Spatio-temporal variation of phosphorus, iron and sulfur in intertidal sediments of Xiamen and associated release risk of phosphorus
-
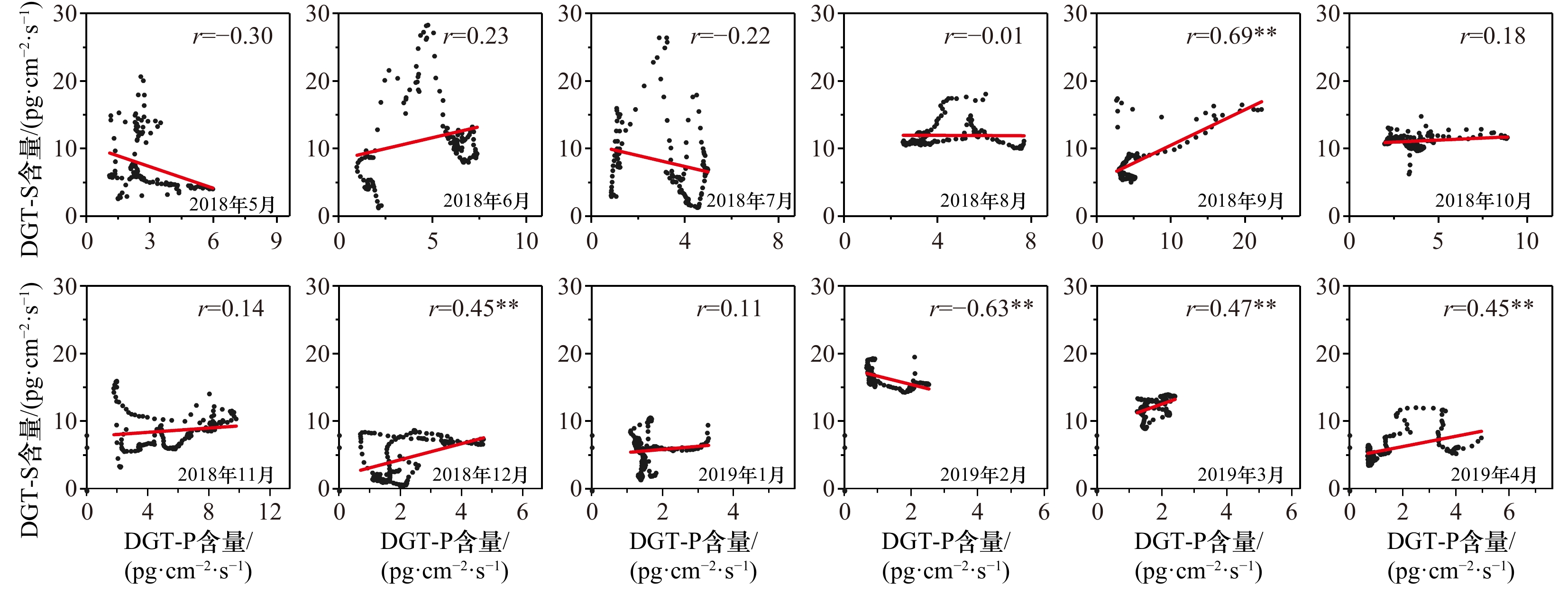
摘要: 为了解潮间带沉积物中铁和硫的氧化还原过程以及上覆水缺氧等对磷再活化和释放的影响,选择厦门翔安海岸带,应用原位、高分辨采样技术,对沉积物、孔隙水以及上覆水进行为期1 a的连续采样和监测。结果表明:上覆海水缺氧和磷含量超标较为严重,二者在多数月份分别低于2 mg/L和高于0.06 mg/L;在垂向剖面上,孔隙水中溶解活性磷含量同溶解铁含量变化规律一致,而薄膜扩散梯度技术有效态磷和有效态硫含量在局部硫高值区分布一致,表明磷的钝化和再活化主要受控于铁,局部受控于硫的氧化还原过程;在季度变化上,孔隙水中溶解活性磷同上覆水中溶解活性磷含量比较一致,归因于缺氧的沉积环境有利于溶解活性磷的跨界面交换,而多种环境因素的叠加,影响着溶解活性磷和膜扩散梯度技术有效态磷的时空变化;表层孔隙水中磷含量梯度不显著,即磷的释放风险不大,但环境因素的变化极易触发内源磷的释放。Abstract: For understanding the effects of iron and sulfur redox processes and overlying water hypoxia on phosphorus remobilization and liberation in intertidal sediments, the coastal zone in Xiang’an, Xiamen was selected to conduct continuous sampling and monitoring for sediments, pore water and overlying water in one year by employing the in-situ high resolution sampling techniques. Results showed that hypoxia and excessive phosphorus content were severe in the overlying water, which were below 2 mg/L and above 0.06 mg/L in most months, respectively. On the vertical profile, the distribution trend of dissolved reactive phosphorus (SRP) content was consistent with that of dissolved iron content in pore water, while the distribution trend of DGT-labile P was consistent with that of DGT-labile S in local, demonstrating that the passivation and remobilization of phosphorus are mainly controlled by the redox process of iron, and locally controlled by the redox process of sulfur. However, deficiency of sediment phosphorus limits the content of phosphorus in the deep reduction zone. In terms of quarterly changes, SRP content in pore water is only consistent with SRP content in overlying water, which is attributed to the hypoxic sedimentary environment favoring the cross-boundary exchange of SRP. However, the superposition of a variety of environmental factors affects the spatiotemporal changes of SRP and DGT-labile P. The SRP content concentration gradient in surface pore water was not significant, that is, the phosphorus release risk was not significant, but the change of environmental factors is very easy to trigger the release of endogenous phosphorus in future.
-
Key words:
- mobile phosphorus /
- dissolved iron /
- dissolved sulfide /
- DGT /
- HR-Peeper /
- spatio-temporal distribution
-
图 3 各个月份垂向剖面中溶解铁、SRP、DGT有效态硫和磷含量的箱型图,以及研究区上覆水SRP含量、DO浓度和表层沉积物TOC含量的点线图
Fig. 3 Box-plot of soluble Fe, SRP, DGT-labile S and DGT-labile P in vertical profile contents, and point plot of SRP content and DO concentration in the overlying water of the study area and TOC content in the surface sediments of each month
表 1 上覆水基本理化特征
Tab. 1 Basic physicochemical characteristics of the overlying water
时间 温度/℃ 盐度 溶解氧浓度/(mg·L−1) pH SRP含量/(mg·L−1) R 2018年5月 33.6 32.65 1.65 8.01 0.131 2.9 2018年6月 23.4 29.66 1.34 8.16 0.134 3.0 2018年7月 30.1 30.43 0.88 7.99 0.086 1.9 2018年8月 31.3 31.57 1.57 8.13 0.077 1.7 2018年9月 31.7 30.00 1.29 8.08 0.067 1.5 2018年10月 25.0 32.67 1.86 8.16 0.062 1.4 2018年11月 22.4 32.04 2.35 7.63 0.062 1.4 2018年12月 20.3 29.39 1.56 8.01 0.049 1.1 2019年1月 15.4 30.56 2.85 7.78 0.051 1.1 2019年2月 16.9 31.24 3.21 7.77 0.052 1.2 2019年3月 18.1 33.12 2.57 8.06 0.060 1.3 2019年4月 24.6 30.89 1.68 8.11 0.058 1.3 注:R为上覆水SRP含量与海水水质标准(GB 3097−1997)第四类水质活性磷酸盐含量(0.045 mg/L)的比值。 表 2 表层沉积物(0~10 cm)基本理化特征
Tab. 2 Basic physicochemical characteristics of the surface sediments (0 cm to 10 cm)
时间 ASC-Fe含量/(g·kg−1) ASC-P含量/(mg·kg−1) TOC含量/% TS含量/(g·kg−1) 碳氮比 砂含量/% 粉砂含量/% 黏土含量/% 2018年5月 0.84 21.3 0.51 1.66 9.53 7.82 68.2 24.0 2018年6月 0.83 20.9 0.55 1.71 9.43 1.69 64.5 33.8 2018年7月 0.88 22.7 0.54 2.40 10.5 0.59 70.8 28.6 2018年8月 0.27 18.3 0.44 2.79 10.0 4.85 70.5 24.6 2018年9月 0.30 21.0 0.39 1.77 11.0 17.5 66.6 15.9 2018年10月 0.79 21.9 0.54 1.32 9.77 2.00 72.1 25.9 2018年11月 0.54 14.2 0.62 1.50 9.35 8.09 69.6 22.4 2018年12月 0.49 8.00 0.52 1.35 8.66 13.2 68.9 18.0 2019年1月 0.68 9.00 0.60 1.32 8.79 18.0 65.5 16.6 2019年2月 0.54 6.90 0.49 1.74 9.35 21.8 74.6 3.60 2019年3月 0.73 7.60 0.64 1.18 8.21 12.3 84.4 3.30 2019年4月 0.57 7.50 0.48 1.42 8.99 14.1 81.5 4.40 -
[1] Conley D J, Paerl H W, Howarth R W, et al. Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus[J]. Science, 2009, 323(5917): 1014−1015. [2] Middelburg J J, Levin L A. Coastal hypoxia and sediment biogeochemistry[J]. Biogeosciences, 2009, 6(7): 1273−1293. [3] Smith V H, Schindler D W. Eutrophication science: where do we go from here?[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2009, 24(4): 201−207. [4] Rozan T F, Taillefert M, Trouwborst R E, et al. Iron-sulfur-phosphorus cycling in the sediments of a shallow coastal bay: implications for sediment nutrient release and benthic macroalgal blooms[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2002, 47(5): 1346−1354. [5] Pan Feng, Guo Zhanrong, Cai Yu, et al. Cyclical patterns and (im)mobilization mechanisms of phosphorus in sediments from a small creek estuary: evidence from in situ monthly sampling and indoor experiments[J]. Water Research, 2020, 171: 115479. [6] Pan Feng, Guo Zhanrong, Cai Yu, et al. Kinetic exchange of remobilized phosphorus related to phosphorus-iron-sulfur biogeochemical coupling in coastal sediment[J]. Water Resources Research, 2019, 55(12): 10494−10517. [7] Pan Feng, Liu Huatai, Guo Zhanrong, et al. Effects of tide and season changes on the iron-sulfur-phosphorus biogeochemistry in sediment porewater of a mangrove coast[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 568: 686−702. [8] Newton A, Icely J. Land ocean interactions in the Coastal Zone, LOICZ: lessons from banda aceh, atlantis, and canute[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2008, 77(2): 181−184. [9] Depew D C, Koehler G, Hiriart-Baer V. Phosphorus dynamics and availability in the nearshore of eastern lake erie: insights from oxygen isotope ratios of phosphate[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2018, 5: 215. [10] Markovic S, Liang Anqi, Watson S B, et al. Biogeochemical mechanisms controlling phosphorus diagenesis and internal loading in a remediated hard water eutrophic embayment[J]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 514: 122−137. [11] Ma Weiwei, Zhu Maoxu, Yang Guipeng, et al. In situ, high-resolution DGT measurements of dissolved sulfide, iron and phosphorus in sediments of the East China Sea: insights into phosphorus mobilization and microbial iron reduction[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 124(1): 400−410. [12] Sun Qiyao, Sheng Yanqing, Yang Jian, et al. Dynamic characteristics of sulfur, iron and phosphorus in coastal polluted sediments, north China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 219: 588−595. [13] Hermans M, Lenstra W K, Helmond N V, et al. Impact of natural re-oxygenation on the sediment dynamics of manganese, iron and phosphorus in a euxinic Baltic Sea basin[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2019, 246: 174−196. [14] Roy E D, Nguyen N T, White J R. Changes in estuarine sediment phosphorus fractions during a large-scale Mississippi River diversion[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 609: 1248−1257. [15] Pan Feng, Liu Huatai, Guo Zhanrong, et al. Geochemical behavior of phosphorus and iron in porewater in a mangrove tidal flat and associated phosphorus input into the ocean[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2017, 150(1): 65−75. [16] Canfield D E, Thamdrup B, Hansen J W. The anaerobic degradation of organic matter in danish coastal sediments: iron reduction, manganese reduction, and sulfate reduction[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(16): 3867−3883. [17] 朱茂旭, 史晓宁, 杨桂朋, 等. 海洋沉积物中有机质早期成岩矿化路径及其相对贡献[J]. 地球科学进展, 2011, 26(4): 355−364.Zhu Maoxu, Shi Xiaoning, Yang Guipeng, et al. Relative contributions of various early diagenetic pathways to mineralization of organic matter in marine sediments: an overview[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2011, 26(4): 355−364. [18] Muyzer G, Stams A J M. The ecology and biotechnology of sulphate-reducing bacteria[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2008, 6(6): 441−454. [19] Kraal P, Burton E D, Rose A L, et al. Sedimentary iron-phosphorus cycling under contrasting redox conditions in a eutrophic estuary[J]. Chemical Geology, 2015, 392: 19−31. [20] Ding Shiming, Chen Musong, Gong Mengdan, et al. Internal phosphorus loading from sediments causes seasonal nitrogen limitation for harmful algal blooms[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 625: 872−884. [21] Chen Musong, Ding Shiming, Chen Xiang, et al. Mechanisms driving phosphorus release during algal blooms based on hourly changes in iron and phosphorus concentrations in sediments[J]. Water Research, 2018, 133: 153−164. [22] Han Chao, Ding Shiming, Yao Lei, et al. Dynamics of phosphorus-iron-sulfur at the sediment-water interface influenced by algae blooms decomposition[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 300: 329−337. [23] Han Chaonan, Qin Yanwen, Zheng Binghui, et al. Geochemistry of phosphorus release along transect of sediments from a tributary backwater zone in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 722: 136964. [24] Rong Nan, Lu Wenzhou, Zhang Chaoyu, et al. In situ high-resolution measurement of phosphorus, iron and sulfur by diffusive gradients in thin films in sediments of black-odorous rivers in the Pearl River Delta region, South China[J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 189: 109918. [25] 潘峰, 郭占荣, 刘花台, 等. 潮滩沉积物−水界面磷、铁的高分辨率分布特征及生物地球化学行为[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(11): 4109−4119.Pan Feng, Guo Zhanrong, Liu Huatai, et al. High-resolution distribution and biogeochemical behavior of phosphorus and iron at sediment-water interface of tidal flat[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(11): 4109−4119. [26] Wang Yan, Ding Shiming, Wang Dan, et al. Static layer: a key to immobilization of phosphorus in sediments amended with lanthanum modified bentonite (Phoslock®)[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 325: 49−58. [27] Chen Musong, Cui Jingzhen, Lin Juan, et al. Successful control of internal phosphorus loading after sediment dredging for 6 years: a field assessment using high-resolution sampling techniques[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 616−617: 927−936. [28] 欧阳玉蓉, 王翠, 李青生, 等. 厦门湾海域营养盐时空分布与富营养化状况分析[J]. 福建农业学报, 2014, 29(1): 88−93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2014.01.018Ouyang Yurong, Wang Cui, Li Qingsheng, et al. Analysis of the space-time distribution of nutrients and the degree of eutrophication in Xiamen Bay[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 29(1): 88−93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2014.01.018 [29] Lin Peng, Guo Laodong, Chen Min, et al. Distribution, partitioning and mixing behavior of phosphorus species in the Jiulong River estuary[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2013, 157: 93−105. [30] Yang Caiyun, Li Yi, Zhou Yanyan, et al. Bacterial community dynamics during a bloom caused by Akashiwo sanguinea in the Xiamen sea area, China[J]. Harmful Algae, 2012, 20: 132−141. [31] Yu Liying, Zhang Yaqun, Li Meizhen, et al. Comparative metatranscriptomic profiling and microRNA sequencing to reveal active metabolic pathways associated with a dinoflagellate bloom[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 699: 134323. [32] Davison W, Zhang H. In situ speciation measurements of trace components in natural waters using thin-film gels[J]. Nature, 1994, 367(6463): 546−548. [33] Teasdale P R, Batley G E, Apte S C, et al. Pore water sampling with sediment peepers[J]. Trac Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 1995, 14(6): 250−256. [34] Xu Di, Wu Wei, Ding Shiming, et al. A high-resolution dialysis technique for rapid determination of dissolved reactive phosphate and ferrous iron in pore water of sediments[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 421−422: 245−252. [35] Zhang H, Davison W, Miller S, et al. In situ high resolution measurements of fluxes of Ni, Cu, Fe, and Mn and concentrations of Zn and Cd in porewaters by DGT[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(20): 4181−4192. [36] Laskov C, Herzog C, Lewandowski J, et al. Miniaturized photometrical methods for the rapid analysis of phosphate, ammonium, ferrous iron, and sulfate in pore water of freshwater sediments[J]. Limnology and Oceanography Methods, 2007, 5(1): 63−71. [37] Ding Shiming, Wang Yan, Xu Di, et al. Gel-based coloration technique for the submillimeter-scale imaging of labile phosphorus in sediments and soils with diffusive gradients in thin films[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(14): 7821−7829. [38] Ding Shiming, Sun Qin, Xu Di, et al. High-resolution simultaneous measurements of dissolved reactive phosphorus and dissolved sulfide: the first observation of their simultaneous release in sediments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(15): 8297−8304. [39] Teasdale P R, Hayward S, Davison W. In situ, high-resolution measurement of dissolved sulfide using diffusive gradients in thin films with computer-imaging densitometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1999, 71(11): 2186−2191. [40] Wang Yan, Ding Shiming, Gong Mengdan, et al. Diffusion characteristics of agarose hydrogel used in diffusive gradients in thin films for measurements of cations and anions[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2016, 945: 47−56. [41] Pan Feng, Liu Huatai, Guo Zhanrong, et al. Metal/metalloid and phosphorus characteristics in porewater associated with manganese geochemistry: a case study in the Jiulong River Estuary, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 255: 113134. [42] Pan Feng, Guo Zhanrong, Cai Yu, et al. High-resolution imaging of labile P & S in coastal sediment: insight into the kinetics of P mobilization associated with sulfate reduction[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2020, 225: 103851. [43] McManus J, Berelson W M, Coale K H, et al. Phosphorus regeneration in continental margin sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(14): 2891−2907. [44] 刘思儒, 赵继东, 肖尚斌, 等. 洱海藻类水华高风险期沉积物氮磷释放通量时空变化[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(2): 734−742.Liu Siru, Zhao Jidong, Xiao Shangbin, et al. Spatio-temporal variation of release flux of sediment nitrogen and phosphorus in high-risk period of algal bloom in lake Erhai[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(2): 734−742. [45] 郝文超, 王从锋, 杨正健, 等. 氧化还原循环过程中沉积物磷的形态及迁移转化规律[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(2): 640−648.Hao Wenchao, Wang Congfeng, Yang Zhengjian, et al. Speciation and transformation of phosphorus in sediments during the redox cycle[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(2): 640−648. -





 下载:
下载: