Seasonal variability of distribution and mixing behavior of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the Changjiang River Estuary and adjacent areas
-
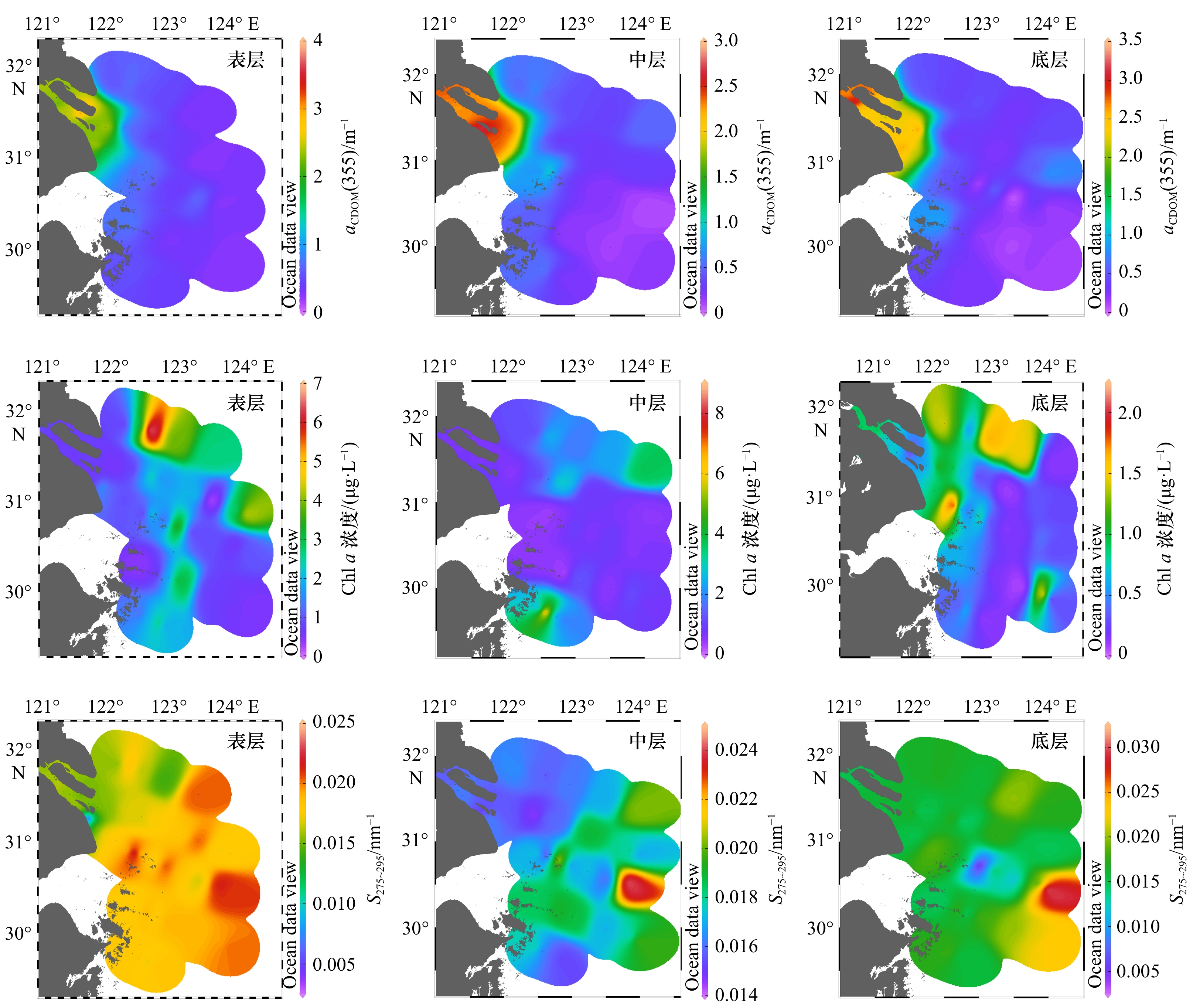
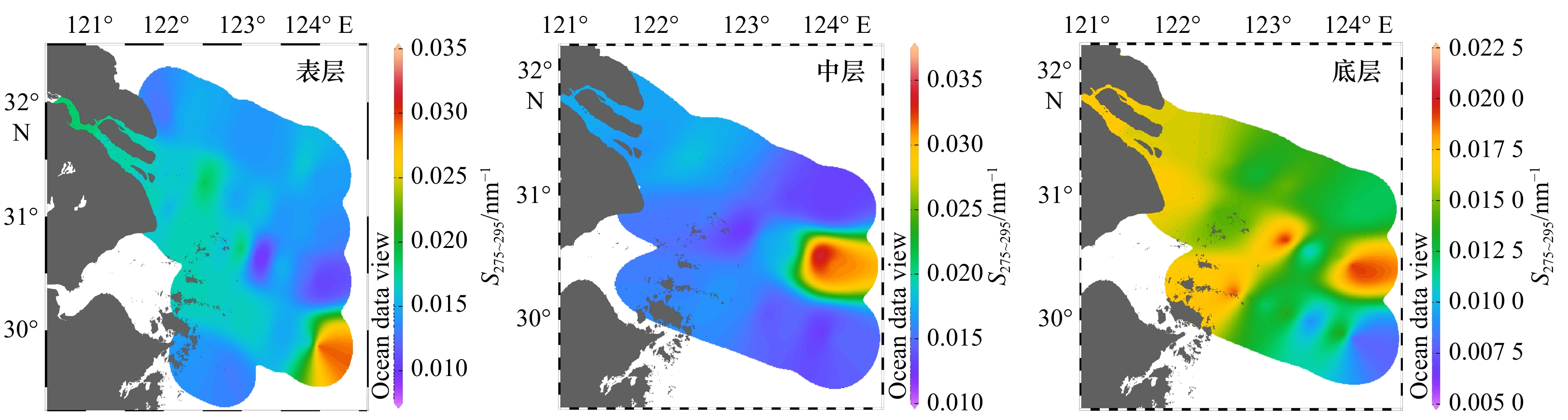
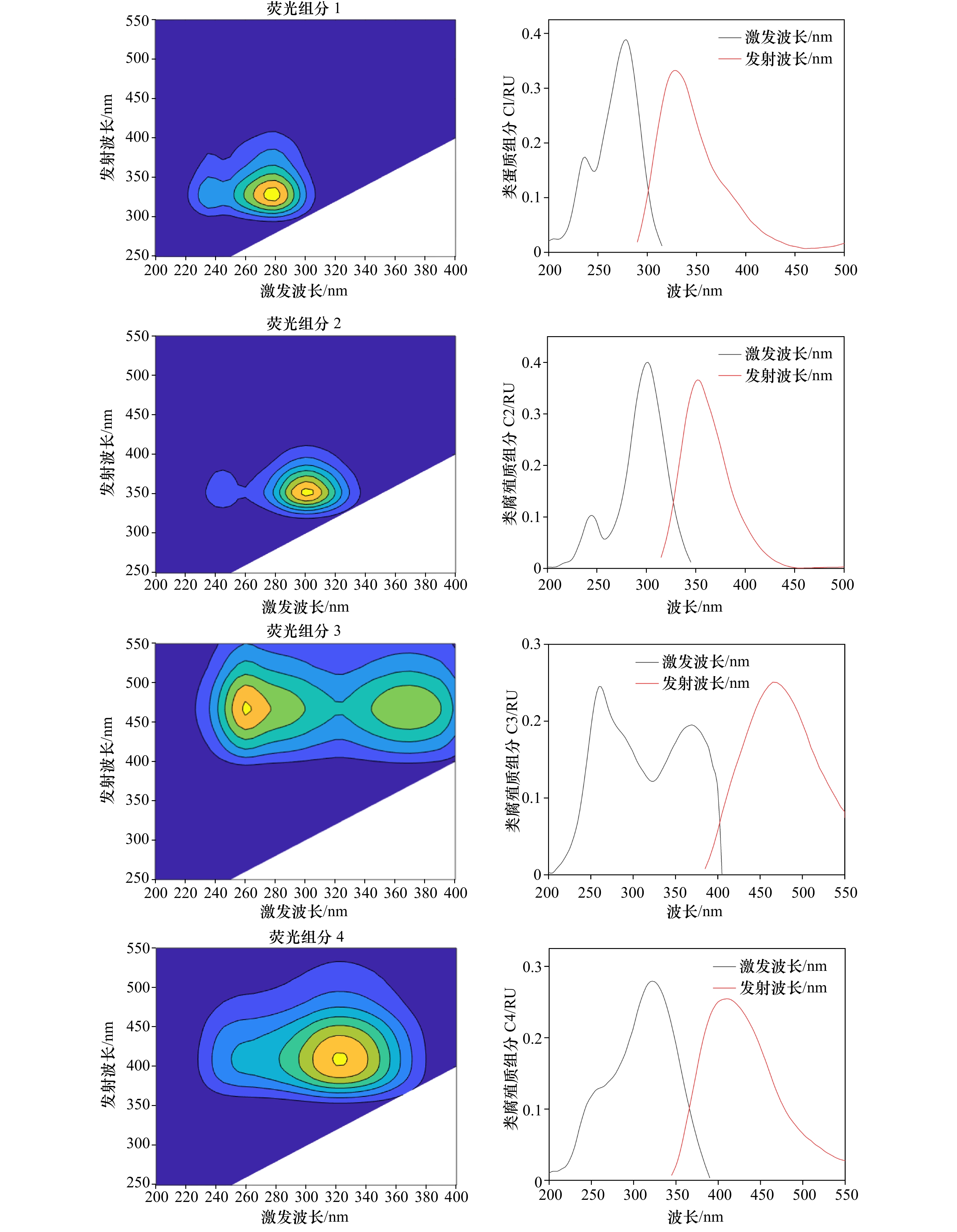
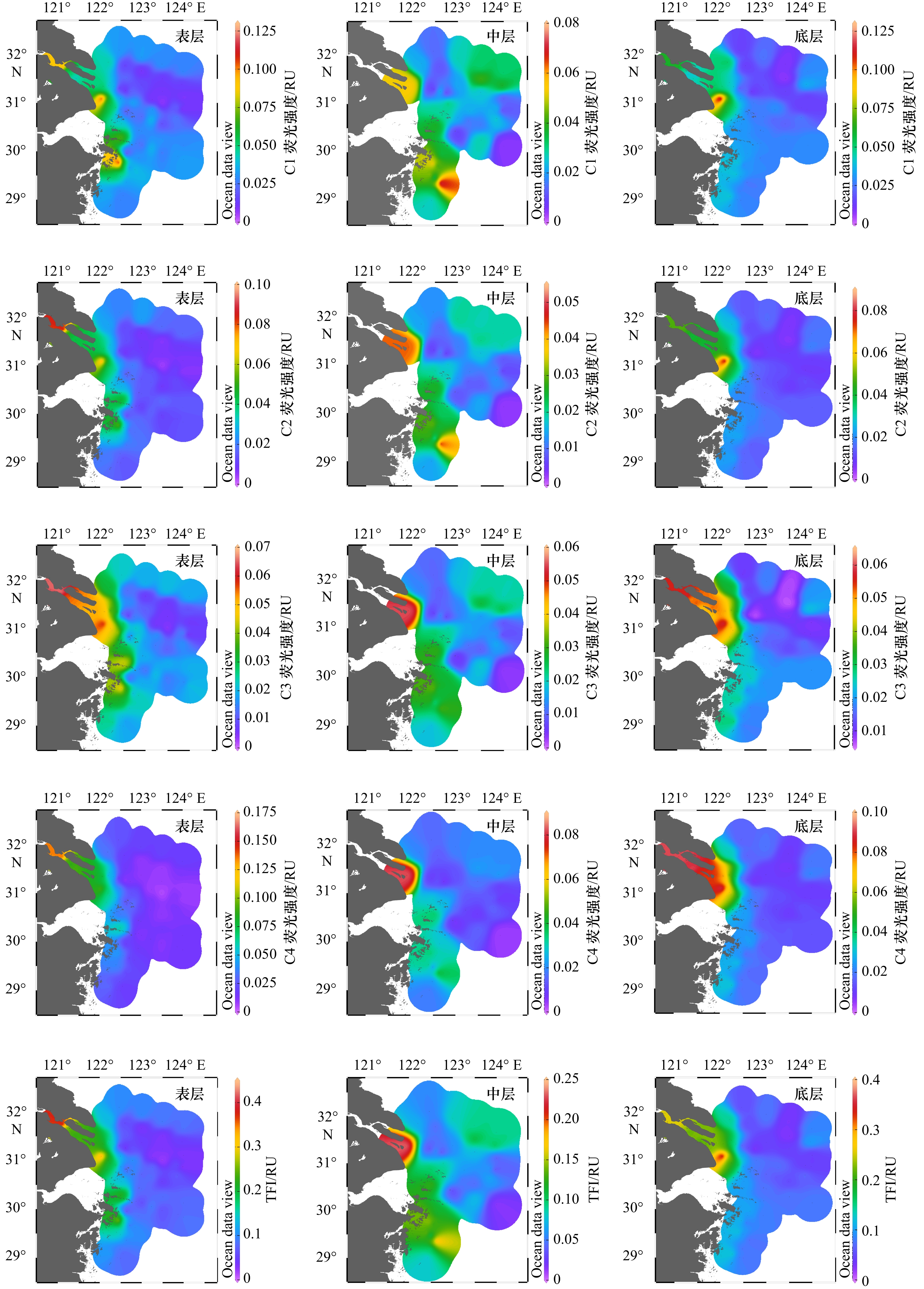
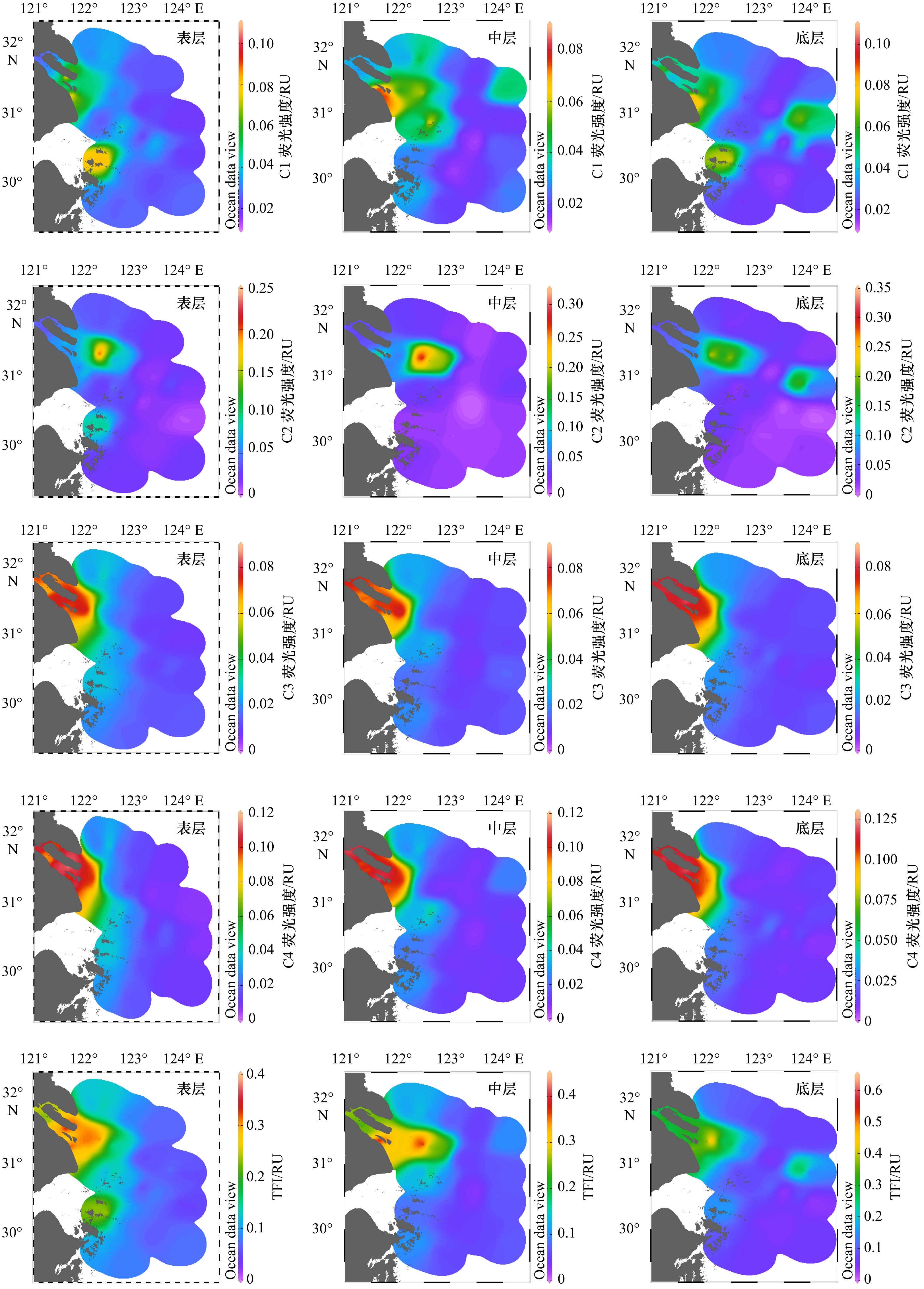
摘要: 于2019年3月、7月和10月对长江口及邻近海域有色溶解有机物(CDOM)的分布及河口混合行为进行分析研究。通过对盐度、吸收光谱斜率S275~295、吸收系数aCDOM(355)以及叶绿素a的分析发现,在河口内低盐度区,7月淡水流量大,陆源输入量最大,aCDOM(355)值最高,3月CDOM来源主要受陆源输入和浮游植物生产活动的影响,aCDOM(355)值较10月高;在口外高盐度区,3月和7月的aCDOM(355)值相近,均低于10月,CDOM分布主要受浮游植物生产活动的影响。利用三维荧光光谱−平行因子分析方法共鉴定出4个荧光组分:类蛋白质组分C1(280/330 nm)、类腐殖质组分C2(300/350 nm)、类腐殖质组分C3(260/465 nm)和类腐殖质组分C4(320/410 nm)。在3月、7月及10月,4个荧光组分强度由长江口内到口外呈递减趋势,受陆源输入和浮游植物生产活动的影响,平均荧光强度的季节变化总体上来说,由大到小依次为7月、10月、3月。3个季节CDOM荧光组分均存在偏离理论稀释线的现象,说明CDOM的来源(陆源输入、沉积物再悬浮和现场生物活动)和去除(被颗粒物吸附、光降解和细菌降解)机制复杂多变,揭示了长江口区域CDOM在不同时空下的不保守混合行为。Abstract: The distribution and mixing behavior of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in the Changjiang River Estuary and adjacent areas were analyzed in March, July and October of 2019. Through discussing the salinity, absorption spectral slope S275-295, absorption coefficient aCDOM(355) and Chl a, it was shown that the terrestrial input and aCDOM(355) had the highest value in July; aCDOM(355) was affected by terrestrial input and phytoplankton production activities in March, and the value in March was higher than that in October in the Changjiang River Estuary low salinity area. In addition, in high-salt offshore regions, aCDOM(355) was similar in March and July, and both were lower than that in October, these distribution of CDOM was mainly influenced by phytoplankton production activities. Four fluorescent components of CDOM were identified by EEMs-PARAFAC technique: one protein-like component C1 (280/330 nm) and three humic-like components C2 (300/350 nm), C3 (260/465 nm) and C4 (320/410 nm) respectively. Four fluorescent components declined from the inside to the outside of the Changjiang River Estuary in March, July and October. Affected by terrestrial input and phytoplankton production activities, the seasonal variation of the average fluorescence intensity from large to small was July, October and March. The fluorescence components of CDOM deviated from the theoretical dilution line in these three seasons. It showed that CDOM source (terrestrial input, sediment resuspension and on-site biological activities) and sink (adsorption of particulate matter, photodegradation and bacterial degradation) were complex and variable, revealing the non-conservative mixed behavior of CDOM in the Changjiang River Estuary.
-
表 1 3月长江口及邻近海域温度、aCDOM(355)、Chl a浓度以及S275~295的值
Tab. 1 The value of temperature, aCDOM(355), Chl a concentration and S275~295 of the Changjiang River Estuary and adjacent areas in March
参数 盐度分区 温度/℃ aCDOM(355)/m−1 Chl a浓度/(μg.L−1) S275~295/nm−1 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 表层 0.13~7.65(盐度小于10) 8.35~8.87 8.58 1.37~2.27 1.85 0.85~3.12 2.2 0.014~0.018 0.016 10.4~34.4(盐度大于10) 7.84~14.6 11.2 0.08~3.13 0.45 0.18~2.39 0.8 0.012~0.033 0.019 中层 0.14~0.15(盐度小于10) 8.52~8.62 8.57 1.85~2.00 1.91 2.18~3.59 2.7 0.015~0.016 0.015 26.1~34.3(盐度大于10) 8.06~13.9 11.2 0.019~0.5 0.31 0.17~1.52 0.6 0.015~0.024 0.019 底层 0.13~8.63(盐度小于10) 8.33~9.00 8.61 1.25~2.43 1.93 1.02~3.30 2.1 0.014~0.017 0.016 13.6~34.3(盐度大于10) 7.82~14.0 11.2 0.03~1.21 0.39 0.12~2.55 0.9 0.002~0.037 0.017 表 2 7月长江口及邻近海域温度、aCDOM(355)、Chl a浓度以及S275~295的值
Tab. 2 The value of temperature, aCDOM(355), Chl a concentration and S275~295 of the Changjiang River Estuary and adjacent areas in July
参数 盐度分区 温度/℃ aCDOM(355)/m−1 Chl a 浓度/(μg.L−1) S275~295/nm−1 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 表层 0.13~0.15(盐度小于10) 26.2~27.0 26.7 0.92~3.52 2.22 0.61~1.75 0.80 0.004~0.018 0.016 16.8~32.6(盐度大于10) 22.1~26.4 24.6 0.24~0.85 0.47 0.18~4.51 1.85 0.014~0.022 0.018 中层 0.14~0.15(盐度小于10) 26.4~27.0 26.7 2.19~2.81 2.39 0.52~1.13 0.77 0.015~0.017 0.016 18.7~33.1(盐度大于10) 21.6~26.3 24.0 0.08~1.18 0.37 0.23~8.28 1.46 0.015~0.024 0.017 底层 0.13~0.15(盐度小于10) 26.5~26.9 26.7 0.83~3.40 2.37 0.17~2.19 0.81 0.013~0.019 0.016 28.1~34.5(盐度大于10) 18.4~23.3 21.7 0.01~0.97 0.37 0.07~1.64 0.55 0.012~0.032 0.017 表 3 10月温度、aCDOM(355)、Chl a浓度以及S275~295的值
Tab. 3 The value of temperature, aCDOM(355), Chl a concentration and S275~295 of the Changjiang River Estuary and adjacent areas in October
参数 盐度分区 温度/℃ aCDOM(355)/m−1 Chl a 浓度/(μg.L−1) S275~295/nm−1 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 表层 0.16~6.43(盐度小于10) 21.1~22.7 22.2 1.49~2.33 1.75 0.52~2.87 1.28 0.015~0.018 0.017 11.0~34.5(盐度大于10) 21.2~24.2 22.8 0.07~2.08 0.65 0.52~5.87 1.85 0.009~0.033 0.016 中层 0.16~0.24(盐度小于10) 22.1~22.6 22.4 1.64~1.84 1.70 0.84~1.30 1.01 0.016~0.018 0.017 23.5~35.5(盐度大于10) 22.4~24.0 23.3 0.04~1.31 0.44 0.29~4.44 1.75 0.011~0.036 0.017 底层 0.16~3.66(盐度小于10) 21.9~22.5 22.3 1.60~2.70 1.82 0.62~1.36 1.08 0.014~0.017 0.017 12.0~34.3(盐度大于10) 21.5~33.6 23.4 0.09~1.33 0.58 0.53~3.39 1.42 0.005~0.020 0.015 表 4 近岸海域的吸收系数值对比
Tab. 4 Comparison of absorption coefficients in coastal waters
海区 采样时间 盐度范围 站位类型 吸收系数(m−1)/波长(nm) 参考文献 南波罗的海 1994年 2.0~8.0 低盐度 (1.2~12)/355 [23] Funka湾 2000年10月至2001年11月 31.6~33.8 高盐度 (0.022~0.14)/440 [24] 阿拉伯海 1994年 36.2~36.9 高盐度 (0.03~0.106)/375 [25] 九龙口 2005年4月 0.11~5.92 低盐度 (2.25~3.32)/355 [16] 10.2~27.08 高盐度 (0.47~1.92)/355 2003年8月 0~5.41 低盐度 (2.3~3.11)/355 [16] 10.14~29.86 高盐度 (0.7~2.26)/355 2005年11月 0.22~9.11 低盐度 (1.54~2.76)/355 [16] 14.4~29.26 高盐度 (0.64~1.41)/355 长江口 2003年8月 0.21~7.89 低盐度 (1.75~2.42)/355 [16] 10~30.91 高盐度 (0.46~1.8)/355 表 5 长江口及邻近海域CDOM的主要荧光组分
Tab. 5 Principle fluorescent component of CDOM in the Changjiang River Estuary and adjacent areas
表 6 3月、7月及10月长江口及邻近海域CDOM各组分荧光强度
Tab. 6 Fluorescent intensity of CDOM component of the Changjiang River Estuary and adjacent areas in March, July and October
季节 荧光组分 表层荧光强度/RU 表层平均荧光强度/RU 中层荧光强度/RU 中层平均荧光强度/RU 底层荧光强度/RU 底层平均荧光强度/RU 3月 C1 0.005 9~0.130 0.036 0.005 3~0.078 0.028 0.008 3~0.130 0.034 C2 0.003 5~0.097 0.024 0.003 3~0.050 0.017 0.005 1~0.085 0.023 C3 0.004 3~0.068 0.027 0.003 6~0.055 0.020 0.005 2~0.060 0.027 C4 0.004 9~0.151 0.036 0.004 3~0.084 0.022 0.006 4~0.094 0.036 7月 C1 0.018 3~0.108 0.037 0.013 0~0.088 0.034 0.010 5~0.101 0.036 C2 0.005 0~0.090 0.046 0.002 7~0.309 0.045 0.004 2~0.346 0.057 C3 0.008 5~0.082 0.036 0.007 0~0.082 0.030 0.006 4~0.087 0.031 C4 0.007 0~0.117 0.047 0.007 0~0.113 0.040 0.005 5~0.126 0.042 10月 C1 0.001 6~0.249 0.033 0.005 0~0.081 0.024 0.008 7~0.229 0.034 C2 0.006 9~0.110 0.027 0.006 4~0.060 0.022 0.006 2~0.113 0.029 C3 0.002 0~0.094 0.031 0.006 8~0.096 0.028 0.001 2~0.092 0.035 C4 0.007 6~0.141 0.042 0.009 1~0.098 0.034 0.007 6~0.109 0.044 -
[1] Bricaud A, Morel A, Prieur L. Absorption by dissolved organic matter of the sea (yellow substance) in the UV and visible domains[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1981, 26(1): 43−53. doi: 10.4319/lo.1981.26.1.0043 [2] Coble P G. Marine optical biogeochemistry: the chemistry of ocean color[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2007, 107(2): 402−418. doi: 10.1021/cr050350+ [3] Guo Weidong, Yang Liyang, Hong Huasheng, et al. Assessing the dynamics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in a subtropical estuary using parallel factor analysis[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2011, 124(1/4): 125−133. [4] Li Baohua, Feng Chenghong, Li Xue, et al. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of PAHs in surficial sediments of the Yangtze Estuary, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2012, 64(3): 636−643. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.12.005 [5] Li Zhanhai, Jia Jianjun, Wu Yongsheng, et al. Correction to: vertical distributions of suspended sediment concentrations in the turbidity maximum zone of the periodically and partially stratified Changjiang estuary[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 2019, 42(7): 1970. doi: 10.1007/s12237-019-00616-z [6] 孙语嫣, 白莹, 苏荣国, 等. 长江口及邻近海域春夏季有色溶解有机物时空分布特征及主要影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(5): 1863−1872.Sun Yuyan, Bai Ying, Su Rongguo, et al. Assessment of the spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and main affecting factors of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in spring and summer at the Changjiang Estuary and adjacent areas[J]. Environment Science, 2017, 38(5): 1863−1872. [7] 徐亚宏, 姚鹏, 苏荣国, 等. 长江口盐度梯度下有色溶解有机物的分布、来源与季节变化[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(6): 21−32.Xu Yahong, Yao Peng, Su Rongguo, et al. Distribution, sources, and seasonal variation of colored dissolved organic matter along salinity gradients in the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(6): 21−32. [8] Zhu Wenzhuo, Zhang Jing, Yang Guipeng. Mixing behavior and photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the Changjiang River estuary and the adjacent East China Sea[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2018, 207: 422−434. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2017.07.019 [9] Guo Weidong, Yang Liyang, Zhai Weidong, et al. Runoff-mediated seasonal oscillation in the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in different branches of a large bifurcated estuary—The Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2014, 119(5): 776−793. doi: 10.1002/2013JG002540 [10] Stedmon C A, Markager S, Kaas H. Optical properties and signatures of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in Danish coastal waters[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2000, 51(2): 267−278. doi: 10.1006/ecss.2000.0645 [11] Twardowski M S, Boss E, Sullivan J M, et al. Modeling the spectral shape of absorption by chromophoric dissolved organic matter[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2004, 89(1/4): 69−88. [12] Ortega-Retuerta E, Reche I, Pulido-Villena E, et al. Distribution and photoreactivity of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the Antarctic Peninsula (Southern Ocean)[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2011, 118(3/4): 129−139. [13] Zepp R G, Sheldon W M, Moran M A. Dissolved organic fluorophores in southeastern US coastal waters: correction method for eliminating Rayleigh and Raman scattering peaks in excitation-emission matrices[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2004, 89(1/4): 15−36. [14] Bahram M, Bro R, Stedmon C, et al. Handling of Rayleigh and Raman scatter for PARAFAC modeling of fluorescence data using interpolation[J]. Journal of Chemometrics, 2006, 20(3/4): 99−105. [15] 马海平. 黄海、东海海域有色溶解有机物(CDOM)的分布特征[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.Ma Haiping. The study on characteristics and distribution of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2014. [16] 韩宇超. 近岸海域溶解有机物的光学性质研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2006.Han Yuchao. The study on optical characteristics of dissolved organic matter in coastal waters[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2006. [17] 邵和宾, 范德江, 张晶, 等. 三峡大坝启用后长江口及邻近海域秋季悬浮体、叶绿素分布特征及影响因素[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2012, 42(5): 94−104.Shao Hebin, Fan Dejiang, Zhang Jing, et al. Distribution and influencing factors of suspended matters and chlorophyll in autumn in Yangtze River Estuary Post-Three Gorges Dam[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2012, 42(5): 94−104. [18] 周正熙, 于仁成, 吕颂辉, 等. 长江口邻近海域春季藻华与水体层化的关系[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(6): 1166−1175. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20160500115Zhou Zhengxi, Yu Rencheng, Lü Songhui, et al. Relationship between harmful algal blooms and water stratification in waters off Changjiang River Estuary[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2016, 47(6): 1166−1175. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20160500115 [19] Del Vecchio R , Blough N V. Photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in natural waters: kinetics and modeling[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2002, 78(4): 231−253. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4203(02)00036-1 [20] Helms J R, Stubbins A, Ritchie J D, et al. Absorption spectral slopes and slope ratios as indicators of molecular weight, source, and photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2008, 53(3): 955−969. doi: 10.4319/lo.2008.53.3.0955 [21] Zhang Yunlin, Van Dijk M A, Liu Mingliang, et al. The contribution of phytoplankton degradation to chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in eutrophic shallow lakes: field and experimental evidence[J]. Water Research, 2009, 43(18): 4685−4697. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.07.024 [22] 朱建荣. 长江口外海区叶绿素a浓度分布及其动力成因分析[J]. 中国科学 D辑:地球科学, 2004, 34(8): 757−762.Zhu Jianrong. Distribution of chlorophyll a concentration and analysis of its dynamics in the offshore waters of the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Science in China Ser D: Earth Sciences, 2004, 34(8): 757−762. [23] Ferrari G M, Dowell M D. CDOM absorption characteristics with relation to fluorescence and salinity in coastal areas of the southern Baltic sea[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1998, 47(1): 91−105. doi: 10.1006/ecss.1997.0309 [24] Sasaki H, Miyamura T, Saitoh S I, et al. Seasonal variation of absorption by particles and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in Funka Bay, southwestern Hokkaido, Japan[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 2005, 64(2): 447−458. doi: 10.1029/92JC02763 [25] Green S A, Blough N V. Optical absorption and fluorescence properties of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in natural waters[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1994, 39(8): 1903−1916. doi: 10.4319/lo.1994.39.8.1903 [26] Stedmon C A, Markager S, Bro R. Tracing dissolved organic matter in aquatic environments using a new approach to fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2003, 82(3/4): 239−254. [27] Coble P G. Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1996, 51(4): 325−346. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(95)00062-3 [28] 白莹. 黄东海春秋季有色溶解有机物(CDOM)的分布特征及季节变化的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.Bai Ying. The study on distribution and seasonal changes of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in spring and autumn in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2014. [29] Stedmon C A, Markager S. Resolving the variability in dissolved organic matter fluorescence in a temperate estuary and its catchment using PARAFAC analysis[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2005, 50(2): 686−697. doi: 10.4319/lo.2005.50.2.0686 [30] Kowalczuk P, Tilstone G H, Zabłocka M, et al. Composition of dissolved organic matter along an Atlantic Meridional Transect from fluorescence spectroscopy and Parallel Factor Analysis[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2013, 157: 170−184. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2013.10.004 [31] Holbrook R D, Yen J H, Grizzard T J. Characterizing natural organic material from the Occoquan Watershed (Northern Virginia, US) using fluorescence spectroscopy and PARAFAC[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 361(1/3): 249−266. [32] Murphy K R, Stedmon C A, Waite T D, et al. Distinguishing between terrestrial and autochthonous organic matter sources in marine environments using fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2008, 108(1/2): 40−58. [33] Guéguen C, Granskog M A, Mccullough G, et al. Characterisation of colored dissolved organic matter in Hudson Bay and Hudson Strait using parallel factor analysis[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2011, 88(3): 423−433. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2010.12.001 [34] 程远月, 郭卫东, 胡明辉. 近岸沉积物再悬浮期间所释放溶解有机物的荧光特征[J]. 地球化学, 2008, 37(1): 51−58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2008.01.007Cheng Yuanyue, Guo Weidong, Hu Minghui. Fluorescence characteristics of dissolved organic matter released from estuarine sediments during resuspension[J]. Geochimica, 2008, 37(1): 51−58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2008.01.007 [35] Su Rongguo, Bai Ying, Zhang Chuansong, et al. The assessment of the spatial and seasonal variability of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the Southern Yellow Sea and the East China Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 100(1): 523−533. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.09.002 [36] Stedmon C A, Markager S. Behaviour of the optical properties of coloured dissolved organic matter under conservative mixing[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2003, 57(5/6): 973−979. [37] 刘材材, 项凌云, 张昊飞, 等. 长江口异养细菌生态分布特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2009, 28(S1): 1−4.Liu Caicai, Xiang Lingyun, Zhang Haofei, et al. Distribution and relationship between heterotrophic bacteria and environmental factors in Changjiang Estuary[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2009, 28(S1): 1−4. [38] 刘晶晶, 杜萍, 曾江宁, 等. 夏季长江口浮游细菌和浮游病毒的分布特征及环境制约因素[J]. 海洋学研究, 2011, 29(3): 118−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2011.03.014Liu Jingjing, Du Ping, Zeng Jiangning, et al. Distribution of bacterioplankton and virioplankton and their relationship with the environmental factors in summer in Changjiang River Estuary and its adjacent East China Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2011, 29(3): 118−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2011.03.014 [39] 郭卫东, 程远月. 天然日光辐照下河口区CDOM的光化学降解[J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(6): 1463−1468. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.06.002Guo Weidong, Cheng Yuanyue. Photodegradation of chromophoric dissolved organic matter from Jiulong River Estuary under natural solar radiation[J]. Environmental Science, 2008, 29(6): 1463−1468. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.06.002 [40] 朱伟健, 沈芳, 洪官林. 长江口及邻近海域有色溶解有机物(CDOM)的光学特性[J]. 环境科学, 2010, 31(10): 2292−2298.Zhu Weijian, Shen Fang, Hong Guanlin. Optical characteristics of colored dissolved organic material (CDOM) in Yangtze Estuary[J]. Environmental Science, 2010, 31(10): 2292−2298. -





 下载:
下载: