Effect of salinity stress on the antioxidant enzymes, non-specific immune enzymes, and Na+/K+-ATPase activities in Larimichthys polyactis
-
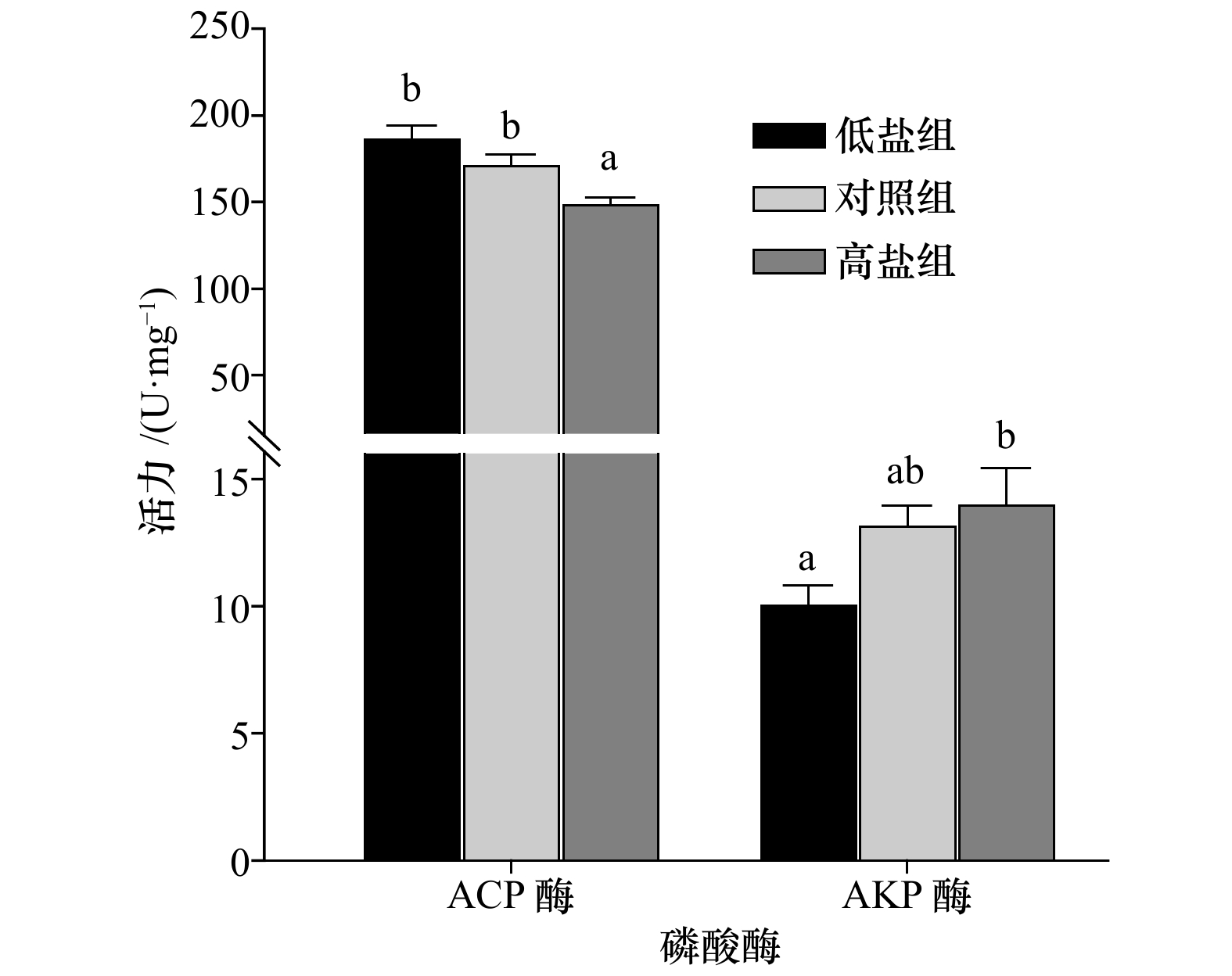
摘要: 为了研究不同盐度对小黄鱼生理的影响,以人工养殖的4月龄小黄鱼(体质量为(12.6 ±3.1)g)为实验对象,将在自然海水(对照组盐度为22.1)中养殖的小黄鱼转入到盐度为5(低盐组)和34.5(高盐组)的海水中进行急性盐度胁迫处理10 d,测定并分析肝脏中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、碱性磷酸酶(AKP)和酸性磷酸酶(ACP)活力以及鳃和肾脏中的Na+/K+-ATP酶活力的变化情况。结果显示,在急性盐度胁迫下,小黄鱼肝脏抗氧化酶(SOD和CAT)活力均上升,其中,低盐组的SOD和高盐组的CAT活力均显著高于对照组(p<0.05);在不同盐度条件下,AKP和ACP表现出相反的变化趋势,即AKP活力随着盐度上升不断增强,而ACP活力则逐渐降低;鳃中Na+/K+-ATP酶活力在低盐组最低,而肾脏中高盐组的活力显著高于对照组(p<0.05)。上述研究结果表明,小黄鱼幼鱼在盐度下降到5时仍可正常存活;不同盐度胁迫可导致小黄鱼肝脏中的非特异性免疫酶以及鳃和肾脏中的Na+/K+-ATP酶活性发生显著变化,表明小黄鱼在适应盐度变化过程中肝脏、鳃和肾脏均发挥着一定的调节作用。研究结果对小黄鱼在高盐或者咸淡水区域养殖提供了一定参考作用。
-
关键词:
- 盐度胁迫 /
- 小黄鱼 /
- 非特异性免疫酶 /
- Na+/K+-ATP酶
Abstract: In order to study the physiological effects of different salinity stress on Larimichthys polyactis, the four-month-old L. polyactis (body weight (12.6±3.1) g) cultured in natural seawater with salinity of 22.1 were applied to salinity stress in seawater salinity of 5 (called as low-salinity group) and 34.5 (called as high-salinity group), and natural seawater was used as a control group. After 10 days of acute salinity stress experimental treatment, the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), alkaline phosphatase (AKP) and acid phosphatase (ACP) in the liver and Na+/K+-ATPase in gills and kidneys were measured and analyzed. The results showed that under acute salinity stress, the activity of antioxidant enzymes (SOD and CAT) in the liver were increased. Among them, the activities of SOD in the low-salinity group and CAT in the high-salinity group were significantly higher than those in the control group (p<0.05). Under different salinity conditions, AKP and ACP showed an opposite trend of change, i.e. AKP activity gradually increased with increasing salinity, while ACP activity gradually decreased. Additionally, Na+/K+-ATPase activity in gills was the lowest in the low salinity group, and the activity of which in the kidney in the high salinity group was significantly higher than that of the control group (p<0.05). The above research results indicate that juveniles of L. polyactis can still survive normally when the salinity drops to 5, without obvious abnormality. And different salinity stress can significantly affect the non-specific immune enzymes activities of the liver, and the Na+/K+-ATPase activity of the gills and kidneys in L. polyactis. In other word, the tissues of liver, gill and kidney play an important role during the process of L. polyactis adapting to changes in salinity. The research results also provide a reference for the cultivation of L. polyactis in high-saline or brackish water areas.-
Key words:
- salinity stress /
- Larimichthys polyactis /
- non-specific immune enzyme /
- Na+/K+-ATPase
-
表 1 不同盐度胁迫下小黄鱼的存活情况
Tab. 1 Survival of L. polyactis under different salinity stress
盐度 出现死亡时间/h 24 h存活率/% 10 d存活率/% 3.9 24 71.0±2.57 0 5.0 − 100 100 22.1 − 100 100 34.5 12 91.0±2.35 85.0±2.04 36.0 6 37.5±1.87 0 37.0 5 25.0±2.35 0 38.0 3 12.5±2.47 0 39.0 3 12.5±1.17 0 40.0 1.5 10.0±2.11 0 41.6 1 0 0 43.5 1 0 0 45.0 1 0 0 注:−表示未出现死亡。 -
[1] Bœuf G, Payan P. How should salinity influence fish growth?[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 2001, 130(4): 411−423. [2] 边平江, 邱成功, 徐善良, 等. 盐度对暗纹东方鲀生长、非特异性免疫和抗氧化酶活力的影响[J]. 水生生物学报, 2014, 3838(1): 108−114. doi: 10.7541/2014.14Bian Pingjiang, Qiu Chenggong, Xu Shanliang, et al. Effects of salinity on growth, activity of non-specific immune and antioxidant enzymes in obscure puffer Takifugu obscures[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2014, 3838(1): 108−114. doi: 10.7541/2014.14 [3] 范春燕, 区又君, 李加儿, 等. 急性盐度胁迫对卵形鲳鲹幼鱼Na+-K+-ATP酶活性和渗透压的影响[J]. 台湾海峡, 2012, 31(2): 218−224.Fan Chunyan, Ou Youjun, Li Jiaer, et al. Effects of acute salinity stress on Na+-K+-ATP and osmotic pressure of juvenile Trachinotus ovatus[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2012, 31(2): 218−224. [4] 刘玲, 陈超, 李炎璐, 等. 短期低盐度胁迫对驼背鲈(♀)×鞍带石斑鱼(♂)杂交子代幼鱼抗氧化及消化生理的影响[J]. 海洋科学, 2018, 42(2): 78−87. doi: 10.11759/hykx20170717004Liu Ling, Chen Chao, Li Yanlu, et al. Effects of short-term salinity stress on antioxidant and digestive physiology of hybrid progeny (Cromilepptes altivelis ♀ × Epinephelus lanceolatus ♂)[J]. Marine Sciences, 2018, 42(2): 78−87. doi: 10.11759/hykx20170717004 [5] Martínez-Álvarez R M, Morales A E, Sanz A. Antioxidant defenses in fish: biotic and abiotic factors[J]. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 2005, 15(1/2): 75−88. [6] Evans D H, Piermarini P M, Choe K P. The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste[J]. Physiological Reviews, 2005, 85(1): 97−177. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00050.2003 [7] 胡静, 叶乐, 吴开畅, 等. 急性盐度胁迫对克氏双锯鱼幼鱼血清皮质醇浓度和Na+-K+-ATP酶活性的影响[J]. 南方水产科学, 2016, 12(2): 116−120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2016.02.017Hu Jing, Ye Le, Wu Kaichang, et al. Effect of acute salinity stress on serum cortisol and activity of Na+-K+-ATPase of juvinileAmphiprion clarkia[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2016, 12(2): 116−120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2016.02.017 [8] 支兵杰, 刘伟, 赵春刚, 等. 盐度对大麻哈鱼幼鱼消化酶及碱性磷酸酶活力的影响[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2009, 18(3): 289−294.Zhi Bingjie, Liu Wei, Zhao Chungang, et al. Effects of salinity on digestive enzyme and alkaline phosphatase activity of young chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta Walbaum)[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2009, 18(3): 289−294. [9] Yin Fei, Peng Shiming, Sun Peng, et al. Effects of low salinity on antioxidant enzymes activities in kidney and muscle of juvenile silver pomfret Pampus argenteus[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(1): 55−60. doi: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2010.11.009 [10] Romão S, Freire C A, Fanta E. Ionic regulation and Na+, K+-ATPase activity in gills and kidney of the Antarctic aglomerular cod icefish exposed to dilute sea water[J]. Journal of Fish Biology, 2001, 59(2): 463−468. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.2001.tb00146.x [11] 刘峰, 陈琳, 楼宝, 等. 小黄鱼(Pseudosciaena polyactis)形态性状与体质量的相关性及通径分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(3): 655−662.Liu Feng, Chen Lin, Lou Bao, et al. Correlation and path coefficient analysis on body weight and morphometric traits of small yellow croakerPseudosciaena polyactis[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2016, 47(3): 655−662. [12] Liu Lianwei, Sui Youzhen, Zhu Wenbin, et al. In-depth transcriptome analysis of Larimichthys polyactis, de novo assembly, functional annotation[J]. Marine Genomics, 2017, 33: 27−29. doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2017.02.002 [13] Cheng Qiqun, Chen Wenming, Ma Li. Genetic diversity and population structure of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) in the Yellow and East China seas based on microsatellites[J]. Aquatic Living Resources, 2019, 32(16): 1−9. [14] Ren J S, Jin Xianshi, Yang Tao, et al. A dynamic energy budget model for small yellow croakerLarimichthys polyactis: Parameterisation and application in its main geographic distribution waters[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2020, 427: 109051. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2020.109051 [15] 楼宝, 詹炜, 陈睿毅, 等. 小黄鱼全人工繁育技术研究[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2016, 35(5): 361−365.Lou Bao, Zhan Wei, Chen Ruiyi, et al. Studies on techniques of the artificial breeding of Larimichthys polyactis[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2016, 35(5): 361−365. [16] Yan Fajun, Tian Xiangli, Dong Shuanglin, et al. Growth performance, immune response, and disease resistance against Vibrio splendidus infection in juvenile sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus fed a supplementary diet of the potential probiotic Paracoccus marcusii DB11[J]. Aquaculture, 2014, 420−421: 105−111. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.10.045 [17] 于娜, 李加儿, 区又君, 等. 盐度胁迫对鲻鱼幼鱼鳃丝Na+/K+-ATP酶活力和体含水量的影响[J]. 动物学杂志, 2011, 46(1): 93−99.Yu Na, Li Jiaer, Ou Youjun, et al. Effects of salinity stresses on gill Na+/K+-atpase (nak) activity and body moisture in juvenile grey mullet Mugil cephalus[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 2011, 46(1): 93−99. [18] 王润萍, 戴铃灵, 陈雅飞, 等. 短期温度、盐度胁迫对海洋青鳉鱼(Oryziasmelastigma)摄食行为及抗氧化的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2019, 50(2): 378−387. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20181000234Wang Runping, Dai Lingling, Chen Yafei, et al. Effects of short-term temperature or salinity stress on feeding behavior and antioxidant of marine medaka (Oryzias Melastigma)[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2019, 50(2): 378−387. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20181000234 [19] 施钢, 张健东, 潘传豪, 等. 盐度渐变和骤变对褐点石斑鱼存活和摄饵的影响[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2011, 31(1): 45−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2011.01.009Shi Gang, Zhang Jiandong, Pan Chuanhao, et al. Effect of gradient and acute salinity stress experiment on survivor ship and food intake of brown-marbled grouper, Epinephelus fuscoguttatus[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2011, 31(1): 45−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2011.01.009 [20] 秦志清, 张雅芝, 林越赳, 等. 盐度对漠斑牙鲆幼鱼生长与存活的影响[J]. 水产学杂志, 2010, 23(4): 1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3832.2010.04.001Qin Zhiqing, Zhang Yazhi, Lin Yuejiu, et al. Effects of salinity on growth and survival of young Paralichthys lethostigma[J]. Chinese Journal of Fisheries, 2010, 23(4): 1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3832.2010.04.001 [21] 黄丽聪. 硬骨鱼类对盐度变化的适应及其渗透压调节机制的研究进展[J]. 科技创新导报, 2016, 13(9): 87−88.Huang Licong. Review on the osmoregulation and adaptation to salinity changes of teleost fish[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2016, 13(9): 87−88. [22] 谢志浩. 鱼类的渗透压调节[J]. 生物学通报, 2002(5): 22−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0006-3193.2002.05.010Xie Zhihao. Osmoregulation of fish[J]. Bulletin of Biology, 2002(5): 22−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0006-3193.2002.05.010 [23] 朱友芳, 肖懿哲, 李文辉, 等. 低盐胁迫对黄鳍棘鲷幼鱼存活率、鳃ATP酶和肝脏抗氧化酶的影响[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 52(3): 414−420.Zhu Youfang, Xiao Yizhe, Li Wenhui, et al. Effects of low salinity stress on survival rate, gill ATPase and liver antioxidant enzymes in the young yellowfin porgy Acanthopagrus latus[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2013, 52(3): 414−420. [24] 周显青, 孙儒泳, 牛翠娟. 应激对水生动物生长、行为和生理活动的影响[J]. 动物学研究, 2001, 22(2): 154−158. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-5853.2001.02.013Zhou Xianqing, Sun Ruyong, Niu Cuijuan. The effects of stress on aquatic animal’s growth, behavior and physiological activity[J]. Zoological Research, 2001, 22(2): 154−158. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-5853.2001.02.013 [25] 陈庆凯. 低盐胁迫对黄姑鱼幼鱼血清免疫和抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 海洋渔业, 2014, 36(6): 516−522. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2014.06.006Chen Qingkai. Effects of low salinity stress on antioxidant and immune parameters in serum of juvenile Nibea albiflora[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2014, 36(6): 516−522. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2014.06.006 [26] Livingstone R D. contaminant-stimulated reactive oxygen species production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2001, 42(8): 656−666. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00060-1 [27] 庄平, 王妤, 章龙珍, 等. 盐度骤降对点篮子鱼存活率及肝脏抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 2011, 50(3): 366−372.Zhuang Ping, Wang Yu, Zhang Longzhen, et al. The effects of ambient salinity decrement on survival and the activity of antioxidant enzymes in livers of Siganus guttatus[J]. Journal of Fudan University (Natural Science), 2011, 50(3): 366−372. [28] 孙鹏, 尹飞, 彭士明, 等. 盐度对条石鲷幼鱼肝脏抗氧化酶活力的影响[J]. 海洋渔业, 2010, 32(2): 154−159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2010.02.007Sun Peng, Yin Fei, Peng Shiming, et al. Effects of salinity on the activity of antioxidant enzymes in livers of juvenile Oplegnathus fasciatus[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2010, 32(2): 154−159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2010.02.007 [29] 邓平平, 施永海, 汪洋, 等. 盐度对长江刀鲚幼鱼非特异性免疫酶和消化酶活力的影响[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 2016, 31(5): 533−537.Deng Pingping, Shi Yonghai, Wang Yang, et al. Effects of salinity on activities of non-specific immune and digestive enzymes in juvenile estuarine tapertail anchovy Coilia nasus[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2016, 31(5): 533−537. [30] 房子恒, 田相利, 董双林, 等. 不同盐度下半滑舌鳎幼鱼非特异性免疫酶活力分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 44(5): 46−53.Fang Ziheng, Tian Xiangli, Dong Shuanglin, et al. Analysis of the activity of non-specific immune enzymes of juvenile tongue soles cultured in various salinities[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2014, 44(5): 46−53. [31] 刘存岐, 王安利, 王维娜, 等. 海水中几种金属离子对中国对虾幼体体内碱性磷酸酶和ATPase的影响[J]. 水产学报, 2001, 25 (4): 298−303.Liu Cunqi, Wang Anli, Wang Weina, et al. Influences of metal ions in seawater on activities of alkaline phosphatase (AKP) and ATPase in mysis and postlarvae of Penaeus chinensis[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2001, 25 (4): 298−303. [32] 白秀娟, 卢伙胜, 张冰. 亚硝酸盐对茂名海域文昌鱼生长及磷酸酶的影响[J]. 水产科技, 2008(5): 6−9.Bai Xiujuan, Lu Huosheng, Zhang Bing. Effects of nitrite on the growth and the phosphatase of Branchiostoma belcheri in Maoming sea area[J]. Fisheries Science and Technology, 2008(5): 6−9. [33] 李娜, 赵玉超, 王仁杰, 等. 高盐胁迫对凡纳滨对虾消化及免疫相关酶活力的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(4): 1411−1417.Li Na, Zhao Yuchao, Wang Renjie, et al. Effects of high salinity on digestive and immunity related enzymes in Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(4): 1411−1417. [34] 章龙珍, 罗集光, 赵峰, 等. 盐度对点篮子鱼血清渗透压、离子含量及鳃丝Na+/K+-ATP酶活力的影响[J]. 海洋渔业, 2015, 37(5): 449−456. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2015.05.008Zhang Longzhen, Luo Jiguang, Zhao Feng, et al. Influence of salinity on serum osmolarity, ion content and gill Na+, K+-ATPase activity of Siganus guttatas[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2015, 37(5): 449−456. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2015.05.008 [35] 张晓燕, 温海深, 张凯强, 等. 花鲈等渗点分析及海水淡化对Na+/K+/Cl−浓度、Na+-K+-ATP酶活性及基因表达的影响[J]. 水产学报, 2018, 42(8): 1199−1208.Zhang Xiaoyan, Wen Haishen, Zhang Kaiqiang, et al. Analysis of the isotonic point and effects of seawater desalination on the Na+/K+/Cl− concentration, Na+-K+-ATPase activity andrelative gene expressions inLateolabrax maculatus[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2018, 42(8): 1199−1208. [36] 李学军, 程臆臻, 胡灿灿, 等. 不同盐度下3种罗非鱼的Na+-K+-ATPase活性比较[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2014, 35(4): 68−73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3075.2014.04.011Li Xuejun, Cheng Yizhen, Hu Cancan, et al. Na+-K+-ATPase activity of Blackchin Tilapia, Nile Tilapia and Israel Red Tilapia at different salinities[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2014, 35(4): 68−73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3075.2014.04.011 [37] 孙鹏, 彭士明, 尹飞, 等. 盐度对条石鲷幼鱼Na+-K+-ATP酶活力的影响[J]. 水产学报, 2010, 34(8): 1204−1209.Sun Peng, Peng Shiming, Yin Fei, et al. Effects of salinity on activity of Na+/-K+-ATPase in juvenileOplegnathus fasciatus[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2010, 34(8): 1204−1209. [38] 区又君, 范春燕, 李加儿, 等. 盐度对卵形鲳鲹幼鱼渗透压调节和饥饿失重的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(24): 7436−7443.Ou Youjun, Fan Chunyan, Li Jiaer, et al. Effects of salinity on the osmoregulation and weight loss from starvation in Trachinotus ovatus juvenile[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(24): 7436−7443. [39] Lambert Y, Dutil J D, Munro J. Effects of intermediate and low salinity conditions on growth rate and food conversion of Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua)[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 1994, 51(7): 1569−1576. doi: 10.1139/f94-155 [40] Imsland A K, Foss A, Gunnarsson S, et al. The interaction of temperature and salinity on growth and food conversion in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus)[J]. Aquaculture, 2001, 198(3/4): 353−367. -





 下载:
下载: