Experimental study on dynamic response characteristics of continental shelf slope to internal solitary waves
-
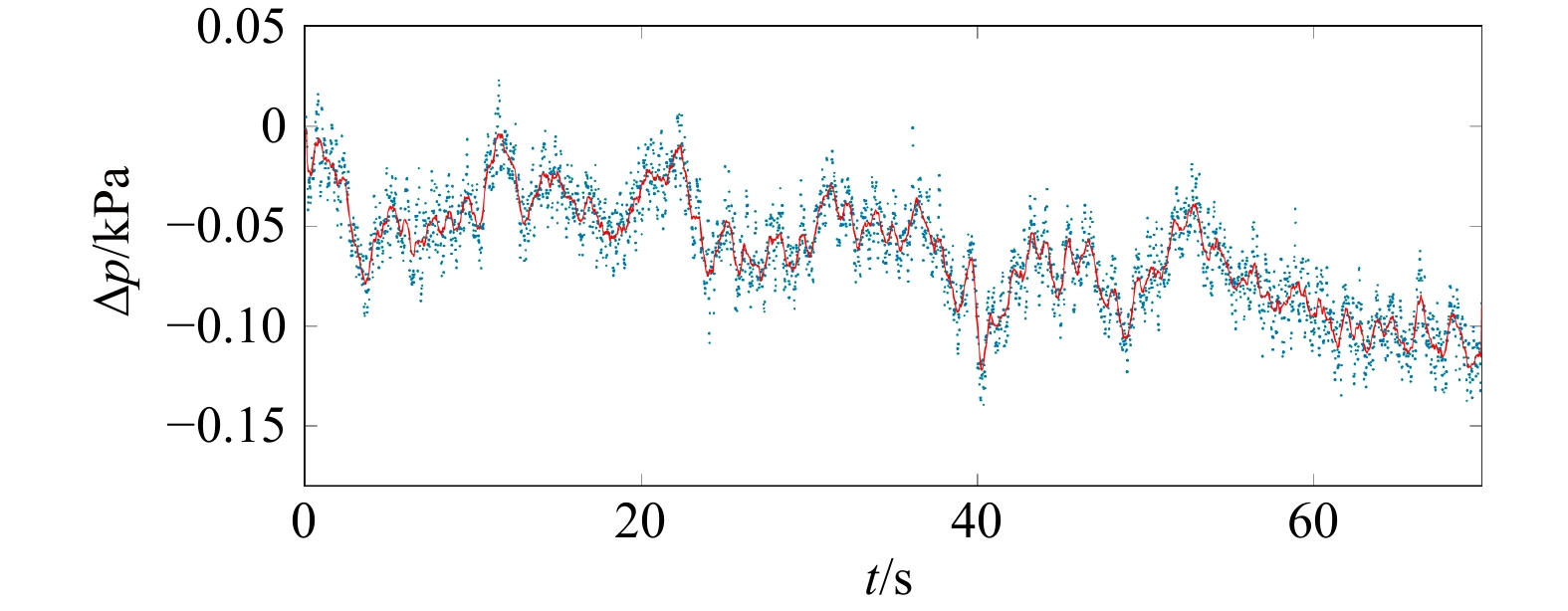
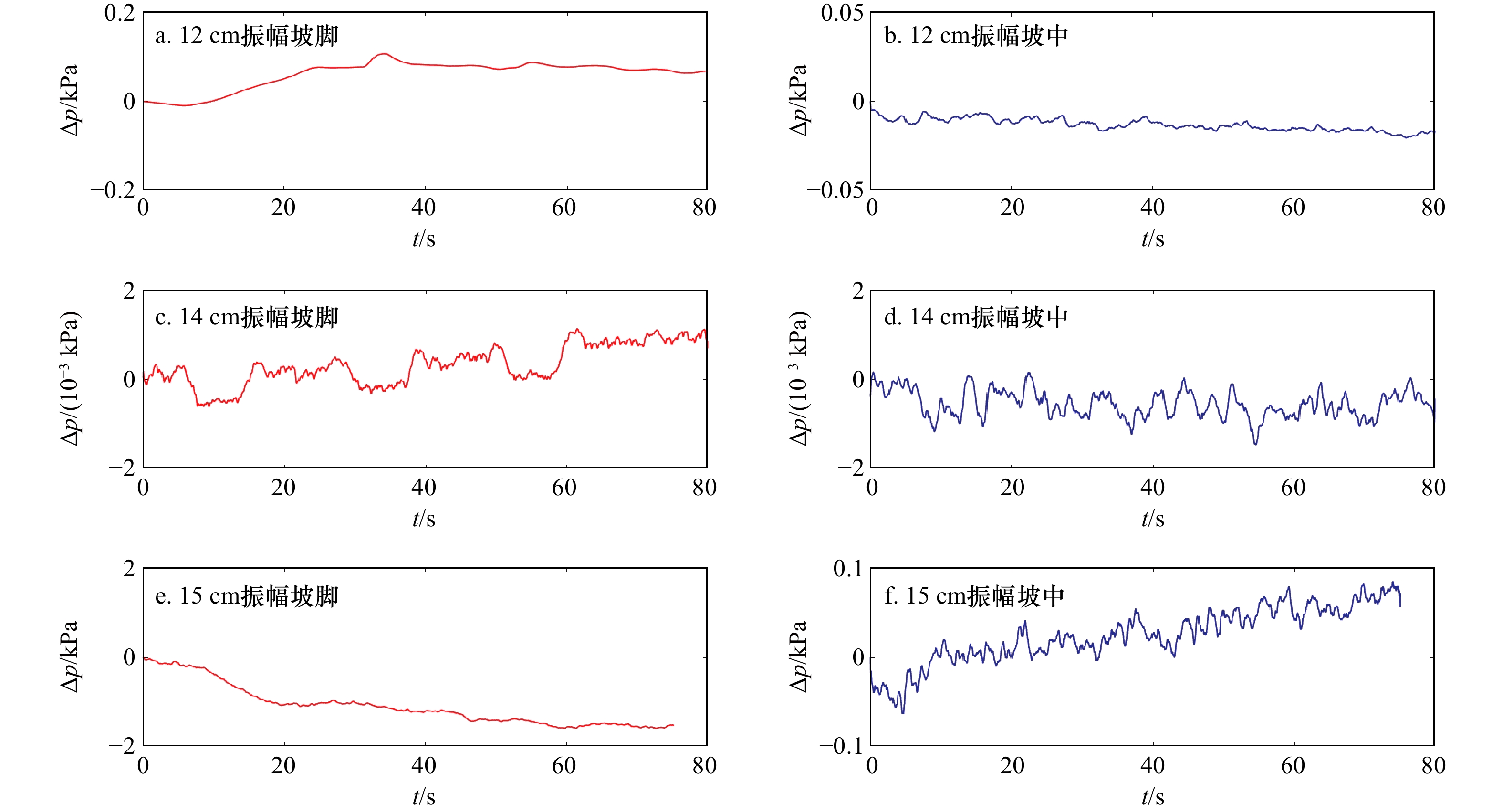
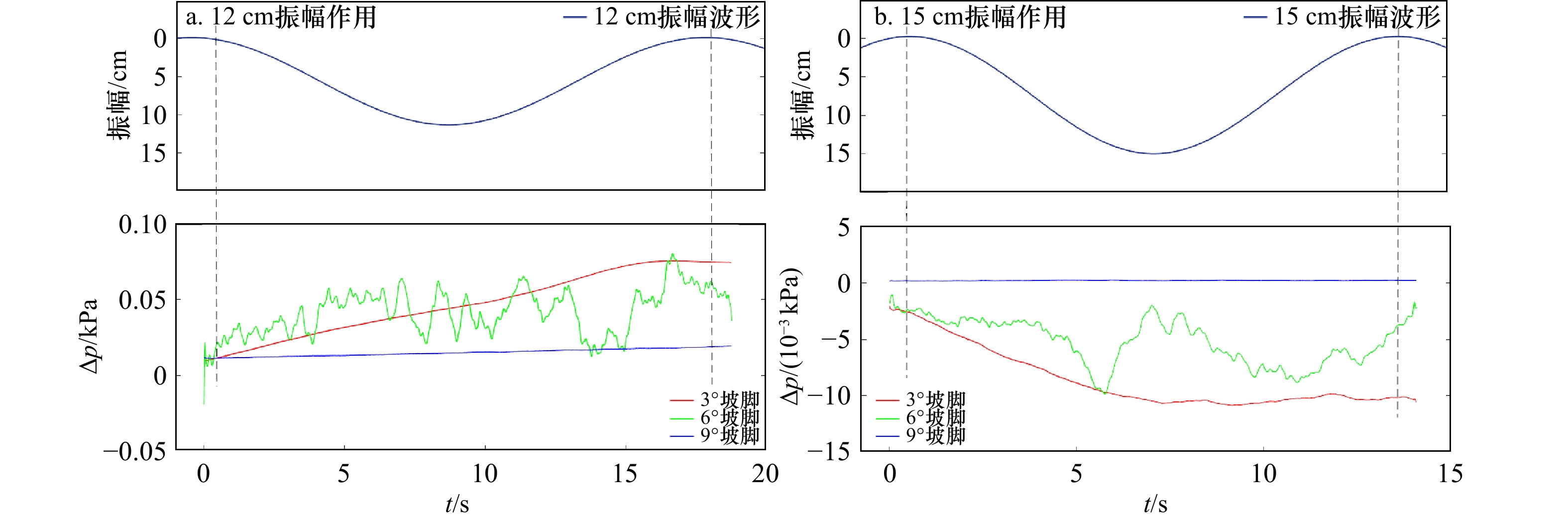
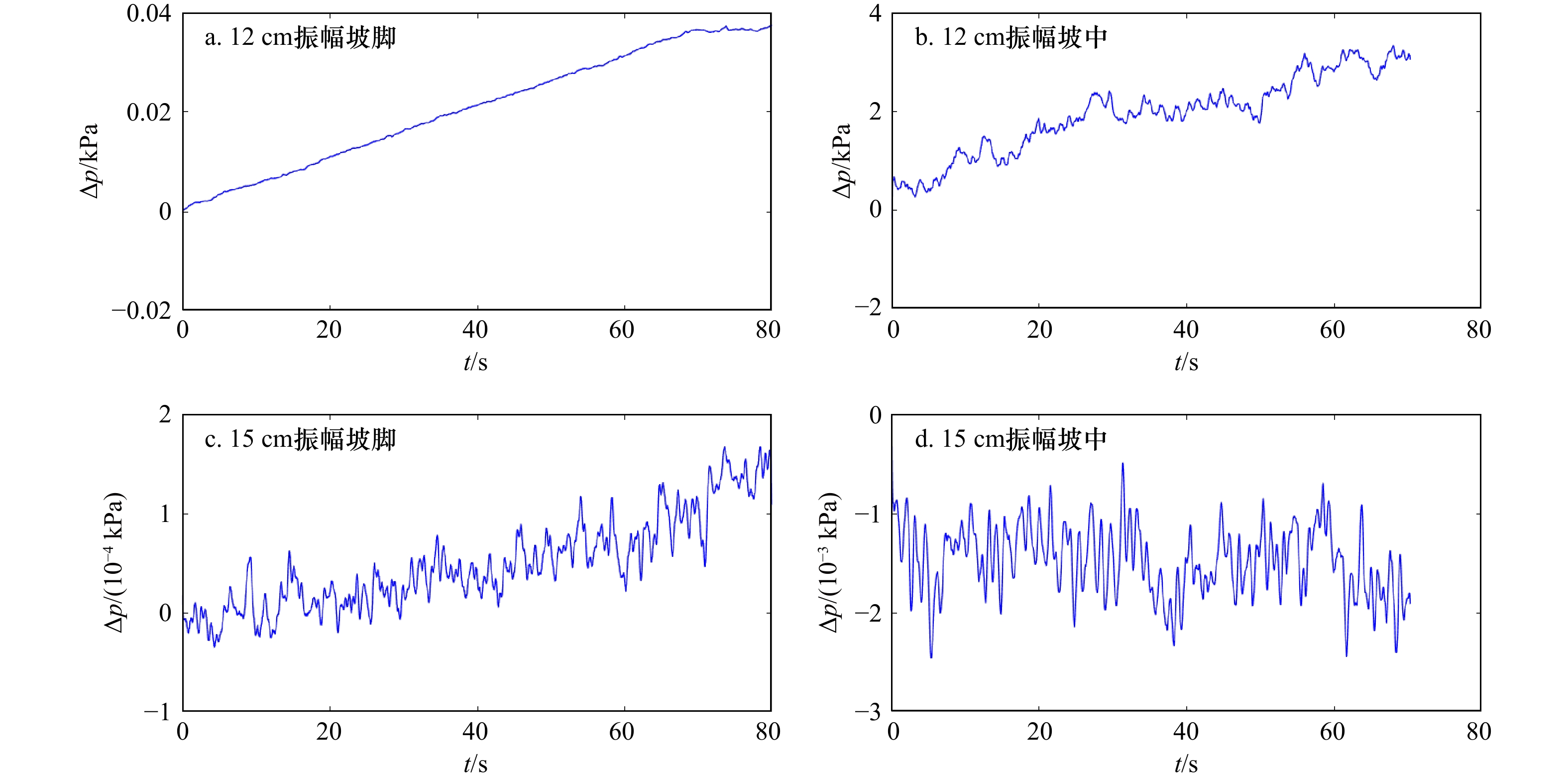
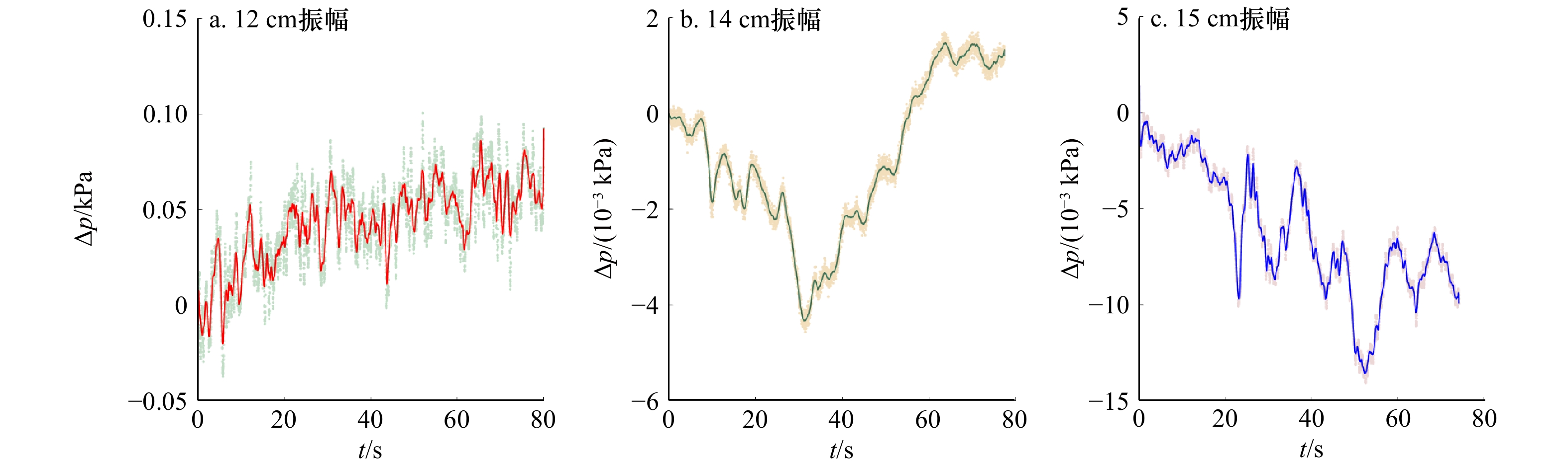
摘要: 针对内孤立波在行进过程中遇到海底斜坡会对海底产生力的作用,不同坡度斜坡对内孤立波的动力响应应该存在差异。本文通过水槽中制造内波,对不同角度的斜坡对内孤立波的动力响应过程进行了研究。结果表明,内孤立波通过陆架斜坡上方,会造成斜坡沉积物超孔隙水压力的积累;在相同振幅条件下,缓坡沉积物动力响应的幅度比陡坡沉积物大;随着振幅的增加,缓坡发生动力破坏程度大于陡坡;在斜坡沉积物稳定性受到破坏之前,超孔隙水压力的积累和释放同时存在,内孤立波振幅的增大会加剧超孔隙水压力的释放。该结果对于斜坡沉积物在内孤立波作用下失稳破坏的动力学研究和斜坡稳定性分析将起到指导作用。Abstract: In view of the effect of internal solitary waves on the seafloor when encountering the seabed slope during their travel, the dynamic response of different slopes to internal solitary waves should be different. This paper studies the dynamic response process of internal solitary waves of slopes with different angles by creating internal waves in a flume. The results show that the internal solitary waves passing over the shelf slope will cause the accumulation of excess pore water pressure in the slope sediments; under the same amplitude conditions, the dynamic response amplitude of the gentle slope sediments is larger than that of the steep slope sediments; as the amplitude increases, gentle slopes occur the degree of dynamic damage is greater than that of steep slopes; the accumulation and release of excess pore water pressure exist at the same time before the stability of slope sediments is destroyed, and the increase of the amplitude of internal solitary waves will aggravate the release of excess pore water pressure. The results will play a guiding role in the dynamic study of the failure of slope sediment under the action of internal solitary waves and the analysis of slope stability.
-
Key words:
- shelf slope /
- slope sediment /
- internal solitary wave /
- dynamic response /
- slope
-
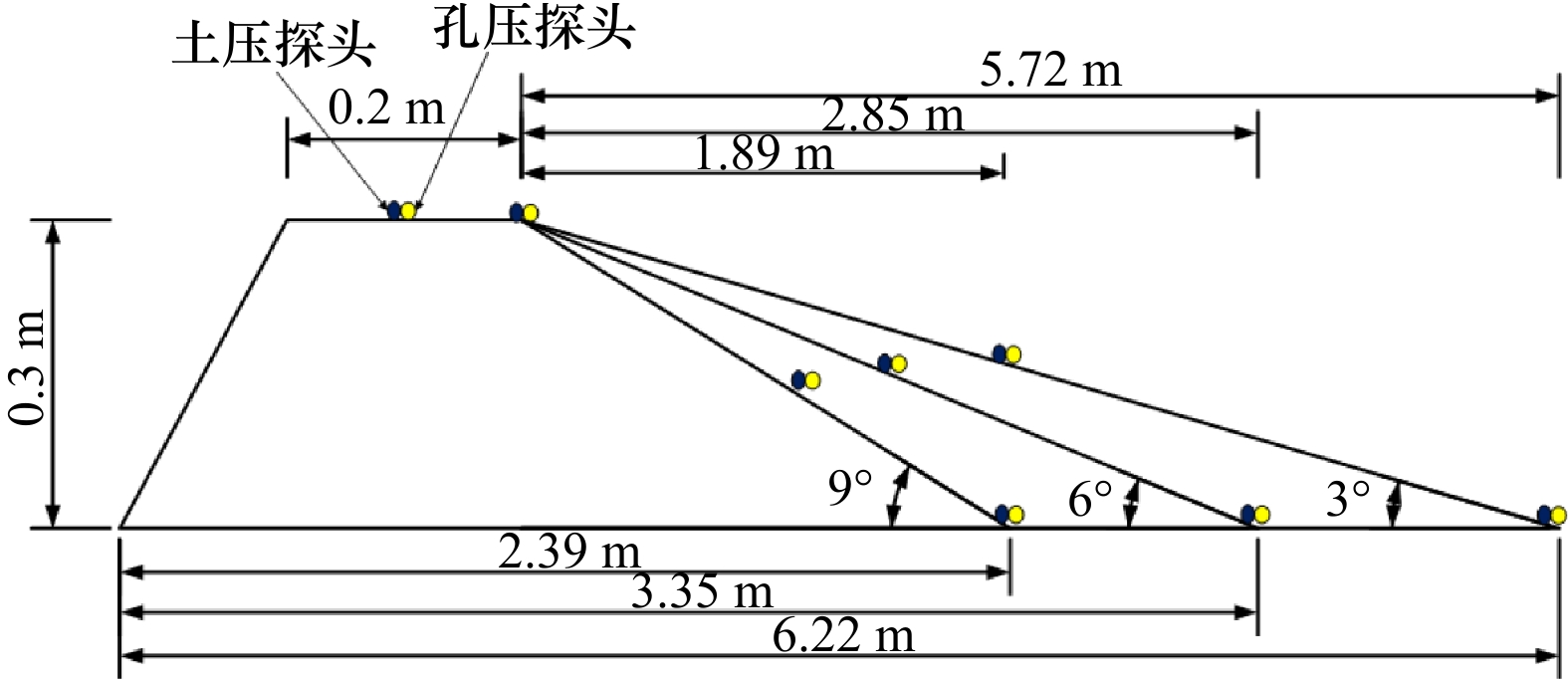
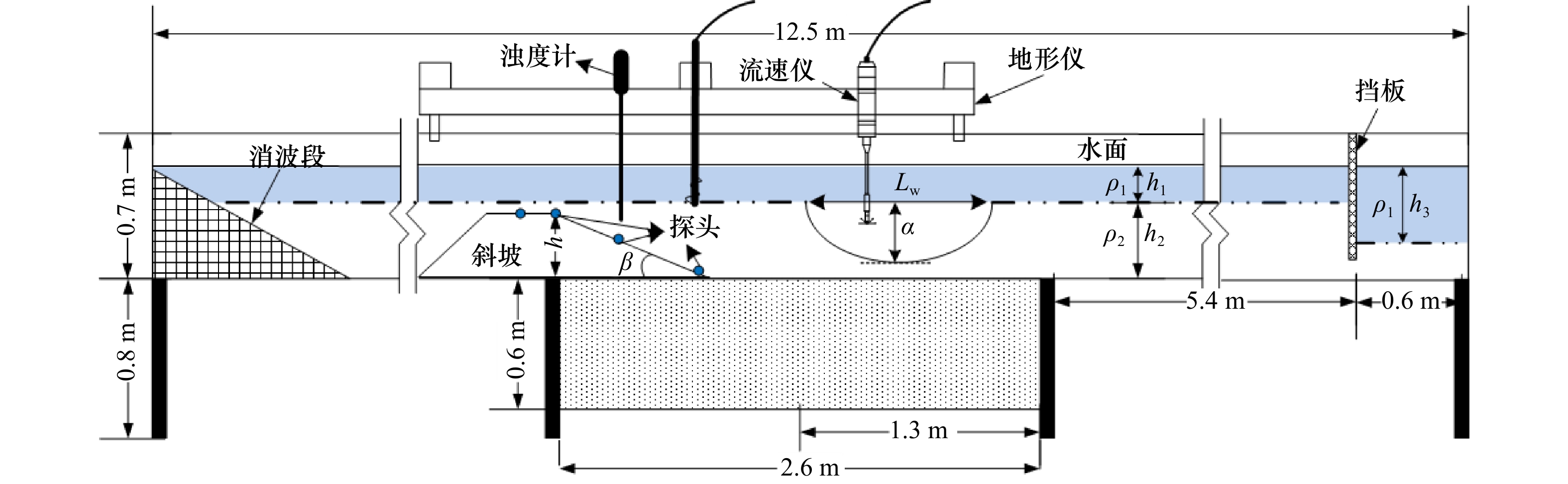
表 1 实验室模拟内孤立波的设计参数
Tab. 1 Design parameter of laboratory simulation internal solitary wave
振幅/cm 上层流体密度${\rho _1}$/(kg·m−3) 下层流体密度${\rho _2}$/(kg·m−3) 12 998 1020 14 998 1024 15 998 1028 -
[1] 方文东, 陈荣裕, 毛庆文. 南海北部大陆坡区的突发性强流[J]. 热带海洋, 2000, 19(1): 70−75.Fang Wendong, Chen Rongyu, Mao Qingwen. Abrupt strong currents over continental slope of northern South China Sea[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 2000, 19(1): 70−75. [2] Lamb K G. Internal wave breaking and dissipation mechanisms on the continental slope/shelf[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2014, 46: 231−254. doi: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-011212-140701 [3] Alford M H, Peacock T, MacKinnon J A, et al. The formation and fate of internal waves in the South China Sea[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7550): 65−69. doi: 10.1038/nature14399 [4] 夏华永, 刘愉强, 杨阳. 南海北部沙波区海底强流的内波特征及其对沙波运动的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2009, 28(6): 15−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2009.06.003Xia Huayong, Liu Yuqiang, Yang Yang. Internal-wave characteristics of strong bottom currents at the sand-wave zone of the northern South China Sea and its role in sand-wave motion[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2009, 28(6): 15−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2009.06.003 [5] Droghei R, Falcini F, Casalbore D, et al. The role of internal solitary waves on deep-water sedimentary processes: the case of up-slope migrating sediment waves off the Messina Strait[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 36376. doi: 10.1038/srep36376 [6] Rivera-Rosario G A, Diamessis P J, Jenkins J T. Bed failure induced by internal solitary waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2017, 122(7): 5468−5485. doi: 10.1002/2017JC012935 [7] 陈珊珊, 孙运宝, 吴时国. 南海北部神狐海域海底滑坡在地震剖面上的识别及形成机制[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2012, 28(6): 40−45.Chen Shanshan, Sun Yunbao, Wu Shiguo. Sea bottom landslide in the Shenhu area on the north margin of South China Sea and triggering mechanisms[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2012, 28(6): 40−45. [8] Boegman L, Stastna M. Sediment resuspension and transport by internal solitary waves[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 51: 129−154. doi: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-122316-045049 [9] Puig P, Palanques A, Guillén J, et al. Role of internal waves in the generation of nepheloid layers on the northwestern Alboran slope: implications for continental margin shaping[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2004, 109(C9): C09011. [10] Quaresma L S, Vitorino J, Oliveira A, et al. Evidence of sediment resuspension by nonlinear internal waves on the western Portuguese mid-shelf[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 246(2/4): 123−143. [11] Tian Zhuangcai, Jia Yonggang, Zhang Shaotong, et al. Bottom and intermediate nepheloid layer induced by shoaling internal solitary waves: impacts of the angle of the wave group velocity vector and slope gradients[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2019, 124(8): 5686−5699. doi: 10.1029/2018JC014721 [12] Jia Yonggang, Tian Zhuangcai, Shi Xuefa, et al. Deep-sea sediment resuspension by internal solitary waves in the northern South China Sea[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 12137. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47886-y [13] Cacchione D A, Drake D E. Nepheloid layers and internal waves over continental shelves and slopes[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1986, 6(3): 147−152. doi: 10.1007/BF02238085 [14] Stastna M, Lamb K G. Sediment resuspension mechanisms associated with internal waves in coastal waters[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2008, 113(C10): C10016. doi: 10.1029/2007JC004711 [15] Butman B, Alexander P S, Scotti A, et al. Large internal waves in Massachusetts Bay transport sediments offshore[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2006, 26(17/18): 2029−2049. [16] Slinn D N, Riley J J. Turbulent mixing in the oceanic boundary layer caused by internal wave reflection from sloping terrain[J]. Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans, 1996, 24(1/4): 51−62. [17] Klymak J M, Moum J N. Internal solitary waves of elevation advancing on a shoaling shelf[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2003, 30(20): 2045. [18] Nakayama K, Shintani T, Kokubo K, et al. Residual currents over a uniform slope due to breaking of internal waves in a two-layer system[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2012, 117(C10): C10002. [19] Pomar L, Morsilli M, Hallock P, et al. Internal waves, an under-explored source of turbulence events in the sedimentary record[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2012, 111(1/2): 56−81. [20] Morsilli M, Pomar L. Internal waves vs. surface storm waves: a review on the origin of hummocky cross-stratification[J]. Terra Nova, 2012, 24(4): 273−282. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3121.2012.01070.x [21] 乔路正, 郭秀军, 田壮才, 等. 内孤立波浅化破碎过程斜坡沉积物孔压响应特征实验分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(1): 68−76.Qiao Luzheng, Guo Xiujun, Tian Zhuangcai, et al. Experimental analysis of pore pressure response characteristics of slope sediments during shallowing and breaking of internal solitary waves[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(1): 68−76. [22] Forgia G L, Adduce C, Falcini F. Laboratory investigation on internal solitary waves interacting with a uniform slope[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2017, 120: 4−18. [23] 杜辉, 魏岗, 张原铭, 等. 内孤立波沿缓坡地形传播特性的实验研究[J]. 物理学报, 2013, 62(6): 64704-1−064704-8.Du Hui, Wei Gang, Zhang Yuanming, et al. Experimental investigations on the propagation characteristics of internal solitary waves over a gentle slope[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(6): 64704-1−064704-8. -




 下载:
下载: