Sediment provenance of the East Siberian Arctic Shelf: Evidence from clay minerals and chemical elements
-
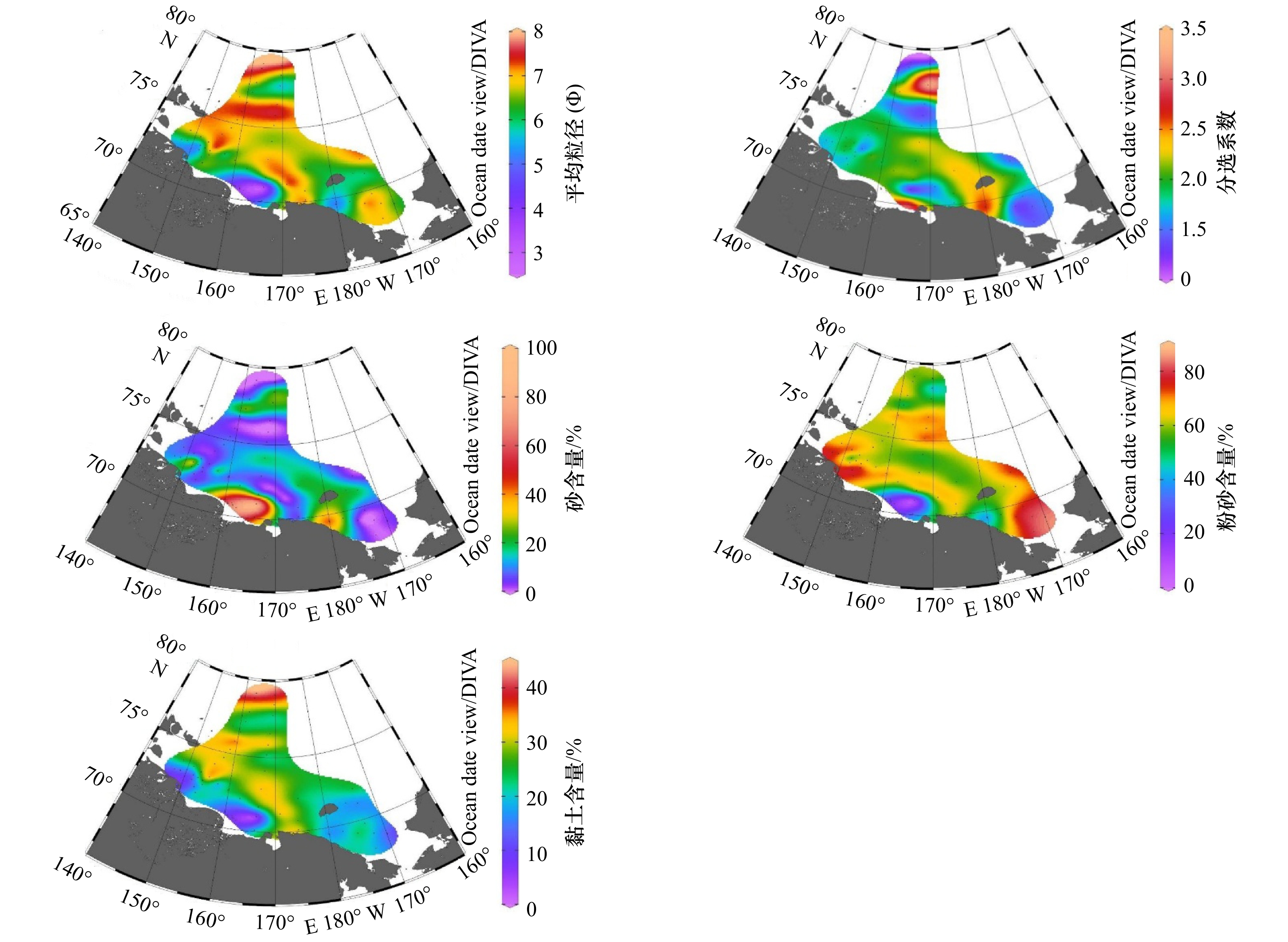
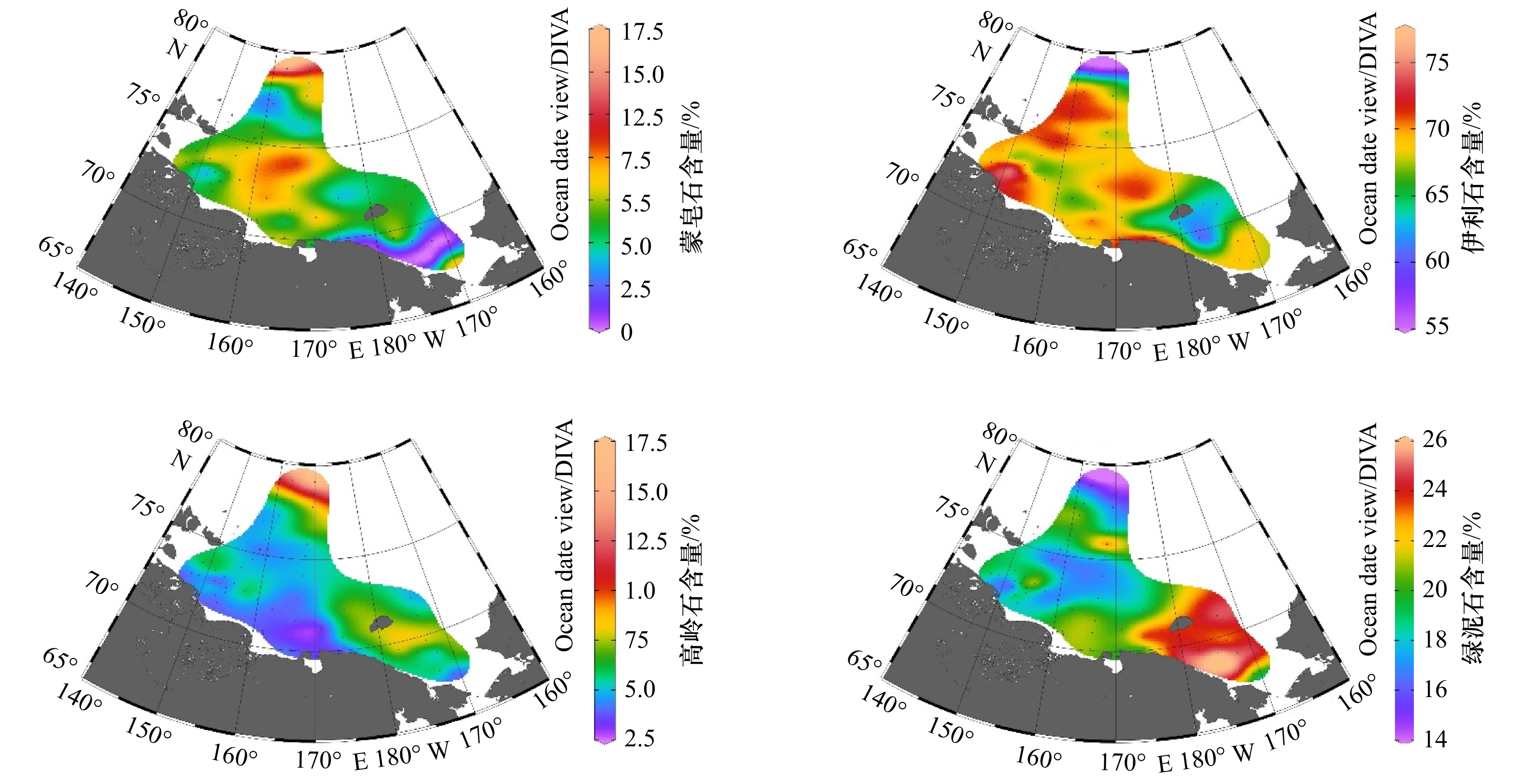
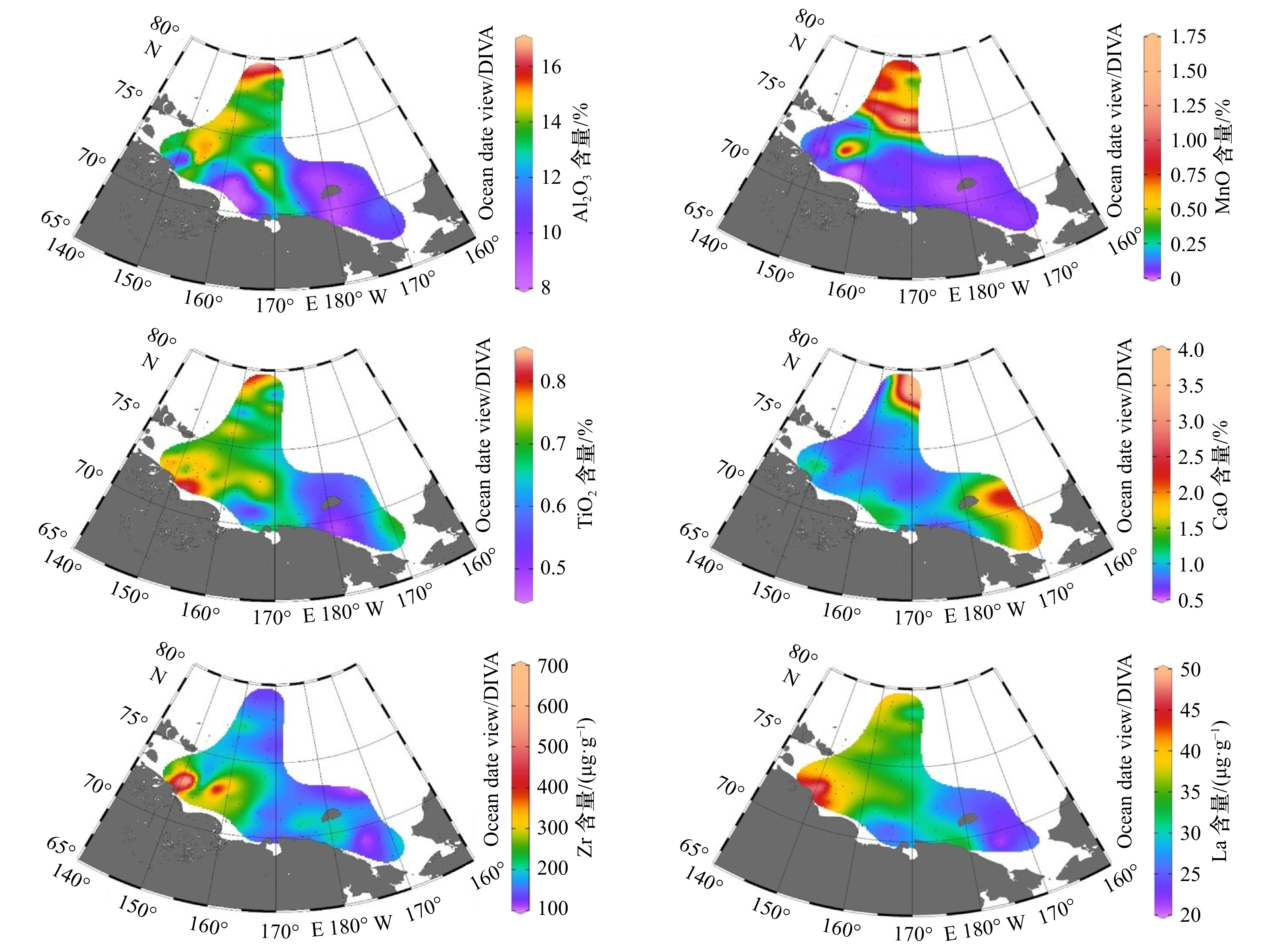
摘要: 本文对北极东西伯利亚陆架表层沉积物进行了粒度、黏土矿物以及常微量元素测定,阐述了粒度、黏土矿物和常微量元素的分布特征。利用因子分析与聚类分析划分了不同的沉积区,并探讨了各区沉积物的主要来源。结果表明,研究区可以划分为4个沉积区:(1)东西伯利亚海近岸河口区(Ⅰ区),沉积物以粉砂和砂质粉砂为主,TiO2、Zr、SiO2含量较高,其他元素在该区都处于低值,La/Th与Zr/Hf比值在4个沉积区中为最大值,黏土矿物中伊利石含量占绝对优势,约为70%,该区受到河流与海岸侵蚀物质输入的强烈影响;(2)东西伯利亚海中部(Ⅱ区),沉积物以粉砂和泥为主,MnO、Ba与Ni等元素在该区含量较高,黏土矿物组合与Ⅰ区类似,La/Th和Zr/Hf比值比Ⅰ区略低,该区沉积物以河流输入的细粒沉积物为主,受海冰等过程的影响发生了混合,随着离岸距离的增加,海洋自生组分开始增多;(3)东西伯利亚海北部深水区(Ⅲ区),沉积物以泥为主,Al2O3、K2O、V、Li等在该区达到最大值,La/Th和Rb/Th比值与Ⅱ区极其类似,伊利石含量在该区为最低值,蒙皂石与高岭石含量在该区达到最大值(>10%),该区细粒沉积物很可能受大西洋水体以及波弗特环流的影响;(4)楚科奇海(Ⅳ区),该区沉积物主要由粉砂和砂质粉砂组成,CaO、P2O5等在该区含量较高,Rb/Th、La/Th与Zr/Hf均为4个沉积区的最小值,绿泥石在该区最为富集,该区沉积物受太平洋入流水的影响强烈。Abstract: Grain size, clay minerals and major and trace elements of surface sediment samples collected from the East Siberian Arctic Shelf are analyzed. Based on factor analysis and cluster analysis the study area is divided into four provinces, the main sediment sources of each province are discussed. The results show that province I covers the estuary area of the Kolyma River and the Indigirka River. The sediments are mainly composed of silt and sandy silt, and characterized by higher content of SiO2, TiO2, Zr and low content of other elements. The ratios of La/Th and Zr/Hf reach the maximum in the four sedimentary areas. Illite is dominant which accounting for 70% of the whole clay minerals. This area is strongly influenced by terrestrial sources from the Kolyma River and the Indigirka River. Province II is located in the middle of the East Siberian Sea, where the sediments are generally silt and mud. The content of MnO, Ba, and Ni are relatively higher. La/Th and Zr/Hf ratio are slightly lower than that in Province I. Clay minerals composition is similar to Province I. The sediments in this area are mainly fine-grained derived by rivers, which are also influenced by sea ice process. As the distance increasing offshore, the content of marine authigenic components begin to increase. Province III is located in the northern East Siberian Sea, and sediments there are mainly mud. Elements such as Al2O3, K2O, V, Li reach the maximum value in this area. The La/Th and Rb/Th ratios are similar to those in the Province II. The content of illite is the lowest, semctite and kaolinite reach the maximum (>10%). Fine-grained sediments in this area are probably influenced by Atlantic waters and the Beaufort Gyre. Province IV is located in Chukchi Sea where the sediments consist of silt and sandy silt. Elements are characterized by higher contents of CaO, P2O5. The ratios of Rb/Th, La/Th and Zr/Hf are the minimum values, the content of chlorite reach peak (>20%). Sediments in this area are significantly influenced by the Pacific inflow water.
-
Key words:
- sediment source /
- clay mineral /
- major and trace elements /
- East Siberian Sea /
- Chukchi Sea
-
图 6 Q型聚类分析树状图(a)和分区图(b),1922−2012年年均海表盐度分布(c)
图b中黄色曲线为1980−2010年夏季最小冰缘线,数据来源于www.meereisportal.de;图c数据来源于http://odv.awi.de
Fig. 6 Dendrogram of Q-mode cluster analysis (a), and provinces of the East Siberian Arctic Shelf according to the Q-mode cluster analysis (b), and annual average sea surface salinity distribution from 1922 to 2012 (c)
The yellow curve in fig.b is the summer minimum sea-ice line from 1980 to 2010, data source: www.meereisportal.de; data source of fig.c: http://odv.awi.de
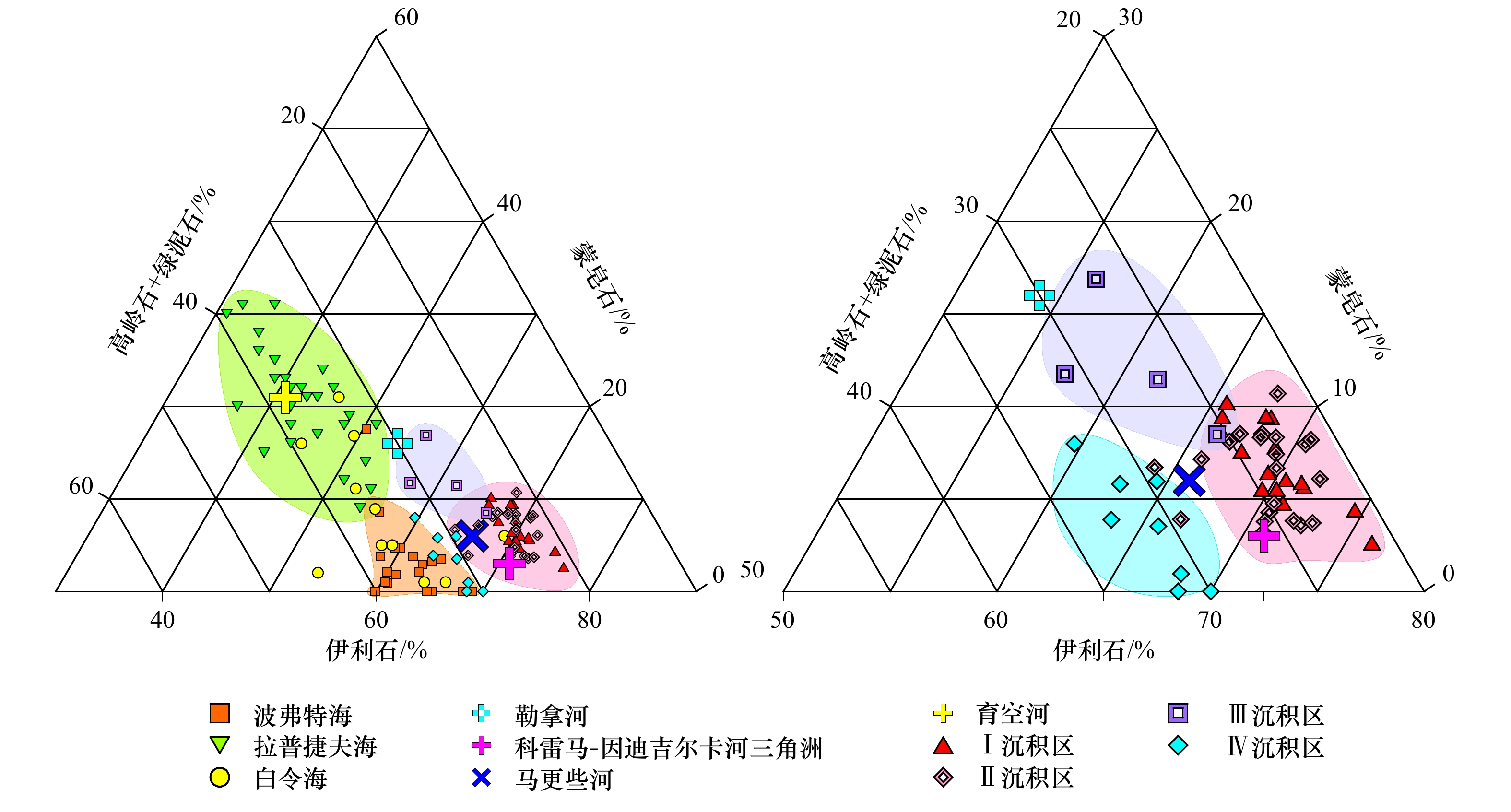
图 7 伊利石−蒙皂石−高岭石+绿泥石三组分图解
勒拿河、马更些河、育空河与科雷马河−因迪吉尔卡河三角洲黏土矿物数据分别来自文献[44]、[49]、[11]、[50];波弗特海、拉普捷夫海和白令海数据来自文献[42, 45, 51]
Fig. 7 Ternary diagram of clay minerals
Clay minerals data of the Lena River, Mackenzie River, Yukon River and Kolyma-Indigirka River Delta are obtained from references [44]、[49]、[11]、[50]; clay minerals data of the Beaufort Sea, Laptev Sea and Bering Sea are obtained from references [42, 45, 51]
图 8 Rb/Th-La/Th比值(a)和Zr/Hf-La/Th比值(b)散点图
勒拿河与亚纳河数据来自于文献[52],西伯利亚高原火山岩与鄂霍次克−楚科奇火山带数据来自于http://georoc.mpch-mainz.gwdg.de/georoc/Entry.html
Fig. 8 Scatter plot of Rb/Th-La/Th (a) and Zr/Hf-La/Th (b) ratio
Data of Lena River and Yana River are obtained from reference [52]; data of Siberian Platform volcanic rocks and Okhotsk–Chukotka volcanogenic belt are obtained from http://georoc.mpch-mainz.gwdg.de/georoc/Entry.html
河流 流域面积/(103 km2) 年径流量/km3 年输沙量/(106 t) 勒拿河 2 448 532 20.7 亚纳河 225 31.9 4.0 因迪吉尔卡河 360 54.2 11.1 科雷马河 647 122 10.1 表 2 北极东西伯利亚陆架表层沉积物黏土矿物相对含量
Tab. 2 Relative content of clay minerals in the surface sediments of the East Siberian Arctic Shelf
黏土矿物 蒙皂石/% 伊利石/% 高岭石/% 绿泥石/% 最小值 0 56 3 14 最大值 17 76 17 26 平均值 6 68 6 20 表 3 东西伯利亚陆架表层沉积物常微量元素含量
Tab. 3 Content of major and trace elements in the surface sediments of the East Siberian Arctic Shelf
常量元素含量/% SiO2 Al2O3 CaO TFe2O3 K2O MgO MnO Na2O P2O5 TiO2 最小值 52.70 8.69 0.69 2.15 1.69 0.75 0.03 2.73 0.10 0.48 最大值 77.02 16.12 3.91 8.62 3.09 2.77 1.52 5.12 0.48 0.82 平均值 64.01 12.79 1.17 5.27 2.59 1.76 0.27 3.51 0.23 0.69 标准差 5.35 2.01 0.65 1.40 0.36 0.49 0.35 0.51 0.06 0.08 微量元素/(μg·g−1) Ba Sr V Zn Zr Li Cr Ni Rb La 最小值 516 139 54 34 105 18 37 10 59 21 最大值 731 233 248 161 659 62 96 86 123 48 平均值 603 178 130 92 217 42 68 32 94 34 标准差 47 22 42 27 107 12 12 17 17 6 表 4 各沉积区内平均水深、粒径、黏土矿物含量以及因子得分统计
Tab. 4 Mean water depth, grain size, clay minerals content and factor score of elements in each province
Ⅰ区 Ⅱ区 Ⅲ区 Ⅳ区 水深/m 16 74 1375 49 平均粒径(Φ) 5.80 6.91 7.47 6.41 蒙皂石/% 7 6 12 4 伊利石/% 70 69 60 65 高岭石/% 5 5 13 6 绿泥石/% 19 19 15 25 F1 −0.83 0.46 1.59 −0.44 F2 0.79 −0.16 −0.06 −1.03 F3 −0.31 −0.12 −0.59 1.19 F4 −0.16 0.31 −0.02 −0.52 F5 0.10 −0.61 1.89 0.47 -
[1] Stein R. Arctic Ocean Sediments: Processes, Proxies, and Paleoenvironment[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2008. [2] Shakhova N, Semiletov I, Leifer I, et al. Geochemical and geophysical evidence of methane release over the East Siberian Arctic Shelf[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2010, 115(C8): C08007. [3] Grebmeier J M, Cooper L W, Feder H M, et al. Ecosystem dynamics of the Pacific-influenced Northern Bering and Chukchi Seas in the Amerasian Arctic[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2006, 71(2/4): 331−361. [4] Stein R, Fahl K, Schade I, et al. Holocene variability in sea ice cover, primary production, and Pacific-Water inflow and climate change in the Chukchi and East Siberian Seas (Arctic Ocean)[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2017, 32(3): 362−379. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2929 [5] Frey K E, Moore G W K, Cooper L W, et al. Divergent patterns of recent sea ice cover across the Bering, Chukchi, and Beaufort seas of the Pacific Arctic Region[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2015, 136: 32−49. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2015.05.009 [6] Semiletov I P, Shakhova N E, Sergienko V I, et al. On carbon transport and fate in the East Siberian Arctic land-shelf-atmosphere system[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2012, 7(1): 015201. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/7/1/015201 [7] Romanovskii N N, Hubberten H W, Gavrilov A V, et al. Permafrost of the east Siberian Arctic shelf and coastal lowlands[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2004, 23(11/13): 1359−1369. [8] Vonk J E, Sanchez-García L, van Dongen B E, et al. Activation of old carbon by erosion of coastal and subsea permafrost in Arctic Siberia[J]. Nature, 2012, 489(7414): 137−140. doi: 10.1038/nature11392 [9] Dudarev O V, Semiletov I P, Charkin A N, et al. Deposition settings on the continental shelf of the East Siberian Sea[J]. Doklady Earth Sciences, 2006, 409(2): 1000−1005. doi: 10.1134/S1028334X06060389 [10] Naugler F P, Silverberg N, Creager J S. Recent sediments of the East Siberian Sea[M]//Herman Y. Marine Geology and Oceanography of the Arctic Seas. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1974: 191−210. [11] Naidu A S, Creager J S, Mowatt T C. Clay mineral dispersal patterns in the north Bering and Chukchi Seas[J]. Marine Geology, 1982, 47(1/2): 1−15. [12] Nikolaeva N A, Derkachev A N, Dudarev O V. Mineral composition of sediments from the Eastern Laptev Sea shelf and East Siberian Sea[J]. Oceanology, 2013, 53(4): 472−480. doi: 10.1134/S0001437013040073 [13] Levitan M A, Lavrushin Y A. The arctic ocean[M]//Levitan M A, Lavrushin Y A. Sedimentation History in the Arctic Ocean and Subarctic Seas for the Last 130 kyr. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Science & Business Media, 2009. [14] 陈志华, 石学法, 韩贻兵, 等. 北冰洋西部表层沉积物粘土矿物分布及环境指示意义[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2004, 22(4): 446−454. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2004.04.006Chen Zhihua, Shi Xuefa, Han Yibing, et al. Clay mineral distributions in surface sediments from the western arctic ocean and their implications for sediment environments[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2004, 22(4): 446−454. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2004.04.006 [15] 董林森, 刘焱光, 石学法, 等. 西北冰洋表层沉积物黏土矿物分布特征及物质来源[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(4): 22−32.Dong Linsen, Liu Yanguang, Shi Xuefa, et al. Distributions and sources of clay minerals in the surface sediments of the western Arctic Ocean[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(4): 22−32. [16] Viscosi-Shirley C, Mammone K, Pisias N, et al. Clay mineralogy and multi-element chemistry of surface sediments on the Siberian-Arctic shelf: implications for sediment provenance and grain size sorting[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2003, 23(11/13): 1175−1200. [17] 陈志华. 北冰洋西部沉积物地球化学特征及环境指示意义[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2004.Chen Zhihua. Geochemistry of sediments in the western Arctic ocean and implications of spatial and temporal changes of sedimentary environments[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2004. [18] 高爱国, 韩国忠, 刘峰, 等. 楚科奇海及其邻近海域表层沉积物的元素地球化学特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(2): 132−139.Gao Aiguo, Han Guozhong, Liu Feng, et al. The elemental geochemistry of the surface sediments in the Chukchi Sea and its adjacent areas[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2004, 26(2): 132−139. [19] 黄晓璇, 王汝建, 肖文申, 等. 西北冰洋楚科奇海台晚第四纪以来陆源沉积物搬运机制及其古环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(2): 52−62.Huang Xiaoxuan, Wang Rujian, Xiao Wenshen, et al. Transportation mechanism of terrigenous sediment and its paleoenvironmental implications on the Chukchi Plateau, western Arctic Ocean during the late Quaternary[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(2): 52−62. [20] 尚婷. 南海和北极海域海洋表层沉积物地球化学研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2008.Shang Ting. Geochemistry study of marine surface sediment in South China sea and Arctic sea area[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2008. [21] 章伟艳, 于晓果, 汪卫国, 等. 近百年来楚科奇海域沉积环境变化的有机碳、氮记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(2): 13−24.Zhang Weiyan, Yu Xiaoguo, Wang Weiguo, et al. Records of organic carbon and total nitrogen for environmental changes in the Chukchi Sea during the past 100 years[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(2): 13−24. [22] 王春娟, 刘焱光, 董林森, 等. 白令海与西北冰洋表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(3): 1−9.Wang Chunjuan, Liu Yanguang, Dong Linsen, et al. The distribution pattern of the surface sediments in the Bering Sea and the western Arcric and its environmental implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(3): 1−9. [23] Pnyushkov A V, Polyakov I V, Ivanov V V, et al. Structure and variability of the boundary current in the Eurasian Basin of the Arctic Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2015, 101: 80−97. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2015.03.001 [24] Jakobsson M. Hypsometry and volume of the Arctic Ocean and its constituent seas[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2002, 3(5): 1−18. [25] Ivanov V V, Piskun A A. Distribution of river water and suspended sediment loads in the deltas of rivers in the basins of the Laptev and East-Siberian Seas[M]//Kassens H. Land-Ocean Systems in the Siberian Arctic. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1999: 239−250. [26] Huh Y, Panteleyev G, Babich D, et al. The fluvial geochemistry of the rivers of Eastern Siberia: II. Tributaries of the Lena, Omoloy, Yana, Indigirka, Kolyma, and Anadyr draining the collisional/accretionary zone of the Verkhoyansk and Cherskiy ranges[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62(12): 2053−2075. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00127-6 [27] Holmes R M, McClelland J W, Peterson B J, et al. A circumpolar perspective on fluvial sediment flux to the Arctic ocean[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2002, 16(4): 45-1−45-14. [28] Gordeev V V. Fluvial sediment flux to the Arctic Ocean[J]. Geomorphology, 2006, 80(1/2): 94−104. [29] Stein R, Macdonald R W. The Organic Carbon Cycle in the Arctic Ocean[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2004. [30] Weingartner T J, Danielson S, Sasaki Y, et al. The Siberian coastal current: a wind- and buoyancy-forced arctic coastal current[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1999, 104(C12): 29697−29713. doi: 10.1029/1999JC900161 [31] Semiletov I, Dudarev O, Luchin V, et al. The East Siberian Sea as a transition zone between Pacific-derived waters and Arctic shelf waters[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(10): L10614. doi: 10.1029/2005GL022490 [32] Folk R L, Andrews P B, Lewis D. Detrital sedimentary rock classification and nomenclature for use in New Zealand[J]. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 1970, 13(4): 937−968. doi: 10.1080/00288306.1970.10418211 [33] McManus J. Grain size determination and interpretation[C]//Tucker M. Techniques in Sedimentology. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1988: 63−85. [34] Biscaye P E. Mineralogy and sedimentation of recent deep-sea clay in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas and oceans[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1965, 76(7): 803−832. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1965)76[803:MASORD]2.0.CO;2 [35] 杨守业, 李从先. 元素地球化学特征的多元统计方法研究──长江与黄河沉积物元素地球化学研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 1999(1): 63−67.Yang Shouye, Li Congxian. Multiple statistic study of element geochemical characteristics element geochemical study on the Changjiang and Huanghe sediments[J]. Journal of Mineral and Petrology, 1999(1): 63−67. [36] 赵一阳. 中国海大陆架沉积物地球化学的若干模式[J]. 地质科学, 1983(4): 307−314.Zhao Yiyang. Some geochemical patterns of shelf sediments of the China seas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1983(4): 307−314. [37] Calvert S E, Pedersen T F. Geochemistry of recent oxic and anoxic marine sediments: implications for the geological record[J]. Marine Geology, 1993, 113(1/2): 67−88. [38] 赵一阳, 喻德科. 黄海沉积物地球化学分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1983, 14(5): 432−446.Zhao Yiyang, Yu Deke. Geochemical analysis of the sediments of the Huanghai sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1983, 14(5): 432−446. [39] 刘英俊, 曹励明. 元素地球化学导论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987.Liu Yingjun, Cao Liming. Introduction to Element Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1987. [40] Viscosi-Shirley C, Pisias N, Mammone K. Sediment source strength, transport pathways and accumulation patterns on the Siberian–Arctic's Chukchi and Laptev shelves[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2003, 23(11/13): 1201−1225. [41] Macdonald R W, Kuzyk Z Z A, Johannessen S C. The vulnerability of Arctic shelf sediments to climate change[J]. Environmental Reviews, 2015, 23(4): 461−479. doi: 10.1139/er-2015-0040 [42] Wahsner M, Müller C, Stein R, et al. Clay-mineral distribution in surface sediments of the Eurasian Arctic Ocean and continental margin as indicator for source areas and transport pathways—a synthesis[J]. Boreas, 1999, 28(1): 215−233. [43] Darby D A. Kaolinite and other clay minerals in Arctic Ocean sediments[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1975, 45(1): 272−279. [44] Dethleff D, Rachold V, Tintelnot M, et al. Sea-ice transport of riverine particles from the Laptev Sea to Fram Strait based on clay mineral studies[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2000, 89(3): 496−502. doi: 10.1007/s005310000109 [45] Rossak B T, Kassens H, Lange H, et al. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the Laptev Sea: indicator for sediment provinces, dynamics and sources[M]//Kassens H, Bauch H A, Dmitrenko I A, et al. Land-Ocean Systems in the Siberian Arctic. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1999: 587−599. [46] Stein R, Grobe H, Wahsner M. Organic carbon, carbonate, and clay mineral distributions in eastern central Arctic Ocean surface sediments[J]. Marine Geology, 1994, 119(3/4): 269−285. [47] McLennan S M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: influence of provenance and sedimentary processes[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 1989, 21(1): 169−200. [48] Crichton J G, Condie K C. Trace elements as source indicators in cratonic sediments: a case study from the Early Proterozoic Libby Creek Group, southeastern Wyoming[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1993, 101(3): 319−332. doi: 10.1086/648226 [49] Naidu A S, Mowatt T C. Sources and dispersal patterns of clay minerals in surface sediments from the continental-shelf areas off Alaska[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1983, 94(7): 841−854. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1983)94<841:SADPOC>2.0.CO;2 [50] Silverberg N. Sedimentology of the surface sediments of the east siberian and laptev seas[D]. Washington: University of Washington, 1972. [51] Naidu A S, Burrell D C, Hood D W. Clay mineral composition and geologic significance of some Beaufort Sea sediments[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1971, 41(3): 691−694. [52] Rachold V. Major, trace and rare earth element geochemistry of suspended particulate material of East Siberian rivers draining to the Arctic Ocean[M]//Kassens H. Land-Ocean Systems in the Siberian Arctic. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1999: 199−222. [53] Münchow A, Weingartner T J, Cooper L W. The summer hydrography and surface circulation of the East Siberian Shelf Sea[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1999, 29(9): 2167−2182. doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1999)029<2167:TSHASC>2.0.CO;2 [54] Suchet P A, Probst J L, Ludwig W. Worldwide distribution of continental rock lithology: implications for the atmospheric/soil CO2 uptake by continental weathering and alkalinity river transport to the oceans[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2003, 17(2): 1038. [55] Nürnberg D, Wollenburg I, Dethleff D, et al. Sediments in Arctic sea ice: implications for entrainment, transport and release[J]. Marine Geology, 1994, 119(3/4): 185−214. [56] Dmitrenko I, Kirillov S, Eicken H, et al. Wind-driven summer surface hydrography of the eastern Siberian shelf[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(14): L14613. [57] Vogt C, Knies J. Sediment dynamics in the Eurasian Arctic Ocean during the last deglaciation—The clay mineral group smectite perspective[J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 250(3/4): 211−222. [58] Clark D L, Whitman R R, Morgan K A, et al. Stratigraphy and Glacial-marine Sediments of the Amerasian Basin, Central Arctic Ocean[M]. Boulder: Geological Society of America, 1980. [59] Moser F C, Hein J R. Distribution of Clay Minerals in the Suspended and Bottom Sediments from the Northern Bering Sea Shelf Area, Alaska[M]. Alexandria: US Government Printing Office, 1984. -





 下载:
下载: