Isolation, identification and polyethylene-degrading characteristics of Bacillus LC-2
-
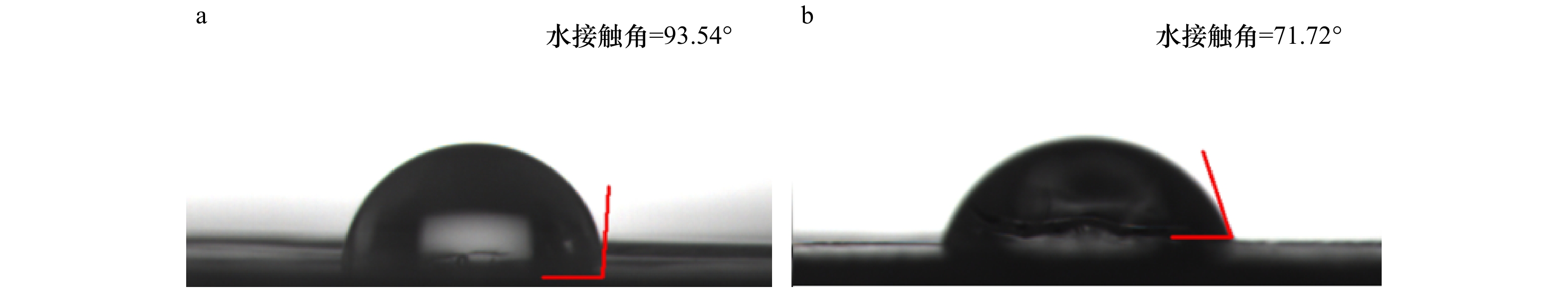
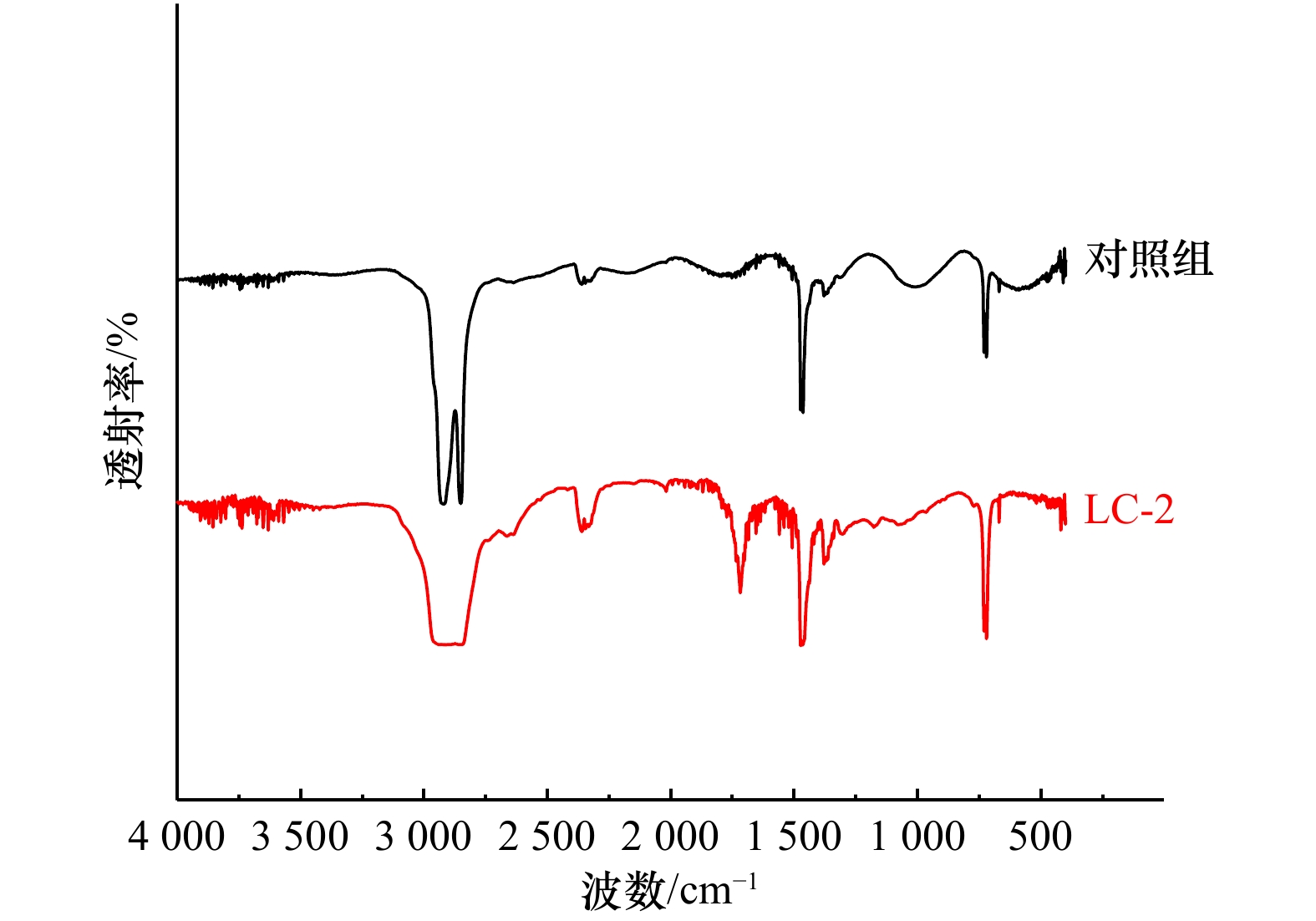
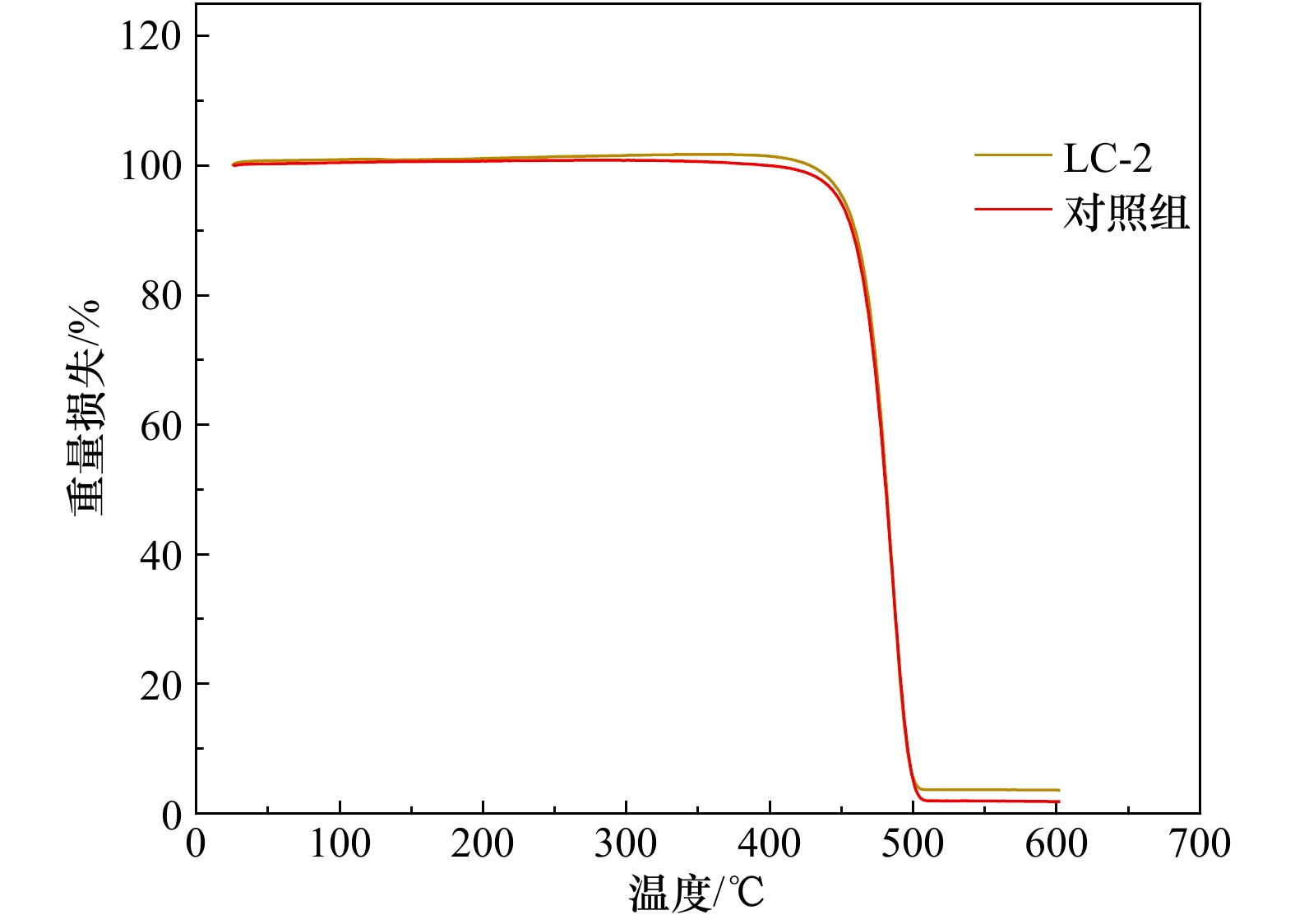
摘要: 塑料在环境中不断地积累,逐渐破碎成为尺寸小于5 mm的微塑料,对环境和人类健康构成严重威胁。本研究从青岛李村河口采集的塑料薄膜上分离出一株能够降解聚乙烯(PE)的细菌,命名为LC-2,通过分子生物学结合形态学和生理生化特征分析将其鉴定为芽孢杆菌(Bacillus aquimaris)。在以PE为唯一碳源的液体培养基中,接种该细菌培养28 d后,通过扫描电镜、接触角测定、热重分析以及傅里叶变换红外光谱等手段分析表明,PE的失重率在9%左右,表面形貌发生变化,疏水性变小且表面发生氧化,产生−C=O官能团,这些证据足以证明LC-2可以降解PE。Abstract: Plastics accumulate in the environment and gradually break into microplastics (MPs, size below 5 mm). It poses a serious threat to the environment and human health. In this study, a strain LC-2 capable of degrading polyethylene (PE) was isolated from plastic films collected from the Licun Estuary of Qingdao. It was identified as Bacillus aquimaris by using a combination of molecular biological technique with morphological, physiological and biochemical characteristics. After the strain was isolated, it was cultured in a liquid medium for 28 days with PE as the sole carbon source. The polyethylene was subsequently separated and examined with a scanning electron microscopy, a contact angle test, a thermogravimetric analysis and a Fourier transform infrared spectrum analysis. The results showed that the weight loss of PE was about 9% after the degradation, with apparent morphologic changes on the surface of PE. It was also showed that the hydrophobicity of PE became smaller, with surface oxidation to produce −C=O functional groups. These evidences are sufficient to prove that the strain LC-2 can degrade PE.
-
Key words:
- polyethylene /
- plastic /
- degradation /
- Bacillus aquimaris
-
图 4 PE塑料的扫描电镜照片
a. 未接种LC-2的PE培养28 d后;b−d. 接种LC-2的PE 培养28 d后,显示出明显的孔洞(b)、裂痕(c)和凹坑(d)
Fig. 4 Scanning electron microscopy photographs of PE plastic
a. After 28 days in culture medium without LC-2 inoculated; b−d. after 28 days in culture medium with LC-2 inoculated showing the appearance of holes (b), cracks (c) and pits (d)
-
[1] Green D S, Boots B, Blockley D J, et al. Impacts of discarded plastic bags on marine assemblages and ecosystem functioning[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(9): 5380−5389. [2] Thompson R C, Moore C J, Vom Saal F S, et al. Plastics, the environment and human health: current consensus and future trends[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2009, 364(1526): 2153−2166. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0053 [3] Geyer R, Jambeck J R, Law K L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made[J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(7): e1700782. [4] Xu Xiyuan, Wang Shuai, Gao Fenglei, et al. Marine microplastic-associated bacterial community succession in response to geography, exposure time, and plastic type in China’s coastal seawaters[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 145: 278−286. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.05.036 [5] Mccormick A, Hoellein T J, Mason S A, et al. Microplastic is an abundant and distinct microbial habitat in an urban river[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(20): 11863−11871. doi: 10.1021/es503610r [6] Kalogerakis N, Karkanorachaki K, Kalogerakis G C, et al. Microplastics generation: onset of fragmentation of polyethylene films in marine environment mesocosms[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2017, 4: 84. [7] Chang Xiaoru, Xue Yuying, Li Jiangyan, et al. Potential health impact of environmental micro- and nanoplastics pollution[J]. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 2020, 40(1): 4−15. doi: 10.1002/jat.3915 [8] Ma Jie, Zhao Jinghua, Zhu Zhilin, et al. Effect of microplastic size on the adsorption behavior and mechanism of triclosan on polyvinyl chloride[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 254: 113104. [9] Qiao Ruxia, Deng Yongfeng, Zhang Shenghu, et al. Accumulation of different shapes of microplastics initiates intestinal injury and gut microbiota dysbiosis in the gut of zebrafish[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 236: 124334. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.07.065 [10] Tourinho P S, Koci V, Loureiro S, et al. Partitioning of chemical contaminants to microplastics: sorption mechanisms, environmental distribution and effects on toxicity and bioaccumulation[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 252: 1246−1256. [11] Camacho M, Herrera A, Gómez M, et al. Organic pollutants in marine plastic debris from Canary Islands beaches[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 662: 22−31. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.422 [12] Shen Maocai, Song Biao, Zeng Guangming, et al. Are biodegradable plastics a promising solution to solve the global plastic pollution?[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 263: 114469. [13] Hadad D, Geresh S, Sivan A. Biodegradation of polyethylene by the thermophilic bacterium Brevibacillus borstelensis[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2005, 98(5): 1093−1100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02553.x [14] Sivan A. New perspectives in plastic biodegradation[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2011, 22(3): 422−426. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2011.01.013 [15] Raddadi N, Fava F. Biodegradation of oil-based plastics in the environment: existing knowledge and needs of research and innovation[J]. Science of the Total Environment,, 2019, 679: 148−158. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.419 [16] Harshvardhan K, Jha B. Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene by marine bacteria from pelagic waters, Arabian Sea, India[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 77(1/2): 100−106. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.10.025 [17] Yang Jun, Yang Yu, Wu Weimin, et al. Evidence of polyethylene biodegradation by bacterial strains from the guts of plastic-eating waxworms[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(23): 13776−13784. doi: 10.1021/es504038a [18] Paco A, Duarte K, Da Costa J P, et al. Biodegradation of polyethylene microplastics by the marine fungus Zalerion maritimum[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 586: 10−15. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.017 [19] Zhang Junqing, Gao Danling, Li Quanhao, et al. Biodegradation of polyethylene microplastic particles by the fungus Aspergillus flavus from the guts of wax moth Galleria mellonella[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 704: 135931. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135931 [20] Lwanga E H, Thapa B, Yang Xiaomei, et al. Decay of low-density polyethylene by bacteria extracted from earthworm's guts: A potential for soil restoration[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 624: 753−757. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.144 [21] Park S Y, Kim C G. Biodegradation of micro-polyethylene particles by bacterial colonization of a mixed microbial consortium isolated from a landfill site[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 222: 527−533. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.159 [22] Mehmood C T, Qazi I A, Hashmi I, et al. Biodegradation of low density polyethylene (LDPE) modified with dye sensitized titania and starch blend using Stenotrophomonas pavanii[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2016, 113: 276−286. [23] Gulmine J V, Janissek P R, Heise H M, et al. Polyethylene characterization by FTIR[J]. Polymer Testing, 2002, 21(5): 557−563. doi: 10.1016/S0142-9418(01)00124-6 [24] Rajandas H, Parimannan S, Sathasivam K, et al. A novel FTIR-ATR spectroscopy based technique for the estimation of low-density polyethylene biodegradation[J]. Polymer Testing, 2012, 31(8): 1094−1099. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2012.07.015 [25] Pometto III A L, Lee B T, Johnson K E. Production of an extracellular polyethylene-degrading enzyme(s) by streptomyces species[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1992, 58(2): 731−733. doi: 10.1128/AEM.58.2.731-733.1992 [26] Fujisawa M, Hirai H, Nishida T. Degradation of polyethylene and Nylon-66 by the laccase-mediator system[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 2001, 9(3): 103−108. doi: 10.1023/A:1020472426516 [27] Ren Liu, Men Li’na, Zhang Zhiwei, et al. Biodegradation of polyethylene byEnterobacter sp. D1 from the guts of wax moth Galleria mellonella[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 16(11): 1941. [28] 代军, 晏华, 郭骏骏, 等. 低密度聚乙烯热氧老化特性[J]. 塑料, 2016, 45(6): 54−58, 68.Dai Jun, Yan Hua, Guo Junjun, et al. Characterization of the degradation behavior of LDPE after artificial thermo-oxidative aging[J]. Plastics, 2016, 45(6): 54−58, 68. -





 下载:
下载: