Research of characteristics of turbulent mixing in the Prydz Bay with intrusion of modified circumpolar deep water
-
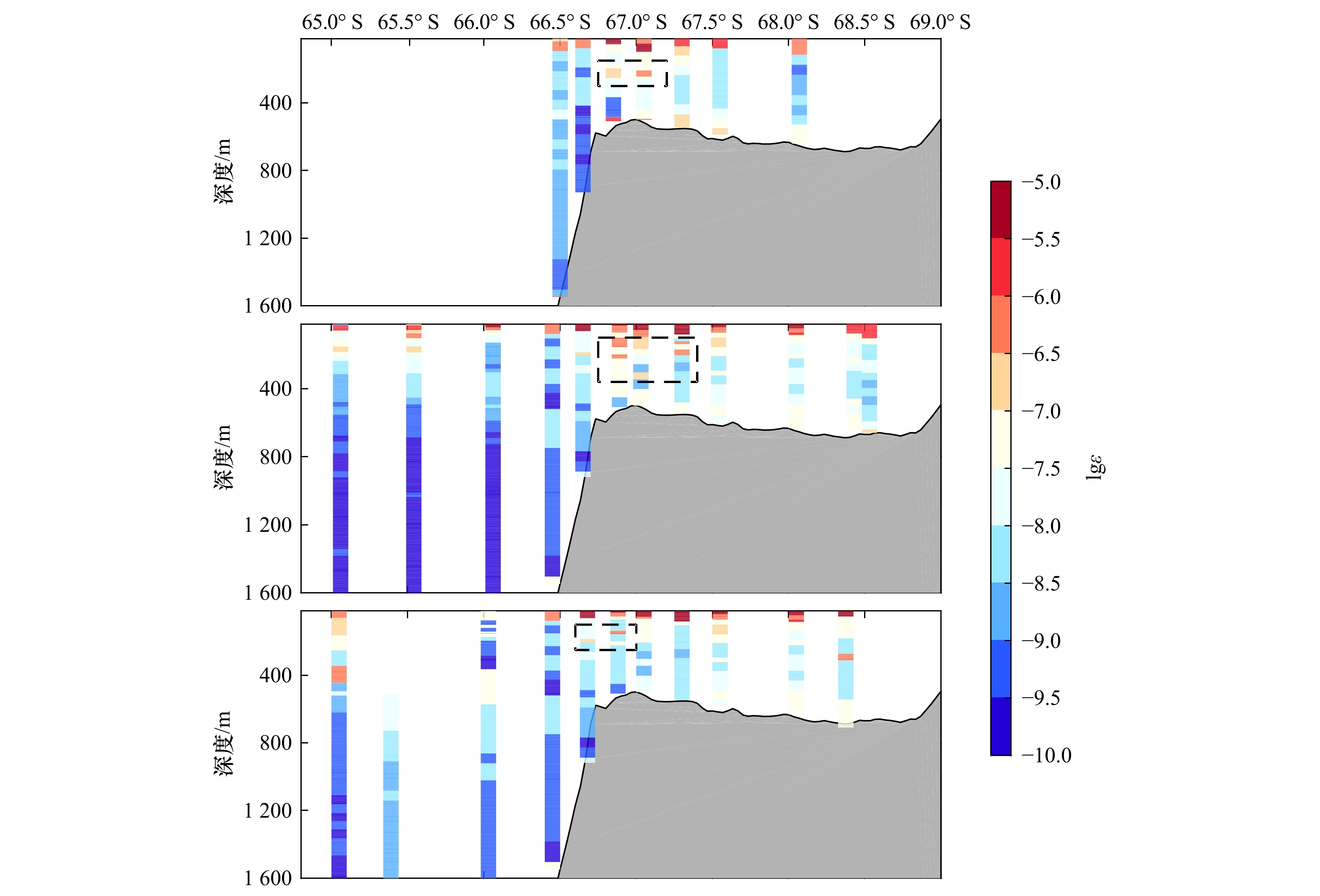
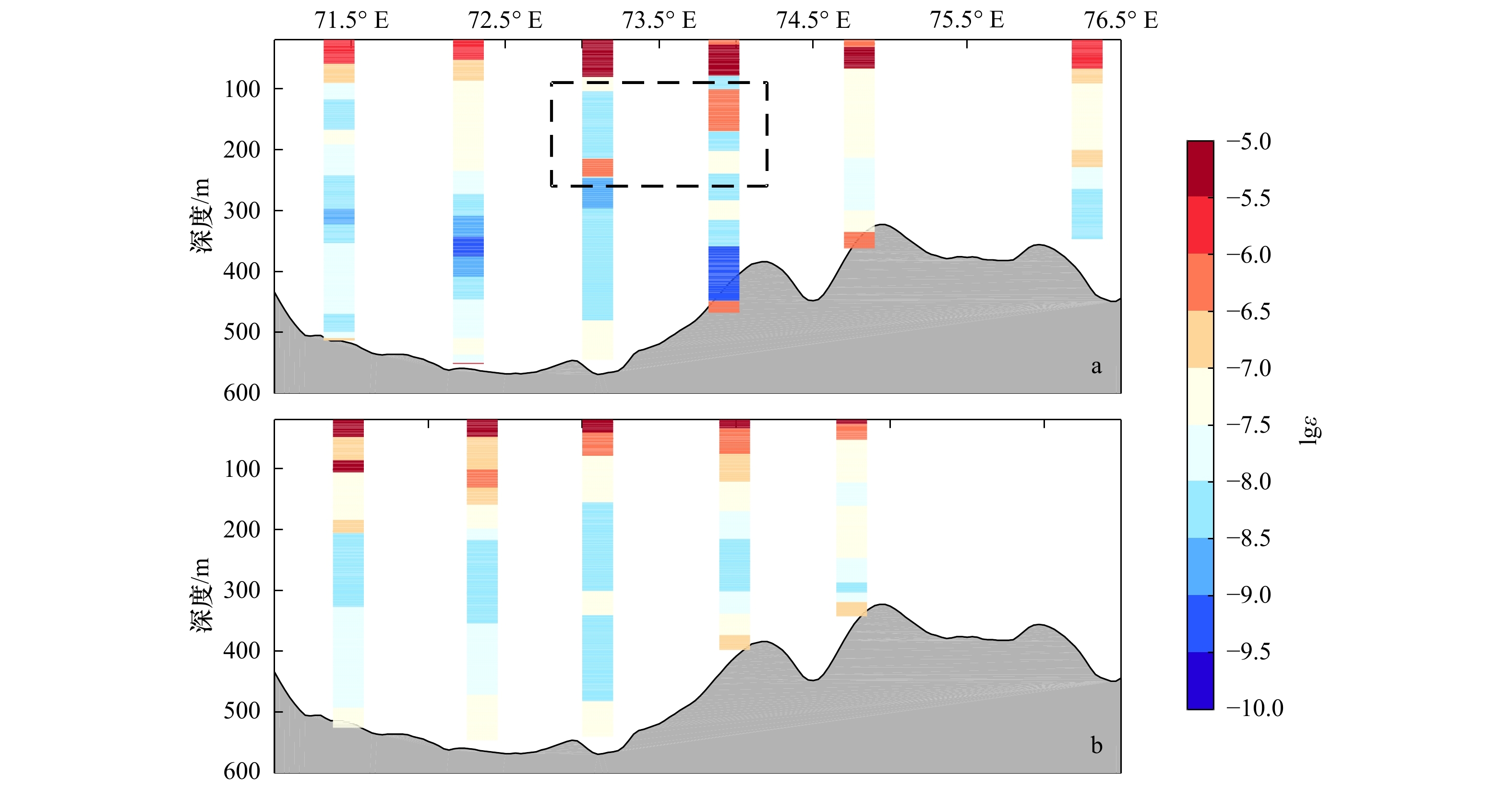
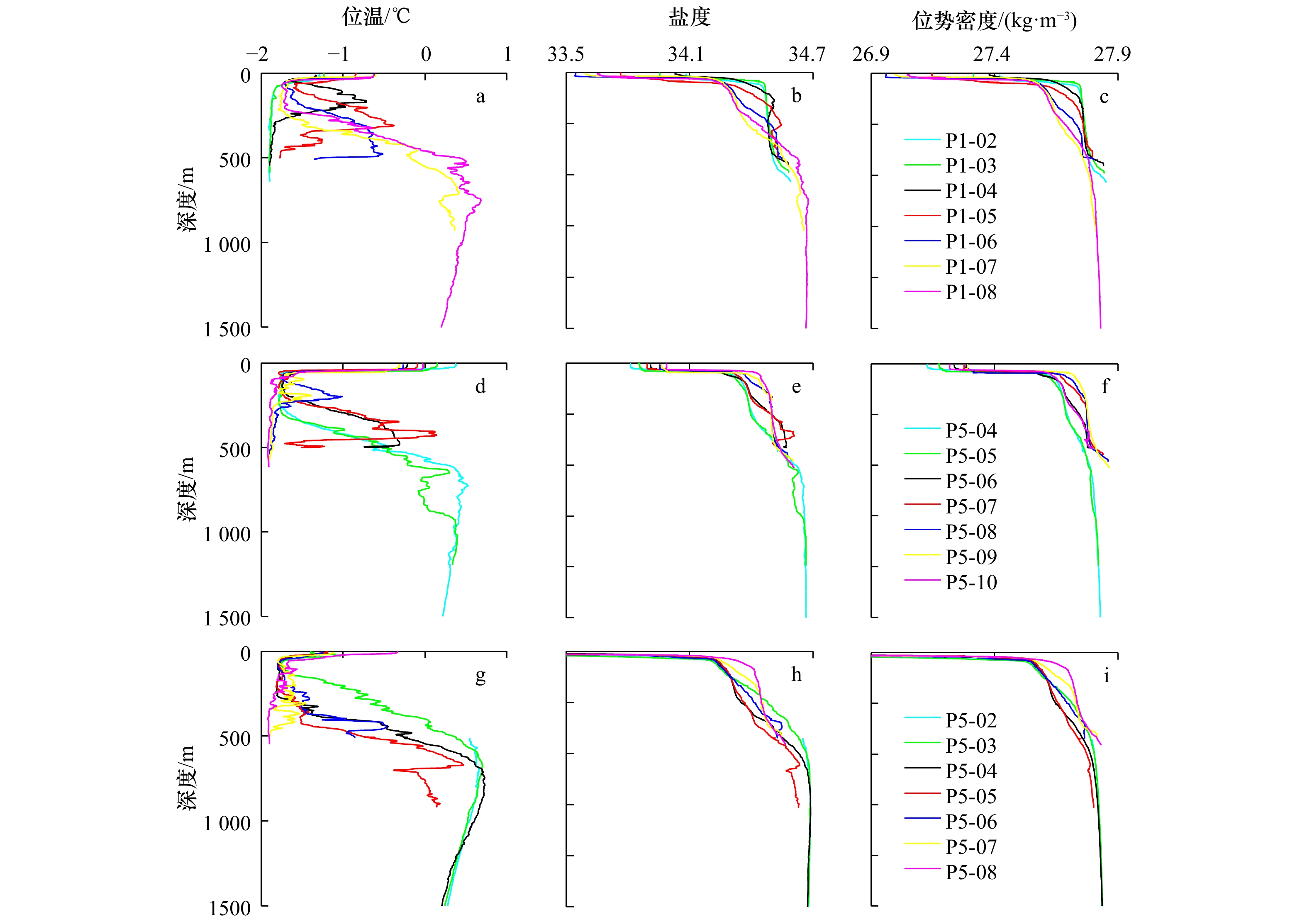
摘要: 基于中国第28、29和31次南极科学考察中的CTD数据,利用Thorpe尺度方法计算了普里兹湾及其附近海域湍动能耗散率,分析了其分布特征,并对当地的水团结构进行研究。结果表明,普里兹湾及其附近海域中,前两个航次观测中次表层湍动能耗散率强度在陆架坡折区域达到最大。在水团分布方面,在第28和29航次中均观测到了变性绕极深层水陆架入侵现象,水团分别向上涌升至海表以下100 m和200 m深度,向南均可达到67.5°S处。普里兹湾陆架坡折区域次表层湍动能耗散率强度分布与当地水团结构存在良好对应关系。研究认为变性绕极深层水入侵陆架,会使该深度水体变得不稳定,发生水体交换现象,最终造成该区域湍流混合强度加强。Abstract: Based on the CTD data from the 28th, 29th and 31st Chinese Antarctic Expedition cruises, we calculated dissipation rate of turbulent kinetic energy by using Thrope scale method, and analyzed the distribution characteristics of the dissipation rate and the structure of water masses in the Prydz Bay and its adjacent waters. Results show that the subsurface dissipation rate intensity of turbulent kinetic energy in the first two cruises reach maximum on the shelf break of Prydz Bay. Moreover, we compared the distribution of water masses among the three cruises and found intrusion of the modified circumplar deep water into the shelf happened on the 28th and 29th cruises. The the modified circumplar deep water could reach the depth of 100 m and 200 m on the cruise of 28th and 29th, respectively, and can extend southward to 67.5°S. Furthermore, the distribution of subsurface dissipation rate of turbulent kinetic energy on the shelf break of Prydz Bay are well related to the structure of local water masses. Therefore, the intrusion of the modified circumplar deep water into the shelf could induce instability of the local waters, promote water exchange and finally enhance local turbulent mixing.
-
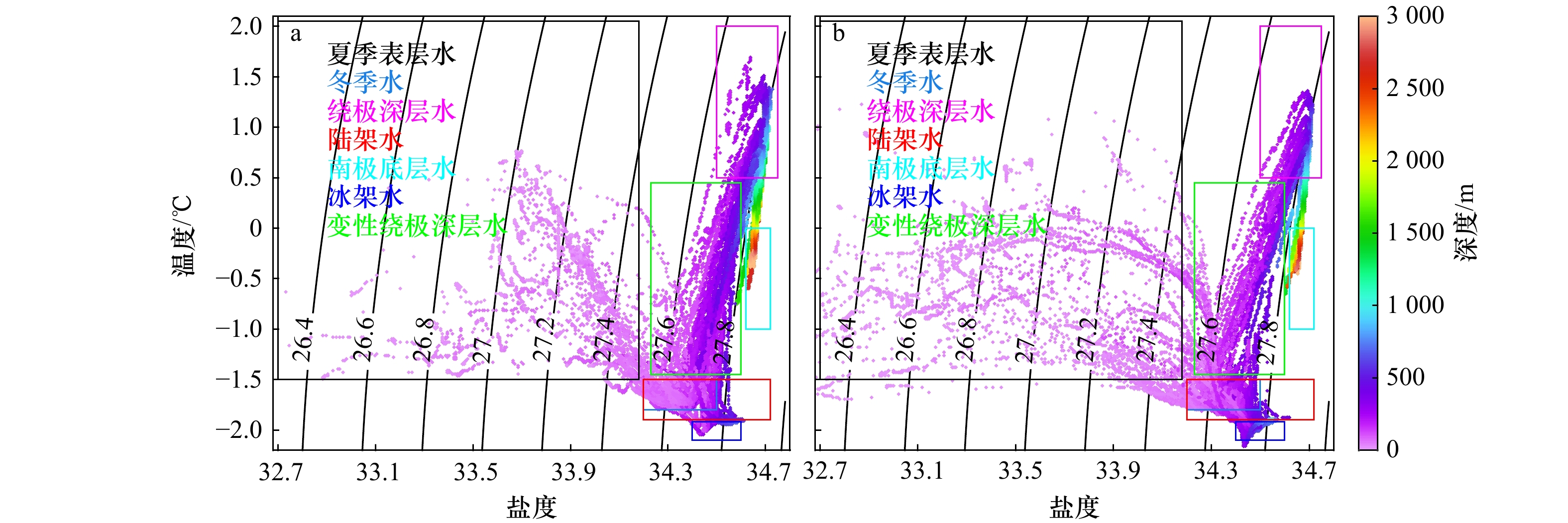
表 1 普里兹湾海域主要水团特征
Tab. 1 The characteristics of water masses in the Prydz Bay and the adjacent sea
水团名称 温度/℃ 盐度 夏季表层水 T≥−1.50 S<34.20 冬季水 T<−1.50 34.20<S<34.50 绕极深层水 0.50≤T≤2.00 34.50≤S≤34.75 陆架水 −1.9<T<−1.50 S>34.20 南极底层水 T<0 34.60<S<34.72 冰架水 T<−1.92 34.40<S<34.60 -
[1] 蒲书箴, 董兆乾. 普里兹湾附近物理海洋学研究进展[J]. 极地研究, 2003, 15(1): 53−64.Pu Shuzhen, Dong Zhaoqian. Progress in physical oceanographic studies of Prydz Bay and its adjacent oceanic area[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2003, 15(1): 53−64. [2] Mosby H. The Waters of the Atlantic Antarctic Ocean[J]. Scientific Results of the Norwegian Antarctic Expeditions 1927−1928. 1934, 11: 1–131. [3] 乐肯堂. 普里兹湾及邻近海区水团和环流研究述评[J]. 海洋科学, 1995(2): 26−30.Le Kentang. Review of the study of water mass and circulation in Prydz Bay and its adjacent sea[J]. Marine Sciences, 1995(2): 26−30. [4] 蒲书箴, 董兆乾, 胡筱敏, 等. 普里兹湾海域的夏季上层水及其北向运动[J]. 极地研究, 2000, 12(3): 157−168.Pu Shuzhen, Dong Zhaoqian, Hu Xiaomin, et al. Water masses and their northward extension in the upper ocean of Prydz Bay, Antarctica[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2000, 12(3): 157−168. [5] 蒲书箴, 胡筱敏, 董兆乾, 等. 普里兹湾附近绕极深层水和底层水及其运动特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2002, 24(3): 1−8.Pu Shuzhen, Hu Xiaomin, Dong Zhaoqian, et al. Features of circumpolar deep water, Antarctic bottom water and their movement near the Prydz Bay[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2002, 24(3): 1−8. [6] Yabuki T, Suga T, Hanawa K, et al. Possible source of the Antarctic bottom water in the Prydz Bay region[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2006, 62(5): 649−655. doi: 10.1007/s10872-006-0083-1 [7] 林丽娜, 陈红霞, 刘娜. 2013年夏季普里兹湾变性绕极深层水涌升陆架特征分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(1): 46−55.Lin Li’na, Chen Hongxia, Liu Na. An analysis on the upwelling of modified circumpolar deep water over the shelf region of Prydz Bay in the summer of 2013[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(1): 46−55. [8] Liu Chengyan, Wang Zhaomin, Cheng Chen, et al. On the modified circumpolar deep water upwelling over the four ladies bank in Prydz Bay, east Antarctica[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2018, 123(11): 7819−7838. doi: 10.1029/2018JC014026 [9] 乐肯堂, 史久新, 于康玲. 普里兹湾区水团和热盐结构的分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1996, 27(3): 229−236. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1996.03.001Le Kentang, Shi Jiuxin, Yu Kangling. An analysis on water masses and thermohaline structures in the region of Prydz Bay, Antarctica[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1996, 27(3): 229−236. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1996.03.001 [10] Vaz R A N, Lennon G W. Physical oceanography of the Prydz Bay region of Antarctic waters[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 1996, 43(5): 603−641. doi: 10.1016/0967-0637(96)00028-3 [11] Middleton J H, Humphries S E. Thermohaline structure and mixing in the region of Prydz Bay, Antarctica[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 1989, 36(8): 1255−1266. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(89)90104-0 [12] 高郭平, 董兆乾, 侍茂崇, 等. 南极普里兹湾关键物理海洋学问题研究进展及未来趋势[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2013, 22(2): 313−320.Gao Guoping, Dong Zhaoqian, Shi Maochong, et al. Advances of physical oceanographic study on Prydz Bay and adjacent region, Antarctica[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2013, 22(2): 313−320. [13] Herraiz-Borreguero L, Church J A, Allison I, et al. Basal melt, seasonal water mass transformation, ocean current variability, and deep convection processes along the Amery Ice Shelf calving front, East Antarctica[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2016, 121(7): 4946−4965. doi: 10.1002/2016JC011858 [14] Williams G D, Herraiz-Borreguero L, Roquet F, et al. The suppression of Antarctic bottom water formation by melting ice shelves in Prydz Bay[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 12577. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12577 [15] 陈红霞, 林丽娜, 史久新. 南极普里兹湾及其邻近海域水团研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(7): 1−8.Chen Hongxia, Lin Lina, Shi Jiuxin. Study on water masses in Prydz Bay and its adjacent sea area[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(7): 1−8. [16] Heywood K J, Garabato A C N, Stevens D P. High mixing rates in the abyssal Southern Ocean[J]. Nature, 2002, 415(6875): 1011−1014. doi: 10.1038/4151011a [17] Garabato A C N, Polzin K L, King B A, et al. Widespread intense turbulent mixing in the Southern Ocean[J]. Science, 2004, 303(5655): 210−213. doi: 10.1126/science.1090929 [18] Sloyan B M. Spatial variability of mixing in the Southern Ocean[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(18): L18603. [19] Yang Qingxuan, Tian Jiwei, Zhao Wei, et al. Turbulent dissipation and mixing in Prydz Bay[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2013, 31(2): 445−453. doi: 10.1007/s00343-013-2040-3 [20] 丁文祥, 梁楚进, 廖光洪, 等. 南极普里兹湾海域湍流扩散系数估计[J]. 海洋学研究, 2017, 35(1): 14−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2017.01.002Ding Wenxiang, Liang Chujin, Liao Guanghong, et al. The turbulent diffusivity estimation in Prydz Bay, Antarctic[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2017, 35(1): 14−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2017.01.002 [21] Liu Chengyan, Wang Zhaomin, Cheng Chen, et al. Modeling modified circumpolar deep water intrusions onto the Prydz Bay continental shelf, east Antarctica[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2017, 122(7): 5198−5217. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012336 [22] 李敏. 基于Thorpe尺度对南海深层混合的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2013.Li Min. Study of abyssal mixing in the South China Sea based on Thorpe scale[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2013. [23] Thorpe S A. Turbulence and mixing in a Scottish loch[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1977, 286(1334): 125−181. doi: 10.1098/rsta.1977.0112 [24] Ferron B, Mercier H, Speer K, et al. Mixing in the Romanche fracture zone[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1998, 28(10): 1929−1945. doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1998)028<1929:MITRFZ>2.0.CO;2 [25] Ozmidov R V. On the turbulent exchange in a stably stratified ocean[J]. Izv, Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics, 1965, 1(8): 853−860. [26] 叶安乐, 李凤岐. 物理海洋学[M]. 青岛: 青岛海洋大学出版社, 1992: 5−187.Ye Anle, Li Fengqi. Physical Oceanography[M]. Qingdao: Qingdao Ocean University Press, 1992: 5−187. [27] Ohlmann J C, Siegel D A, Gautier C. Ocean mixed layer radiant heating and solar penetration: a global analysis[J]. Journal of Climate, 1996, 9(10): 2265−2280. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1996)009<2265:OMLRHA>2.0.CO;2 [28] Robertson R, Padman L, Levine M D. Fine structure, microstructure, and vertical mixing processes in the upper ocean in the western Weddell Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1995, 100(C9): 18517−18535. doi: 10.1029/95JC01742 -





 下载:
下载: