Distributions, seasonal variations and influence factors of different manganese species in the Sanggou Bay
-
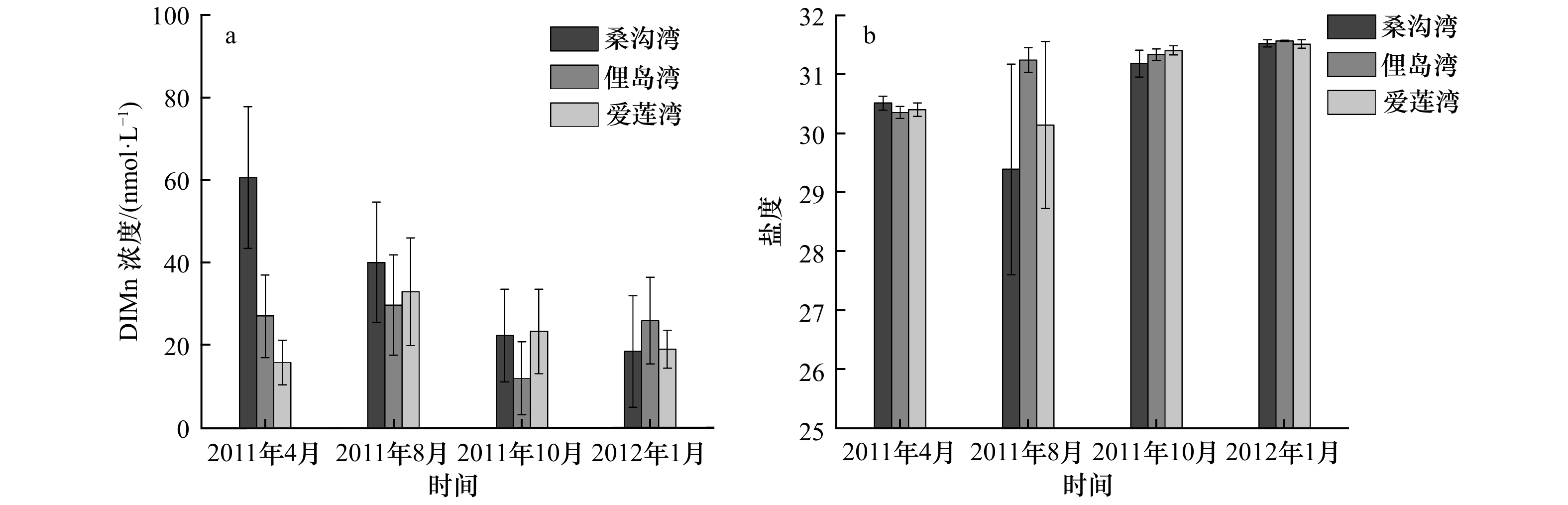
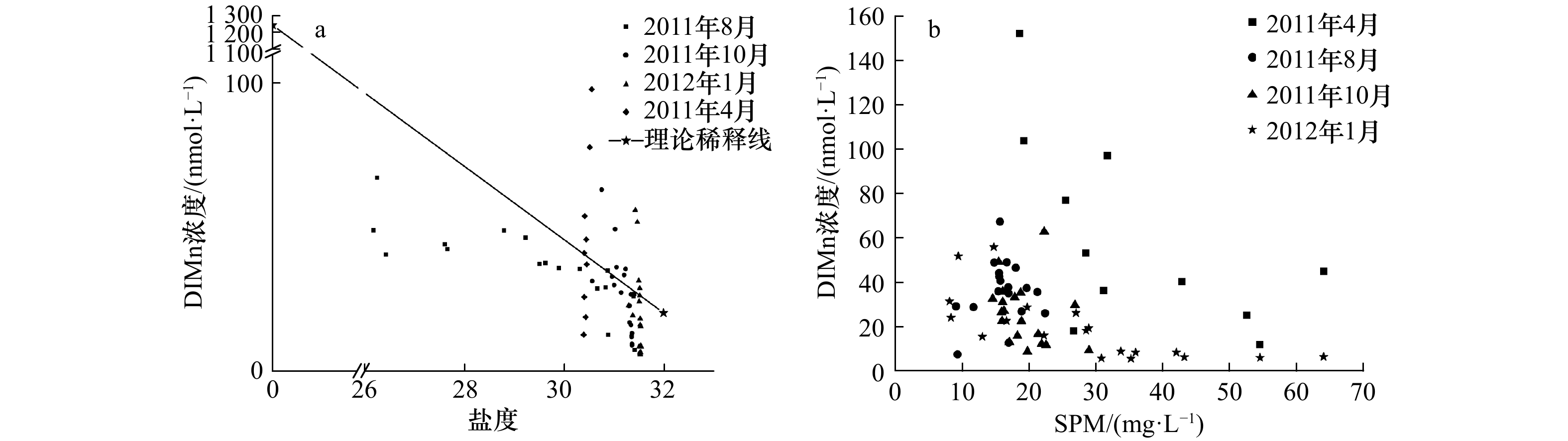
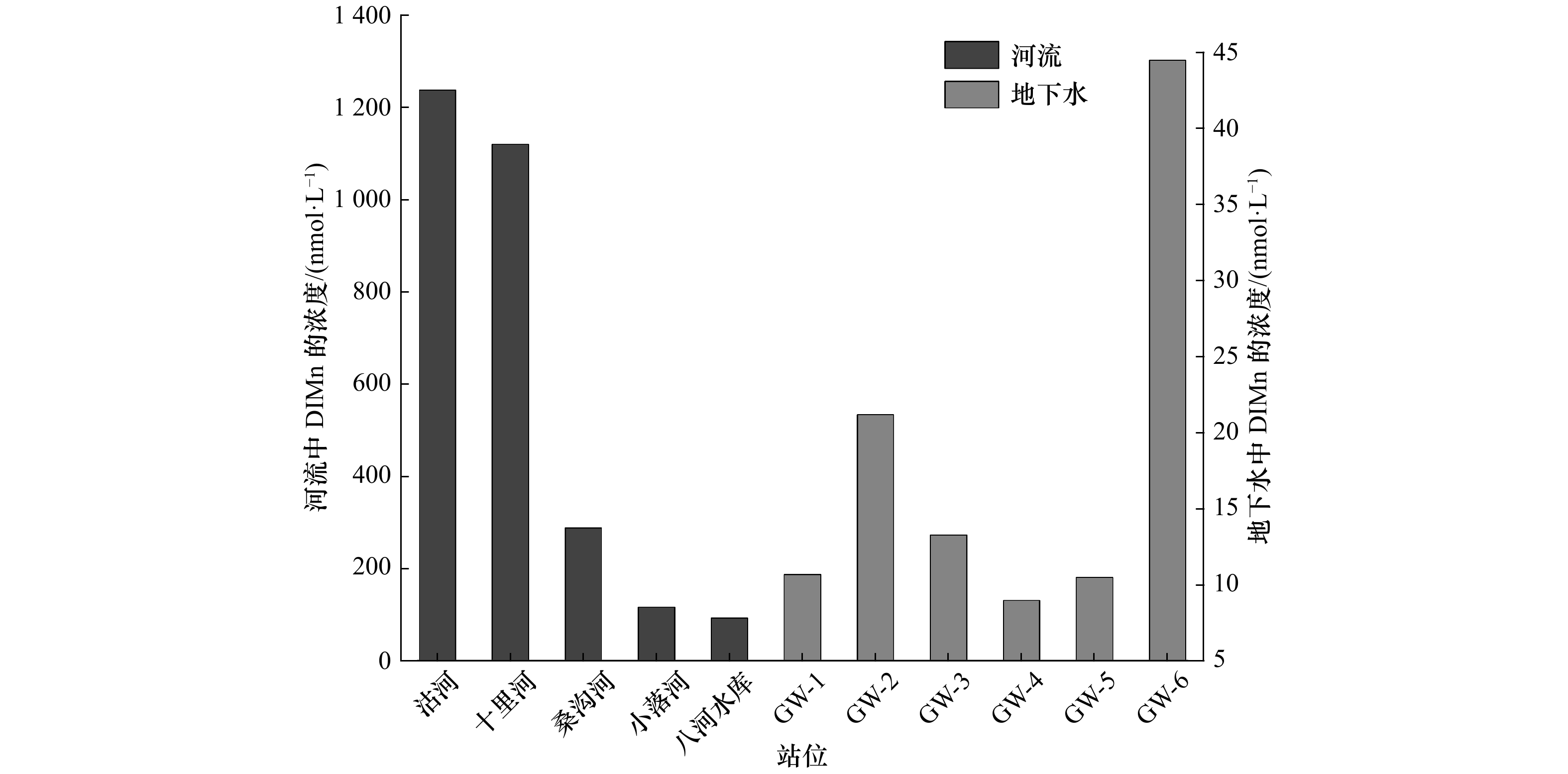
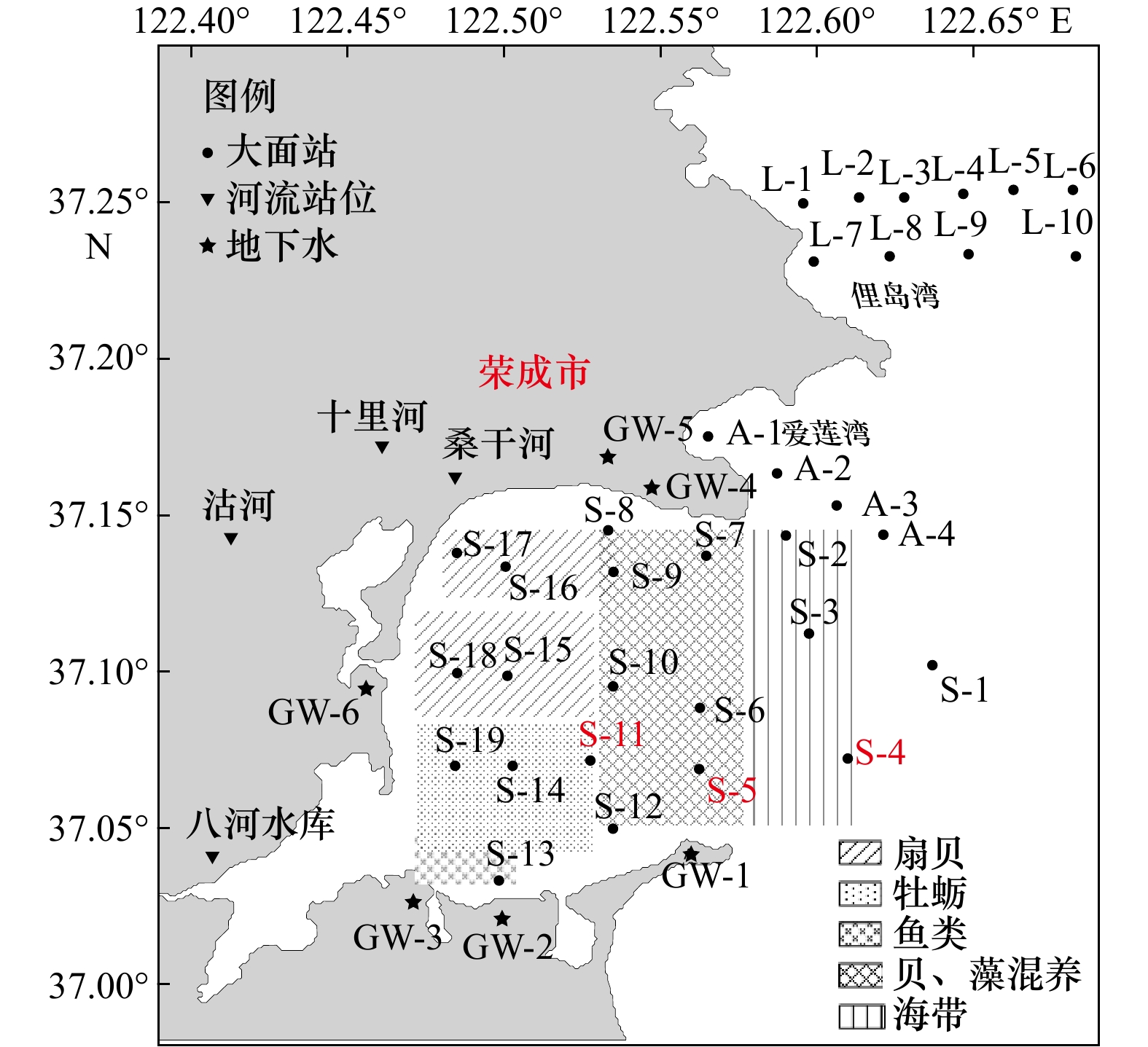
摘要: 利用催化动力学分光光度法和两步提取法对2011年4月(春)、8月(夏)、10月(秋)和2012年1月(冬)桑沟湾海域溶解态无机锰(DIMn)和表层沉积物中的锰的含量进行测定。结果表明,桑沟湾4个季节(春季至冬季,后同)DIMn浓度呈现出近岸高、远岸低的分布特点,其平均浓度分别为(60.5±43.1) nmol/L、(42.0±30.5) nmol/L、(23.4±11.2) nmol/L和(18.2±13.5) nmol/L,呈现出明显的季节变化,即春季最高,夏季、秋季次之,冬季最低;与相邻的俚岛湾和爱莲湾相比,桑沟湾春季、夏季DIMn的浓度较高,秋季、冬季则没有显著性差异。桑沟湾表层沉积物中总Mn在4个季节的含量分别为(861±308) mg/kg、(915±322) mg/kg、(589±108) mg/kg、(653±185) mg/kg,表层沉积物中醋酸提取态Mn在4个季节的含量分别为(500±272) mg/kg、(502±232) mg/kg、(322±81) mg/kg、(345±91) mg/kg,两者均表现出近岸高、远岸低的分布特点。醋酸提取态Mn的含量在春季、夏季要显著高于秋季、冬季。悬浮颗粒物的吸附和浮游生物的利用是影响桑沟湾DIMn浓度与分布的重要因素。桑沟湾DIMn的源主要包括河流及地下水输送、大气输送、沉积物−水界面释放;汇主要包括养殖生物的清除、向黄海的输送等。简单箱式模型收支计算结果显示,桑沟湾DIMn的源略大于汇,表明除了养殖生物的清除和向黄海的输送,桑沟湾DIMn还存在其他汇。本研究的结果为桑沟湾DIMn的生物地球化学循环的深入认识提供了基础数据。Abstract: The distribution of dissolved manganese (DIMn) and manganese in surface sediment in the Sanggou Bay were investigated in April, August, October 2011 and January 2012. The concentrations of DIMn and manganese in surface sediment were measured by the the catalytic-kinetic spectrophotometric and two-step extraction method, respectively. The results showed that the average concentration of DIMn in 2011−2012 were (60.5±43.1) nmol/L in April, (42.0±30.5) nmol/L in August, (23.4±11.2) nmol/L in October and (18.2±13.5) nmol/L in January. The high concentrations of DIMn always being found in the estuary and decreased from nearshore to the coastal area. There exists significant seasonal variation for concentrations of DIMn with highest value in spring, followed by summer and autumn, and lowest value in winter. The concentrations of DIMn in the Sanggou Bay were higher than the Ailian Bay and the Lidao Bay in spring and summer, and with insignificant variation in autumn and winter. The average content of total manganese (TMns) in surface sediment were (861±308) mg/kg in April 2011, (915±322) mg/kg in August 2011, (589±108) mg/kg in October 2011 and (653±185) mg/kg in January 2012. The average content of acetic acid-soluble manganese (HAc-Mn) in surface sediment were (500±272) mg/kg in April 2011, (502±232) mg/kg in August 2011, (322±81) mg/kg in October 2011, (345±91) mg/kg in January 2012. The content of TMns and HAc-Mn in the sediment of the bay were both decreased with the increasing distance from the coast. There exists significant seasonal variation for concentrations of HAc-Mn in the surface sediments during the investigations, with higher concentrations occurred in spring and summer than that in autumn and winter. The adsorption of SPM and utilization of plankton were important factors affecting the content and distribution of DIMn in the Sanggou Bay. The major sources for DIMn in the Sanggou Bay included the inputs from riverine, groundwater discharge, atmospheric deposition and release from the sediment-water interface. The major sinks for DIMn included the output into the Yellow Sea and the absorption or accumulation by biological activities. A preliminary box model was established to estimate the budgets of DIMn for the Sanggou Bay, which demonstrated that in addition to output into the Yellow Sea and biological activities, there was other sinks of DIMns in the Sanggou Bay. The results provide basic data for further understanding the biogeochemical cycle of DIMn in the Sanggou Bay.
-
Key words:
- dissolved manganese /
- sediment /
- distribution /
- seasonal variation /
- influence factors /
- flux and budget /
- Sanggou Bay
-
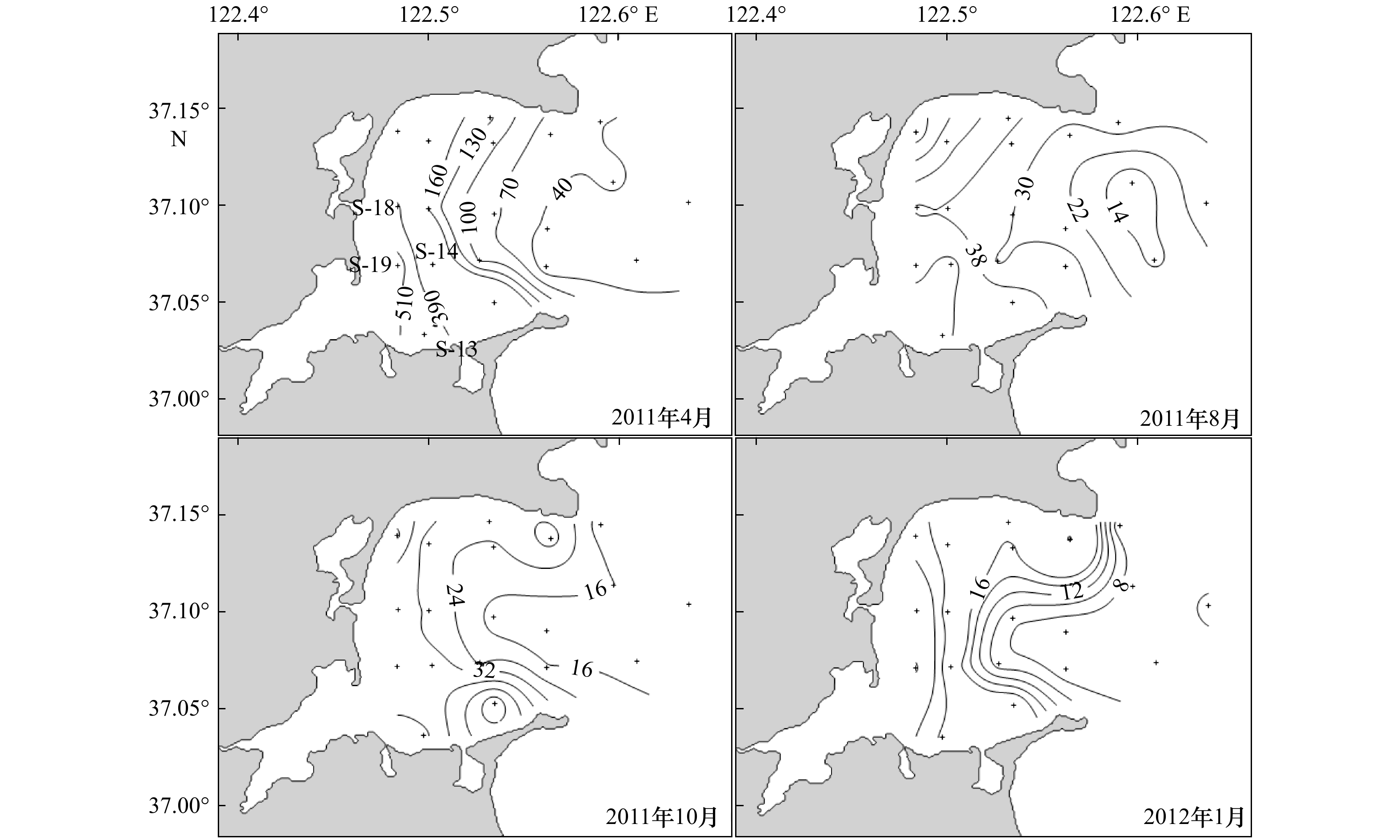
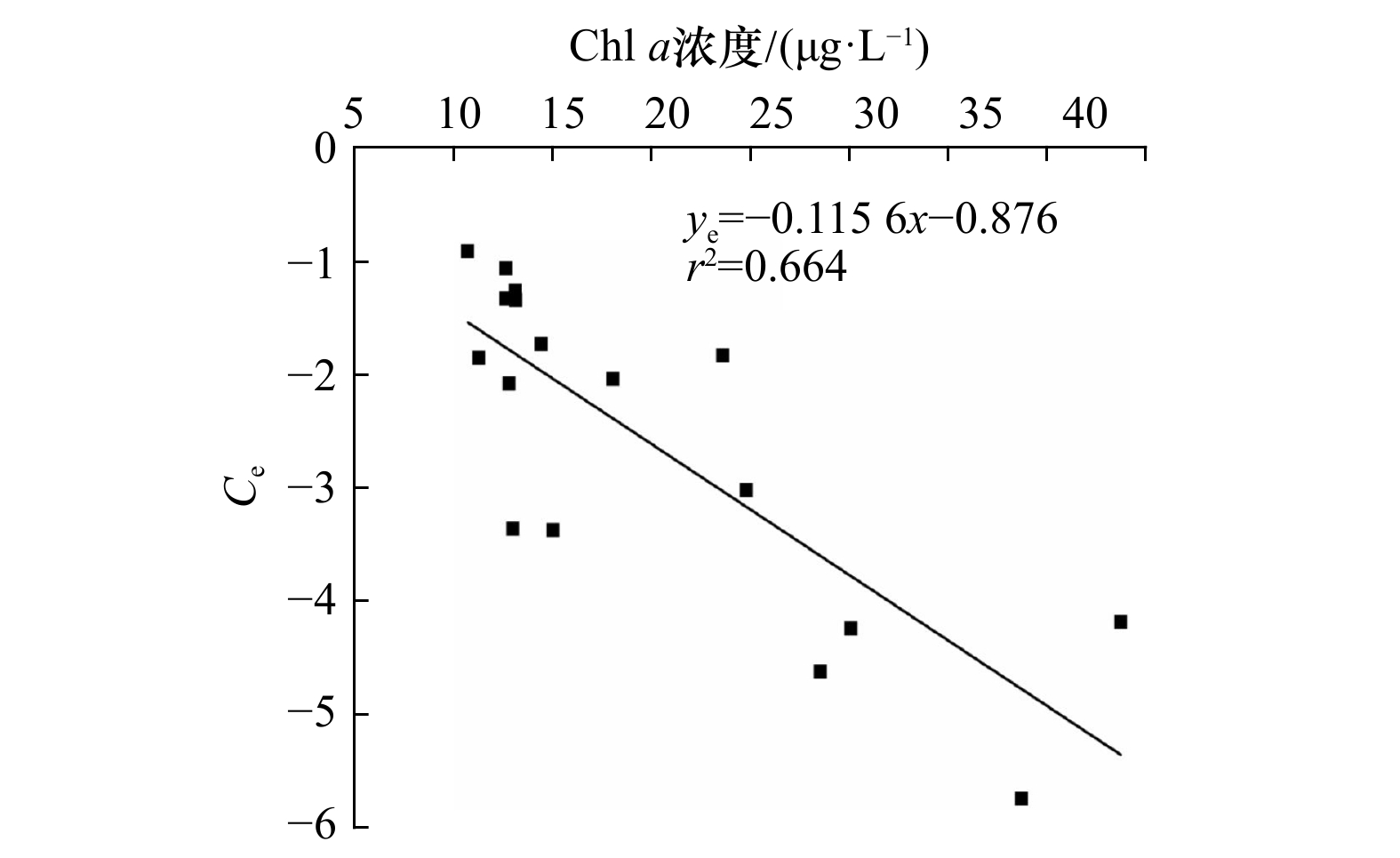
表 1 2011−2012年桑沟湾4个航次的温度、盐度、SPM、Chl a和DIMn的浓度范围
Tab. 1 The ranges of temperature, salinity, SPM, and concentrations of Chl a and DIMn in the Sanggou Bay from 2011 to 2012
航次 2011年4月 2011年8月 2011年10月 2012年1月 温度/℃ 5.5~11.6 18.5~24.2 14.9~17.5 1.9~5.6 (9.0±2.1) (21.4±2.0) (16.5±0.8) (3.8±1.2) 盐度 30.21~30.74 26.17~31.41 30.57~31.37 31.32~31.57 (30.51±0.12) (29.39±1.78) (31.18±0.23) (31.52±0.06) SPM/(mg·L−1) 10.8~63.98 9.2~32.8 13.8~73.9 8.0~67.2 (29.9±15.2) (17.3±3.5) (22.5±6.3) (28.2±15.5) DIMn浓度/(nmol·L−1) 12.5~579.3 19.1~182.9 8.9~49.4 5.4~56.0 (170.0±163.7) (42.0±30.5) (23.4±11.2) (18.2±13.5) Chl a浓度
/(µg·L−1)0.7~2.7 5.7~38.7 0.7~19.6 0.4~2.9 (1.3±0.6) (14.4±9.7) (6.5±6.0) (0.9±0.6) 注:括号内为平均值±标准偏差。 表 2 部分海湾、陆架边缘海及大洋中DIMn的浓度
Tab. 2 The concentration of DIMn in some bays, shelf marginal seas and oceans of the world
海域 时间 表层DIMn浓度/(nmol·L−1) 底层DIMn浓度/(nmol·L−1) 参考文献 桑沟湾 2011年4月 12.5~152.7 本文 2011年8月 7.4~67.1 19.2~84 本文 2011年10月 9.1~63.1 7.2~48.2 本文 2012年10月 5.8~56 5.4~52.3 本文 长江口 2012年3月 2.5~55.1 2.1~59.6 [23] 2012年7月 4.2~74.1 6.9~63.3 [23] 珠江口 2009年5−8月 2.1~1 660 [24] 东海 2011年5月 2.6~21.8 1.5~10.2 [25] 2011年8月 4.2~15.5 3.8~140.7 [25] 2011年11月 2.5~13.9 3.5~19.5 [25] 2013年5月 2.9~29.1 2.5~27.7 未发表数据 2013年8月 3.1~43.6 2.3~81.5 未发表数据 2013年11月 2.2~10.2 1.1~15.2 未发表数据 南海 2011年8月 3.0~28.2 1.3~30 未发表数据 2014年10月 3.7~6.1 0.8~4.6 [26] 2015年6月 1.8~7 0.5~4.1 [26] 2015年7月 1.9~16.2 0.6~14.7 未发表数据 哈德逊河口 1995年10月/1996年10月 33.0~1 460 [27] 杰克逊港口 1999年2月−2001年1月 5.9~1 836.4 [28] 太平洋(HOT−ALOHA) 2001年4月/2002年6月 1.2~1.7 0.26~0.31 [29] 西北太平洋 2008年7−8月 1.3~2.6 0.3~0.7 [30] 南大洋 2008年2−3月 0.04~0.64 0.07~0.23 [3] 加利福尼亚湾 1996年9月/1997年3月 1.7~6.9 >6 [31] 黑海 2001年6月 <100 6 000~8 000 [32] 波罗的海 2008年7−8月 1 000 5 000 [30] 表 3 2011−2012年桑沟湾表层沉积物中TMns和HAc-Mn的含量范围
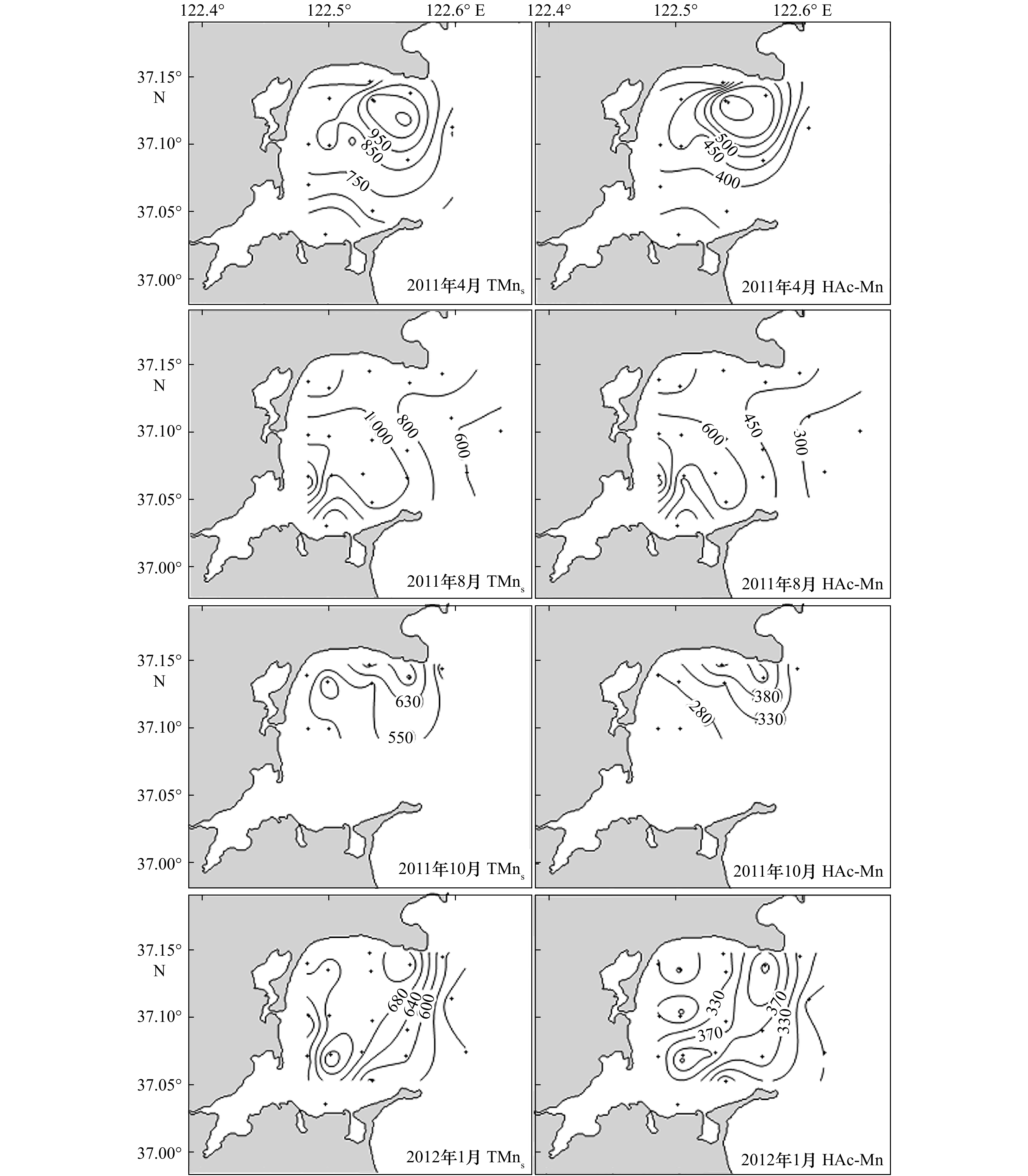
Tab. 3 The content ranges of TMns and HAc-Mn in the surface sediment of the Sanggou Bay from 2011 to 2012
时间 TMns含量/(mg·kg−1) HAc-Mn含量/(mg·kg−1) 2011年4月 363~1 507(861±308) 297~1 129(500±272) 2011年8月 392~1 742(915±322) 177~1 108(502±232) 2011年10月 474~760(589±108) 238~450(322±81) 2012年1月 487~801(653±85) 219~552(345±91) 注:括号内为平均值±标准偏差。 表 4 桑沟湾水产品养殖周期及产量
Tab. 4 Aquaculture cycle and yield of aquatic products in the Sanggou Bay
养殖种类 播种期 收获期 产量/103 t 海带 11−12月 次年5−6月 85(干重) 龙须菜 6月 当年10月 25.4(湿重) 扇贝 10−11月 次年6−7月 15(湿重) 牡蛎 .4−5月 次年11月 60(湿重) -
[1] Wedepohl K H. The composition of the continental crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(7): 1217−1232. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00038-2 [2] Landing W M, Bruland K W. Manganese in the North Pacific[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 49(1): 45−56. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(80)90149-1 [3] Middag R, De Baar H J W, Laan P, et al. Dissolved manganese in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2011, 58(25/26): 2661−2677. [4] Resing J A, Sedwick P N, German C R, et al. Basin-scale transport of hydrothermal dissolved metals across the South Pacific Ocean[J]. Nature, 2015, 523(7559): 200−203. doi: 10.1038/nature14577 [5] Sunda W G, Huntsman S A, Harvey G R, et al. Photoreduction of manganese oxides in seawater and its geochemical and biological implications[J]. Nature, 1983, 301(5897): 234−236. doi: 10.1038/301234a0 [6] 任景玲, 张桂玲, 刘素美, 等. 海洋中锰的生物地球化学循环研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2012, 30(3): 432−440. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2012.03.014Ren Jingling, Zhang Guiling, Liu Sumei, et al. Review on the study of biogeochemical cycle of manganese in the oceans[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2012, 30(3): 432−440. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2012.03.014 [7] Calvert S E, Pedersen T F. Sedimentary geochemistry of manganese; implications for the environment of formation of manganiferous black shales[J]. Economic Geology, 1996, 91(1): 36−47. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.91.1.36 [8] Bruland K W, Donat J R, Hutchins D A. Interactive influences of bioactive trace metals on biological production in oceanic waters[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1991, 36(8): 1555−1577. doi: 10.4319/lo.1991.36.8.1555 [9] Buma A G J, De Baar H J W, Nolting R F, et al. Metal enrichment experiments in the Weddell-Scotia Seas: effects of iron and manganese on various plankton communities[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1991, 36(8): 1865−1878. doi: 10.4319/lo.1991.36.8.1865 [10] Peers G, Price N M. A role for manganese in superoxide dismutases and growth of iron-deficient diatoms[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2004, 49(5): 1774−1783. doi: 10.4319/lo.2004.49.5.1774 [11] 中国海湾志编纂委员会. 中国海湾志: 第三分册[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1991: 377−424.Chinese Gulf Compilation Committee. Chinese Gulf (3rd Volume)[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1991: 377−424. [12] 蒋增杰, 方建光, 门强, 等. 桑沟湾贝类筏式养殖与环境相互作用研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 2006, 2(1): 23−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2006.01.005Jiang Zengjie, Fang Jianguang, Men Qiang, et al. Studies on the interaction between shellfish long-line culture and environment in the Sungo Bay[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2006, 2(1): 23−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2006.01.005 [13] Zhang Jihong, Hansen P K, Fang Jianguang, et al. Assessment of the local environmental impact of intensive marine shellfish and seaweed farming—Application of the MOM system in the Sungo Bay, China[J]. Aquaculture, 2009, 287(3/4): 304−310. [14] 孙耀, 赵俊, 周诗赉, 等. 桑沟湾养殖海域的水环境特征[J]. 中国水产科学, 1998, 5(3): 69−75. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.1998.03.013Sun Yao, Zhao Jun, Zhou Shilai, et al. Environmental features of cultural waters in Sanggou Bay[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 1998, 5(3): 69−75. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.1998.03.013 [15] 闫哲, 任景玲, 刘素美, 等. 桑沟湾总溶解态无机砷的分布与季节变化[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2008, 27(5): 432−436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2008.05.008Yan Zhe, Ren Jingling, Liu Sumei, et al. Distribution and seasonal variation of total dissolved inorganic arsenic in Sanggou Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2008, 27(5): 432−436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2008.05.008 [16] 李磊, 任景玲, 刘素美, 等. 桑沟湾溶解态无机砷的分布、季节变化及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(7): 2705−2713.Li Lei, Ren Jingling, Liu Sumei, et al. Distribution, seasonal variation and influence factors of dissolved inorganic arsenic in the Sanggou Bay[J]. Environment Science, 2014, 35(7): 2705−2713. [17] 张国玲, 任景玲, 张继红, 等. 桑沟湾养殖区铝的分布及季节变化[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2010, 29(6): 843−847. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2010.06.015Zhang Guoling, Ren Jingling, Zhang Jihong, et al. Distributions and seasonal variations of aluminum in Sanggou Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2010, 29(6): 843−847. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2010.06.015 [18] 房瑞雪, 任景玲, 李磊, 等. 桑沟湾溶解态铝的分布、季节变化及影响因素[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2015, 33(3): 342−351. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2015.03.008Fang Ruixue, Ren Jingling, Li Lei, et al. The distributions, seasonal variations and influence factors of dissolved aluminium in the Sanggou Bay[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2015, 33(3): 342−351. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2015.03.008 [19] 王希龙, 杜金洲, 张经. 基于223Ra和224Ra的桑沟湾海底地下水排放通量[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(4): 16−27.Wang Xilong, Du Jinzhou, Zhang Jing. Submarine groundwater discharge into Sanggou Bay traced 223Ra and 224Ra[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(4): 16−27. [20] Zhu Xunchi, Zhang Ruifeng, Liu Sumei, et al. Seasonal distribution of dissolved iron in the surface water of Sanggou Bay, a typical aquaculture area in China[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2017, 189: 1−9. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2016.12.004 [21] 张晓慧, 李磊, 任景玲, 等. 桑沟湾溶解态铁的分布、季节变化及影响因素[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(5): 656−662. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190502Zhang Xiaohui, Li Lei, Ren Jingling, et al. The distributions, seasonal variations and influence factors of dissolved iron in the Sanggou Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2019, 38(5): 656−662. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190502 [22] 房瑞雪. 桑沟湾不同形态锰的分布、季节变化及其影响因素[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015.Fang Ruixue. Distributions, seasonal variations and influence factors of the different manganese species in the Sanggou Bay[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2015. [23] 杨亭亭, 任景玲, 王召伟, 等. 长江口及邻近海域溶解态锰的分布及影响因素[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2016, 34(2): 260−270. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2016.02.011Yang Tingting, Ren Jingling, Wang Zhaowei, et al. Distributions and influence factors of dissolved manganese in the Changjing Estuary and its adjacent area[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2016, 34(2): 260−270. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2016.02.011 [24] Wang Deli, Lin Wenfang, Yang Xiqian, et al. Occurrences of dissolved trace metals (Cu, Cd, and Mn) in the Pearl River Estuary (China), a large river-groundwater-estuary system[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2012, 50−51: 54−63. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2012.10.009 [25] Wang Zhaowei, Ren Jingling, Jiang Shuo, et al. Geochemical behavior of dissolved manganese in the East China Sea: seasonal variation, estuarine removal, and regeneration under suboxic conditions[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2016, 17(2): 282−299. doi: 10.1002/2015GC006128 [26] Wang Zhaowei, Ren Jingling, Zhang Ruifeng, et al. Physical and biological controls of dissolved manganese on the northern slope of the South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2019, 167(9): 25−33. [27] Yang Min, Sañudo-Wilhelmy S A. Cadmium and manganese distributions in the Hudson River estuary: interannual and seasonal variability[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 160(3/4): 403−418. [28] Hatje V, Apte S C, Hales L T, et al. Dissolved trace metal distributions in Port Jackson estuary (Sydney Harbour), Australia[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2003, 46(6): 719−730. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00061-4 [29] Boyle E A, Bergquist B A, Kayser R A, et al. Iron, manganese, and lead at Hawaii Ocean time-series station ALOHA: temporal variability and an intermediate water hydrothermal plume[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(4): 933−952. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.07.034 [30] Yakushev E, Pakhomova S, Sørenson K, et al. Importance of the different manganese species in the formation of water column redox zones: observations and modeling[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2009, 117(1/4): 59−70. [31] Delgadillo-Hinojosa F, Segovia-Zavala J A, Huerta-Díaz M A, et al. Influence of geochemical and physical processes on the vertical distribution of manganese in Gulf of California waters[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2006, 53(8): 1301−1319. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2006.06.002 [32] Yemenicioglu S, Erdogan S, Tugrul S. Distribution of dissolved forms of iron and manganese in the Black Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2006, 53(17/19): 1842−1855. [33] 刘赛, 杨庶, 杨茜, 等. 桑沟湾沉积碳库年汇入速率的长期变化及其区域性差异[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(1): 47−56.Liu Sai, Yang Shu, Yang Qian, et al. The long-term changes of annual carbon sequestration rate and regional difference in culture areas of Sanggou Bay[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(1): 47−56. [34] Burnett W C, Bokuniewicz H, Huettel M, et al. Groundwater and pore water inputs to the coastal zone[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2003, 66(1): 3−33. [35] Gordon D C, Boudreau P R, Mann K H, et al. LOICZ Biogeochemical Modelling Guidelines[C]//LOICZ Research & Studies. Den Burg: LOICZ International Project Office, 1996. [36] 刘昌岭, 张经, 于志刚. 黄海海域大气气溶胶特征及重金属的大气输入量研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 1998, 17(4): 1−6.Liu Changling, Zhang Jing, Yu Zhigang. Study on the characteristics of the aerosol and atmospheric flux of the heavy metals over the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 1998, 17(4): 1−6. [37] Baker A R, Jickells T D, Witt M, et al. Trends in the solubility of iron, aluminium, manganese and phosphorus in aerosol collected over the Atlantic Ocean[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2006, 98(1): 43−58. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2005.06.004 [38] De Jong J T M, Boyé M, Gelado-Caballero M D, et al. Inputs of iron, manganese and aluminium to surface waters of the Northeast Atlantic Ocean and the European continental shelf[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2007, 107(2): 120−142. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2007.05.007 [39] 杨一超, 薛金林, 任景玲, 等. 夏季南海气溶胶微量元素浓度、溶解度及干沉降通量[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(7): 2365−2374.Yang Yichao, Xue Jinlin, Ren Jingling, et al. Trace element concentrations, solubilities and dry deposition fluxes in aerosol samples collected in the South China Sea in summer[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(7): 2365−2374. [40] 孙玲玲, 宋金明, 林强, 等. 海带中12种元素ICP-OES检测的三种前处理方法对比研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2015, 39(5): 9−15.Sun Lingling, Song Jinming, Lin Qiang, et al. Comparison of three pretreatment methods for the determination of 12 elements in thallus laminariae by ICP-OES[J]. Marine Sciences, 2015, 39(5): 9−15. [41] 张改荣, 向志文. 原子吸收光谱法测定龙须菜中7种微量元素含量[J]. 光谱实验室, 2007, 24(6): 1005−1008. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8138.2007.06.003Zhang Gairong, Xiang Zhiwen. Determination of seven trace elements in gracilaria lemaneiformis by atomic absorption spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Spectroscopy Laboratory, 2007, 24(6): 1005−1008. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8138.2007.06.003 [42] 朱逊驰. 中国近岸到陆架区典型水体中溶解铁的生物地球化学过程[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2018.Zhu Xunchi. Biogeochemical processes of dissolved iron in typical waters in the nearshore to continental shelf area of China[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2018. [43] 高淑英, 邹栋梁. 湄洲湾生物体内重金属含量及其评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 1994, 13(1): 39−45.Gao Shuying, Zou Dongliang. Concentrations and assessment of heavy metals in aquatic organisms from the Meizhou Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 1994, 13(1): 39−45. [44] 宁劲松, 尚德荣, 赵艳芳, 等. 青岛市场养殖贝类体内重金属含量的分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(21): 11154−11155, 11219. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.21.050Ning Jinsong, Shang Derong, Zhao Yanfang, et al. Analysis of heavy metal content in shellfish from Qingdao markets[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(21): 11154−11155, 11219. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2010.21.050 [45] Boudreau. Diagenetic Models and Their Implementation[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1997. -




 下载:
下载: