The relationship between the growth discontinuity of polymetallic crusts and phosphatization events
-
摘要: 磷酸盐化的发生会造成多金属结壳主要成矿元素的贫化,总体上抑制结壳的生长。磷酸盐化作用呈幕式在太平洋内发生,已有研究将其发生期次与多金属结壳中的磷酸盐化层位及其P、Ca等元素地球化学特征对应,为结壳的年代厘定提供证据。然而,由于磷酸盐化多次发生且在结壳多个层位中显现,首先需要厘定出较为可靠的多金属结壳年代框架,才能与磷酸盐化事件相互佐证。本研究通过定年范围较大,同时可以识别结壳中存在的生长间断的Co-Os法定年体系,为中、西太平洋6块多金属结壳定年,并参考肉眼识别的磷酸盐化矿化特征和地球化学特征佐证年代框架,同时分析磷酸盐化作用对结壳成矿的影响。39~34 Ma和27~21 Ma的两次大规模磷酸盐化期次全部对应多金属结壳的大规模间断期,而71 Ma、55 Ma和31 Ma等小规模磷酸盐化事件多数可在多金属结壳的层位和地球化学特征中识别,对应P和Ca百分含量的飙升和峰值特征。这一方面证实了磷酸盐化的发生整体抑制了结壳的生长,且具有广泛的影响范围和明确的时代区间,另一方面则佐证了多金属结壳年代框架的准确性。Abstract: The occurrence of phosphatization will lead to the dilution of major ore-forming elements in polymetallic crusts and thus inhibit the growth of crusts in general. Phosphatization occurred in the Pacific Ocean in an episodic manner, and the occurrence periods correspond to the phosphatization layers in crusts and the geochemical characteristics of P, Ca and other elements, providing evidence for the dating of crusts. However, due to the frequent occurrence of phosphatization in multiple layers of crusts, a more reliable age frame needs to be determined before it can be mutually corroborated with phosphatization events. In this study, the Co-Os dating system with large dating range and the ability to determine hiatus was applicated in dating for the crust samples from central Pacific and western Pacific. With the naked eye identification of phosphatization mineralization features and geochemical profile characteristics, the age frames were proved and the effect of phosphatization on crust mineralization were discussed. The two large-scale phosphatization phases of 39–34 Ma and 27–21 Ma all correspond to the large-scale discontinuous phases of the crusts, while most small-scale phosphatization events in 71 Ma, 55 Ma and 31 Ma can be identified in the layers and geochemical profiles, corresponding to the rising and peak characteristics of P and Ca content. On the one hand, it is confirmed that the occurrence of phosphatization inhibits the growth of crusts, and has a wide range of influence area and a clear time interval in Pacific. On the other hand, it proves the accuracy of the chronological framework of polymetallic crusts.
-
Key words:
- phosphatization /
- polymetallic crusts /
- paleoceanographyic events /
- age frame proving /
- growing hiatus
-
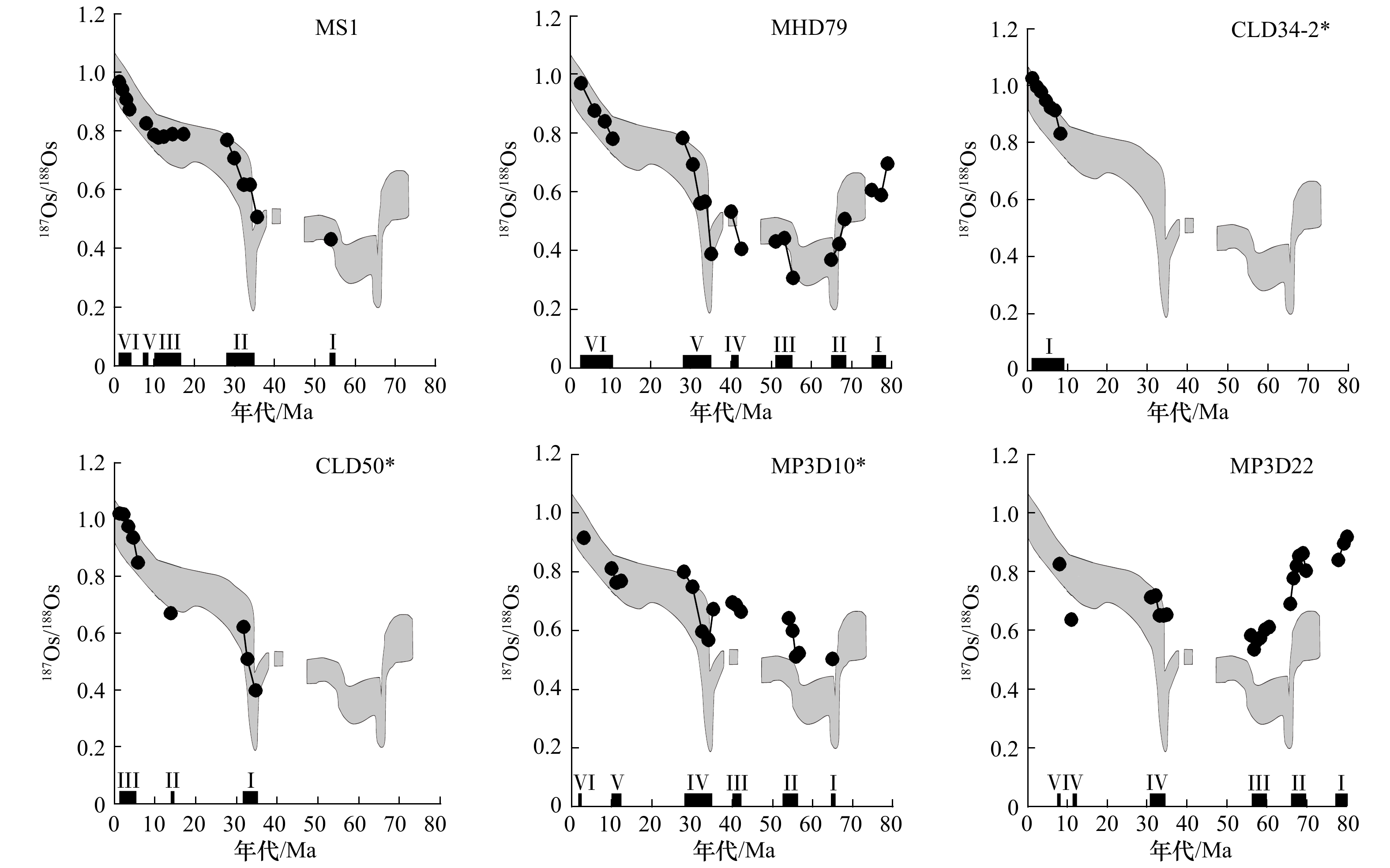
图 2 多金属结壳年代框架
年代框架由Co经验公式法结合Os同位素标准曲线法获得。灰色框体为标准曲线(据文献[19]),实心圆为结壳Os同位素组成测定值,横坐标上的黑色线段为生长期,*样品MP3D10的Os同位素数据见文献[4],样品CLD34-2和CLD50的数据见文献[20]
Fig. 2 Age frame of polymetallic crusts
The age frame is obtained by cobalt experiential formula and osmium isotope standard curve method. Gray background is standard curve (from the reference [19]); solid circles are measured Os isotopic composition; black segments are the growing periods; *the Os isotopic data of sample MP3D10 are shown in reference [4], and the data of samples CLD34-2 and CLD50 are shown in reference [20]
图 3 中、西太平洋多金属结壳磷酸盐化指示元素P、Ca质量百分含量年代剖面
实心菱形是P质量百分比含量,空心圆形是Ca质量百分比含量;点线框体和虚线分别是两次大规模和3次小规模磷酸盐化事件对应年代;*样品MP3D10的P、Ca数据见文献[4],样品CLD34-2和CLD50的数据见文献[20]
Fig. 3 Weight percentage contents of phosphatization indicator elements P and Ca in age profile of polymetallic crusts from the central Pacific and western Pacific
P weight percentage contents for solid diamonds, Ca weight percentage contents for hollow circles; corresponding age of two large-scale and three small-scale phosphatization events for point line frames and dotted lines respectively; *the P, Ca data of sample MP3D10 are shown in reference [4], and the data of samples CLD34-2 and CLD50 are shown in reference [20]
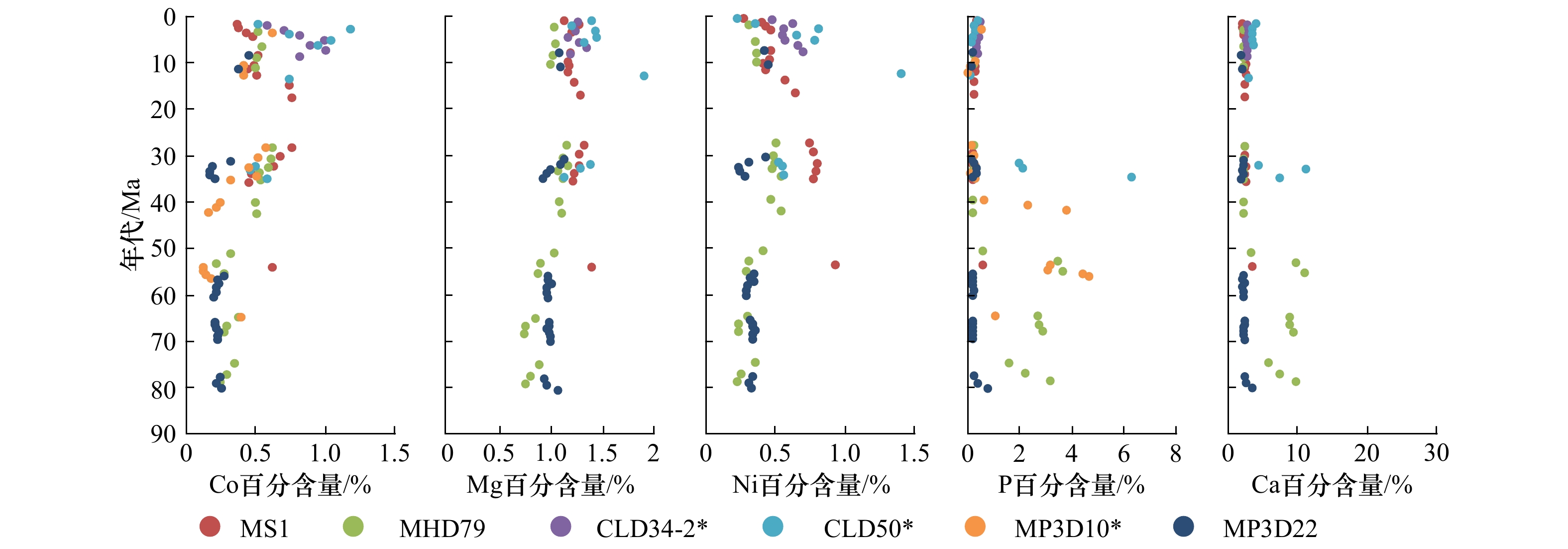
图 4 中、西太平洋多金属结壳Co、Mg、Ni、P、Ca元素的百分含量年代剖面
*样品MP3D10的元素百分含量数据见文献[4],样品CLD34-2和CLD50的数据见文献[20]
Fig. 4 Weight percentage contents of Co, Mg, Ni, P and Ca in age profile of polymetallic crusts from the central Pacific and western Pacific
*The element content data of sample MP3D10 are shown in reference [4], and the data of samples CLD34-2 and CLD50 are shown in reference [20]
表 1 多金属结壳分层结构构造与磷酸盐化痕迹描述
Tab. 1 The description of layered structure and phosphatization characteristics in crusts
样品名称 层位 磷酸盐化程度 宏观描述 磷酸盐化痕迹 MS1 III 弱 结核状结壳,环绕核心生长 无 I 弱 整体致密,按生长纹理大致可分为5层,无明显疏松层 无 MHD79 III 强 亮黑色−黑褐色,致密块状,组成纯净,横纵节理发育,
贝壳状断口无 II 强 黄白色−黄褐色,质地疏松,杂质较多 夹有较多灰白−黄白色团块和细脉 I 强 亮黑色−黑褐色,致密块状,片理发育 夹有黄褐色薄膜状薄层 CLD34−2 III 弱 黑褐色,致密块状,组成纯净,具柱状构造 夹有不规则黄褐色细脉 CLD50 III 强 黑褐色,同心圆构造,具柱状构造 无 II 强 黑褐色,多孔,充填大量碎屑,构造杂乱 充填黄褐色细脉 I 强 亮黑色,组成纯净,具平行纹层构造,具生物痕迹 充填黄绿色岩屑 MP3D10 III 强 黑褐色,致密块状 无 II 强 黑褐色−黄褐色,裂隙和孔洞多,含大量杂质 含土黄色、灰白色斑点或斑块状沉积物杂质 I 强 亮黑色−黄白色,致密块状,节理裂隙发育 具树枝状疑似碳氟磷灰石矿物 MP3D22 III 弱 褐黑色,呈层状,金属光泽 夹有灰白色条带 II 弱 灰黑−黄褐色,裂隙和孔洞多 具灰白色填充物 I 弱 亮黑色,致密块状,组成纯净 不规则磷酸盐细脉和颗粒 -
[1] Halbach P, Puteanus D. The influence of the carbonate dissolution rate on the growth and composition of Co-rich ferromanganese crusts from Central Pacific seamount areas[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1984, 68(1): 73−87. [2] Bogdanov Y A, Bogdanova O Y, Dubinin A V, et al. Composition of ferromanganese crusts and nodules at Northwestern Pacific guyots and geologic and paleoceanographic considerations[C]//Haggerty J A, Silva P I, Rack F, et al. Proceedings of the Oceans Drlling Program Scientific Reports. Galveston: College Station, TX: Ocean Drilling Program, 1995: 745−768. [3] Koschinsky A, Halbach P, Hein J R, et al. Ferromanganese crusts as indicators for paleoceanographic events in the NE Atlantic[J]. Geologische Rundschau, 1996, 85(3): 567−576. [4] 丁旋, 高莲凤, 方念乔, 等. 太平洋海山富钴结壳生长过程与新生代海洋演化关系[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2008, 52(8): 1091−1103.Ding Xuan, Gao Lianfeng, Fang Nianqiao, et al. The relationship between the growth process of the ferromanganese crusts in the Pacific Seamount and cenozoic ocean evolvement[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2008, 52(8): 1091−1103. [5] 潘家华, 刘淑琴, DeCarlo E. 大洋磷酸盐化作用对富钴结壳元素富集的影响[J]. 地球学报, 2002, 23(5): 403−407. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.05.003Pan Jiahua, Liu Shuqin, DeCarlo E. The effects of marine phospharization on element concentration of cobalt-rich crusts[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2002, 23(5): 403−407. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2002.05.003 [6] 任向文, 刘季花, 石学法, 等. 西太平洋Lamont海山中新世以来富钴结壳成矿环境的演化[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2006, 24(1): 17−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2006.01.003Ren Xiangwen, Liu Jihua, Shi Xuefa, et al. Evolution of ore-forming condition of Co-rich crusts from Lamont Guyot in the Western Pacific since the Miocene[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2006, 24(1): 17−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2006.01.003 [7] Segl M, Mangini A, Bonani G, et al. 10Be-dating of a manganese crust from Central North Pacific and implications for ocean palaeocirculation[J]. Nature, 1984, 309(5968): 540−543. [8] Hein J R, Bohrson W A, Schulz M S, et al. Variations in the fine-scale composition of a central Pacific ferromanganese crust: Paleoceanographic implications[J]. Paleoceanography, 1992, 7(1): 63−77. [9] Hein J R, Yeh H W, Gunn S H, et al. Two major Cenozoic episodes of phosphogenesis recorded in equatorial Pacific seamount deposits[J]. Paleoceanography, 1993, 8(2): 293−311. [10] Halbach P, Sattler C D, Teichmann F, et al. Cobalt-rich and platinum-bearing manganese crust deposits on seamounts: nature, formation, and metal potential[J]. Marine Mineralogy, 1989, 8(1): 23−29. [11] Koschinsky A, Stascheit A, Bau M, et al. Effects of phosphatization on the geochemical and mineralogical composition of marine ferromanganese crusts[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(19): 4079−4094. [12] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Bau M, et al. Cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts in the Pacific[C]//Cronan D S. Handbook of Marine Mineral Deposits. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 2000: 239−279. [13] 武光海, 周怀阳, 凌洪飞, 等. 富钴结壳中的磷酸盐岩及其古环境指示意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2005, 25(1): 39−44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2005.01.007Wu Guanghai, Zhou Huaiyang, Ling Hongfei, et al. Phosphorites in Co-rich crusts and their palaeooceanographic singificance[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2005, 25(1): 39−44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2005.01.007 [14] 李江山, 方念乔, 屈文俊, 等. 中太平洋富钴结壳的Os同位素定年与结壳生长间断[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2008, 51(10): 1452−1459.Li Jiangshan, Fang Nianqiao, Qu Wenjun, et al. Os isotope dating and growth hiatuses of Co-rich crust from Central Pacific[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2008, 51(10): 1452−1459. [15] 王晓红, 周力平, 王毅民, 等. 太平洋富钴结壳高密度环境记录解读[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2008, 51(10): 1460−1469.Wang Xiaohong, Zhou Liping, Wang Yimin, et al. Paleoenvironmental implications of high-density records in Co-rich seamount crusts from the Pacific ocean[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2008, 51(10): 1460−1469. [16] Manheim F T, Lane -Bostwick C M. Cobalt in ferromanganese crusts as a monitor of hydrothermal discharge on the Pacific sea floor[J]. Nature, 1988, 335(6185): 59−62. doi: 10.1038/335059a0 [17] McMurtry G M, VonderHaar D L, Eisenhauer A, et al. Cenozoic accumulation history of a Pacific ferromanganese crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 125(1/4): 105−118. [18] Du Andao, Wu Shuqi, Sun Dezhong, et al. Preparation and certification of Re-Os dating reference materials: Molybdenites HLP and JDC[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004, 28(1): 41−52. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2004.tb01042.x [19] Klemm V, Levasseur S, Frank M, et al. Osmium isotope stratigraphy of a marine ferromanganese crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 238(1/2): 42−48. [20] 周涛. 中−西太平洋新生代海山纬向迁移对富钴结壳生长环境的影响[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2014.Zhou Tao. The zonal migration of the seamounts in Middle-West Pacific during Cenozoic and its influence on the formation of cobalt bearing crust[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2014. -





 下载:
下载: