Biodiversity and functional enzymes of actinomycetes isolated from mangrove soil in the Maowei Sea, Guangxi
-
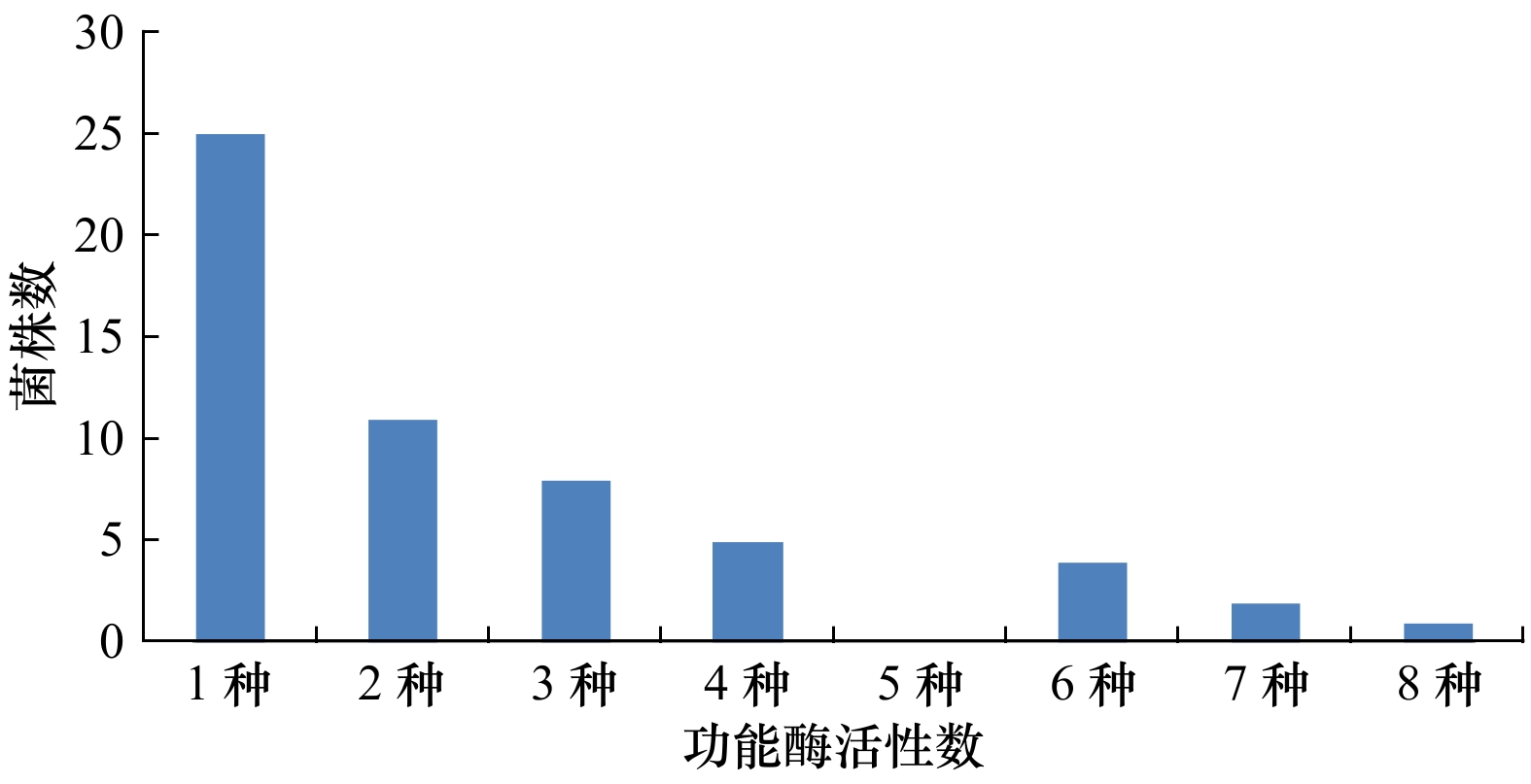
摘要: 研究广西茅尾海红树林自然保护区内红树林土壤中可培养放线菌的多样性,挖掘具有高产多种功能酶活性的放线菌类群。应用可培养技术和基于16S rRNA基因序列的系统发育分析研究红树林土壤中可培养放线菌的多样性;并以10种酶活底物为指示物,结合点植法和透明圈法对可培养的放线菌进行功能酶活性筛选。结果显示,从红树林土壤中共分离到444株放线菌,隶属于6目13科24属63种,其中3株放线菌为潜在新种。从63株不同种的放线菌中筛选出56株放线菌在至少1种功能酶活性检测中显示阳性,总阳性率为88.89%;其中具有2种以上功能酶活性的放线菌31株,链霉菌属、微杆菌属和短小杆菌属的产酶菌株最为丰富。综上所述,广西茅尾海红树林自然保护区内红树林土壤中可培养放线菌的种类丰富多样,潜藏着放线菌新资源,且功能酶活性显著,具有较大的挖掘潜力。Abstract: The purpose of this study was to investigate the diversity of actinomycetes collected from the Maowei Sea Natural Reserve of Mangrove in Guangxi, and screen the functional enzymes activities from these actinomycetes. Actinobacterial diversity of Mangrove soil was studied by culturable method and phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. Ten enzyme active substrates were selected as indicator reaction. Activity for functional enzymes was tested by inoculating single colony method. Total of 444 strains of culturable actinomycetes were obtained from mangrove soil environment, they were classified into 63 species, 24 genera, 13 families and 6 orders by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. The three strains of them was potential new species. Streptomyces sp. was the dominant genus. Among them, 56 strains were screened with at least one or more enzymes activity. The total positive rate was 88.89%. And two enzymes activity at least could be screened from the 31 strains. And the dominant strains capable of enzyme-producing were of Streptomyces sp., Microbacterium sp. and Curtobacterium sp. Our results showed that in the Maowei Sea Natural Reserve of Mangrove soil, there existed a higher diversity of culturable actinomycetes, and there are large numbers of unknown actionobacterial groups here. These actinomycetes have the abilities to produce excellent functional enzymes.
-
Key words:
- Guangxi; mangrove in the Maowei Sea /
- soil /
- actinomycetes /
- functional enzymes
-
表 1 分离培养基配方
Tab. 1 Recipe of media for actinomycetes isolation
培养基 主要成分 其他成分 AGG 可溶性淀粉10.0 g,葡萄糖1.0 g,甘油10 mL 复合盐母液10 mL琼脂14.0 g,去离子水1 000 mL,pH7.2~7.4 M7 酵母提取粉5.0 g,L-天冬酰胺1.0 g,甘油10 mL 复合盐母液10 mL琼脂14.0 g,去离子水1 000 mL,pH7.2~7.4 P7 L-酪氨酸0.5 g,L-天门冬酰胺1.0 g,甘油10 mL 复合盐母液10 mL琼脂14.0 g,去离子水1 000 mL,pH7.2~7.4 M10 可溶性淀粉1.0 g,水解酪素0.5 g 复合盐母液10 mL琼脂14.0 g,去离子水1 000 mL,pH7.2~7.4 M4 L-天门冬酰胺1.0 g,海藻糖5.0 g,甘油6 mL 复合盐母液10 mL琼脂14.0 g,去离子水1 000 mL,pH7.2~7.4 M5 海藻糖5.0 g,脯氨酸1.0 g,土壤浸出液20 mL 复合盐母液10 mL琼脂14.0 g,去离子水1 000 mL,pH7.2~7.4 M9 精氨酸1.0 g,甘油6 mL 复合盐母液10 mL琼脂14.0 g,去离子水1 000 mL,pH7.2~7.4 P3 燕麦粉20.0 g 复合盐母液10 mL琼脂14.0 g,去离子水1 000 mL,pH7.2~7.4 注:复合盐母液按如下成分比例配制:KNO3 1.0 g,NaCl 2.5 g,MgSO4·7H2O 0.5 g,K2HPO4 0.5 g,NH4NO3 0.1 g,FeSO4 0.01 g,MnCl2·H2O 0.001 g,ZnSO4·7H2O 0.001 g,去离子水10 mL。 表 2 红树林土壤放线菌的分布
Tab. 2 Distribution of actinomycetes from mangrove soil
目 科 属 株数 种数 动饱菌目 动孢菌科 动球菌属Kineococcus 7 1 四折叠球菌属Quadrisphaera 1 1 微球菌目 间孢囊菌科 两面神菌属Janibacter 2 1 皮杆菌科 短状杆菌属Brachybacterium 19 2 短杆菌科 短杆菌属Brevibacterium 3 1 原小单孢菌科 纤维微菌属Cellulosimicrobium 5 1 纤维单孢菌科 去甲基醌菌属Demequina 14 1 微杆菌科 短小杆菌属Curtobacterium 167 5 壤霉菌属Agromyces 20 1 微杆菌属Microbacterium 37 8 微球菌科 考克氏菌属Kocuria 1 1 微球菌属Micrococcus 18 1 节杆菌属Paenarthrobacter 1 1 假节杆菌属Pseudarthrobacter 4 1 小单孢菌目 小单孢菌科 科氏游动菌属Couchioplanes 1 1 小单孢菌属Micromonospora 9 3 植物产孢放线菌属Plantactinospora 1 1 分枝杆菌目 诺卡氏菌科 戈登氏菌属Gordonia 25 5 红球菌属Rhodococcus 21 2 分枝杆菌科 分枝杆菌属Mycobacterium 6 2 Mycolicibacterium 24 6 丙酸杆菌目 类诺卡氏菌科 大理石雕菌属Marmoricola 4 1 类诺卡氏菌属Nocardioides 36 2 链霉菌目 链霉菌科 链霉菌属Streptomyces 18 14 表 3 不同培养基分离到的细菌多样性
Tab. 3 Bacterial diversity isolated from different media
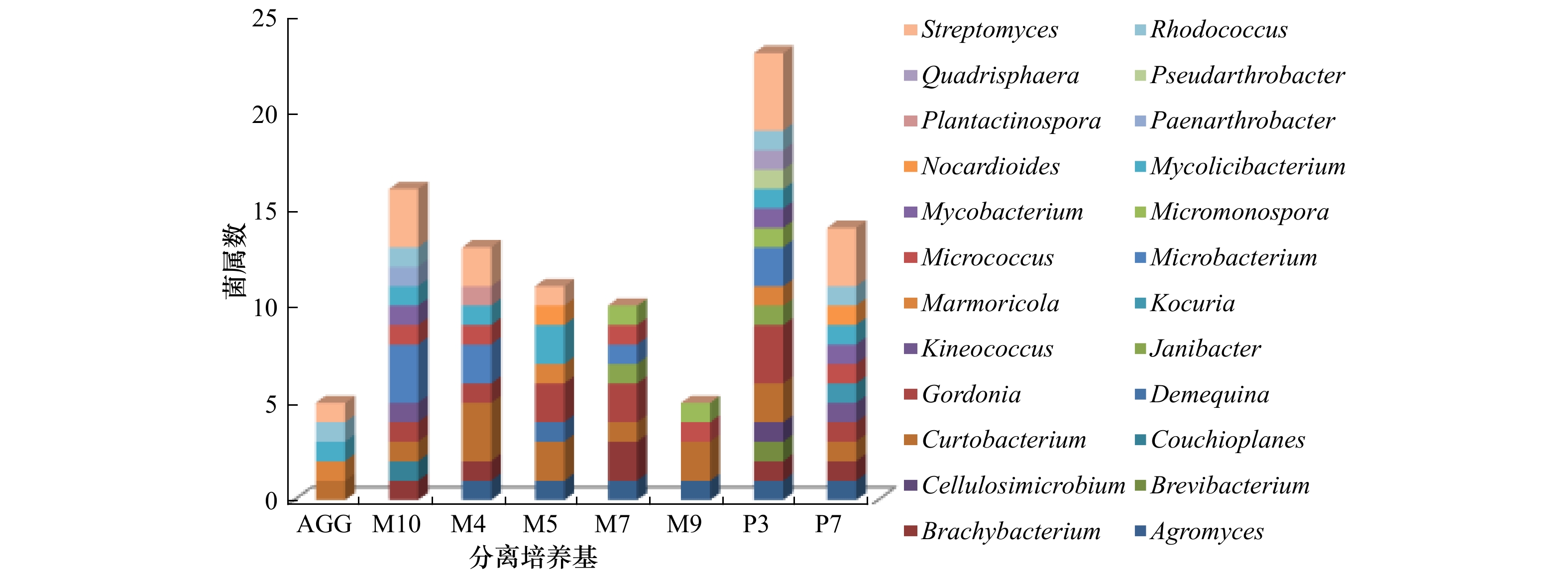
细菌多样性 培养基 AGG M10 M4 M5 M7 M9 P3 P7 菌株数 34 73 53 108 27 24 72 53 菌种数 5 16 13 11 10 5 24 14 菌属数 5 12 9 8 8 4 16 12 Shannon-Wiener指数 1.213 2.202 2.068 1.693 2.262 1.457 2.776 2.107 Simpon指数 0.647 0.849 0.817 0.769 0.832 0.733 0.910 0.804 Pielou指数 0.344 0.513 0.521 0.362 0.686 0.459 0.649 0.531 表 4 56株放线菌的功能酶活性
Tab. 4 Enzyme-producing activities of 56 actinomycetes
放线菌类群 产酶菌数 脲酶 酯酶 过氧化氢酶 纤维素酶 蛋白酶 氧化酶 淀粉酶 几丁质酶 褐藻胶裂解酶 酶活菌株数 吐温20 吐温80 2种酯酶 Agromyces − − − − 1 − 1 − − − − 1 Brachybacterium 2 − − − − − − − − − − 2 Brevibacterium 1 − − − 1 − − − − − − 1 Cellulosimicrobium − 1 − 1 1 − − − − − − 1 Couchioplanes − − − − − 1 − − − − − 1 Curtobacterium 1 4 1 4 4 3 5 − 2 1 1 5 Demequina − 1 1 1 1 − 1 1 − − 1 1 Gordonia − − − 1 3 − − − − − − 3 Janibacter − − − − 1 1 1 − − − 1 1 Kineococcus − − − − 1 − − − − − − 1 Kocuria − − − − 1 − − − − − − 1 Marmoricola − 1 − 1 1 − 1 − − 1 − 1 Microbacterium − 3 2 3 4 2 2 1 1 − 1 5 Micrococcus 1 − − − − − − − − − − 1 Micromonospora − − − − 2 2 1 − − − − 3 Mycobacterium − 1 1 2 1 − − − − − − 2 Mycolicibacterium − − 1 1 4 1 − − − − − 6 Nocardioides − 1 − 1 − 1 − − − − − 2 Paenarthrobacter 1 − − − 1 − 1 − − − − 1 Plantactinospora 1 1 1 1 1 1 − − − 1 − 1 Pseudarthrobacter 1 − − − − − − − − − − 1 Quadrisphaera − − − − − − 1 − − − − 1 Rhodococcus 1 − − − 2 − − − − − − 2 Streptomyces 3 5 6 9 6 5 10 − 1 2 1 13 注:−表示无功能酶活性。 -
[1] 黎高翔. 中国酶工程的兴旺与崛起[J]. 生物工程学报, 2015, 31(6): 805−819.Li Gaoxiang. The rise of enzyme engineering in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2015, 31(6): 805−819. [2] 殷亮, 杨文竹, 王新宇, 等. 黑曲霉Aspergillus niger 963植酸酶基因phyA2 N-糖基化突变体的构建与表达分析[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2010, 30(6): 54−59.Yin Liang, Yang Wenzhu, Wang Xinyu, et al. Construction and expression analyse of N-linked glycosylation site mutants of phyA2 gene from Aspergillus niger 963[J]. China Biotechnology, 2010, 30(6): 54−59. [3] 史悦, 于慧敏, 罗晖, 等. 诺卡氏菌腈水合酶突变基因在重组大肠杆菌中的高活性表达[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 47(12): 2176−2179. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0054.2007.12.022Shi Yue, Yu Huimin, Luo Hui, et al. High level expression of a mutated nitrile hydratase gene of Nocardia sp. in recombinant Escherichia coli[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2007, 47(12): 2176−2179. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0054.2007.12.022 [4] 王淑军, 陆兆新, 吕明生, 等. 一株深海热液口超嗜热古菌的分类鉴定及高温酶活性研究[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2009, 32(2): 130−136.Wang Shujun, Lu Zhaoxin, Lü Mingsheng, et al. Identification and hyperthermophilic enzyme activities of a hyperthermophilic archaeon isolated from deep-sea hydrothermal vent[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2009, 32(2): 130−136. [5] 何勇, 王艳. 一种酸性β−甘露聚糖酶作用特性的分析研究[J]. 饲料工业, 2010, 31(8): 16−18.He Yong, Wang Yan. Research on the functional characteristics of acidic β-mannanase[J]. Feed Inductry, 2010, 31(8): 16−18. [6] Duke N C. Mangrove floristics and biogeography revisited: further deductions from biodiversity hot spots, ancestral discontinuities, and common evolutionary processes[M]//Rivera-Monroy V, Lee S, Kristensen E, et al. Mangrove Ecosystems: A Global Biogeographic Perspective: Structure, Function and Services. Cham: Springer, 2017: 17−53. [7] Sangkanu S, Rukachaisirikul V, Suriyachadkun C, et al. Evaluation of antibacterial potential of mangrove sediment-derived actinomycetes[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis, 2017, 112: 303−312. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.10.010 [8] 胡亚强. 红树林区团水虱肠道微生物多样性及可培养微生物抑菌活性研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2016.Hu Yaqiang. Analysis of intestinal microbial diversity Sphaeroma and bacteriostatic activity of culturable microorganism[D]. Haikou: Hainan University, 2016. [9] Ek-Ramos M J, Gomez-Flores R, Orozco-Flores A A, et al. Bioactive products from plant-endophytic gram-positive bacteria[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10(2): 463. [10] Zhao Huaxian, Yan Bing, Mo Xueyan, et al. Prevalence and proliferation of antibiotic resistance genes in the subtropical mangrove wetland ecosystem of South China Sea[J]. MicrobiologyOpen, 2019, 87(1): 1−14. [11] 李菲, 高程海, 竺利波, 等. 茅尾海无瓣海桑内生细菌多样性及其细胞毒活性[J]. 微生物学报, 2016, 56(4): 689−697.Li Fei, Gao Chenghai, Zhu Libo, et al. Diversity and cytotoxic activity of endophytic bacteria isolated from Sonneratia apetala of Maowei Sea[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2016, 56(4): 689−697. [12] 李蜜, 候师师, 银江林, 等. 北部湾徐闻海域红树内生细菌物种多样性及其杀线虫活性研究[J]. 广西植物, 2020, 40(3): 301−310. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201905006Li Mi, Hou Shishi, Yin Jianglin, et al. Diversity and nematicidal activity of endophytic bacteria from mangrove plants collected from Beibu Gulf coast at Xuwen[J]. Guihaia, 2020, 40(3): 301−310. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201905006 [13] Bhatnagar D, Imelda J, Paulraj R. Amylase and acid protease production by solid state fermentation using Aspergillus niger from mangrove swamp[J]. Indian Journal of Fisheries, 2010, 57(1): 45−51. [14] Chen W C, Tseng W N, Hsieh J L, et al. Biodegradation and microbial community changes upon shrimp shell wastes amended in mangrove river sediment[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part. B, Pesticides, Food Contaminants, and Agricultural Wastes, 2010, 45(5): 473−477. [15] Gao Zhaoming, Ruan Lingwei, Chen Xiulan, et al. A novel salt-tolerant endo-β-1,4-glucanase Cel5A in Vibrio sp. G21 isolated from mangrove soil[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 87(4): 1373−1382. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2554-y [16] Kafilzadeh F, Dehdari F. Amylase activity of aquatic actinomycetes isolated from the sediments of mangrove forests in south of Iran[J]. The Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 2015, 41(2): 197−201. doi: 10.1016/j.ejar.2015.04.003 [17] 李菲, 高程海, 余炼, 等. 秋茄内生细菌多样性及抑制甘蔗黑穗霉菌活性研究[J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 2017, 42(4): 318−327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8689.2017.04.010Li Fei, Gao Chenghai, Yu Lian, et al. Diversity of endophytic bacteria isolated from Kandelia candel and its in-vitro activity against Ustilago scitaminea Sydow[J]. Chinese Journal of Antibiotics, 2017, 42(4): 318−327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8689.2017.04.010 [18] 宋朝霞, 范玲, 李鹏, 等. 一株纤维素酶高产细菌的筛选及鉴定[J]. 河南工程学院学报(自然科学版), 2018, 30(4): 76−81.Song Zhaoxia, Fan Ling, Li Peng, et al. Screening and identification of a cellulase-producing strain[J]. Journal of Henan University of Engineering (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 30(4): 76−81. [19] 赵雅慧, 张舒琳, 吴家法, 等. 山口红树林根际土壤可培养细菌多样性及其活性筛选[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(8): 138−151.Zhao Yahui, Zhang Shulin, Wu Jiafa, et al. Screening the diversity and activity of culturable bacteria isolated from mangrove rhizosphere soil at Shankou[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(8): 138−151. [20] Roberts W K, Selitrennikoff C P. Plant and bacterial chitinases differ in antifungal activity[J]. Journal of General Microbiology, 1988, 134(1): 169−176. [21] 李恒, 朱思婷, 刘旭梅, 等. 褐藻胶裂解酶产生菌的分离鉴定及产酶发酵优化[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2014, 34(9): 94−101.Li Heng, Zhu Siting, Liu Xumei, et al. Identification of an alginate lyase producing strain Halomonas sp. WF6 and fermentation optimization[J]. China Biotechnology, 2014, 34(9): 94−101. [22] 周双清, 黄小龙, 黄东益, 等. Chelex-100 快速提取放线菌DNA作为PCR扩增模板[J]. 生物技术通报, 2010, 26(2): 123−125.Zhou Shuangqing, Huang Xiaolong, Huang Dongyi, et al. A rapid method for extracting DNA from actinomycetes by Chelex-100[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2010, 26(2): 123−125. [23] Walsh P S, Metzger D A, Higuchi R. Chelex 100 as a medium for simple extraction of DNA for PCR-based typing from forensic material[J]. Biotechniques, 1991, 10(4): 506−513. [24] 李菲, 高程海, 余炼, 等. 川蔓藻内生及根际细菌多样性与抑菌活性研究[J]. 广西植物, 2018, 38(7): 924−933. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201709013Li Fei, Gao Chenghai, Yu Lian, et al. Diversity and antifungal activity of endophytic and rhizospheric bacteria isolated from Ruppia maritima[J]. Guihaia, 2018, 38(7): 924−933. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201709013 [25] Kim K H, Roh S W, Chang H W, et al. Nocardioides basaltis sp. nov., isolated from black beach sand[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2009, 59: 42−47. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.65785-0 [26] Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, et al. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2011, 28(10): 2731−2739. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr121 [27] Kim M, Oh H S, Park S C, et al. Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2014, 64: 346−351. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.059774-0 [28] Subramani R, Aalbersberg W. Marine actinomycetes: an ongoing source of novel bioactive metabolites[J]. Microbiological Research, 2012, 167(10): 571−580. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2012.06.005 [29] Kulkarni C P, Maurya C B. Characterization of the cellulase enzyme produced by actinomycetes isolated from the mangrove Coastal areas[J]. Biosciences Biotechnology Research Asia, 2017, 14(2): 685−690. doi: 10.13005/bbra/2495 [30] Kiranmayi M U, Poda S, Vijayalakshmi M. Production and optimization of L-asparaginase by an actinobacterium isolated from Nizampatnam mangrove ecosystem[J]. Journal of Environmental Biology, 2014, 35(5): 799−805. [31] 何洁, 张道锋, 徐盈, 等. 印度洋红树林沉积物可培养海洋放线菌多样性及其活性[J]. 微生物学报, 2012, 52(10): 1195−1202.He Jie, Zhang Daofeng, Xu Ying, et al. Diversity and bioactivities of culturable marine actinobacteria isolated from mangrove sediment in Indian Ocean[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2012, 52(10): 1195−1202. [32] Lee L H, Zaina N, Azman A S, et al. Diversity and antimicrobial activities of actinobacteria isolated from tropical mangrove sediments in Malaysia[J]. The Scientific World Journal, 2014, 2014: 698178. [33] 林鹏, 张瑜斌, 邓爱英, 等. 九龙江口红树林土壤微生物的类群及抗菌活性[J]. 海洋学报, 2005, 27(3): 133−141.Lin Peng, Zhang Yubin, Deng Aiying, et al. Microflora and antimicrobial activities of soil microorganisms in mangrove forests in the Jiulong Estuary, China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2005, 27(3): 133−141. [34] Dias A C F, Dini Andreote F, Dini-Andreote F, et al. Diversity and biotechnological potential of culturable bacteria from Brazilian mangrove sediment[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2009, 25(7): 1305−1311. doi: 10.1007/s11274-009-0013-7 [35] 孙静, 王素英, 张德超, 等. 海南红树林根系土壤中可培养细菌的多样性分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2014, 38(7): 27−33. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130608001Sun Jing, Wang Suying, Zhang Dechao. Diversity of culturable bacteria from the soil of root system of mangrove forest of Beigang island in Hainan Province[J]. Marine Sciences, 2014, 38(7): 27−33. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130608001 [36] 冯玲玲, 杨芹, 张露, 等. 海南三亚红树林放线菌多样性及抗菌活性[J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 2018, 43(11): 1355−1363. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8689.2018.11.006Feng Lingling, Yang Qin, Zhang Lu, et al. Diversity and anti-microbial activity of actinobacteria isolated from mangrove in Sanya of Hainan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Antibiotics, 2018, 43(11): 1355−1363. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8689.2018.11.006 [37] 张瑶, 夏占峰, 曹鑫波, 等. 阿克苏高盐咸水滩放线菌分离新策略及系统发育多样性[J]. 微生物学报, 2013, 53(8): 798−808.Zhang Yao, Xia Zhanfeng, Cao Xinbo, et al. New isolation methods and phylogenetic diversity of Actinobacteria from hypersaline beach in Aksu[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2013, 53(8): 798−808. [38] 关统伟, 向慧平, 冯栩, 等. 硝尔库勒湖可培养放线菌多样性及其功能酶和抗细菌活性[J]. 微生物学报, 2018, 58(10): 1864−1874.Guan Tongwei, Xiang Huiping, Feng Xu, et al. Diversity and antibacterial activity of culturable actinobacteria from Xiaoerkule Lake[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2018, 58(10): 1864−1874. [39] Niladevi K N, Prema P. Mangrove actinomycetes as the source of ligninolytic enzymes[J]. Actinomycetologica, 2005, 19(2): 40−47. doi: 10.3209/saj.19.40 [40] 孟昊, 薛智权, 唐杰, 等. 深圳福田红树林土壤可培养微生物和土壤酶活性研究[J]. 广东农业科学, 2013, 40(1): 53−56.Meng Hao, Xue Zhiquan, Tang Jie, et al. Soil culturable microorganisms and the activity of enzymes in mangrove sediment from Futian, Shenzhen[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 40(1): 53−56. -





 下载:
下载: