Distribution characteristics of microplastics in the surface seawater of the Jinzhou Bay
-
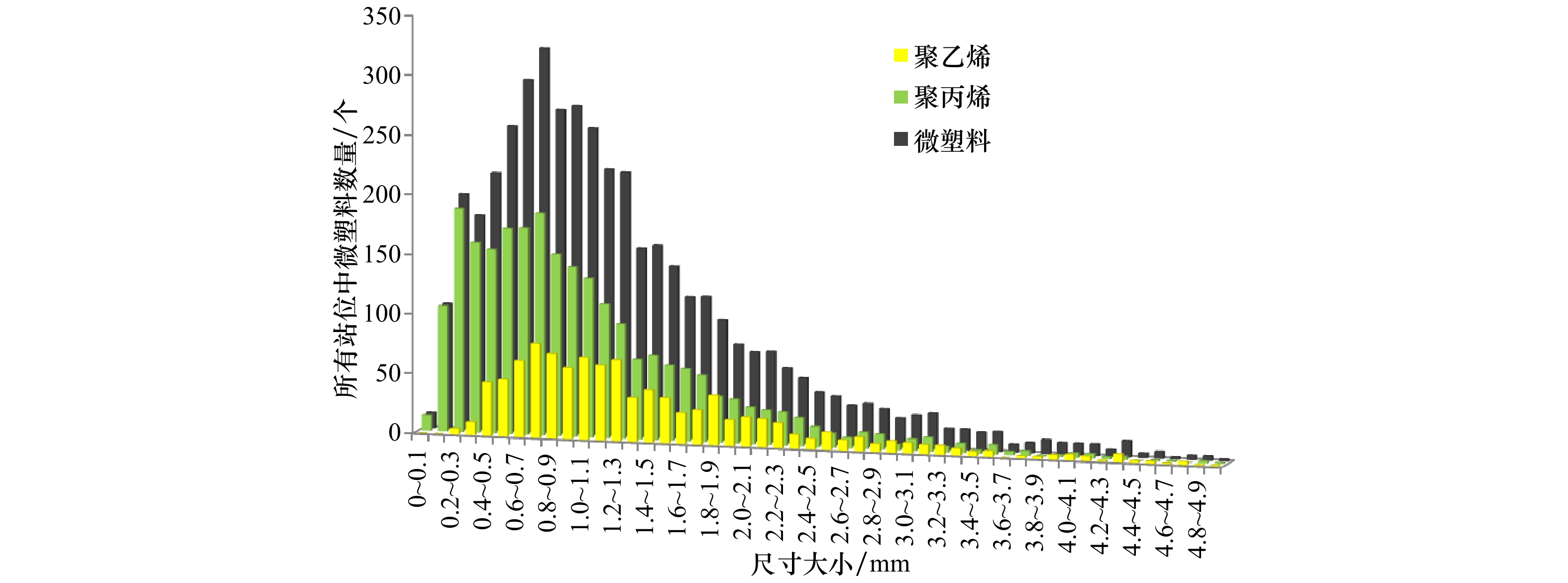
摘要: 海洋微塑料是全球关注的新兴环境问题,海湾由于特殊的地理环境特征,成为微塑料分布研究的热点区域。本研究以锦州湾为研究海域,于2017年10月布设了11个点位开展表层海水微塑料样品采集,在实验室采用湿式氧化法开展样品前处理,应用傅立叶变换显微红外光谱仪分析鉴定微塑料成分。研究结果表明,锦州湾表层水体微塑料平均丰度为(0.93±0.59)个/m3,微塑料数量占全部塑料样品的96.2%。微塑料的主要成分为聚丙烯和聚乙烯,分别占55.0%和23.5%;线状和片状塑料的比例最高,分别占41.7%和26.2%;白色、蓝色和半透明微塑料分别占35.1%、26.0%和21.4%。受水动力条件和陆域河流输入等影响,锦州湾表层水体中微塑料的空间分布整体呈现北部偏高,向南部递减的趋势。Abstract: Marine microplastics pollution is an emerging marine environmental issue and has attracted worldwide attention. Due to the special geographical environment characteristics, the coastal bays become the hotspot for microplastics distribution research. Here we report data on the abundance and characteristics of microplastics collected from surface seawater of the Jinzhou Bay. Samples were collected from 11 sites by horizontal trawling of a plankton net in October 2017. Wet peroxide oxidation process and micro Fourier-transform infrared absorption spectroscopy were conducted to remove the organic material mixed in the sample and identified the composition of microplastics. The research results showed that the average abundance of microplastics in the Jinzhou Bay was (0.93±0.59) items/m3, and accounting for 96.2% of the total plastic debris. Polypropylene and polyethylene were the main components of microplastics, accounting for 55.0% and 23.5%, respectively. The main types of microplastics were lines and fragments, accounting for 41.7% and 26.2%, respectively. White, blue and translucent was the most common color, accounting for 35.1%, 26.0% and 21.4%, respectively. Affected by hydrodynamic conditions and riverine input, the spatial distribution of microplastics in the surface seawater of the Jinzhou Bay was higher in the north areas than that in the south.
-
Key words:
- Jinzhou Bay /
- surface seawater /
- plastic debris /
- microplastics /
- distribution
-
表 1 锦州湾各站位采样信息
Tab. 1 Sampling information of each site in the Jinzhou Bay
站位 采集时长/min 过水体积/m3 采集塑料
样品个数采集微塑料个数 微塑料丰度/(个·m−3) JZ01 12 507 432 414 0.82 JZ02 10 426 1 025 1 007 2.36 JZ03 10 426 681 668 1.57 JZ04 10 524 646 610 1.16 JZ05 12 396 258 247 0.62 JZ06 12 362 299 290 0.80 JZ07 11 383 265 261 0.68 JZ08 11 397 179 165 0.42 JZ09 10 414 153 139 0.34 JZ10 11 489 449 413 0.85 JZ11 10 363 211 209 0.58 表 2 不同海湾表层海水中微塑料的丰度对比
Tab. 2 Abundance comparison of microplastics in the surface seawater in different sea areas
调查海域 网具类型 网衣孔径/μm 丰度/(个·m−3) 主要形状 主要成分 文献 伊朗恰巴哈尔海湾 Neuston网 333 0.49±0.43 纤维 聚丙烯、聚乙烯 [17] 墨西哥托多斯桑托斯湾 Manta 网 333 0.19±0.21 碎片、纤维 − [18] 法国布列塔尼布雷斯特湾 Manta 网 335 0.24±0.35 碎片 聚乙烯 [19] 巴西瓜纳巴拉湾 浮游生物网(直径0.6 m) 300 7.1±7.3 碎片、薄膜 聚乙烯 [20] 佛罗里达州坦帕湾 浮游生物网(直径0.5 m) 330 4.5±2.3 纤维 − [21] 象山湾 浮游生物网(直径0.2 m) 330 8.91±4.70 泡沫 聚乙烯 [22] 渤海 Manta网 330 0.35±0.13 线、碎片 聚乙烯、聚丙烯 [16] 锦州湾 Manta 网 330 0.93±0.59 线、碎片、颗粒 聚丙烯、聚乙烯 本研究 注:−代表文献中未提及成分。 -
[1] Geyer R, Jambeck J R, Law K L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made[J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(7): e1700782. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1700782 [2] Eriksen M, Lebreton L C M, Carson H S, et al. Plastic pollution in the world’s oceans: more than 5 trillion plastic pieces weighing over 250, 000 tons afloat at sea[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(12): e111913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111913 [3] Cózar A, Echevarría F, González-Gordillo J I, et al. Plastic debris in the open ocean[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(28): 10239−10244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1314705111 [4] Andrady A L. Microplastics in the marine environment[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(8): 1596−1605. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.05.030 [5] Arthur C, Baker J, Bamford H, et al. Proceedings of the international research workshop on the occurrence, effects and fate of microplastic marine debris[C]. Tacoma: NOAA, 2009: 49. [6] Murray F, Cowie P R. Plastic contamination in the decapod crustacean Nephrops norvegicus (Linnaeus, 1758)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 62(6): 1207−1217. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.03.032 [7] Lusher A L, Hernandez-Milian G, O’Brien J, et al. Microplastic and macroplastic ingestion by a deep diving, oceanic cetacean: the True’s beaked whale Mesoplodon mirus[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2015, 199: 185−191. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.01.023 [8] Provencher J F, Bond A L, Hedd A, et al. Prevalence of marine debris in marine birds from the North Atlantic[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 84(1/2): 411−417. [9] Farrell P, Nelson K. Trophic level transfer of microplastic: Mytilus edulis (L.) to Carcinus maenas (L.)[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 177: 1−3. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.01.046 [10] Setälä O, Fleming-Lehtinen V, Lehtiniemi M. Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014, 185: 77−83. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.10.013 [11] Kershaw P J, Turra A, Galgani F. Guidelines for the monitoring and assessment of plastic litter in the ocean[R]. GESAMP Reports and Studies, 2019: 99. [12] 全国颜色标准化技术委员会. GB/T 15608−2006, 中国颜色体系[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007: 4.National Technical Committee 120 on Colors of Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 15608−2006, The Chinese color system[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2007: 4. [13] Song Y K, Hong S H, Jang M, et al. Large accumulation of micro-sized synthetic polymer particles in the sea surface microlayer[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(16): 9014−9021. [14] Isobe A, Uchiyama-Matsumoto K, Uchida K, et al. Microplastics in the southern ocean[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 114(1): 623−626. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.09.037 [15] Zhang Weiwei, Zhang Shoufeng, Wang Juying, et al. Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 231: 541−548. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.058 [16] Zhang Weiwei, Zhang Shoufeng, Zhao Qian, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of plastic and microplastic debris in the surface water of the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2020, 158: 111343. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111343 [17] Aliabad M K, Nassiri M, Kor K. Microplastics in the surface seawaters of Chabahar Bay, Gulf of Oman (Makran Coasts)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 143: 125−133. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.04.037 [18] Ramírez-Álvarez N, Mendoza L M R, Macías-Zamora J V, et al. Microplastics: sources and distribution in surface waters and sediments of Todos Santos Bay, Mexico[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 703: 134838. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134838 [19] Frère L, Paul-Pont I, Rinnert E, et al. Influence of environmental and anthropogenic factors on the composition, concentration and spatial distribution of microplastics: a case study of the Bay of Brest (Brittany, France)[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 225: 211−222. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.03.023 [20] Olivatto G P, Martins M C T, Montagner C C, et al. Microplastic contamination in surface waters in Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 139: 157−162. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.12.042 [21] McEachern K, Alegria H, Kalagher A L, et al. Microplastics in Tampa Bay, Florida: Abundance and variability in estuarine waters and sediments[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 148: 97−106. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.068 [22] Chen Minglong, Jin Meng, Tao Peiran, et al. Assessment of microplastics derived from mariculture in Xiangshan Bay, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 242: 1146−1156. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.133 [23] Derraik J G B. The pollution of the marine environment by plastic debris: a review[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2002, 44(9): 842−852. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00220-5 [24] Barnes D K A, Galgani F, Thompson R C, et al. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2009, 364(1526): 1985−1998. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0205 [25] Thiel M, Hinojosa I, Vásquez N, et al. Floating marine debris in coastal waters of the SE-Pacific (Chile)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2003, 46(2): 224−231. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00365-X [26] Lattin G L, Moore C J, Zellers A F, et al. A comparison of neustonic plastic and zooplankton at different depths near the southern California shore[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2004, 49(4): 291−294. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.01.020 [27] 《中国海湾志》编纂委员会. 中国海湾志(第二分册)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1997: 344−359.Editorial Board of China Bay Survey. Survey of China Bays (Vol. 2)[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1997: 344−359. [28] De Falco F, Gullo M P, Gentile G, et al. Evaluation of microplastic release caused by textile washing processes of synthetic fabrics[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 236: 916−925. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.057 [29] Ziajahromi S, Neale P A, Rintoul L, et al. Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway for microplastics: Development of a new approach to sample wastewater-based microplastics[J]. Water Research, 2017, 112: 93−99. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.042 [30] Essel R, Engel L, Carus M, et al. Sources of microplastics relevant to marine protection in Germany[R]. Germany: Umweltbundesamt, 2015: 64. -





 下载:
下载: