Provenance systems and their control on the deep-water gravity flow deposition of the Member 2 of Neogene Yinggehai Formation, Qiongdongnan Basin
-
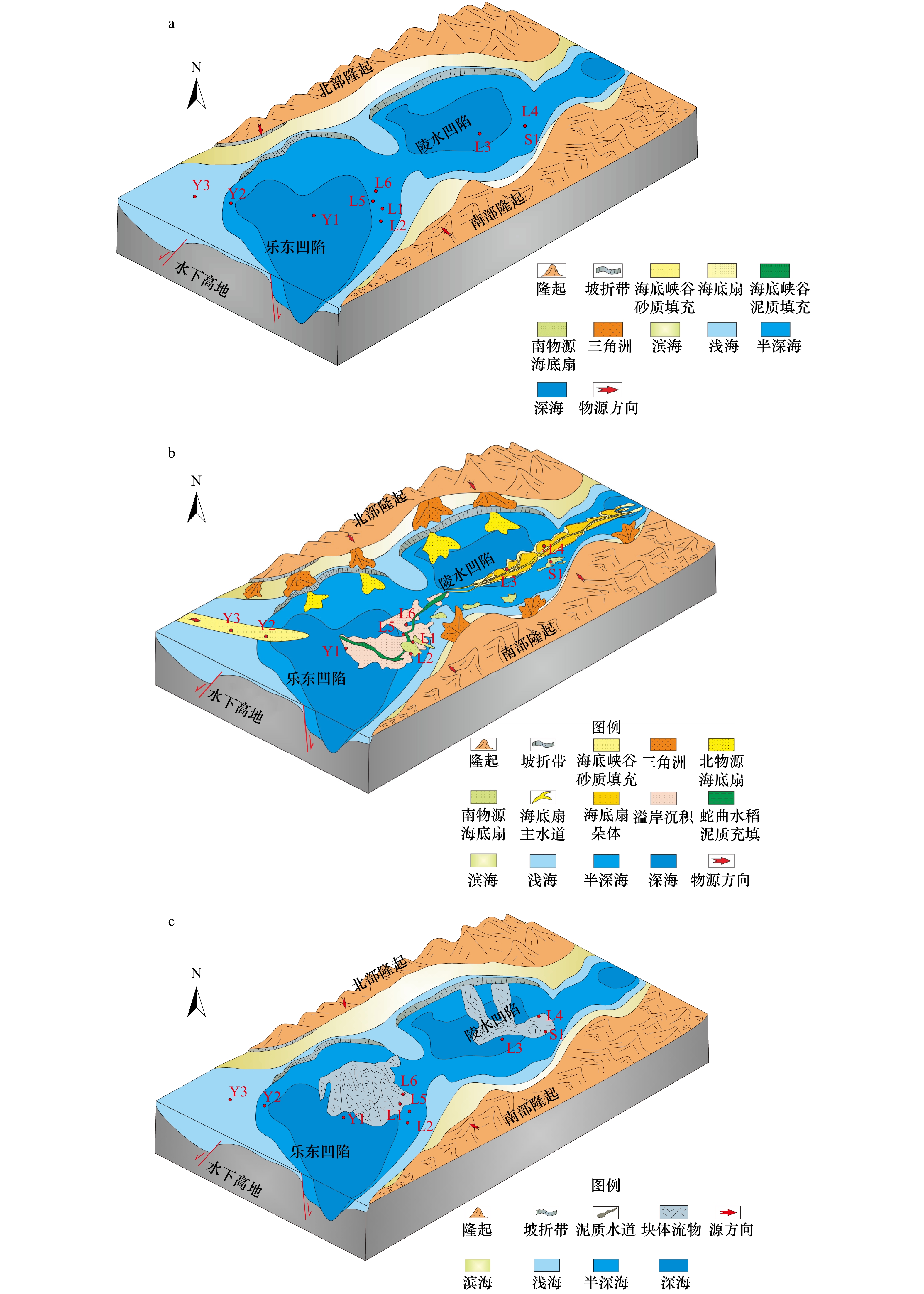
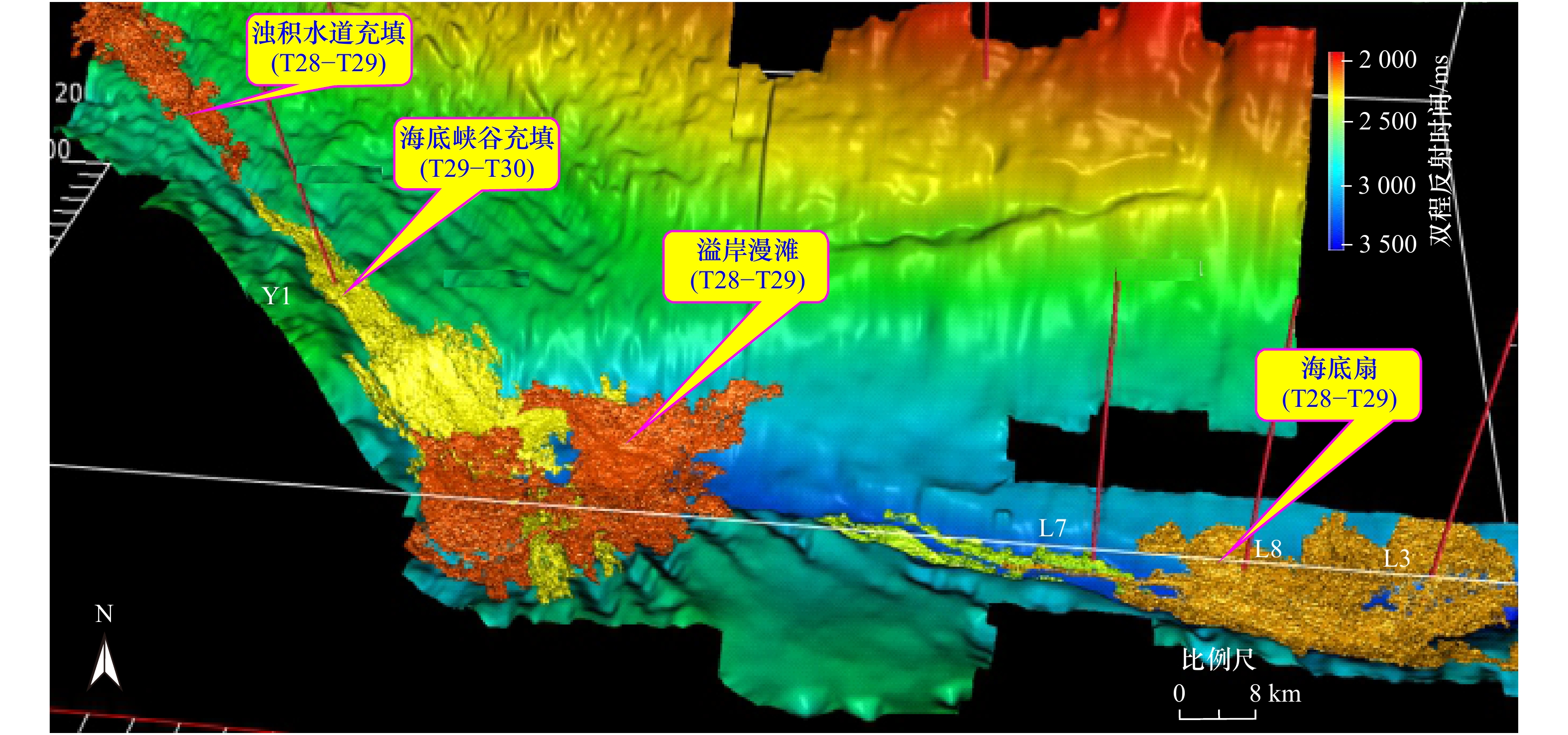
摘要: 近年来在琼东南盆地超深水区莺歌海组发现了多个深水气藏,展现了广阔的勘探前景。但随着油气勘探进一步推进,关于莺二段的储层物性问题日益凸显,严重制约了下一步的勘探进程。本文研究基于前人总结的区域地质资料,结合岩芯、测井和三维地震等资料,建立了莺二段三级层序格架,综合分析了层序格架内物源体系及其控制下的重力流沉积特征。研究表明,重力流沉积体系主要发育在莺二段下、中层序,具有南、北、轴向三大物源体系。不同物源体系控制了重力流储集体的空间展布和沉积特征:(1)南物源控制的海底峡谷充填深海泥岩,而北物源控制的海底峡谷充填的厚层浊积水道砂岩,孔渗物性好,是良好的储集层;(2)轴向物源影响的溢岸漫滩沉积,由于物性条件好,可以作为良好的油气储层;(3)南物源控制海底扇砂岩的厚度薄、粒度细、泥质含量较高,而北物源和轴向物源供应的海底峡谷和海底扇朵体的砂体面积广、厚度大、粒度粗、物性好,是深水区莺二段最重要的优质产气储层。Abstract: In recent years, several deep-water gas fields of Yinggehai Formation have been discovered in ultra-deep water area of Qiongdongnan Basin, showing a broad exploration prospect. However, the reservoir physical property prediction of the Member 2 of Neogene Yinggehai Formation have become increasingly prominent which seriously restricts the further exploration of oil and gas. Based on the regional geological data summarized by predecessors, combined with core, logging and three-dimensional seismic data, the third-order sequence framework of the Member 2 of Neogene Yinggehai Formation is established, and the provenance systems in the sequence framework and the sedimentary characteristics of gravity flow under its control are comprehensively analyzed. The results show that gravity flow sedimentary system mainly developed in Ⅱ2-ygh2c and Ⅱ2-ygh2b, and include three major provenance systems which are the south, the north and the axis. Different rovenance systems control the spatial distribution and sedimentary characteristics of gravity flow reservoirs. (1)The submarine canyons controlled by the south provenance are mainly filled by abyssal mudstone, while the canyons controlled by the north provenance are mainly filled with thick turbidite channel sandstone with fine porosity and permeability, which is a good reservoir. (2) The flood plain deposit affected by axial provenance can also be a good oil and gas reservoir because of its good physical properties. (3) The submarine fans controlled by the south provenance is characterized by thin sandstone with fine grain size and high argillaceous content. While the submarine canyons and fans controlled by the north and the axis provenance formed large scale sandstone with big thickness, coarse grain size and good reservoir physical properties, which are the most important high-quality gas-producing reservoirs of deep water area.
-
表 1 琼东南盆地地层划分
Tab. 1 Stratigraphic division of the Qiongdongnan Basin

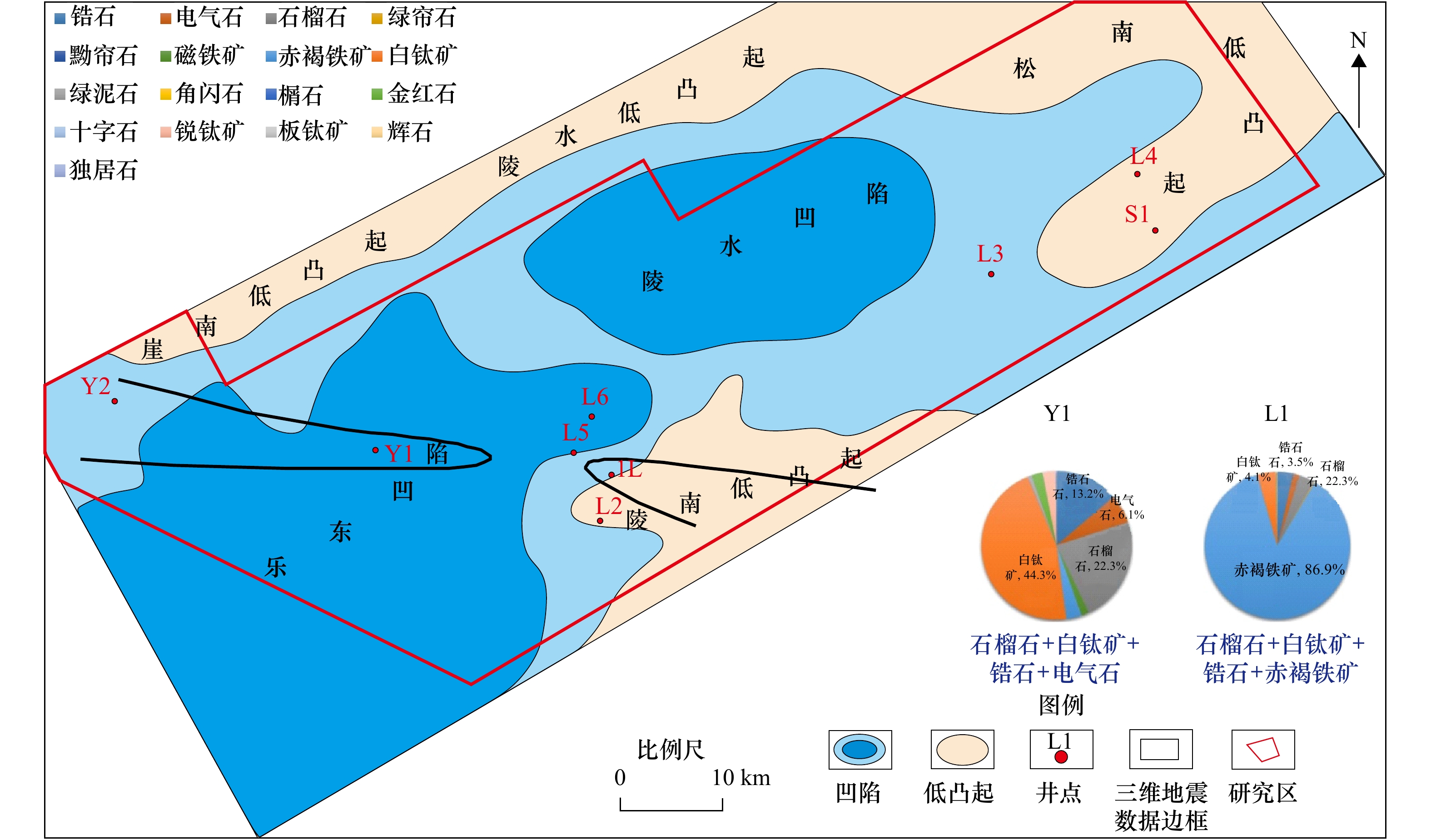
表 2 乐东−陵水凹陷钻井莺二段重矿物统计(%)
Tab. 2 Heavy mineral statistics of the Yinggehai Formation from wells of the Qiongdongnan Basins(%)
井名 层段 锆石 电气石 石榴石 绿帘石 磁铁矿 赤褐铁矿 白钛矿 绿泥石 角闪石 榍石 金红石 十字石 锐钛矿 板钛矿 辉石 独居石 Y1 莺二段下
(T29−T30)13.2 6.1 22.3 − 1.6 3.2 44.3 0.9 − − 2.3 − 2.7 − − 0.2 L1 3.5 1.5 3.4 0.2 − 86.9 4.1 − 0.1 − 0.1 − 0.2 − − − L3 莺二段中
(T28−T29)7.9 6.1 2.9 2.0 5.5 57.4 16.6 − 0.3 0.3 − 0.6 − − 0.1 0.3 L4 2.9 1.9 2.0 1.2 − 52.6 38.8 0.1 − − 0.1 0.5 − − − − Y1 11.2 5.2 0.3 − 8.2 17.6 36.2 − − − 2.7 − 3.6 0.3 − 0.3 L2 9.1 3.8 1.8 − 22.0 22.3 38.5 − − − 0.3 0.1 1.3 − − 0.6 S1 0.9 − − − 4.5 77.5 3.6 0.9 − − 0.0 − 0.0 − 12.6 − 注:−代表实验过程中未检测到相关数据。 -
[1] 王振峰, 孙志鹏, 朱继田, 等. 南海西部深水区天然气地质与大气田重大发现[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(10): 11−20. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.10.002Wang Zhenfeng, Sun Zhipeng, Zhu Jitian, et al. Natural gas geological characteristics and great discovery of large gas fields in deep water area of the western South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(10): 11−20. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.10.002 [2] 吕明. 琼东南盆地沉积相展布及演化[C]//第十届全国古地理学及沉积学学术会议论文摘要集. 成都: 中国矿物岩石地球化学学会, 中国地质学会, 中国石油学会, 2008.Lü Ming. Distribution and evolution of sedimentary facies in Qiongdongnan Basin[C]//Abstracts of the 10th National Conference on Paleogeography and Sedimentology. Chengdu: Chinese Society for Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, Geological Society of China, Chinese Petroleum Society, 2008. [3] 吴时国, 秦蕴珊. 南海北部陆坡深水沉积体系研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(5): 922−930.Wu Shiguo, Qin Yunshan. The research of deepwater depositional system in the northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(5): 922−930. [4] 黄卫, 解习农, 何云龙, 等. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷西段莺歌海组沉积演化及储层预测[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 33(4): 809−816.Huang Wei, Xie Xinong, He Yunlong, et al. Evolution and reservoir prediction of Yinggehai formation in western central canyon in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 33(4): 809−816. [5] 付超, 于兴河, 金丽娜, 等. 琼东南盆地莺歌海组重力流沉积演化过程[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(3): 552−560.Fu Chao, Yu Xinghe, Jin Li’na, et al. Sedimentary evolution of gravity flow disposition of Yinggehai formation in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(3): 552−560. [6] 李冬, 王英民, 王永凤, 等. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷深水天然堤—溢岸沉积[J]. 沉积学报, 2011, 29(4): 689−684.Li Dong, Wang Yingmin, Wang Yongfeng, et al. The sedimentary and foreground of prospect for levee-overbank in Central Canyon, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(4): 689−684. [7] 张道军, 王亚辉, 赵鹏肖, 等. 南海北部琼东南盆地陵水段峡谷沉积建造及勘探意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(2): 25−35.Zhang Daojun, Wang Yahui, Zhao Pengxiao, et al. Sedimentary Formation and exploration significance of the Lingshui Canyon system in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(2): 25−35. [8] 李伟, 左倩媚, 张道军, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区中央峡谷黄流组储层特征及主控因素[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(11): 117−124.Li Wei, Zuo Qianmei, Zhang Daojun, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors about the reservoir of Huangliu Formation in the central canyon of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(11): 117−124. [9] 左倩媚, 张道军, 何卫军, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区中央峡谷黄流组物源特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(5): 15−23.Zuo Qianmei, Zhang Daojun, He Weijun, et al. Provenance analysis of Huangliu Formation of the central canyon system in the deepwater area of the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(5): 15−23. [10] 姚哲, 朱继田, 左倩媚, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区重力流沉积体系及油气勘探前景[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(10): 21−30. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.10.003Yao Zhe, Zhu Jitian, Zuo Qianmei, et al. Gravity flow sedimentary system and petroleum exploration prospect of deep water area in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(10): 21−30. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.10.003 [11] 王振峰, 李绪深, 孙志鹏, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区油气成藏条件和勘探潜力[J]. 中国海上油气, 2011, 23(1): 7−13, 31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2011.01.002Wang Zhenfeng, Li Xushen, Sun Zhipeng, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and exploration potential in the deep-water region, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2011, 23(1): 7−13, 31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2011.01.002 [12] 朱伟林, 钟锴, 李友川, 等. 南海北部深水区油气成藏与勘探[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(24): 3121−3129. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4940-yZhu Weilin, Zhong Kai, Li Youchuan, et al. Characteristics of hydrocarbon accumulation and exploration potential of the northern South China Sea Deepwater Basins[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(24): 3121−3129. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4940-y [13] 王英民, 徐强, 李冬, 等. 南海西北部晚中新世的红河海底扇[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(14): 1488−1494. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4441-zWang Yingmin, Xu Qiang, Li Dong, et al. Late Miocene Red River submarine fan, northwestern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(14): 1488−1494. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4441-z [14] 左倩媚, 张道军, 王亚辉, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区新近系海底扇沉积特征与资源潜力[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(11): 105−116.Zuo Qianmei, Zhang Daojun, Wang Yahui, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and exploration potential of Neogene submarine fan in the deepwater area of the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(11): 105−116. [15] 能源, 吴景富, 漆家福, 等. 南海北部深水区新生代盆地三层结构及其构造演化[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(3): 403−414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.03.010Neng Yuan, Wu Jingfu, Qi Jiafu, et al. Three structural layers and its evolution of Cenozoic basins in deep water area of Northern Margin, South China Sea[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(3): 403−414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.03.010 [16] 邵磊, 李昂, 吴国瑄, 等. 琼东南盆地沉积环境及物源演变特征[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(4): 548−552. doi: 10.7623/syxb201004005Shao Lei, Li Ang, Wu Guoxuan, et al. Evolution of sedimentary environment and provenance in Qiongdongnan Basin in the northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(4): 548−552. doi: 10.7623/syxb201004005 [17] 何云龙, 解习农, 李俊良, 等. 琼东南盆地陆坡体系发育特征及其控制因素[J]. 地质科技情报, 2010, 29(2): 118−122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2010.02.020He Yunlong, Xie Xinong, Li Junliang, et al. Depositional characteristics and controlling factors of continental slope system in the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2010, 29(2): 118−122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2010.02.020 [18] 王海荣, 王英民, 邱燕, 等. 南海北部陆坡的地貌形态及其控制因素[J]. 海洋学报, 2008, 30(2): 70−79.Wang Hairong, Wang Yingmin, Qiu Yan, et al. Geomorphology and its control of deep-water slope of the margin of the South China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2008, 30(2): 70−79. -




 下载:
下载: