Relationship between dinoflagellate cysts and water eutrophication and ENSO index in the Changjiang River Estuary
-
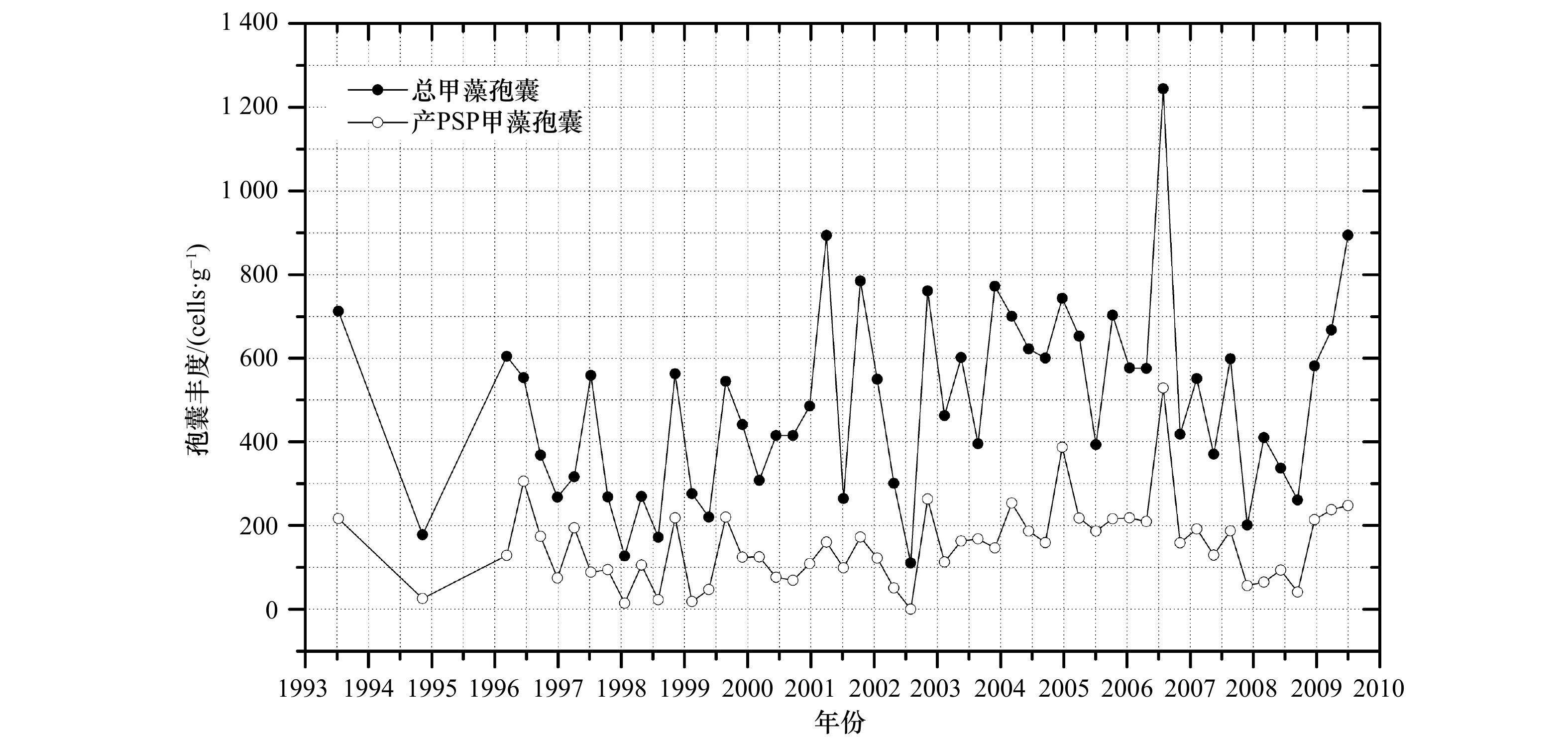
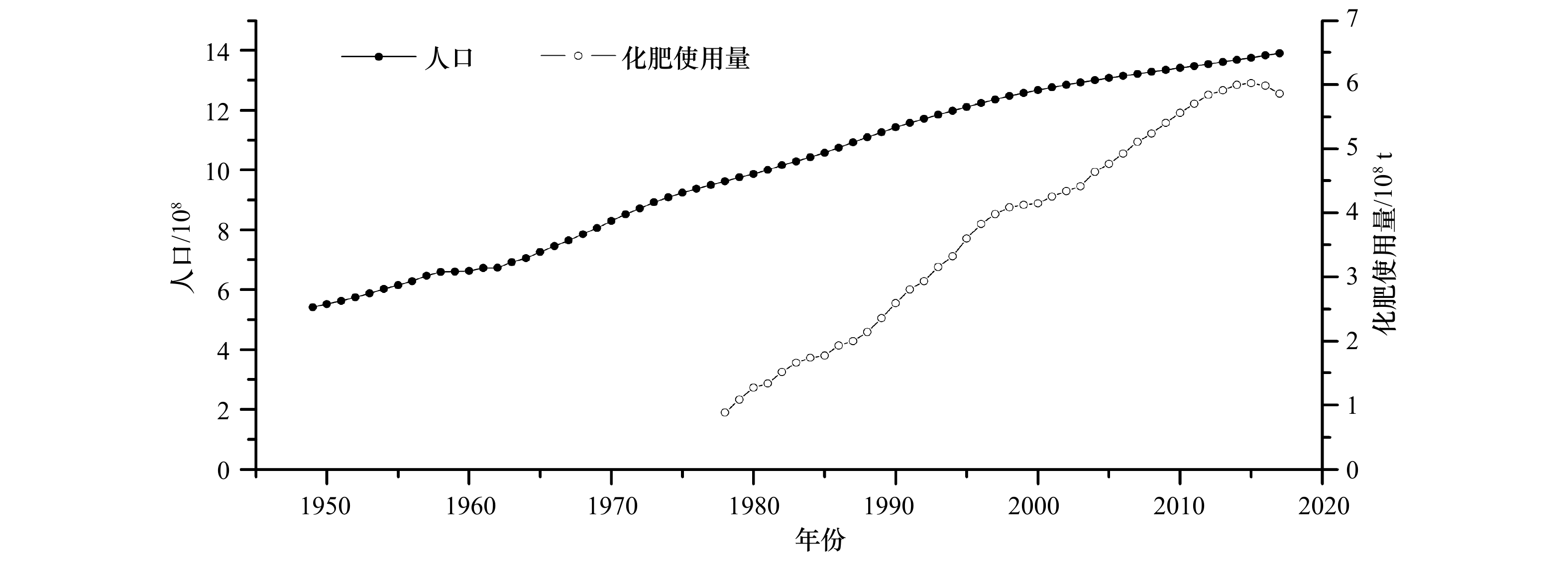
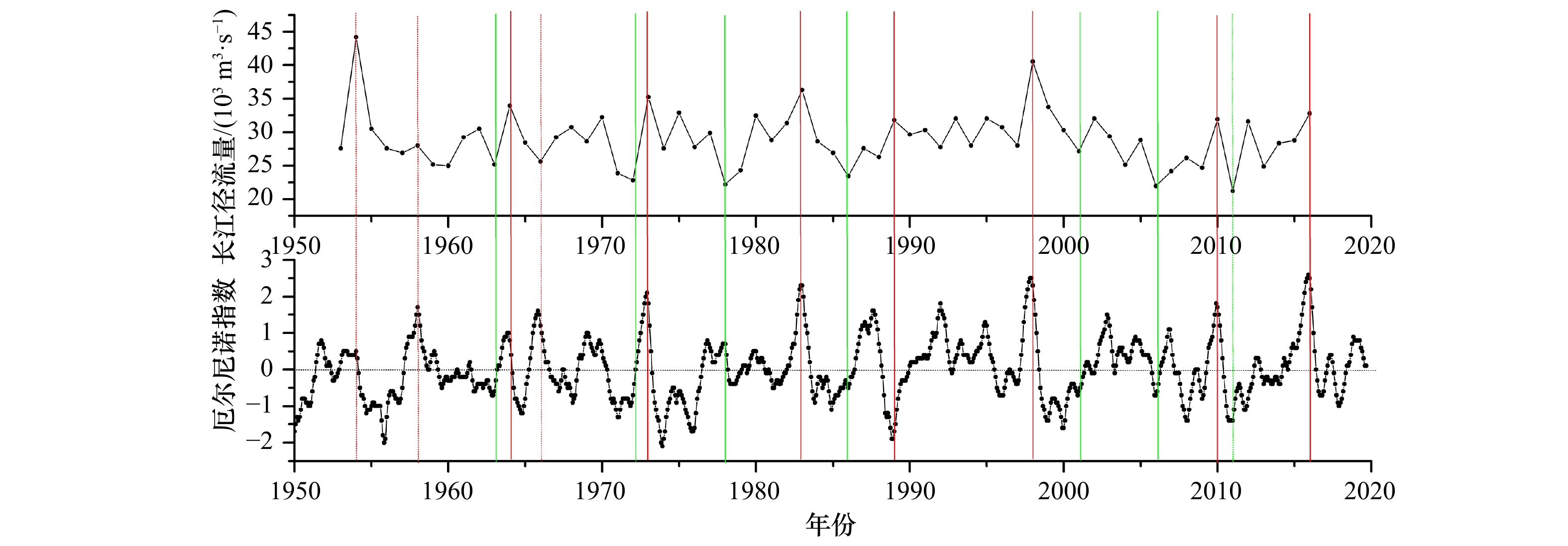
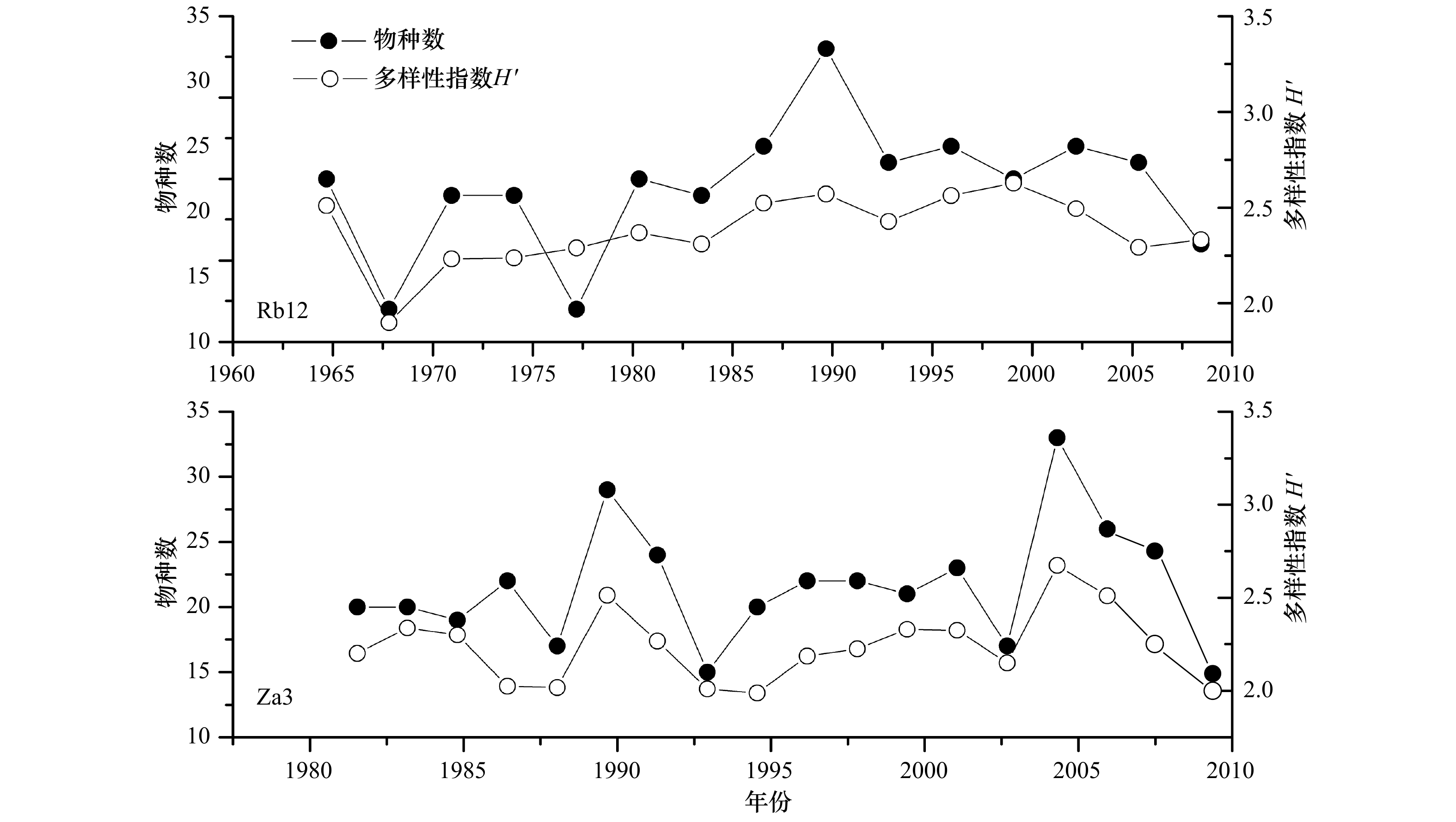
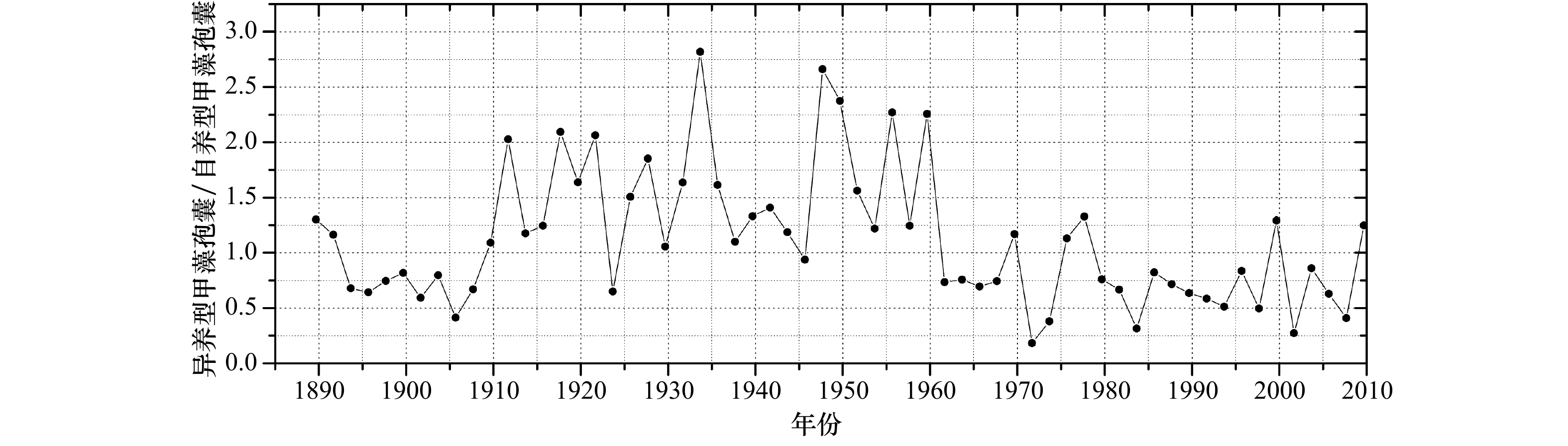
摘要: 甲藻孢囊是一种可用于追溯环境变化历史的生物微化石,如指示水体富营养化和气候变化,但是如何指示水体富营养化存在争议,并且如何区分甲藻孢囊中的水体富营养化信号和气候变化信号也是一个科学难题。为了研究这两个科学问题,我们利用长江口海域受到水体富营养化和厄尔尼诺事件双重影响的特点,在该海域不同位置采集了4根沉积柱,分析了其中的甲藻孢囊。结果显示,长江口海域水体富营养化会引起总甲藻孢囊以及产麻痹性贝毒甲藻孢囊丰度上升,并且导致异养型和自养型甲藻孢囊的比率下降,这说明引起长江口海域富营养化主要原因还是以氮、磷、钾为主导的农业和生活污水。受长江冲淡水流影响,这种富营养化信号在近处相对较弱;中间处信号明显;远处信号几乎未见。同时入海口近处高沉积速率沉积柱样的分析结果显示,甲藻孢囊丰度存在季节性的变化规律,其中以冬季甲藻孢囊丰度最低,推测低温起了主导作用。而厄尔尼诺气候事件可以通过影响陆地径流从而改变陆源营养盐的输入来改变甲藻孢囊丰度,反映在沉积柱中的信息即为甲藻孢囊丰度峰谷值的出现。该信号也随距离入海口的远近不同而不同:近处受水流突然增大或减弱导致甲藻孢囊丰度谷值和峰值出现;中间处水流与甲藻孢囊丰度峰谷值重叠且信号较强;远处丰度峰值信号明显但主导因素多样化。这些结果对该海域环境演变历史重建,赤潮发生历史和厄尔尼诺现象研究都具有十分重要的科学意义。Abstract: Dinoflagellate cysts, as micro-fossil, could be used to trace environmental change history, such as water eutrophication and climate change. But there is controversy on how to indicate water eutrophication, and also it is a problem how to differ the signals between water eutrophication and climate change in dinoflagellate cysts. In order to address these problems, we collected four sediment cores in the Changjiang River Estuary and analyzed their dinoflagellate cysts. Results showed that eutrophication could lead to the increase of total dinoflagellate cysts and Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP) productive dinoflagellate cysts abundance. And the ratio of hetero/autotrophic dinoflagellate cysts decreased, which implied that the eutrophication mainly resulted from agriculture and domestic sewage in the Changjiang River Estuary. Because of water plume, the eutrophication signal was relatively weak near estuary, strong in middle distance and almost none in far distance. Seasonal change of dinoflagellate cysts was observed in the high sediment sinking area in the estuary, with the lowest production in winter as a result of low temperature. ENSO events will lead to the peak and valley value of dinoflagellate cysts abundance by affecting nutrient input which is transferred by river downloading. Moreover, the signal also varied with the distance: valley and peak value of dinoflagellate cysts present because of strong and weak river runoff pulse near estuary, peak and valley value of dinoflagellate cysts and runoff overlapped and were clear in middle distance, and peak value of dinoflagellate cysts was obvious in far distance but the domain reason was complex. These findings are of great significance to environment history reconstruction, study of red tide history and ENSO events.
-
Key words:
- dinoflagellate cyst /
- eutrophication /
- ENSO /
- climate change
-
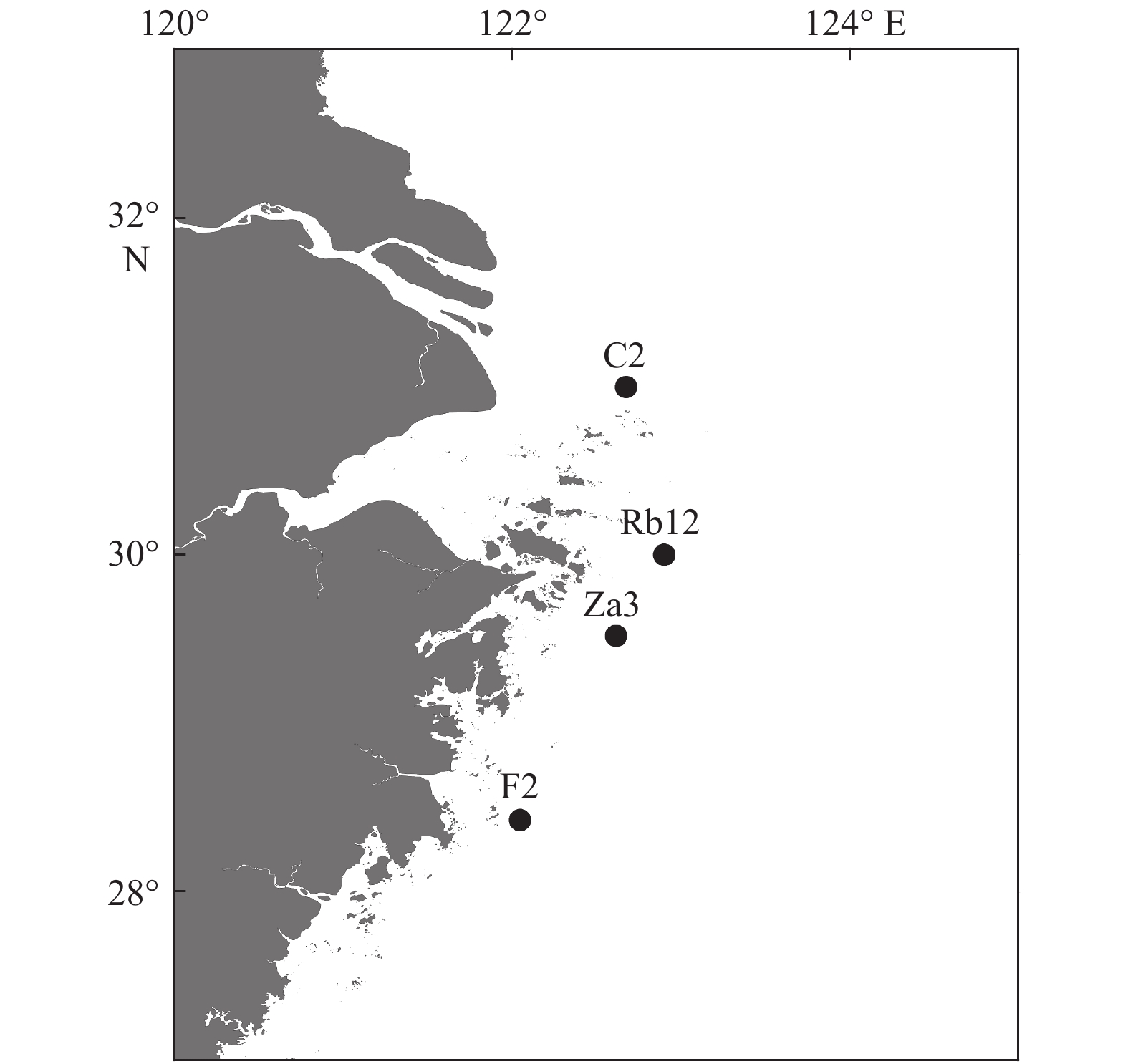
表 1 沉积柱站位信息
Tab. 1 Station information of sediment cores
站位 经纬度 水深/m 采样日期 柱子长度/cm C2 30.998°N,122.672°E 21 2009年6月5日 200 Rb12 30.000°N,122.898°E 52 2010年5月10日 30 Za3 29.520°N,122.614°E 43 2010年5月11日 36 F2 28.428°N,122.044°E 26 2009年8月 200 -
[1] 周名江, 颜天, 邹景忠. 长江口邻近海域赤潮发生区基本特征初探[J]. 应用生态学报, 2003, 14(7): 1031−1038. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2003.07.001Zhou Mingjiang, Yan Tian, Zou Jingzhong. Preliminary analysis of the characteristics of red tide areas in Changjiang River Estuary and its adjacent sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2003, 14(7): 1031−1038. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2003.07.001 [2] 苏纪兰. 中国的赤潮研究[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2001, 16(5): 339−342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3045.2001.05.006Su Jilan. Harmful algal bloom and its research in China[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2001, 16(5): 339−342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3045.2001.05.006 [3] 周名江, 朱明远, 张经. 中国赤潮的发生趋势和研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2001, 13(2): 54−59, 53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0374.2001.02.002Zhou Mingjiang, Zhu Mingyuan, Zhang Jing. Status of harmful algal blooms and related research activities in China[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2001, 13(2): 54−59, 53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0374.2001.02.002 [4] Lu Douding, Goebel J, Qi Yuzao, et al. Morphological and genetic study of Prorocentrum donghaiense Lu from the East China Sea, and comparison with some related Prorocentrum species[J]. Harmful Algae, 2005, 4(3): 493−505. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2004.08.015 [5] Wang Hongxia, Lu Douding, Huang Haiyan, et al. First observation of Karlodinium veneficum from the East China Sea and the coastal waters of Germany[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2011, 30(6): 112−121. doi: 10.1007/s13131-011-0168-6 [6] 黄海燕, 陆斗定. 甲藻孢囊研究进展[J]. 海洋学研究, 2009, 27(3): 85−92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2009.03.012Huang Haiyan, Lu Douding. Recent progress in the study of dinoflagellate cyst[J]. Journal of Marine Science, 2009, 27(3): 85−92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2009.03.012 [7] Dale B. The sedimentary record of dinoflagellate cysts: looking back into the future of phytoplankton blooms[J]. Scientia Marina, 2001, 65(S2): 257−272. doi: 10.3989/scimar.2001.65s2257 [8] Dale B. Eutrophication signals in the sedimentary record of dinoflagellate cysts in coastal waters[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 2009, 61(1/2): 103−113. [9] Pospelova V, Esenkulova S, Johannessen S C, et al. Organic-walled dinoflagellate cyst production, composition and flux from 1996 to 1998 in the central Strait of Georgia (BC, Canada): a sediment trap study[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2010, 75(1/4): 17−37. [10] Rouis-Zargouni I, Turon J L, Londeix L, et al. Environmental and climatic changes in the central Mediterranean Sea (Siculo–Tunisian Strait) during the last 30 ka based on dinoflagellate cyst and planktonic foraminifera assemblages[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010, 285(1/2): 17−29. [11] Matsuoka K, Joyce L B, Kotani Y, et al. Modern dinoflagellate cysts in hypertrophic coastal waters of Tokyo Bay, Japan[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2003, 25(12): 1461−1470. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbg111 [12] Sluijs A, Pross J, Brinkhuis H. From greenhouse to icehouse; organic-walled dinoflagellate cysts as paleoenvironmental indicators in the Paleogene[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2005, 68(3/4): 281−315. [13] Dale B, Fjellså A. Dinoflagellate cysts as paleoproductivity indicators: state of the art, potential and limits[M]//Zahn R, Pedersen T F, Kaminski M A, et al. Carbon Cycling in the Glacial Ocean: Constraints on the Ocean's Role in Global Change. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1994. [14] Matsuoka K. Eutrophication process recorded in dinoflagellate cyst assemblages—a case of Yokohama Port, Tokyo Bay, Japan[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 1999, 231(1): 17−35. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00087-X [15] 王朝晖, Matsuoka K, 齐雨藻, 等. 柘林湾近代沉积物中甲藻孢囊的垂直分布[J]. 海洋通报, 2004, 23(3): 46−53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2004.03.007Wang Zhaohui, Matsuoka K, Qi Yuzao, et al. Vertical distribution of dinoflagellate resting cysts in recent sediments from Zhelin Bay, the South China Sea[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2004, 23(3): 46−53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2004.03.007 [16] 王朝晖, Matsuoka K, 齐雨藻, 等. 深圳湾表层沉积物中甲藻孢囊的垂直分布[J]. 生态学报, 2003, 23(10): 2073−2081. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.10.016Wang Zhaohui, Matsuoka K, Qi Yuzao, et al. Vertical distribution of dinoflagellate resting cysts in surface sediments from Shenzhen Bay of the South China Sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2003, 23(10): 2073−2081. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.10.016 [17] Wang Zhaohui, Qi Yuzao, Jiang Tianjiu, et al. Vertical distribution of dinoflagellate resting cysts in recent sediments from Daya Bay, the South China Sea[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2004, 28(5): 504−510. [18] 付永虎, 王朝晖, 康伟, 等. 长江口及其邻近海域近代沉积物中甲藻孢囊的垂直分布[J]. 暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版), 2009, 30(1): 106−110.Fu Yonghu, Wang Zhaohui, Kang Wei, et al. Vertical distribution of dinoflagellate resting cysts in recent sediments from the Changjiang River Estuary and adjacent waters[J]. Journal of Jinan University (Natural Science & Medicine Edition), 2009, 30(1): 106−110. [19] Dale B. Marine dinoflagellate cysts as indicators of eutrophication and industrial pollution: a discussion[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2001, 264(3): 235−240. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00719-1 [20] Dai Xinfeng, Lu Douding, Xia Ping, et al. A 50-year temporal record of dinoflagellate cysts in sediments from the Changjiang estuary, East China Sea, in relation to climate and catchment changes[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2012, 112: 192−197. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2012.07.016 [21] Thorsen T A, Dale B. Dinoflagellate cysts as indicators of pollution and past climate in a Norwegian fjord[J]. The Holocene, 1997, 7(4): 433−446. doi: 10.1177/095968369700700406 [22] Matsuoka K, Fukuyo Y. Technical Guide for Modern Dinoflagellate Cyst Study[M]. Tokyo: Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, 2000: 6−7. [23] 王朝晖. 中国沿海甲藻孢囊与赤潮研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2007.Wang Zhaohui. Study of Dinoflagellate Resting Cysts and Red Tides in Chinese Coastal Water[M]. Bejing: China Ocean Press, 2007. [24] 邹振华, 李琼芳, 夏自强, 等. 人类活动对长江径流量特性的影响[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 35(6): 622−626.Zou Zhenhua, Li Qiongfang, Xia Ziqiang, et al. Human-induced alterations in runoff of the Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2007, 35(6): 622−626. [25] 张璇. 长江口及邻近海域营养盐的历史演变及其在赤潮中的作用研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.Zhang Xuan. Historical comparison on evolution of nutrient and its function on the harmful algae blooms in Yangtze Estuary and its adjacent sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012. [26] Wang Bin, Chen Jianfang, Jin Haiyan, et al. Diatom bloom-derived bottom water hypoxia off the Changjiang estuary, with and without typhoon influence[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2017, 62(4): 1552−1569. doi: 10.1002/lno.10517 [27] Dale B. Cyst formation, sedimentation, and preservation: factors affecting dinoflagellate assemblages in recent sediments from Trondheimsfjord, Norway[J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 1976, 22(1): 39−60. doi: 10.1016/0034-6667(76)90010-5 [28] Wang Zhaohui, Qi Yuzao, Lu Songhui, et al. Seasonal distribution of dinoflagellate resting cysts in surface sediments from Changjiang River Estuary[J]. Phycological Research, 2004, 52(4): 387−395. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1835.2004.tb00347.x [29] 黄海燕, 陆斗定, 夏平, 等. 2006−2007年冬季长江口海域甲藻孢囊的分布及其与环境的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(20): 5569−5576.Huang Haiyan, Lu Douding, Xia Ping, et al. Distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in Changjiang Estuary during the winter of 2006−2007 and their relationship with the environment[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(20): 5569−5576. [30] Shin H H, Park J S, Kim Y O, et al. Dinoflagellate cyst production and flux in Gamak Bay, Korea: a sediment trap study[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2012, 94−95: 72−79. doi: 10.1016/j.marmicro.2012.06.005 [31] 刘录三, 李子成, 周娟, 等. 长江口及其邻近海域赤潮时空分布研究[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(9): 2497−2504.Liu Lusan, Li Zicheng, Zhou Juan, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of red tide in Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent waters[J]. Envionmental Science, 2011, 32(9): 2497−2504. [32] Liu Dongyan, Shi Yajun, Di Baoping, et al. The impact of different pollution sources on modern dinoflagellate cysts in Sishili Bay, Yellow Sea, China[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 2012, 84−85: 1−13. doi: 10.1016/j.marmicro.2011.11.001 [33] 金媛娟. 莆田南日岛鲍鱼养殖区环境变化评价[J]. 化学工程与装备, 2012(8): 213−215, 191.Jin Yuanjuan. Environment change evaluation in abalone cultivation area at Nanri Island of Putian[J]. Chemical Engineering & Equipment, 2012(8): 213−215, 191. [34] 董书航. 东海营养盐分布特征及跨陆架交换研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015.Dong Shuhang. Distribution and variations and cross shelf exchange of nutrients in the East China Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2015. [35] 黄江婵. 近50年东海海水中营养盐时空分布特征[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2011.Huang Jiangchan. Distribution and changes of nutrient concentration in the East China Sea in late 50 years[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2011. [36] 许武成, 王文, 马劲松, 等. 1951−2007年的ENSO事件及其特征值[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2009, 18(4): 18−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2009.04.004Xu Wucheng, Wang Wen, Ma Jinsong, et al. ENSO events during 1951−2007 and their characteristic indices[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2009, 18(4): 18−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2009.04.004 [37] 腾琳. 中国沿海甲藻孢囊的水平和垂直分布研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2006.Teng Lin. Horizontal and vertical distribution of dinoflagellate cysts from China Sea[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2006. -




 下载:
下载: