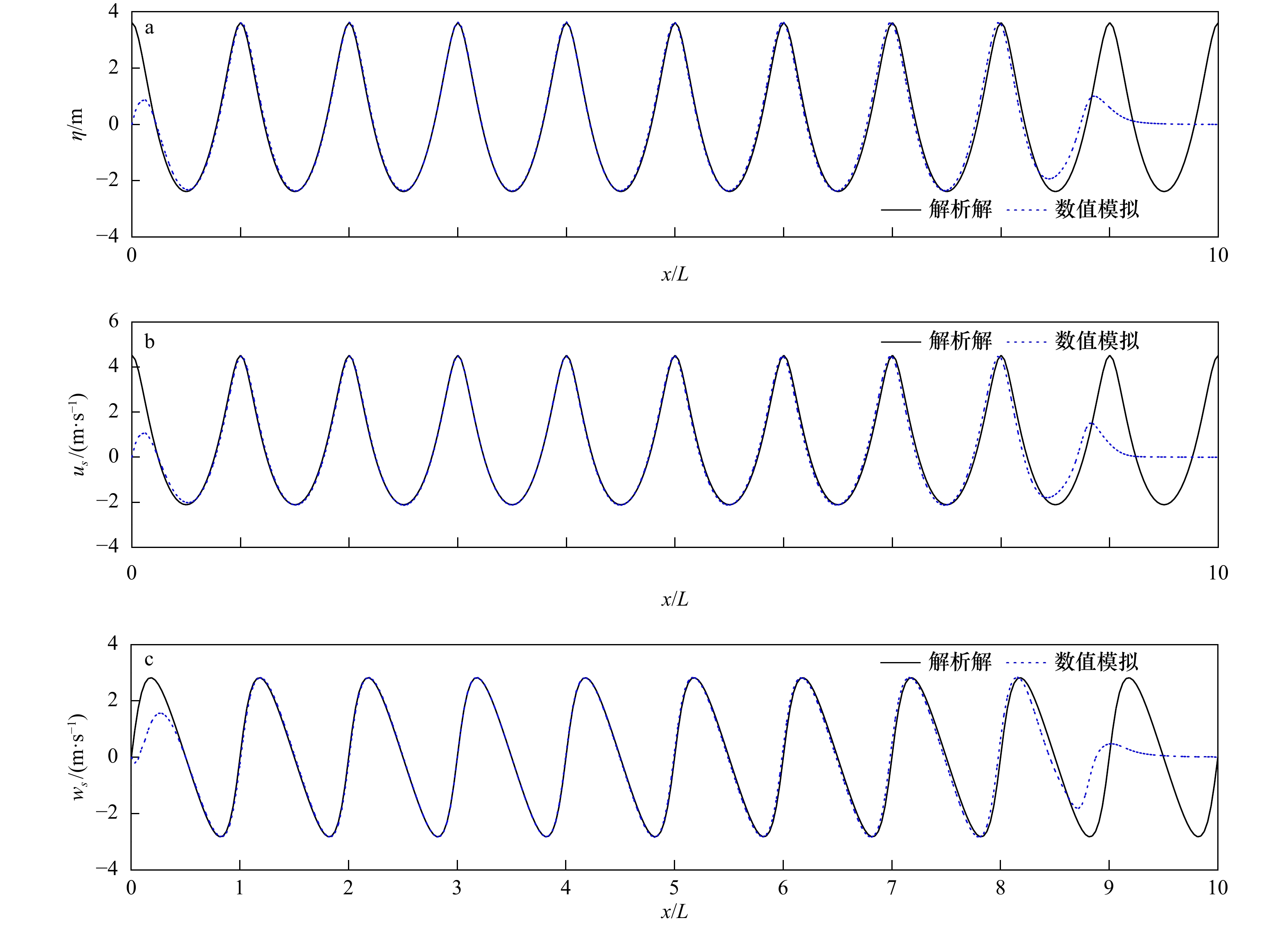
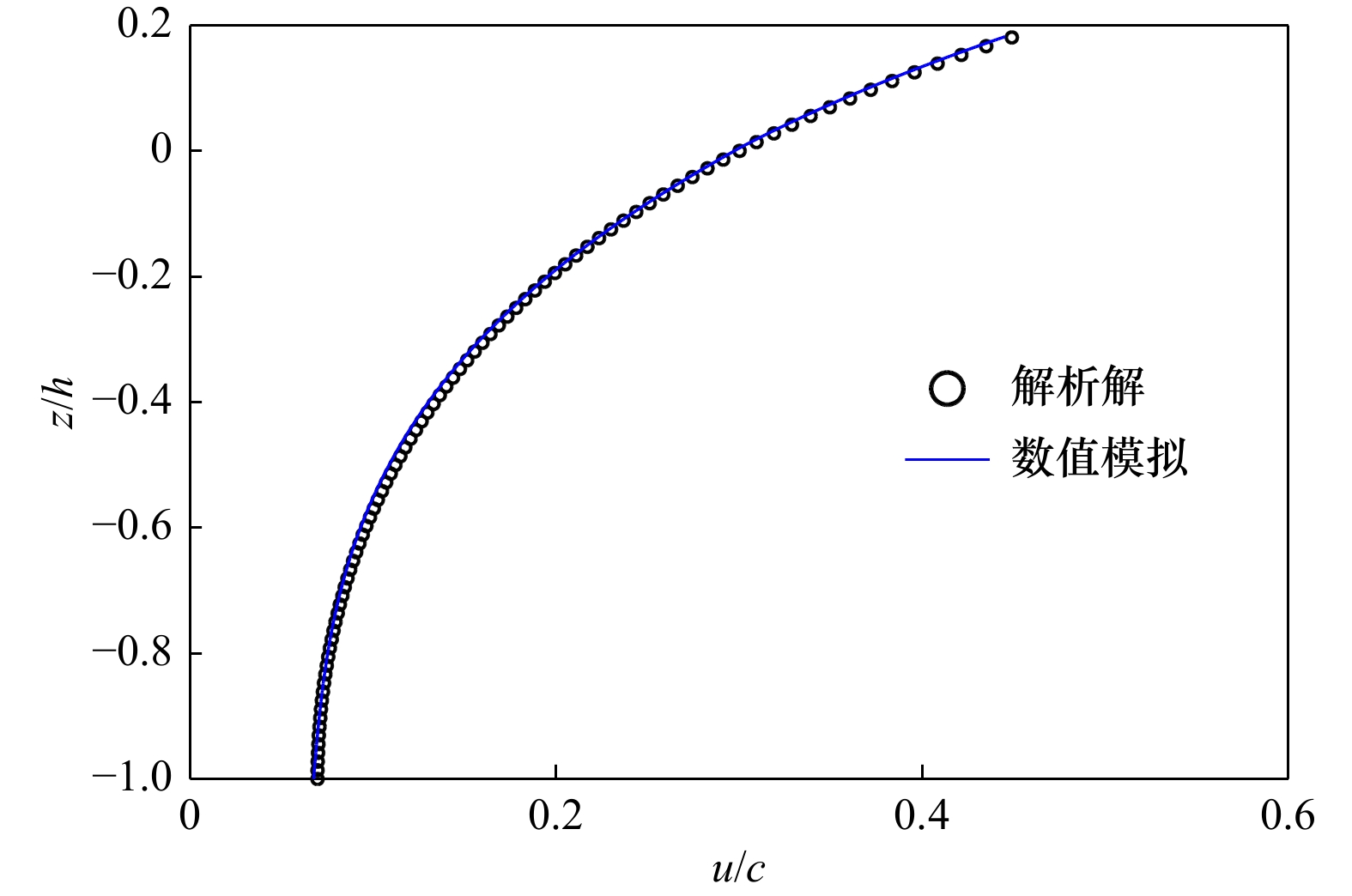
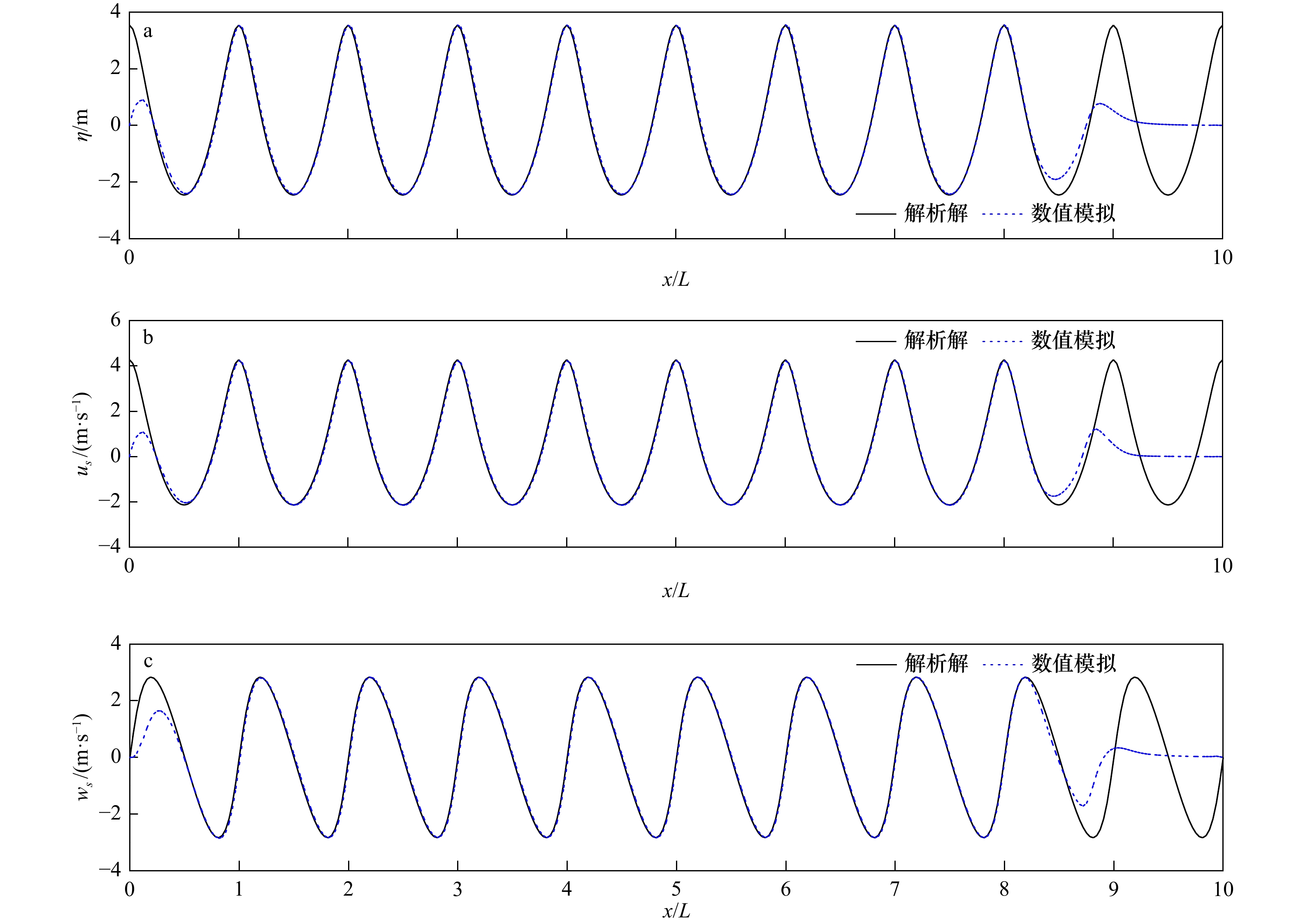
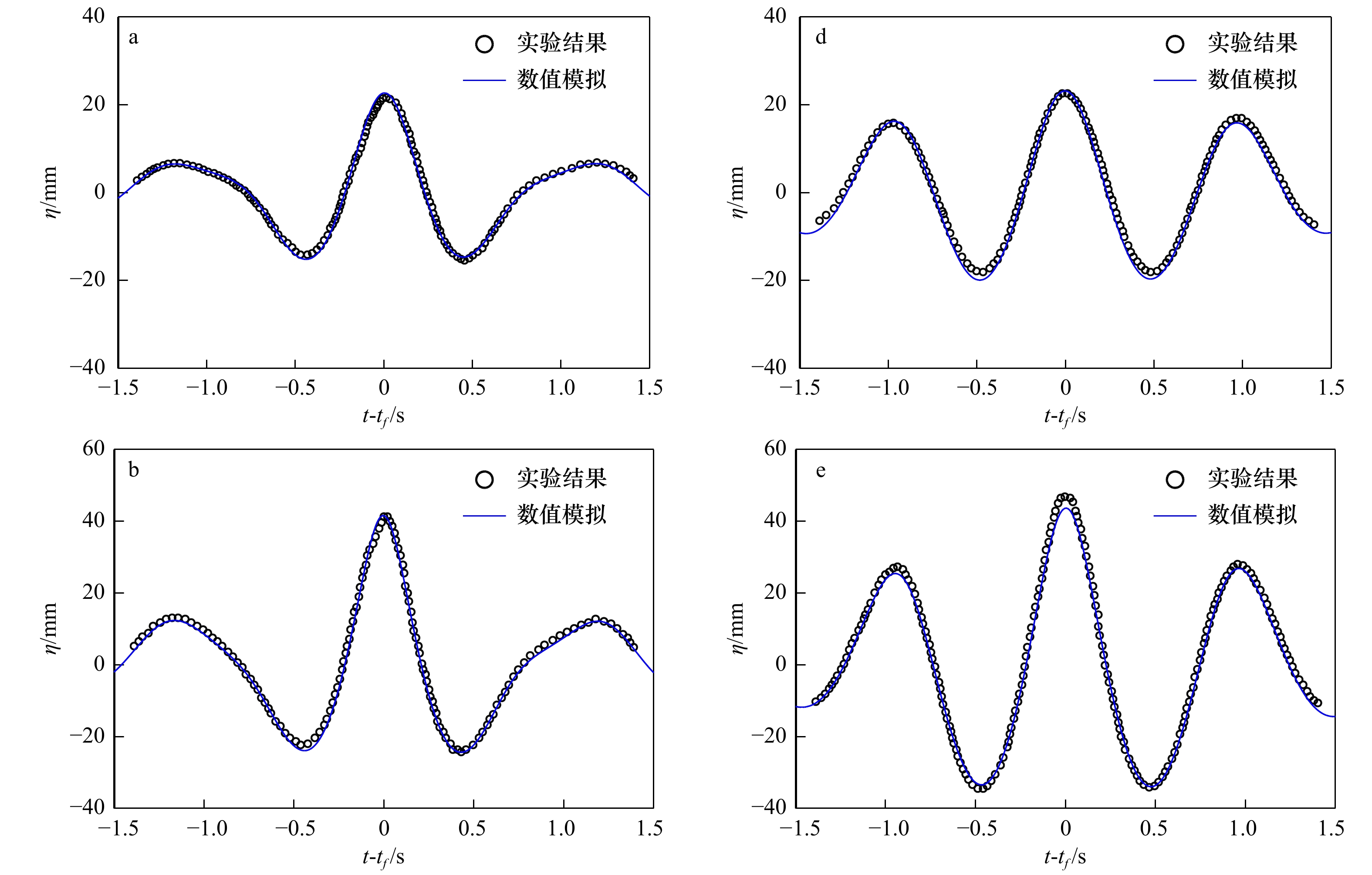
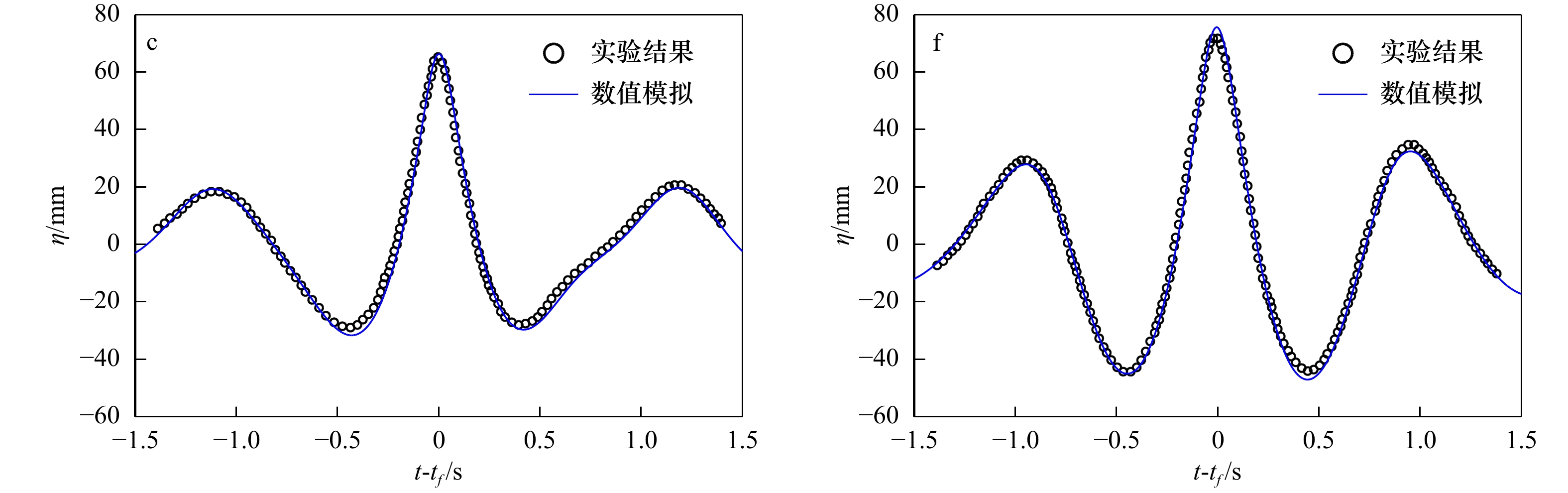
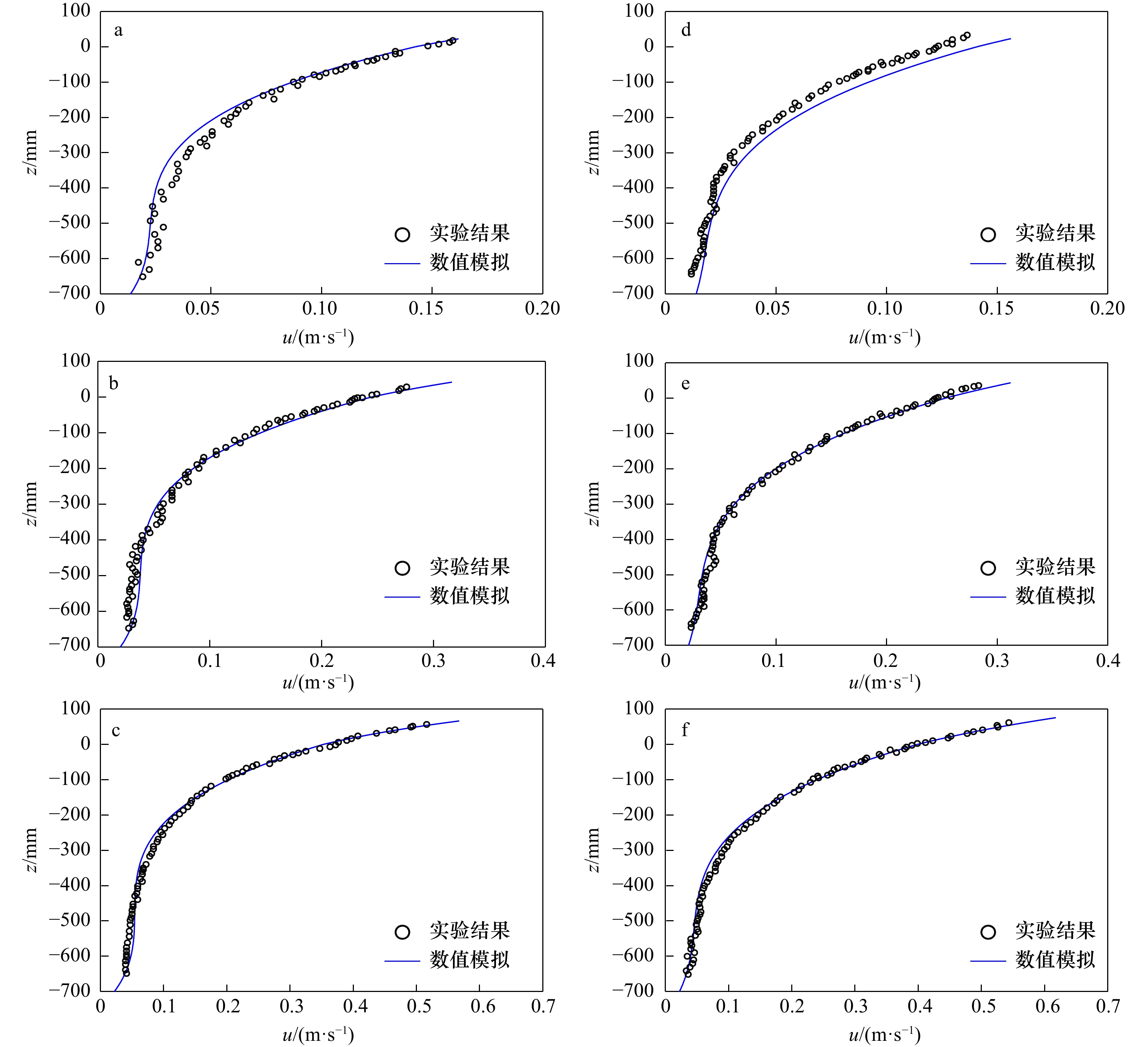
摘要: 基于最高导数为3阶的单层Boussinesq方程,建立了聚焦波的时域波浪计算模型。数值模型求解采用了预报−校正的有限差分法。对于时间差分格式,预报和校正分别采用3阶Adams-Bashforth格式和4阶Adams-Moulton格式。首先,针对不同水深条件下水槽中传播的强非线性波进行模拟,并将数值结果与流函数的数值解析解进行了比较,结果表明无论是波面位移、波面处的水平速度和垂向速度均与解析解符合较好,最大波峰面的速度分布伴随水深的增加与解析解吻合程度变差,非线性速度分布的适用范围与线性解析解适应范围kh<3.5基本一致。其次,对深水聚焦波演化进行了模拟研究,研究中聚焦波的生成采用在边界点累加不同频率线性规则波的方法。应用聚焦波物理模型实验结果验证模型,计算聚焦位置处的波面位移和沿水深的速度分布与实验结果的对比表明,波面位移吻合程度较好,垂向的水平速度分布基本吻合。最后,保持中心频率(周期)不变,数值模拟了周期范围变化下最大聚焦波峰面以及波峰面水平速度的变化趋势,结果表明波峰面值和波峰面水平速度随着周期范围缩小而增大。
-
关键词:
- Boussinesq数值模型 /
- 聚焦波 /
- 波面位移 /
- 速度分布
Abstract: Based on the one-layer Boussinesq model with highest spatial derivative being 3, a numerical model is established for focused wave group. The numerical model is solved with predictor-corrector scheme in finite differential method. For time integration, a third-order Adams-Bashforth scheme and a fourth-order Adams-Moulton scheme are separately used in predicting stage and correcting stage. Firstly, the numerical simulations are carried out upon nonlinear regular wave evolution over a constant water-depth in a flume, and the computed results are compared with the semi-analytical solutions. The results demonstrate that the simulated surface elevations, the horizontal velocity and vertical velocity on the free surface can well match the related analytical solutions, while the agreement of the horizontal velocity profile under the crest becomes worse with the increase of water-depth, and the range of the model with respect to nonlinear horizontal velocity profile is for kh<3.5, which is similar to the range of the related linear model with respect to horizontal velocity profile. Secondly, the numerical simulations are conducted upon the nonlinear focused wave group evolution in deep-water. The linear wave groups are used as incident wave conditions. The laboratory experiments conducted by Baldock and Swan (1996) are used to examine the present model. Both the computed surface elevations and the horizontal velocity profile at the focused position are compared with the related experimental data. The results show that the agreement of the surface elevations is pretty good, while the agreement of the horizontal velocity profile is moderate. Finally, with the middle frequency being kept unchanged, the numerical simulations upon the maximum surface elevation and horizontal velocity under the crest are conducted with the variation of the range of focused wave period, the results show that both the crest and the horizontal velocity increase with the increase of the range of the wave periods.-
Key words:
- Boussinesq model /
- focused wave /
- surface elevations /
- velocity profile
1) 林鹏程,刘忠波,刘勇. 基于Boussinesq数值模型的波浪速度垂向分布模拟研究. 海洋湖沼通报,已采用. -
表 1 计算结果与实验结果的比较
Tab. 1 Comparisons of results between modeled and experimental data
△T/s 计算ηmax/mm 计算uη/(m·s−1) 计算时间偏移/s 计算空间偏移/m 实验ηmax/mm 实验时间偏移/s 实验空间偏移/m 0.4 75.63 0.617 7 0.57 1.08 73.2 0.67 1.285 0.5 71.87 0.590 96 0.36 0.72 − − − 0.6 69.56 0.578 93 0.24 0.52 69.42 0.27 0.784 0.7 67.94 0.572 72 0.18 0.4 − − − 0.8 66.39 0.567 11 0.14 0.32 65.22 0.2 0.392 注:−表示没有相应的试验数据。 -
[1] Kharif C, Pelinovsky E. Physical mechanisms of the rogue wave phenomenon[J]. European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids, 2003, 22(6): 603−634. doi: 10.1016/j.euromechflu.2003.09.002 [2] Baldock T E, Swan C, Taylor P H, et al. A laboratory study of nonlinear surface waves on water[J]. Philosophical Transactions of The Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1996, 354(1707): 649−676. doi: 10.1098/rsta.1996.0022 [3] 柳淑学, 洪起庸. 三维极限波的产生方法及特性[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(6): 133−142.Liu Shuxue, Hong Qiyong. The generation method of three-dimensional focusing wave and its properties[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2004, 26(6): 133−142. [4] 裴玉国, 张宁川, 张运秋. 畸形波数值模拟和定点生成[J]. 海洋工程, 2006, 24(4): 20−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2006.04.004Pei Yuguo, Zhang Ningchuan, Zhang Yunqiu. Numerical simulation of freak waves and its generation at a certain location[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2006, 24(4): 20−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2006.04.004 [5] 赵西增, 孙昭晨, 梁书秀. 模拟畸形波的聚焦波浪模型[J]. 力学学报, 2008, 40(4): 447−454. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.2008.04.003Zhao Xizeng, Sun Zhaochen, Liang Shuxiu. Focusing models for generating freak waves[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2008, 40(4): 447−454. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.2008.04.003 [6] 赵西增, 孙昭晨, 梁书秀. 高阶谱数值方法及其应用[J]. 船舶力学, 2008, 12(5): 685−691. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2008.05.002Zhao Xizeng, Sun Zhaochen, Liang Shuxiu. A high order spectral method and its application to nonlinear water waves[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2008, 12(5): 685−691. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2008.05.002 [7] Li Jinxuan, Liu Shuxue. Focused wave properties based on a high order spectral method with a non-periodic boundary[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2015, 29(1): 1−16. doi: 10.1007/s13344-015-0001-7 [8] Ai Congfang, Ding Weiye, Jin Sheng. A general boundary-fitted 3D non-hydrostatic model for nonlinear focusing wave groups[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2014, 89: 134−145. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2014.08.002 [9] Ning Dezhi, Teng Bin, Taylor R E, et al. Numerical simulation of non-linear regular and focused waves in an infinite water-depth[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2008, 35(8): 887−899. [10] Li Mengyu, Zhao Xizeng, Ye Zhouteng, et al. Generation of regular and focused waves by using an internal wave maker in a CIP-based model[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 167: 334−347. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.08.048 [11] Liu Zhongbo, Fang Kezhao. A new two-layer Boussinesq model for coastal waves from deep to shallow water: Derivation and analysis[J]. Wave Motion, 2016, 67: 1−14. doi: 10.1016/j.wavemoti.2016.07.002 [12] Madsen P A, Bingham H B, Schäffer H A. Boussinesq-type formulations for fully nonlinear and extremely dispersive water waves: Derivation and analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2003, 459(2033): 1075−1104. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2002.1067 [13] Kirby J T, Wei G, Chen Q, et al. Funwave 1.0. Fully nonlinear Boussinesq wave model documentation and user’s manual[R]. Delaware: University of Delaware, 1998. [14] Liu Zhongbo, Fang Kezhao. Numerical verification of a two-layer Boussinesq-type model for surface gravity wave evolution[J]. Wave Motion, 2019, 85: 98−113. doi: 10.1016/j.wavemoti.2018.11.007 [15] Fuhrman D R. Numerical solutions of Boussinesq equations for fully nonlinear and extremely dispersive water waves[D]. Kgs. Lyngby: Technical University of Denmark, 2004. [16] Liu Zhongbo, Fang Kezhao, Sun Jiawen. A multi-layer Boussinesq-type model with second-order spatial derivatives: Theoretical analysis and numerical implementation[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 191: 106545. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106545 -





 下载:
下载: